Spring循環依賴原理
Spring循環依賴的原理解析
1、什麼是循環依賴?
我們使用Spring的時候,在一個對象中注入另一個對象,但是另外的一個對象中也包含該對象。如圖:
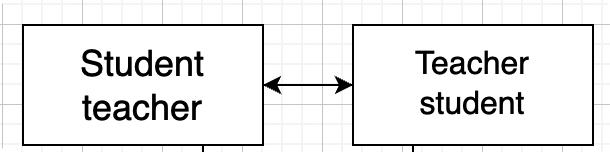
在Student中包含了teacher的一個屬性;
在Teacher中包含有student的屬性。這樣就形成了一個循環依賴。
2、代碼描述
xml配置文件

testCycle.java
private static void testCycle(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cycle.xml");
Teacher teacher = applicationContext.getBean(Teacher.class);
System.out.println(teacher);
Student student = applicationContext.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println(student);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testCycle();
}
Student.java
public class Student {
private Teacher teacher;
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
}
Teacher.java
public class Teacher {
private Student student;
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
}
3、 測試結果
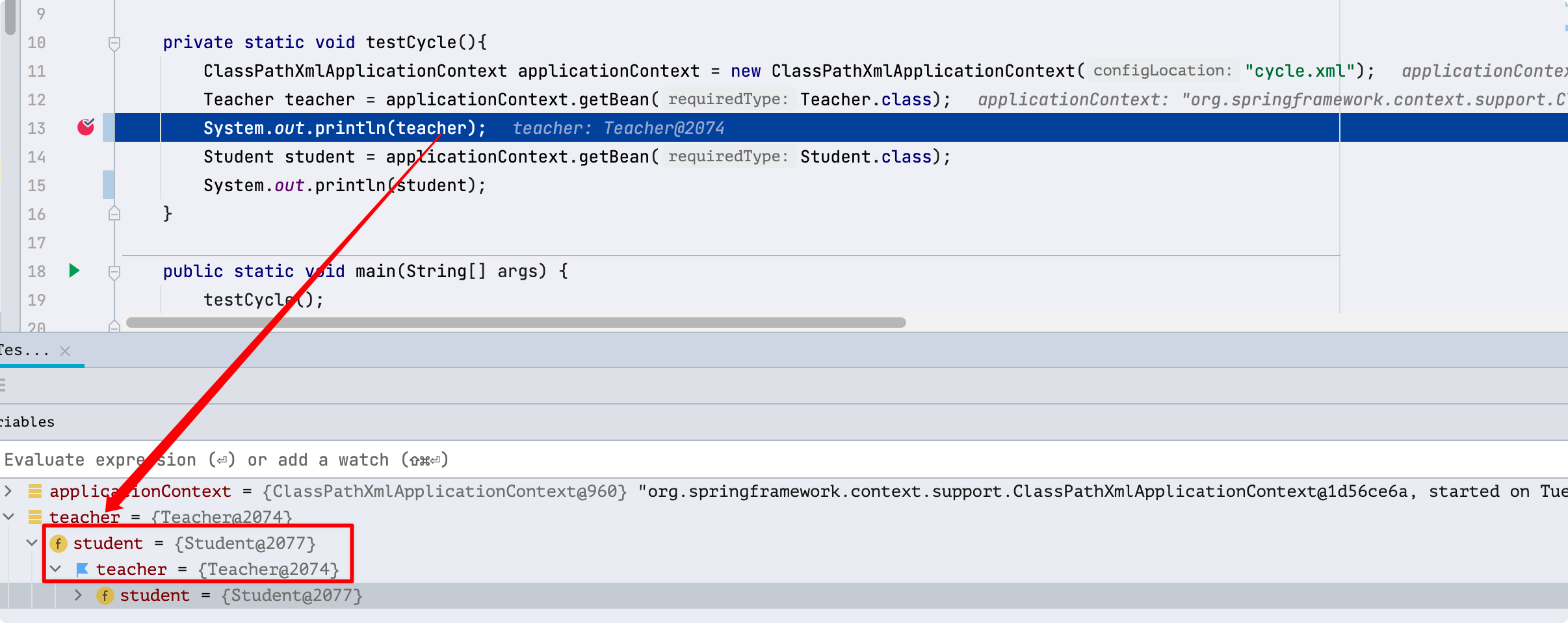
此處輸出的teacher中包含有student對象,student對象中也包含有teacher對象,且包含的對象都是不為null的。
4、為什麼能夠循環依賴解釋
先給出一張圖
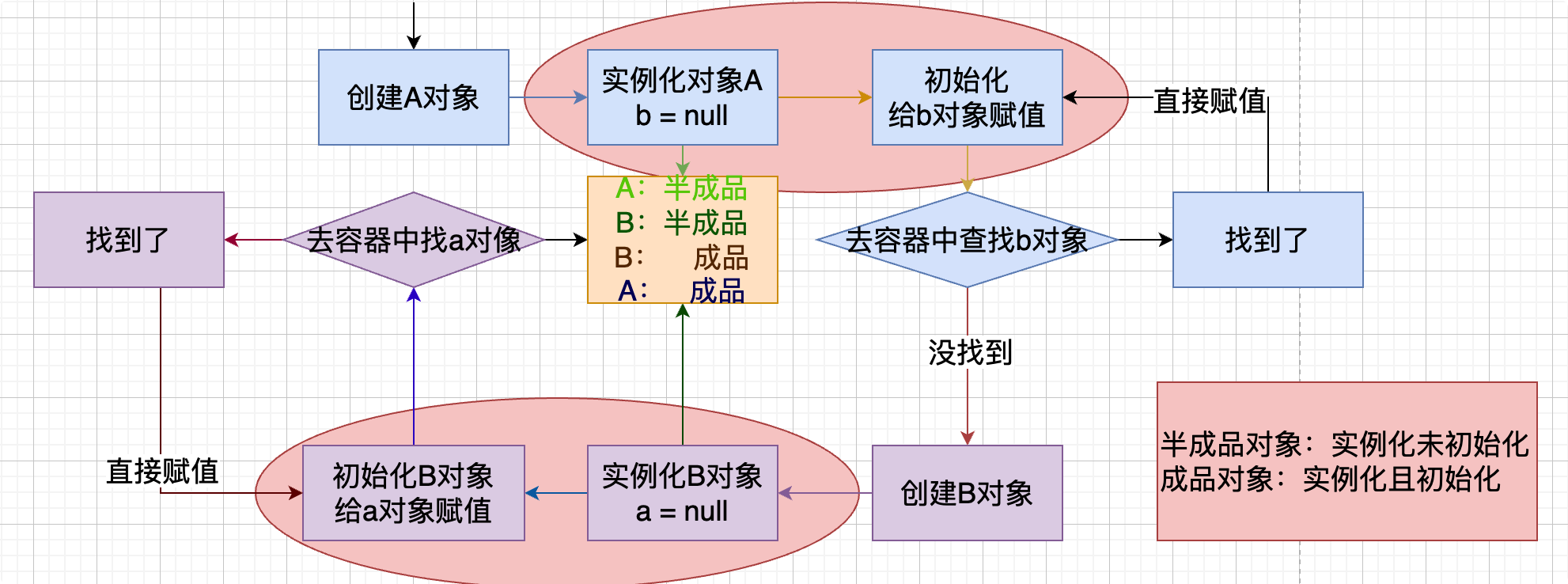
在Spring創建bean的時候肯定也是一個一個去創建的。首先肯定會先去走一個(Teacher/Student)生命周期。這裡以Teacher為例,當Spring去getBean(teacher)的時候,首先會去容器中獲取,獲取不到就會去創建teacher,當teacher創建完成後,會給teacher的屬性(student)賦值,實際上容器中沒有student對象,這時候也會去創建student對象,當student創建的時候會去給student中的teacher屬性賦值,teacher之前已經創建過了,此時去getBean(teacher)是能夠拿到的(注意:此時的teacher中student屬性並沒有賦值),這樣student就創建完成了,那麼就會回到teacher的student屬性賦值的步驟,此時student已經創建是可以用getBean()拿到的,這樣teacher對象就創建完畢了。然後回到第一步去創建student對象,這裡student對象在創建teacher的時候就已經創建,可以直接使用getBean()獲取到。給student中的屬性賦值的時候也是一樣,能夠直接獲取到teacher。自此循環依賴就已經結束了。
5、疑問
- 當我在給Teacher屬性student的賦值的時候是怎麼去getBean()的?
- 當給student中屬性teacher賦值的時候getBean()為什麼能夠取到teacher?
