Spring系列(六):Spring事务源码解析
- 2019 年 10 月 13 日
- 笔记
一、事务概述
1.1 什么是事务
事务是一组原子性的SQL查询,或者说是一个独立的工作单元。要么全部执行,要么全部不执行。
1.2 事务的特性(ACID)
①原子性(atomicity)
一个事务必须被视为一个不可分割的最小工作单元,整个事务中的所有操作要么全部提交成功,要么全部回滚,对于一个事务来说,不可能只执行其中的一部分操作
②一致性(consistency)
数据库总是从一个一致性的状态转换到另外一个一致性的状态。
③隔离性(isolation)
一个事务所做的修改在最终提交以前,对其他事务是不可见的。也就是说多个并发事务之间要相互隔离。
④持久性(durability)
一旦事务提交,则其所做的修改就会永久的保存在数据库中,接下来即使数据库系统崩溃了,修改的数据也不会丢失
1.3 事务的隔离级别
①读未提交(READ UNCOMMITTED)
事务中的修改,即使没有提交,对其他事务也是可见的,也就是说事务可以读取到未提交的数据,这也被称为脏读。
②读已提交(READ COMMITTED)
一个事务从开始到提交之前,所做的任何修改对其他事务都是不可见的,这个级别有时候也叫不可重复读,因为两次执行同样的查询,可能会得到不一样的结果。
③可重复读(REPEATABLE READ)
该隔离级别保证了在同一个事务中多次读取同样的记录的结果是一致的,但是无法解决另外一个幻读的问题,所谓的幻读就是指当某个事务在读取某个范围内的记录是,另外一个事务又在该范围内插入了新的记录,当之前的事务再次读取该范围的记录时就会产生幻行。
④可串行化(SERIALIZABLE)
SERIALIZABLE是最高的隔离级别,通过强制事务的串行执行,避免了前面说的幻读问题,简单来说,SERIALIZABLE会在读取的每一行数据上加上锁。
二、Spring事务关键接口
1 PlatformTransactionManager 事务管理器
public interface PlatformTransactionManager { /** * 获取事务 */ TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException; /** * 提交 */ void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException; /** * 回滚 */ void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException; }
2 TransactionDefinition 事务定义信息
public interface TransactionDefinition { /** * Support a current transaction; create a new one if none exists. 支持当前事物,若当前没有事物就创建一个事物 */ int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0; /** * Support a current transaction; execute non-transactionally if none exists. 如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式运行 */ int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1; /** * Support a current transaction; throw an exception if no current transaction exists. 如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常 */ int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2; /** * Create a new transaction, suspending the current transaction if one exists.创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起 */ int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3; /** * Do not support a current transaction; rather always execute non-transactionally.以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起 */ int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4; /** * Do not support a current transaction; throw an exception if a current transaction exists. 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常 */ int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5; /** * Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists.如果外层存在事务,就以嵌套事务运行,被嵌套的事务可以独立于外层事务进行提交或者回滚(保存点), 如果外层不存在事务,行为跟PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW */ int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6; /** * Use the default isolation level of the underlying datastore. 使用数据库默认的隔离级别
*/ int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1; /** * 读未提交
*/ int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED; /** * 读已提交
*/ int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED; /** * 可重复读*/ int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ; /** * 可串行化
*/ int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE; /** * 使用默认的超时时间 */ int TIMEOUT_DEFAULT = -1; /** * 获取事物的传播行为
*/ int getPropagationBehavior(); /** * 获取事物的隔离级别
*/ int getIsolationLevel(); /** * 获取事物的超时时间
*/ int getTimeout(); /** * 是否为只读事物
*/ boolean isReadOnly(); /** * 获取当前事物的名称
*/ String getName(); }
3 TransactionStatus 事务运行状态
public interface TransactionStatus extends SavepointManager, Flushable { /** * 是否为新事务 */ boolean isNewTransaction(); /** * 是否有保存点*/ boolean hasSavepoint(); /** * 设置为只回滚*/ void setRollbackOnly(); /** * 是否为只回滚 */ boolean isRollbackOnly(); /** * 讲会话刷新到数据库中 */ @Override void flush(); /** * 当前事务是否已经完成*/ boolean isCompleted(); }
三、Spring事务启动过程
1 @EnableTransactionManagement
1.1 在主配置类中添加@EnableTransactionManagement注解,开启Spring事务的支持,配置如下:
@EnableTransactionManagement @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.toby"}) public class TransactionConfig { @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource(); dataSource.setUsername("root"); dataSource.setPassword("123qwe"); dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false"); dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); return dataSource; } @Bean public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) { return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); } @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) { return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource); } }
1.2 @EnableTransactionManagement 到底做了什么?
