Java集合系列(四):HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap的使用方法及區別
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
本篇部落格主要講解Map介面的4個實現類HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap的使用方法以及四者之間的區別。
注意:本文中程式碼使用的JDK版本為1.8.0_191
值得注意的是,Map介面是獨立的介面,並沒有繼承Collection介面(這裡是重點,面試常問):
public interface Map<K,V> { ...... }1. HashMap使用
HashMap是Map介面最常用的實現類,存儲Key Value鍵值對,HashMap不保證元素的順序但保證Key必須唯一。
HashMap類的程式碼聲明如下所示:
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { ...... }1.1 添加元素
使用HashMap添加元素有以下3個方法:
- put
- putIfAbsent
- putAll
首先看下put()方法的使用方法:
HashMap<String, String> platformMap = new HashMap<>(); // 添加元素 System.out.println(platformMap.put("cnblogs.com", "部落格園")); System.out.println(platformMap.put("juejin.im", "掘金")); System.out.println(platformMap.put("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公眾號")); System.out.println(platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格")); // 添加重複的Key,沒有添加成功,但是會更新Key對應的Value值 // 不過程式碼不會報錯,而是返回已經存在Key對應的Value System.out.println(platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格"));以上程式碼運行的輸出結果是:
null
null
null
null
個人部落格
調試程式碼也會發現platformMap只有4個元素,而且元素的順序和添加的順序不同:
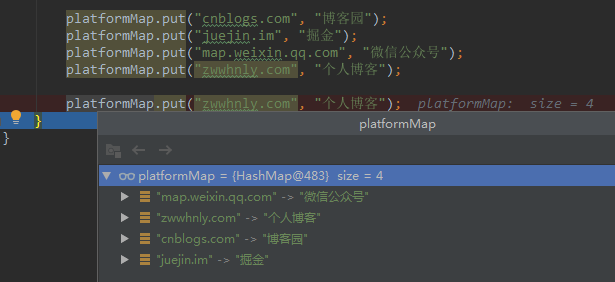
值得注意的是最後一行程式碼platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格")的返回值是「個人部落格」,即之前已存在的Key:zwwhnly.com,對應的Value值。
簡單修改下這句程式碼為:
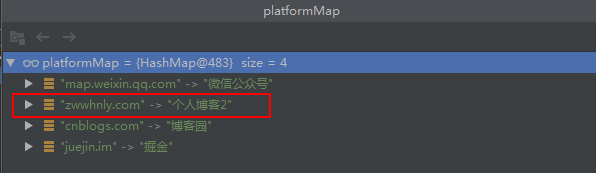
System.out.println(platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格2"));再次運行程式碼,發現輸出結果沒變,platformMap也還是4個元素,但是platformMap元素的內容變了:
如果Key存在時,不希望Value值被覆蓋,可以將程式碼修改為:
System.out.println(platformMap.putIfAbsent("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格2"));另外,HashMap還提供了一個putAll()方法來批量添加元素,使用方法如下所示:
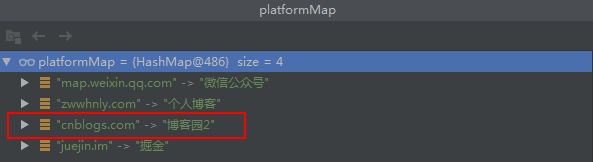
HashMap<String, String> platformMap = new HashMap<>(); HashMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new HashMap<>(); // 添加元素 majorPlatfromMap.put("cnblogs.com", "部落格園"); majorPlatfromMap.put("juejin.im", "掘金"); HashMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new HashMap<>(); otherPlatformMap.put("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公眾號"); otherPlatformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格"); otherPlatformMap.put("cnblogs.com", "部落格園2"); platformMap.putAll(majorPlatfromMap); platformMap.putAll(otherPlatformMap);值得注意的是,由於majorPlatfromMap與otherPlatformMap存在相同的key:cnblogs.com,最終platformMap中Key為」cnblogs.com「的Value值為:「部落格園2「,如下圖所示:
1.2 獲取元素
使用HashMap獲取元素有以下2個方法:
- get()
- getOrDefault()
首先看下get()方法的使用方法:
System.out.println(platformMap.get("cnblogs.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.get("csdn.com"));輸出結果:
部落格園
null
當key不存在時,如果需要設置默認值,可以使用getOrDefault():
System.out.println(platformMap.getOrDefault("csdn.com", "CSDN"));上面這句程式碼的輸出結果為:CSDN。
1.3 獲取集合元素個數
獲取HashMap元素個數的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("platformMap的元素個數為:" + platformMap.size());1.4 刪除元素
使用HashMap刪除元素有以下2個重載:
public V remove(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? null : e.value; } @Override public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) { return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null; }使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公眾號")); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("juejin.im", "部落格園"));上面程式碼的輸出結果為:
個人部落格
null
true
false
1.5 修改元素
使用HashMap修改元素有以下2個重載:
@Override public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) { Node<K,V> e; V v; if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null && ((v = e.value) == oldValue || (v != null && v.equals(oldValue)))) { e.value = newValue; afterNodeAccess(e); return true; } return false; } @Override public V replace(K key, V value) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } return null; }使用方法如下所示:
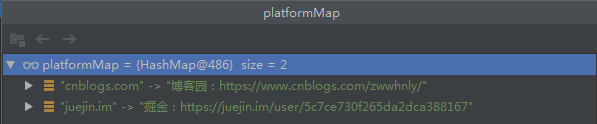
System.out.println(platformMap.replace("cnblogs.com", "部落格園:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/")); System.out.println(platformMap.replace("juejin.im", "掘金", "掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167"));上面程式碼的輸出結果為:
部落格園
true
1.6 判斷集合是否為空
判斷HashMap是否為空的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformMap.isEmpty());1.7 遍曆元素(面試常問)
遍歷HashMap的元素主要有以下4種方式:
- 使用keySet獲取所有的Key,然後遍歷
- 使用Map.entrySet獲取所有的元素,然後使用iterator遍歷
- 使用Map.entrySet獲取所有的元素,然後使用foreach循環遍歷
- 直接使用values獲取到所有的值,該種方式無法遍歷Key
其中2和3的方式,使用的是Set集合的2種遍歷方式,因為platformMap.entrySet()返回的類型是一個Set集合,裡面的元素類型是Map.Entry<K,V>:
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es; return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es; }使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("方式1:使用keySet遍歷"); for (String key : platformMap.keySet()) { System.out.println("Key:" + key + ",Value:" + platformMap.get(key)); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("方式2:通過Map.entrySet使用iterator遍歷"); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = platformMap.entrySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next(); System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue()); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("方式3:通過Map.entrySet使用iterator遍歷"); for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : platformMap.entrySet()) { System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue()); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("方式4:使用values遍歷,使用這種方式無法遍歷Key"); for (String value : platformMap.values()) { System.out.println(value); }1.8 清空集合
清空HashMap中所有元素的使用方法如下所示:
platformMap.clear();1.9 完整示例程式碼
上面講解的幾點,完整程式碼如下所示:
package collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; public class MapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String, String> platformMap = new HashMap<>(); HashMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new HashMap<>(); // 添加元素 majorPlatfromMap.put("cnblogs.com", "部落格園"); majorPlatfromMap.put("juejin.im", "掘金"); HashMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new HashMap<>(); otherPlatformMap.put("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公眾號"); otherPlatformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "個人部落格"); platformMap.putAll(majorPlatfromMap); platformMap.putAll(otherPlatformMap); System.out.println(platformMap.get("cnblogs.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.get("csdn.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.getOrDefault("csdn.com", "CSDN")); System.out.println("platformMap的元素個數為:" + platformMap.size()); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com")); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公眾號")); System.out.println(platformMap.remove("juejin.im", "部落格園")); System.out.println(platformMap.replace("cnblogs.com", "部落格園:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/")); System.out.println(platformMap.replace("juejin.im", "掘金", "掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167")); System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformMap.isEmpty()); System.out.println("方式1:使用keySet遍歷"); for (String key : platformMap.keySet()) { System.out.println("Key:" + key + ",Value:" + platformMap.get(key)); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("方式2:通過Map.entrySet使用iterator遍歷"); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = platformMap.entrySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next(); System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue()); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("方式3:通過Map.entrySet使用iterator遍歷"); for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : platformMap.entrySet()) { System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue()); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("方式4:使用values遍歷,使用這種方式無法遍歷Key"); for (String value : platformMap.values()) { System.out.println(value); } platformMap.clear(); System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformMap.isEmpty()); } }輸出結果為:
部落格園
null
CSDN
platformMap的元素個數為:4
個人部落格
null
true
false
部落格園
true
isEmpty:false
方式1:使用keySet遍歷
Key:cnblogs.com,Value:部落格園:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
Key:juejin.im,Value:掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
方式2:通過Map.entrySet使用iterator遍歷
Key:cnblogs.com,Value:部落格園:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
Key:juejin.im,Value:掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
方式3:通過Map.entrySet使用iterator遍歷
Key:cnblogs.com,Value:部落格園:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