- 為什麼獲取到的teacher屬性是為完成注入的?
6、源碼解釋
整體的方法線

先看看源碼:
getBean()->doGetBean()
getBean()->doGetBean()實際上是doGetBean在去獲取bean對象
public <T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object... args)
throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, requiredType, args, false);
}
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* 返回指定 bean 的一個實例,該實例可以是共享的,也可以是獨立的。
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
// 轉換beanName,FactoryBean的情況下beanName為&beanName,這裡就是去掉&符號
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object beanInstance;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 急切檢查單例緩存從手動創建的單例中,獲取bean判斷是否存在當前beanName的bean
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
... 省略代碼...
}
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 沒有獲取到,如果已經創建bean的實例,我們在一個循環引用中。當前的bean是否為正在創建中
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
// 檢查該工廠中是否存在bean的定義
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
... 省略代碼...
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
// 標記bean已經創建,正在創建
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
StartupStep beanCreation = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.beans.instantiate")
.tag("beanName", name);
try {
if (requiredType != null) {
beanCreation.tag("beanType", requiredType::toString);
}
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 保證當前的bean所依賴的bean已經初始化
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
// 創建bean的實例
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
// 從單例緩存中刪除實例,它可能已經在這裡
// 通過創建過程-允許循環引用解析
// 刪除接收到任何對bean引用的臨時bean
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
... 省略代碼...
finally {
beanCreation.end();
}
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}
此處傳入進來的beanName為teacher
doGetBean()->createBean()
分開看
// Create bean instance.
// 創建bean的實例
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
// 從單例緩存中刪除實例,它可能已經在這裡
// 通過創建過程-允許循環引用解析
// 刪除接收到任何對bean引用的臨時bean
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
重要的點在這裡當沒有獲取到bean的時候就會去調用createBean方法,創建bean,最終其實是走的doCreateBean方法取創建bean
createBean()->doCreateBean()
這裡就到了上面方法線的第四部
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
// BeanWrapper:持有創建出來的Bean
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
/**
* 創建bean的實例
* 實例化但是並未初始化,就是沒有給bean的屬性複製
*/
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
// 允許增強器修改合併的bean definition
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 緩存單例的bean能夠解析循環引用
// 即使生命周期接口觸發像BeanFactoryAware,
// 判斷當前的bean是否需要提前曝光(加入singletonFactories緩存):bean是單例的&允許循環依賴&bean正在創建
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 將bean添加到singletonFactories 也就是說的三級緩存,但是這個地方的屬性是沒有賦值的
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// 到這裡,bean就已經實例化完成,並且將bean放入到了singletonFactories緩存中
// Initialize the bean instance.
// 初始化bean的實例
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
/**
* 填充bean,填充Bean的屬性
*/
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* 去執行
* BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
* */
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
// 將bean註冊為一次性的
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
分開解釋
doCreateBean方法
// Instantiate the bean.
// BeanWrapper:持有創建出來的Bean
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
/**
* 創建bean的實例
* 實例化但是並未初始化,就是沒有給bean的屬性複製
*/
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
初始化bean,這個地方開始調用createBeanInstance方法創建一個bean的實例
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
// 緩存單例的bean能夠解析循環引用
// 即使生命周期接口觸發像BeanFactoryAware,
// 判斷當前的bean是否需要提前曝光(加入singletonFactories緩存):bean是單例的&允許循環依賴&bean正在創建
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 將bean添加到singletonFactories 也就是說的三級緩存,但是這個地方的屬性是沒有賦值的
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
記住addSingletonFactory()方法,這是循環依賴的核心
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
// 將beanName,singletonFactory放入到單例工廠的緩存【beanName-singletonFactory】
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
// 從早起的單例對象緩存中移除【beanName-bean實例】
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
// 將beanName添加到已經註冊的實例中
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
此處存入的singletonFactory是一個lambda表達式,ObjectFactory是一個函數接口,當執行getObject方法的時候會去調用存入的getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)
doCreateBean() -> createBeanInstance()
這裡也沒什麼好說的就是通過反射去創建Teacher對象
createBeanInstance() -> populateBean()
這裡就是開始給創建的Teacher屬性student賦值了
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance
* 允許屬性值填充給BeanWrapper中的Bean實例
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // for postProcessPropertyValues 後處理屬性值
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
... 省略代碼 ...