源码解析跟Spring系列(五):Spring AOP源码解析中的@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解一样,可以参考下。主要给Spring容器加入如下组件:
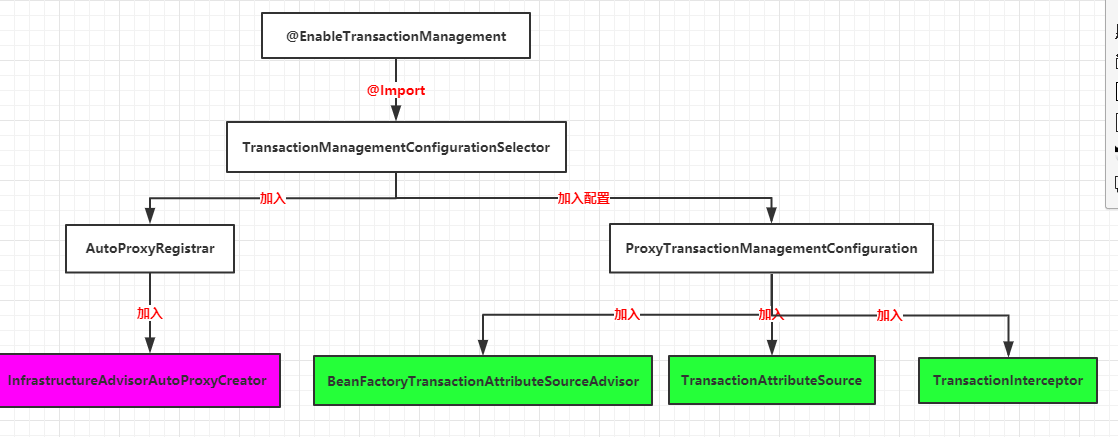
2 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(重点)
2.1 首先看下类继承图
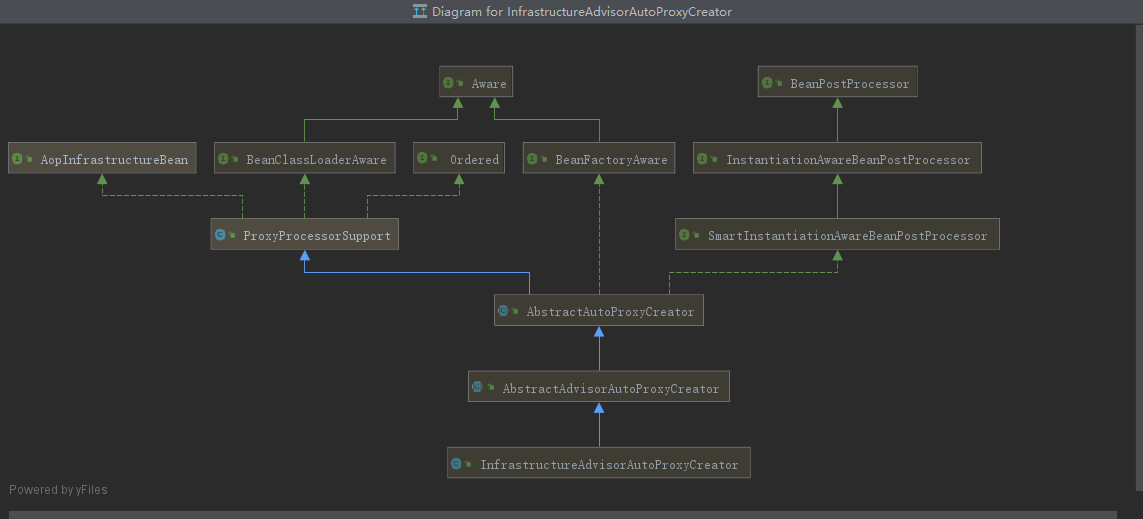
2.2 实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
该接口有2个方法postProcessBeforeInstantiation和postProcessAfterInstantiation,其中实例化之前会执行postProcess BeforeInstantiation方法:
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { //构建我们的缓存key Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { //如果被解析过直接返回 if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null; } /** * 判断是不是基础的bean * 判断是不是应该跳过 (此处Spring Aop解析直接解析出我们的切面信息(并且把我们的切面信息进行缓存),
* 而事务在这里是不会解析的,为什么?原因事务的话已经把事务拦截器通过@Bean,而Aop的需要寻找) */ if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null; } } TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName); if (targetSource != null) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) { this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName); } Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } return null; }
2.3 实现了BeanPostProcessor接口
该接口有2个方法postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization,其中组件初始化之后会执行postProcessAfterInitialization(该方法创建Aop和事务的代理对象)方法:
/** * 在该后置方法中 我们的事务和aop的代理对象都是在这生成的 * @param bean bean实例 * @param beanName bean的名称 * @return * @throws BeansException */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { //获取缓存key Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { //如果有必要就代理 return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
进去wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey)方法:
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { //已经被处理过 if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } //不需要增强的 if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } //是不是基础的bean 是不是需要跳过的 if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } //如果有匹配的通知,就创建代理对象 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); //如果不为空,表述需要代理 if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { //设置当前的对象已处理 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); //创建我们的真正的代理对象 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); //加入到缓存 this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
进入getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null)方法:
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { /** * 找合适的增强器对象 */ List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); //若合适的通知器为空 if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
进入findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName)方法:
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { //找到Spring IoC容器中所有的候选通知 包括Aop的和事务的 List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); //判断找到的通知能不能作用到当前的类上 List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); //对我们的advisor进行排序 if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
① 进入findCandidateAdvisors()方法,通过增强器检索器检索增强器:
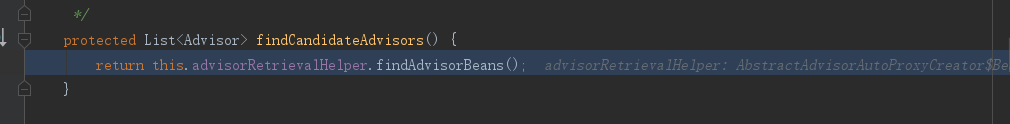
进入findAdvisorBeans()方法:
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() { String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames; if (advisorNames == null) { /** * 去容器中获取到实现了Advisor接口的实现类 我们的事务注解@EnableTransactionManagement导入了一个叫ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration配置类 * 而在这个配置类中配置了: * @Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME) * @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) * public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(); * 然后把他的名字获取出来保存到 本类的属性变量cachedAdvisorBeanNames中 */ advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false); this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames; } //若在容器中没有找到,直接返回一个空的集合 if (advisorNames.length == 0) { return new ArrayList<>(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>(); //容器中找到了我们事务配置的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor for (String name : advisorNames) { //判断他是不是一个合适的 if (isEligibleBean(name)) { //BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor是不是正在创建的Bean if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'"); } } //不是的话 else { try { //显示的调用getBean方法方法创建我们的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor返回去 advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class)); } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause(); if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) { BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause; String bceBeanName = bce.getBeanName(); if (bceBeanName != null && this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bceBeanName)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping advisor '" + name + "' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage()); } // Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise. // We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself. continue; } } throw ex; } } } } return advisors; }
进入到isEligibleBean(name)方法:

进入isEligibleAdvisorBean(beanName)方法:
protected boolean isEligibleAdvisorBean(String beanName) { /** * 容器中包含了这个Bean定义,并且Bean定义的角色为BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE */ return (this.beanFactory != null && this.beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition(beanName) && this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName).getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); }
如果是合适的就保存在advisors中并返回;至此findCandidateAdvisors()执行完毕!!!
