OpenGl 实现鼠标分别移动多个物体 ———-移动一个物体另外一个物体不动–读取多个3d模型操作的前期踏脚石
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 笔记
原文作者:aircraft
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/DOMLX/p/11620088.html
前言:
因为接下来的项目需求是要读取多个3D模型,并且移动拼接,那么我就先实现鼠标控制两个物体移动互不干扰来当踏脚石。
一.鼠标控制函数准备
我们需要对鼠标信息的获取,那么必然需要一个鼠标事件的响应函数来控制,很好opengl已经有内部的鼠标控制函数了,我们直接拿来使用就行了。
glutMouseFunc( (void*)Func(int button, int state, int x, int y) );
glutMouseFunc这个是调用鼠标函数的入口,func是我们给鼠标处理函数的命名, 三个参数分别是鼠标响应的事件类型,比如左键点击,右键点击之类,x,y则是当前鼠标在窗口的位置坐标。
下面这个是处理鼠标移动时候的调用函数
glutMotionFunc(&func(int x,inty)); // 鼠标移动的时候的函数 x,y当前鼠标坐标
反正调用起来非常的简单只要自己写好一个鼠标点击类事件处理函数和一个鼠标移动事件处理函数,然后传入进去就行了,调用函数放在main函数里。反正后面代码有。
比如:
// 鼠标运动时 void onMouseMove(int x, int y) { //当鼠标状态为按下时进入后续判断 if (mousetate) { //x对应y是因为对应的是法向量 if (choose == 1) { movX1 = (x - x1) / width1; glutPostRedisplay(); movY1 = -((y - Y1) / height1); glutPostRedisplay(); std::cout << " 移动 x1 = " << x << " y1 = " << y << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "not choose" << std::endl; } if (choose == 2) { movX2 = (x - x2) / width2; glutPostRedisplay(); movY2 = -((y - y2) / height2); glutPostRedisplay(); std::cout << " 移动 x2 = " << x << " y2 = " << y << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "not choose" << std::endl; } } } glutMotionFunc(&onMouseMove); // 鼠标移动的时候的函数调用
二.一些鼠标的响应事件
if(state == GLUT_DOWN) //相当于“如果某个鼠标键被按下”
if(state == GLUT_UP) //相当于“如果某个鼠标键被放开”
if(button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON) //相当于“如果鼠标左键被按下或者被放开”
if(button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON) //相当于“如果鼠标右键被按下或被放开”
if(button == GLUT_MIDDLE_BUTTON) //相当于“如果鼠标中键被按下或者被放开”
还有鼠标的滚轮事件
GLUT_WHEEL_UP
GLUT_WHEEL_DOWN
这两个可能有时候会遇到自己gult库没有定义,那么就是版本比较老的缘故,不想麻烦下新版本或者下了新版本还是没有解决的话就直接像这样定义在文件头部:
#define GLUT_WHEEL_UP 3 //定义滚轮操作
#define GLUT_WHEEL_DOWN 4
三.实现过程介绍
首先我们要画出多个物体,那么这个是入门就不讲了。
其次我们鼠标要点击选取一个物体,当我们鼠标按住移动时,物体跟随我们的鼠标移动。按住鼠标点击选取的范围可以是这个物体中心为定点坐标,以边长为d的一个矩形区域,当鼠标点击在这个区域时,我们则判定选取了这个物体。
当两个物体重叠时,我们优先选取画出的第一个物体进行移动。
那么问题就来了,选取了物体后,如何实现物体跟随我们鼠标移动呢?