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the 給所有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors有修改的機會
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 設置屬性之前bean的狀態,例如
// 支持字段注入
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable. 通過名稱自動注入參數的值
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable. 通過類型注入參數的值
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
/**
* 有沒有實例化的AwareBeanPostProcessor
*/
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
/**
* 是否需要深度檢查
*/
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 應用給定的屬性值,解決任何在這個bean工廠運行時它bean的引用。必須使用深copy。所以不會永久的修改此屬性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
分開解析
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的方法postProcessAfterInstantiation,該方法的返回值是boolean,如果返回true,則什麼都不幹,如果返回false,那麼此類則不會進行自動裝配(屬性填充),這裡就是可以讓我們通過postprocessor的方式控制某些bean不用屬性填充。這裡很明顯如果我們沒做特殊處理,這裡最裏面的if的return是不會被執行到的。
if (pvs != null) {
// 應用給定的屬性值,解決任何在這個bean工廠運行時它bean的引用。必須使用深copy。所以不會永久的修改此屬性
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
這裡就是給Teacher的student屬性賦值的
/**
* Apply the given property values, resolving any runtime references
* to other beans in this bean factory. Must use deep copy, so we
* don't permanently modify this property.
* @param beanName the bean name passed for better exception information
* @param mbd the merged bean definition
* @param bw the BeanWrapper wrapping the target object
* @param pvs the new property values
* 應用給定的屬性值,解析對此 bean 工廠中其他 bean 的任何運行時引用。必須使用深拷貝,所以我們不會永久修改這個屬性
*/
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
// 如果pvs沒有propertyValues,直接結束
return;
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List<PropertyValue> original;
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values. 創建一個深copy,解析任何引用值
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
// 獲取屬性的名稱
String propertyName = pv.getName();
// 獲取屬性的值
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
if (originalValue == AutowiredPropertyMarker.INSTANCE) {
Method writeMethod = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName).getWriteMethod();
if (writeMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Autowire marker for property without write method: " + pv);
}
originalValue = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(writeMethod, 0), true);
}
// 解析屬性值
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
解析屬性值
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
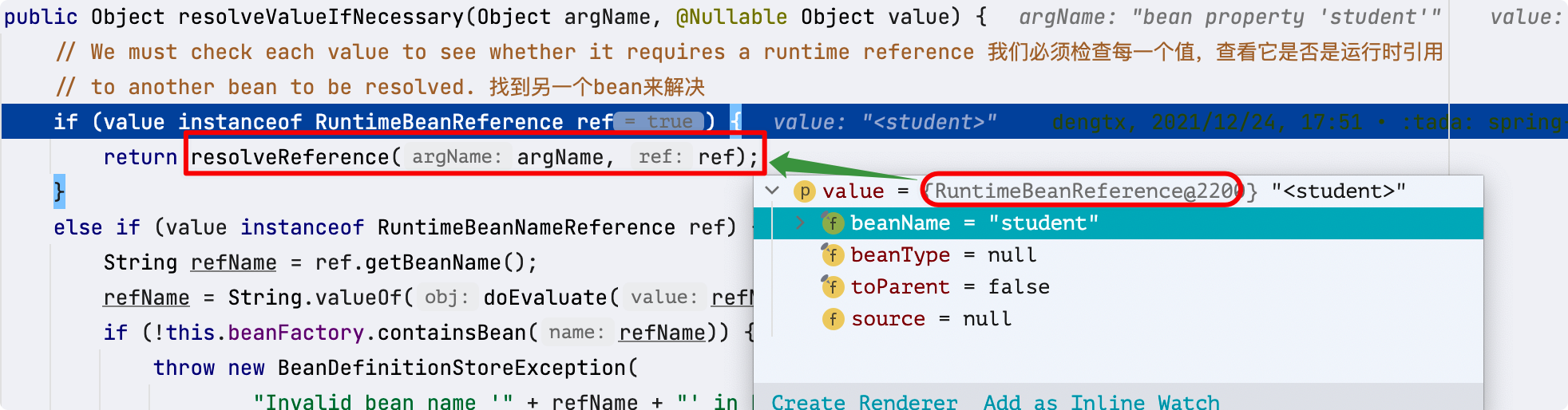
此處會直接走到resolveReference方法中去
/**
* Resolve a reference to another bean in the factory.解析對另一個bean的引用
*/
@Nullable
private Object resolveReference(Object argName, RuntimeBeanReference ref) {
try {
// 用來存放實例化出來的bean
Object bean;
// 獲取bean的類型
Class<?> beanType = ref.getBeanType();
if (ref.isToParent()) {
BeanFactory parent = this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent == null) {
... 省略代碼 ...
