Android View post 方法
- 2021 年 9 月 23 日
- 筆記
- Android, Android-101
解析View.post方法。分析一下這個方法的流程。
說起post方法,我們很容易聯想到Handler的post方法,都是接收一個Runnable對象。那麼這兩個方法有啥不同呢?
Handler的post方法
先來簡單看一下Handler的post(Runnable)方法。這個方法是將一個Runnable加到消息隊列中,並且會在這個handler關聯的執行緒里執行。
下面是關聯的部分源碼。可以看到傳入的Runnable對象,裝入Message後,被添加進了queue隊列中。
Handler 有關的部分源碼
// android.os Handler 有關的部分源碼
public final boolean post(@NonNull Runnable r) {
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
}
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(@NonNull Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
private boolean enqueueMessage(@NonNull MessageQueue queue, @NonNull Message msg,
long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
msg.workSourceUid = ThreadLocalWorkSource.getUid();
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
具體流程,可以看handler介紹
View的post方法
我們直接跟著post的源碼走。
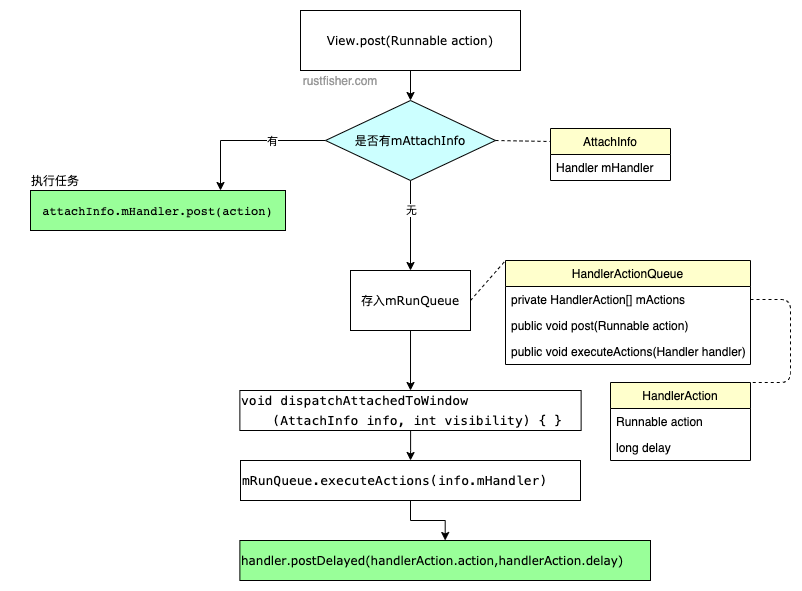
public boolean post(Runnable action) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null) {
return attachInfo.mHandler.post(action);
}
// Postpone the runnable until we know on which thread it needs to run.
// Assume that the runnable will be successfully placed after attach.
getRunQueue().post(action);
return true;
}
private HandlerActionQueue getRunQueue() {
if (mRunQueue == null) {
mRunQueue = new HandlerActionQueue();
}
return mRunQueue;
}
可以看到一開始就查詢是否有attachInfo,如果有,則用attachInfo.mHandler來執行這個任務。
如果沒有attachInfo,則添加到View自己的mRunQueue中。確定運行的執行緒後,再執行任務。
post(Runnable action)的返回boolean值,如果為true,表示任務被添加到消息隊列中了。
如果是false,通常表示消息隊列關聯的looper正在退出。
那麼我們需要了解AttachInfo和HandlerActionQueue。
AttachInfo
AttachInfo是View的靜態內部類。View關聯到父window後,用這個類來存儲一些資訊。
AttachInfo存儲的一部分資訊如下:
WindowId mWindowIdwindow的標誌View mRootView最頂部的viewHandler mHandler這個handler可以用來處理任務
HandlerActionQueue
當View還沒有handler的時候,拿HandlerActionQueue來快取任務。HandlerAction是它的靜態內部類,存儲Runnable與延時資訊。
public class HandlerActionQueue {
private HandlerAction[] mActions;
public void post(Runnable action)
public void executeActions(Handler handler)
// ...
private static class HandlerAction {
final Runnable action;
final long delay;
// ...
}
}
View的mRunQueue
將任務(runnable)排成隊。當View關聯上窗口並且有handler後,再執行這些任務。
/**
* Queue of pending runnables. Used to postpone calls to post() until this
* view is attached and has a handler.
*/
private HandlerActionQueue mRunQueue;
這個mRunQueue里存儲的任務啥時候被執行?我們關注dispatchAttachedToWindow方法。
void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
// ...
// Transfer all pending runnables.
if (mRunQueue != null) {
mRunQueue.executeActions(info.mHandler);
mRunQueue = null;
}
// ...
}
這個方法里調用了mRunQueue.executeActions。
executeActions(Handler handler)方法實際上是用傳入的handler處理隊列中的任務。
而這個dispatchAttachedToWindow會被ViewGroup中被調用。
或者是ViewRootImpl中調用
host.dispatchAttachedToWindow(mAttachInfo, 0);
小結
View的post方法,實際上是使用了AttachInfo的handler。
如果View當前還沒有AttachInfo,則把任務添加到了View自己的HandlerActionQueue隊列中,然後在dispatchAttachedToWindow中把任務交給傳入的AttachInfo的handler。也可以這樣認為,View.post用的就是handler.post。
我們在獲取View的寬高時,會利用View的post方法,就是等View真的關聯到window再拿寬高資訊。
流程圖歸納如下
更多請參見Android合集的最近更新