Key:juejin.im,Value:掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
方式4:使用values遍歷,使用這種方式無法遍歷Key
部落格園:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
isEmpty:true
2. Hashtable使用
Hashtable也是Map介面的實現類,值得注意的是,它的方法都是同步的,即是執行緒安全的。
public synchronized int size() { return count; } public synchronized boolean isEmpty() { return count == 0; }HashTable類的程式碼聲明如下所示:
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { { ...... }從以上程式碼也能看出,Hashtable的基類是Dictionary,而HashMap的基類是AbstractMap(這裡是重點,面試常問)。
HashTable類的使用方法和HashMap基本一樣,只需修改下聲明處的程式碼即可:
Hashtable<String, String> platformMap = new Hashtable<>(); Hashtable<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new Hashtable<>(); Hashtable<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new Hashtable<>();3. LinkedHashMap使用
LinkedHashMap也是Map介面的實現類,相比於HashMap,它使用到了鏈表,因此可以保證元素的插入順序,即FIFO(First Input First Output 先進先出)。
LinkedHashMap類的程式碼聲明如下所示:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> { ...... }從以上程式碼也能看出,LinkedHashMap類繼承了HashMap類。
LinkedHashMap類的使用方法和HashMap基本一樣,只需修改下聲明處的程式碼即可:
LinkedHashMap<String, String> platformMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); LinkedHashMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); LinkedHashMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();4. TreeMap使用
TreeMap也是Map介面的實現類,值得注意的是,TreeMap中的元素是有序的,默認的排序規則是按照key的字典順序升序排序。
TreeMap類的程式碼聲明如下所示:
public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { ...... }TreeMap類的使用方法和HashMap基本一樣,只需修改下聲明處的程式碼即可:
TreeMap<String, String> platformMap = new TreeMap<>(); TreeMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new TreeMap<>(); TreeMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new TreeMap<>();5. HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap的區別(面試常問)
5.1 相同點
1)HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap都實現了Map介面
2)四者都保證了Key的唯一性,即不允許Key重複
5.2 不同點
5.2.1 排序
HashMap不保證元素的順序
Hashtable不保證元素的順序
LinkHashMap保證FIFO即按插入順序排序
TreeMap保證元素的順序,支援自定義排序規則
空口無憑,上程式碼看效果:
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>(); LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(); String[] letterArray = new String[]{"B", "A", "D", "C", "E"}; for (String letter : letterArray) { hashMap.put(letter, letter); hashtable.put(letter, letter); linkedHashMap.put(letter, letter); treeMap.put(letter, letter); } System.out.println("HashMap(我不保證順序):" + hashMap); System.out.println("Hashtable(我不保證順序):" + hashtable); System.out.println("LinkedHashMap(我保證元素插入時的順序):" + linkedHashMap); System.out.println("TreeMap(我按排序規則保證元素的順序):" + treeMap);上面程式碼的輸出結果為:
HashMap(我不保證順序):{A=A, B=B, C=C, D=D, E=E}
Hashtable(我不保證順序):{A=A, E=E, D=D, C=C, B=B}
LinkedHashMap(我保證元素插入時的順序):{B=B, A=A, D=D, C=C, E=E}
TreeMap(我按排序規則保證元素的順序):{A=A, B=B, C=C, D=D, E=E}
5.2.2 null值
HashMap,LinkedHashMap允許添加null值(Key和Value都允許),所以以下程式碼是合法的:
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); hashMap.put(null, null); linkedHashMap.put(null, null);TreeMap不允許Key有null值,但允許Value有null值,所以以下程式碼是合法的:
TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(); treeMap.put("cnblogs.com", null);但是treeMap.put(null, null);會引發java.lang.NullPointerException異常:

Hashtable不允許添加null值(Key和Value都不允許),添加null值時會拋出java.lang.NullPointerException異常。
Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>(); hashtable.put("cnblogs.com", null); hashtable.put(null, null);運行上面的程式碼,報錯資訊如下所示:
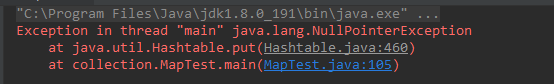
5.2.3 執行緒安全
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap不是執行緒安全的。
Hashtable是執行緒安全的,這是它的優點,同時也導致在理論情況下,Hashtable的效率沒有HashMap高。
所以如果對執行緒安全沒有要求,建議使用HashMap。
5.2.4 繼承
Hashtable的父類是Dictionary。
HashMap的父類是AbstractMap。
LinkedHashMap的父類是HashMap,HashMap的父類是AbstractMap,所以LinkedHashMap也繼承了AbstractMap。
TreeMap的父類是AbstractMap。
6. TreeMap的兩種排序方式(面試常問)
TreeMap默認的排序規則是按照key的字典順序升序排序。
先來看下TreeMap存儲String類型的例子:
TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(); String[] letterArray = new String[]{"B", "A", "D", "C", "E"}; for (String letter : letterArray) { treeMap.put(letter, letter); } for (String key : treeMap.keySet()) { System.out.println("key:" + key + ",Value:" + treeMap.get(key)); }輸出結果:
key:A,Value:A
key:B,Value:B
key:C,Value:C
key:D,Value:D
key:E,Value:E
那如果TreeMap中放入的元素類型是我們自定義的引用類型,它的排序規則是什麼樣的呢?