}
else {
String resolvedName;
if (beanType != null) {
... 省略代碼...
}
else {
resolvedName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(ref.getBeanName()));
// 獲取resolvedName的bean對象
bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(resolvedName);
}// 註冊依賴的bean
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(resolvedName, this.beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof NullBean) {
bean = null;
}
return bean;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve reference to bean '" + ref.getBeanName() + "' while setting " + argName, ex);
}
}
方法會走到這裡去getBean() 之前的getBean還沒走完是不是有走到getBean(),從這裡開始就是套娃。
resolvedName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(ref.getBeanName()));
// 獲取resolvedName的bean對象
bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(resolvedName);
}// 註冊依賴的bean
到此處就會去尋找Student的實例,就會走一遍之前的方法,但是走到pupolate()方法的時候給student的teacher屬性賦值,會去容器中獲取一個teacher,還記得之前存在singletonFactories中的teacher嗎?這裡獲取的時候就會直接拿到之前的存儲的teacher。下面看一看
省略之前創建個邏輯,直接到賦值的操作

到這裡就開始去獲取teacher對象了,看一下getSingleton()方法是怎麼拿的;
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
// 從單例對象緩存(singletonObjects--一級緩存)中獲取bean對象
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果單例對象中沒有找到,並且改bean正在創建中
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// 從早期單例對象緩存中獲取單例對象(之所以成為早期單例對象,是因為earlySingletonObjects裏面
// 的對象都是通過提前曝光的ObjectFactory創建出來的。還沒有進行屬性填充等操作)
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 早期單例對象緩存(二級緩存)中也沒有並且允許創建早期單例對象
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 如果為空,則鎖定全局變量進行處理
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
//在完整的單例鎖中一致地創建早期引用
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
// 當某些方法需要提前初始化的時候則會調用addSingletonFactory方法將對應的objectFactory初始化策略儲存在singletonFactories中
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
// 如果存在單例對象工廠,則使用該工廠創建一個單例對象
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
// 創建的單例對象放如早期單例對象緩存中
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
// 移除對應的單例對象工廠
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}

這裡拿到了之前存入singletonFactoriesMap中的lambda表達式,調用getObject()方法去執行getEarlyBeanReference方法
/**
* Obtain a reference for early access to the specified bean,
* typically for the purpose of resolving a circular reference.
* @param beanName the name of the bean (for error handling purposes)
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @return the object to expose as bean reference
*
* 獲得對指定bean的早期訪問的引用 通常用於解析循環依賴
*/
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
// 默認最終公開的對象是bean,通過createBeanInstance創建出來的普通對象
Object exposedObject = bean;
// mbd的synthetic屬性:設置bean定義是否是synthetic的,一般是指只有AOP相關的pointCut配置或者advice配置才會將synthetic設置為true
// 如果mbd不是synthetic且此工廠擁有InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 遍歷工廠的所有後置處理器,並獲取smartInstantiationAware-ArrayList
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
// 讓exposedObject對象經過每一個smartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor報裝
exposedObject = bp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
// 返回最終經過層次報裝後的對象
return exposedObject;
}
這個方法沒有什麼好解釋的,注釋很明確的表明了方法的作用
拿到teacher之後就給Student中的teacher屬性賦值
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
就此Student對像創建完畢,會將創建完成的Student對象放入
try {
// 去容器中獲取bean對象
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
// 將beanName和singletonObject的映射關係添加到該工廠的單例緩存中
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);放入緩存中
至此會返回去給Teacher中的student屬性賦值。至此一次的循環依賴就完成了。Spring還回去創建Student對象,但是這次容器中存在直接取出來就可以了。
疑問解答
為什麼最後還要去創建一次Student對象,因為開始創建Student對象是因為創建Teacher對象的時候需要使用Student得實例,所以去創建了一次,但是最後一次去創建Student對象的時候不會真的創建,直接從緩存singletonObjects中就能去獲取到。
如文章中有錯誤歡迎指出,剛開始閱讀代碼,參考了一些資料。

