数据源管理 | 主从库动态路由,AOP模式读写分离
- 2020 年 4 月 1 日
- 笔记
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里
一、多数据源应用
1、基础描述
在相对复杂的应用服务中,配置多个数据源是常见现象,例如常见的:配置主从数据库用来写数据,再配置一个从库读数据,这种读写分离模式可以缓解数据库压力,提高系统的并发能力和稳定性,执行效率。
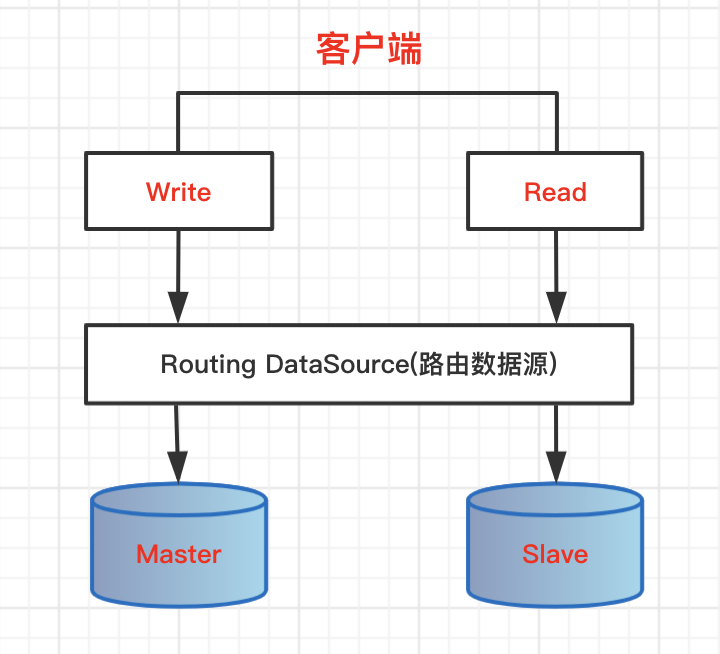
2、核心API
在处理这种常见问题,要学会查询服务基础框架的API,说直白点就是查询Spring框架的API(工作几年,还没用过Spring之外的框架搭建环境),这种常用的业务模式,基本上Spring都提供了API支持。
核心API:AbstractRoutingDataSource
底层维护Map容器,用来保存数据源集合,提供一个抽象方法,实现自定义的路由策略。
@Nullable private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources; @Nullable protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey(); 补刀一句:为何框架的原理很难通过一篇文章看明白?因为使用的不多,基本意识没有形成,熟悉框架原理的基本要求:对框架的各种功能都熟悉,经常使用,自然而然的就明白了,盐大晒的久,咸鱼才够味。
二、数据源路由
1、数据源管理
配置两个数据源
spring: datasource: type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver master: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/data_master username: root password: 123456 slave: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/data_slave username: root password: 123456 从实际开发角度,这两个数据源需要配置主从复制流程,再基于安全角度,写库可以只给写权限,读库只给读权限。
Map容器加载
@Configuration public class DruidConfig { // 忽略参数加载,源码中有 @Bean @Primary public DataSource primaryDataSource() { Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("masterDataSource", masterDataSource()); map.put("slaveDataSource", slaveDataSource()); RouteDataSource routeDataSource = new RouteDataSource(); routeDataSource.setTargetDataSources(map); routeDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource()); return routeDataSource ; } private DataSource masterDataSource() { return getDefDataSource(masterUrl,masterUsername,masterPassword); } private DataSource slaveDataSource() { return getDefDataSource(slaveUrl,slaveUsername,slavePassword); } private DataSource getDefDataSource (String url,String userName,String passWord){ DruidDataSource datasource = new DruidDataSource(); datasource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName); datasource.setUrl(url); datasource.setUsername(userName); datasource.setPassword(passWord); return datasource; } } 这里的Map容器管理两个key,masterDataSource和slaveDataSource代表两个不同的库,使用不同的key即加载对应的库。
2、容器Key管理
使用ThreadLocal管理当前会会话中线程参数,存取使用极其方便。
public class RouteContext implements AutoCloseable { private static final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void setRouteKey (String key){ threadLocal.set(key); } public static String getRouteKey() { String key = threadLocal.get(); return key == null ? "masterDataSource" : key; } @Override public void close() { threadLocal.remove(); } } 3、路由Key实现
获取ThreadLocal中,当前数据源的key,适配相关联的数据源。
public class RouteDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { return RouteContext.getRouteKey(); } } 三、读写分离
1、AOP思维
基于AOP的切面思想,不同的方法类型,去设置对应路由Key,这样就可以在业务逻辑执行之前,切换到不同的数据源。
Aspect @Component @Order(1) public class ReadWriteAop { private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReadWriteAop.class) ; @Before("execution(* com.master.slave.controller.*.*(..))") public void setReadDataSourceType() { HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest(); String method = request.getRequestURI() ; boolean rwFlag = readOrWrite(method) ; if (rwFlag){ RouteContext.setRouteKey("slaveDataSource"); } else { RouteContext.setRouteKey("masterDataSource"); } LOGGER.info("请求方法:"+method+";执行库:"+RouteContext.getRouteKey()); } private String[] readArr = new String[]{"select","count","query","get","find"} ; private boolean readOrWrite (String method){ for (String readVar:readArr) { if (method.contains(readVar)){ return true ; } } return false ; } } 常见的读取方法:select、count、query、get、find等等,方法的命名要遵循自定义的路由规则。
2、提供测试接口
控制层API
import com.master.slave.entity.User; import com.master.slave.service.UserService; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RestController public class UserController { @Resource private UserService userService ; @GetMapping("/selectById") public User selectById (@RequestParam("id") Integer id) { return userService.selectById(id) ; } @GetMapping("/insert") public String insert () { User user = new User("张三","write") ; userService.insert(user) ; return "success" ; } } 服务实现
@Service public class UserService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper ; public User selectById (Integer id) { return userMapper.selectById(id) ; } public void insert (User user){ userMapper.insert(user); } } 这样数据源基于不同的类型方法就会一直的动态切换。
四、源代码地址
GitHub·地址 https://github.com/cicadasmile/data-manage-parent GitEE·地址 https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/data-manage-parent 