帶著這個疑問,我們新建個Student類如下:
package collection; public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }然後添加如下驗證程式碼:
TreeMap<Student, Student> studentTreeMap = new TreeMap<>(); Student student1 = new Student("zhangsan", 20); Student student2 = new Student("lisi", 22); Student student3 = new Student("wangwu", 24); Student student4 = new Student("zhaoliu", 26); Student student5 = new Student("zhangsan", 22); studentTreeMap.put(student1, student1); studentTreeMap.put(student2, student2); studentTreeMap.put(student3, student3); studentTreeMap.put(student4, student4); studentTreeMap.put(student5, student5); for (Student student : studentTreeMap.keySet()) { System.out.println("name:" + student.getName() + ",age:" + student.getAge()); }滿心歡喜的運行程式碼想看下效果,結果卻發現報如下錯誤:

為什麼會這樣呢?
這是因為我們並沒有給Student類定義任何排序規則,TreeMap說我也不知道咋排序,還是甩鍋拋出異常吧,哈哈。
怎麼解決呢?有以下兩種方式:
- 自然排序
- 比較器排序
6.1 自然排序
自然排序的實現方式是讓Student類實現介面Comparable,並重寫該介面的方法compareTo,該方法會定義排序規則。
package collection; public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { // 省略其它程式碼 @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { return 0; } }使用IDEA默認生成的compareTo()方法如上所示。
這個方法會在執行add()方法添加元素時執行,以便確定元素的位置。
如果返回0,代表兩個元素相同,只會保留第一個元素
如果返回值大於0,代表這個元素要排在參數中指定元素o的後面
如果返回值小於0,代表這個元素要排在參數中指定元素o的前面
因此如果對compareTo()方法不做任何修改,直接運行之前的驗證程式碼,會發現集合中只有1個元素:
name:zhangsan,age:20
然後修改下compareTo()方法的邏輯為:
@Override public int compareTo(Student o) { // 排序規則描述如下 // 按照姓名的長度排序,長度短的排在前面,長度長的排在後面 // 如果姓名的長度相同,按字典順序比較String // 如果姓名完全相同,按年齡排序,年齡小的排在前面,年齡大的排在後面 int orderByNameLength = this.name.length() - o.name.length(); int orderByName = orderByNameLength == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(o.name) : orderByNameLength; int orderByAge = orderByName == 0 ? this.age - o.age : orderByName; return orderByAge; }再次運行之前的驗證程式碼,輸出結果如下所示:
name:lisi,age:22
name:wangwu,age:24
name:zhaoliu,age:26
name:zhangsan,age:20
name:zhangsan,age:22
6.2 比較器排序
比較器排序的實現方式是新建一個比較器類,繼承介面Comparator,重寫介面中的Compare()方法。
注意:使用此種方式Student類不需要實現介面Comparable,更不需要重寫該介面的方法compareTo。
package collection; import java.util.Comparator; public class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Student> { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { // 排序規則描述如下 // 按照姓名的長度排序,長度短的排在前面,長度長的排在後面 // 如果姓名的長度相同,按字典順序比較String // 如果姓名完全相同,按年齡排序,年齡小的排在前面,年齡大的排在後面 int orderByNameLength = o1.getName().length() - o2.getName().length(); int orderByName = orderByNameLength == 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : orderByNameLength; int orderByAge = orderByName == 0 ? o1.getAge() - o2.getAge() : orderByName; return orderByAge; } }然後修改下驗證程式碼中聲明studentTreeSet的程式碼即可:
TreeMap<Student, Student> studentTreeMap = new TreeMap<>(new StudentComparator());輸出結果和使用自然排序的輸出結果完全一樣。
7. 源碼及參考
Java集合中List,Set以及Map等集合體系詳解(史上最全)
8. 最後
打個小廣告,歡迎掃碼關注微信公眾號:「申城異鄉人」,定期分享Java技術乾貨,讓我們一起進步。