非常简单,水平方向上,只要在鼠标移动时将移动后的坐标减去移动前的坐标然后除以物体的宽度或者长度 ,就得到了移动的法向量。movX1 = (x – x1) / width1;
垂直方向上,同理可得movY1 = -((y – Y1) / height1); 为什么这里多个负号,是因为向下移动是负数,向上是正数。
然后将移动后改变的移动法向量,让程序调用窗口重新绘制一次即可。如果出现闪烁问题,可以使用双缓冲。
鼠标点击事件处理代码:
整个代码唯一的坑就在两行上,理解这两行,那么就毫无难度了 x1 = 400; Y1 = 400;
// 鼠标交互 void myMouse(int button, int state, int x, int y) { //鼠标左键按下或者松开 if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) { mousetate = 1; if (!choose) { if (x<(x1 + chooseWidth) && x>(x1 - chooseWidth)) { if (y<(Y1 + chooseHeight) && y>(Y1 - chooseHeight)) { x1 = 400; Y1 = 400; movX1 = (x - x1) / width1; movY1 = -((y - Y1) / height1); choose = 1; } } else if (x<(x2 + chooseWidth) && x>(x2 - chooseWidth)) { if (y<(y2 + chooseHeight) && y>(y2 - chooseHeight)) { x2 = 400; y2 = 400; movX2 = (x - x2) / width2; movY2 = -((y - y2) / height2); choose = 2; } } } std::cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << std::endl; } if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_UP) { if (choose == 1) { x1 += (movX1*width1); Y1 += -(movY1*height1); } if (choose == 2) { x2 += (movX2*width2); y2 += -(movY2*height2); } mousetate = 0; choose = 0; std::cout << "x = " << x1 << " y = " << Y1 << std::endl; } //滚轮事件 //scale 增加就是放大 减小就是缩小 //currentfile 对不同的模型用不用的scale if (state == GLUT_UP && button == GLUT_WHEEL_UP) { } else scale = 0.2; if (state == GLUT_UP && button == GLUT_WHEEL_DOWN) { } else scale = 0.2; //glutPostRedisplay();//促使主程序尽快的重绘窗口 }
鼠标移动处理程序代码:
// 鼠标运动时 void onMouseMove(int x, int y) { //当鼠标状态为按下时进入后续判断 if (mousetate) { //x对应y是因为对应的是法向量 if (choose == 1) { movX1 = (x - x1) / width1; glutPostRedisplay(); movY1 = -((y - Y1) / height1); glutPostRedisplay(); std::cout << " 移动 x1 = " << x << " y1 = " << y << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "not choose" << std::endl; } if (choose == 2) { movX2 = (x - x2) / width2; glutPostRedisplay(); movY2 = -((y - y2) / height2); glutPostRedisplay(); std::cout << " 移动 x2 = " << x << " y2 = " << y << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "not choose" << std::endl; } } }
我们预览程序运行,分别控制两个正方体的移动。
移动前:
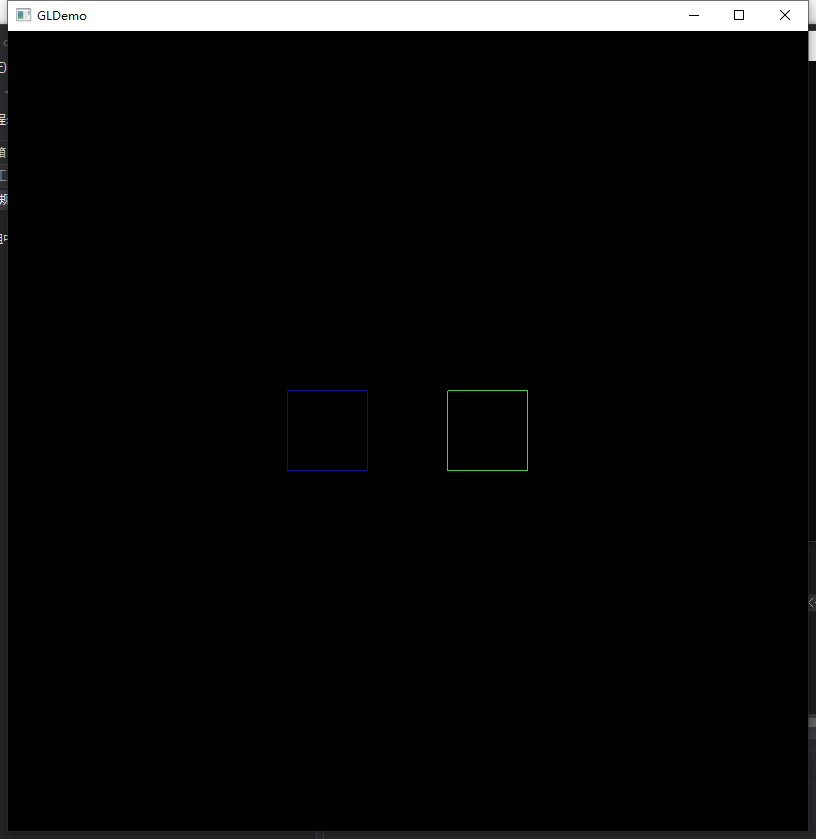
移动后:
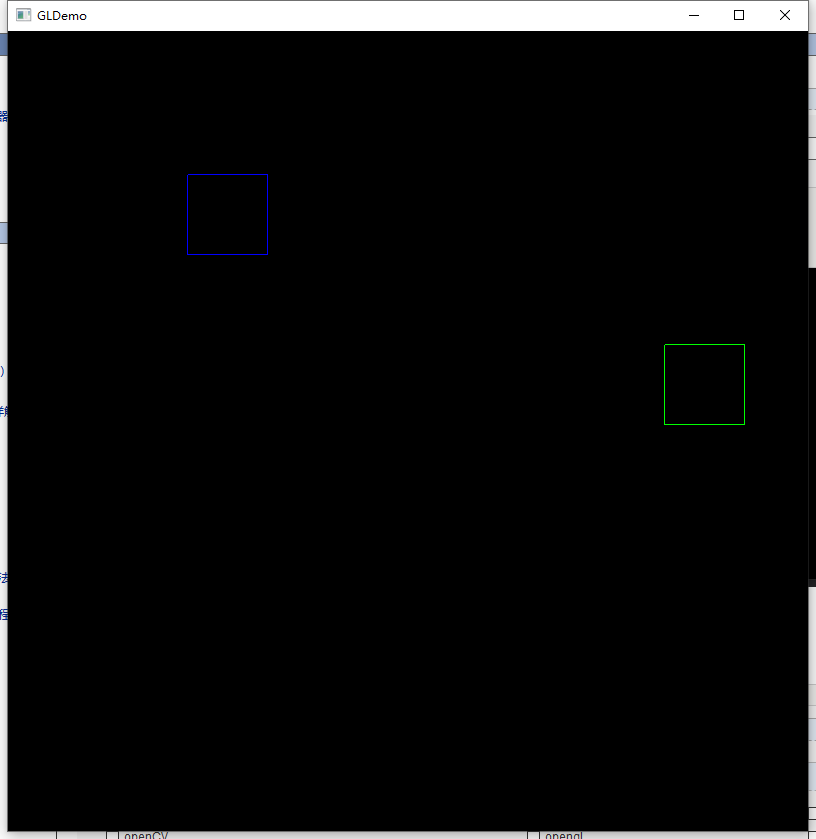
这个就是我们本文实现的内容,后面就可以用于读取多个3d模型分别进行移动。
项目完整代码,配置好Opengl环境可以直接运行,更多项目分享以及学习教程,请关注在下!!!!:
#include <GL/glut.h> #include <iostream> // 绘制立方体 // 将立方体的八个顶点保存到一个数组里面 static GLfloat vertex_list[][3] = { -0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, }; // 将要使用的顶点的序号保存到一个数组里面 static GLint index_list[][4] = { 0, 2, 3, 1, 0, 4, 6, 2, 0, 1, 5, 4, 4, 5, 7, 6, 1, 3, 7, 5, 2, 6, 7, 3, }; #define GLUT_WHEEL_UP 3 //定义滚轮操作 #define GLUT_WHEEL_DOWN 4 const int windowsWidth = 800; const int windowsHeight = 800; GLfloat scale = 0.2; GLfloat movX1 = -1.0f, movX2 = 1.0f, movY1 = 0.0f, movY2 = 0.0f; GLfloat width1 = (windowsWidth / 2.0)*scale,height1 = (windowsHeight / 2)*scale; GLfloat width2 = (windowsWidth / 2)*scale, height2 = (windowsHeight / 2)*scale; GLfloat x1 = (windowsWidth / 2)+(width1*movX1), x2 = (windowsWidth / 2) + (width1*movX2), Y1 = (windowsHeight / 2)+(height1*movY1), y2 = (windowsHeight / 2) + (height1*movY2), z1 = 0.0f, z2 = 0.0f; GLfloat chooseWidth = 20,chooseHeight = 20; GLfloat dx = 0, dy = 0; bool mousetate = 0; int choose = 0; // 鼠标交互 void myMouse(int button, int state, int x, int y) { //鼠标左键按下或者松开 if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) { mousetate = 1; if (!choose) { if (x<(x1 + chooseWidth) && x>(x1 - chooseWidth)) { if (y<(Y1 + chooseHeight) && y>(Y1 - chooseHeight)) { x1 = 400; Y1 = 400; movX1 = (x - x1) / width1; movY1 = -((y - Y1) / height1); choose = 1; } } else if (x<(x2 + chooseWidth) && x>(x2 - chooseWidth)) { if (y<(y2 + chooseHeight) && y>(y2 - chooseHeight)) { x2 = 400; y2 = 400; movX2 = (x - x2) / width2; movY2 = -((y - y2) / height2); choose = 2; } } } std::cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << std::endl; } if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_UP) { if (choose == 1) { x1 += (movX1*width1); Y1 += -(movY1*height1); } if (choose == 2) { x2 += (movX2*width2); y2 += -(movY2*height2); } mousetate = 0; choose = 0; std::cout << "x = " << x1 << " y = " << Y1 << std::endl; } //滚轮事件 //scale 增加就是放大 减小就是缩小 //currentfile 对不同的模型用不用的scale if (state == GLUT_UP && button == GLUT_WHEEL_UP) { } else scale = 0.2; if (state == GLUT_UP && button == GLUT_WHEEL_DOWN) { } else scale = 0.2; //glutPostRedisplay();//促使主程序尽快的重绘窗口 } // 鼠标运动时 void onMouseMove(int x, int y) { //当鼠标状态为按下时进入后续判断 if (mousetate) { //x对应y是因为对应的是法向量 if (choose == 1) { movX1 = (x - x1) / width1; glutPostRedisplay(); movY1 = -((y - Y1) / height1); glutPostRedisplay(); std::cout << " 移动 x1 = " << x << " y1 = " << y << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "not choose" << std::endl; } if (choose == 2) { movX2 = (x - x2) / width2; glutPostRedisplay(); movY2 = -((y - y2) / height2); glutPostRedisplay(); std::cout << " 移动 x2 = " << x << " y2 = " << y << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "not choose" << std::endl; } } } // 绘制立方体 void DrawCube(void) { glPushMatrix(); glFrontFace(GL_CCW);//逆时针 glCullFace(GL_BACK); glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE); glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE); int i, j; glBegin(GL_QUADS); //glBegin(GL_LINES); for (i = 0; i < 6; ++i) // 12 条线段 { for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j) // 每条线段 2个顶点 { glVertex3fv(vertex_list[index_list[i][j]]); } } glEnd(); } static float rotate = 0; static int times = 0; void renderScene2(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); glColor3f(0, 0, 1); glScalef(0.3, 0.3, 0.3); // 缩放 glPushMatrix(); //glTranslatef(-0.2, 0, 0); // 平移 //glScalef(2, 1, 1); // 缩放 times++; if (times > 100) { times = 0; } if (times % 100 == 0) { rotate += 0.3; } glPushMatrix(); glTranslatef(-2, 0, 0); // 平移 glRotatef(rotate, 0, 1, 0); glRotatef(rotate, 1, 0, 0); DrawCube(); glPopMatrix(); glTranslatef(2, 0, 0); // 平移 glRotatef(rotate, 0, 1, 0); glRotatef(rotate, 1, 0, 0); //glScalef(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); // 缩放 DrawCube(); glPopMatrix(); glutSwapBuffers(); } void renderScene(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); glScalef(scale, scale, scale); // 缩放 glPushMatrix(); glColor3f(0, 0, 1); glTranslatef(movX1, movY1, 0); DrawCube(); glPopMatrix(); glPushMatrix(); glColor3f(0, 1, 0); glTranslatef(movX2, movY2, 0); DrawCube(); glPopMatrix(); glutSwapBuffers(); } void main(int argc, char **argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA); glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100); glutInitWindowSize(windowsWidth, windowsHeight); glutCreateWindow("GLDemo"); glutMouseFunc(&myMouse); //鼠标点击处理函数 glutMotionFunc(&onMouseMove); // 鼠标移动的时候的函数 glutDisplayFunc(&renderScene); glutIdleFunc(&renderScene); glutMainLoop(); }