② 找到的增强器是否能作用在当前的类上,findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName)方法:
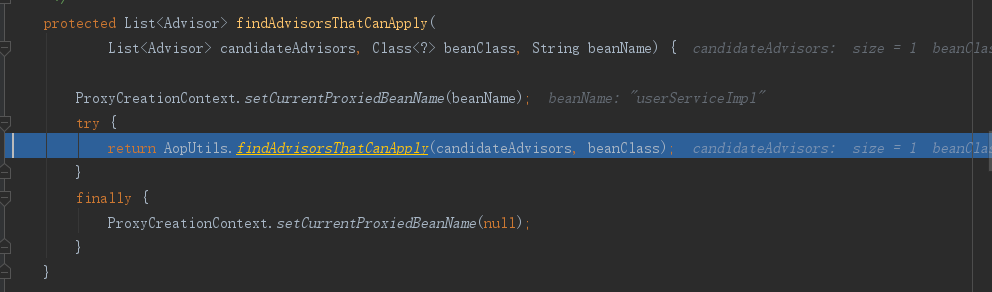
进入到AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass)方法:
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { //若候选的增强器集合为空直接返回 if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } //定义一个合适的增强器集合对象 List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(); //循环我们候选的增强器对象 for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { //判断我们的增强器对象是不是实现了IntroductionAdvisor (很明显我们事务的没有实现 所以不会走下面的逻辑) if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } //不为空 boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { //判断我们的增强器对象是不是实现了IntroductionAdvisor (很明显我们事务的没有实现 所以不会走下面的逻辑) if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { //在上面已经处理过 ,不需要处理 continue; } /** * 真正的判断增强器是否合适当前类 */ if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; }
真正的判断增强器是否合适当前类,canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)方法:
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { //判断我们的增强器 IntroductionAdvisor if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } //判断我们事务的增强器BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor是否实现了PointcutAdvisor else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { //转为PointcutAdvisor类型 PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; //找到真正能用的增强器 return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { // It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies. return true; } }
找到真正能用的增强器,canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions)方法:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null"); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false; } /** * 通过切点获取到一个方法匹配器对象 */ MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { // No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway... return true; } //判断匹配器是不是IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } //创建一个集合用于保存targetClass的class对象 Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>(); //判断当前class是不是代理的class对象 if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { //加入到集合中去 classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass)); } //获取到targetClass所实现的接口的class对象,然后加入到集合中 classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); //循环所有的class对象 for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { //通过class获取到所有的方法 Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); //循环我们的方法 for (Method method : methods) { //通过methodMatcher.matches来匹配我们的方法 if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ? introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) : //通过方法匹配器进行匹配 methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true; } } } return false; }
进入methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)方法:
public boolean matches(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { if (targetClass != null && TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) { return false; } /** * 获取我们@EnableTransactionManagement注解为我们容器中导入的ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration * 配置类中的TransactionAttributeSource对象 */ TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); //若事务属性原为null或者 解析出来的事务注解属性不为空 表示方法匹配 return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null); }
进入到获取事务注解属性tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass)方法:
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { //判断method所在的class 是不是Object类型 if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { return null; } //构建我们的缓存key Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass); //先去我们的缓存中获取 TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey); //缓存中不为空 if (cached != null) { //判断缓存中的对象是不是空事务属性的对象 if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) { return null; } else { return cached; } } else { //查找我们的事务注解 TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass); //若解析出来的事务注解属性为空 if (txAttr == null) { //往缓存中存放空事务注解属性 this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE); } else { //我们执行方法的描述符 包名+类名+方法名 String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass); //把方法描述设置到事务属性上去 if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) { ((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr); } //加入到缓存 this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr); } return txAttr; } }
进入查找我们的事务注解,computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass)方法:
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { //判断我们的事务方法上的修饰符是不是public的 if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { return null; } // The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class. // If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged. Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass); //第一:先去目标对象的方法上去找我们的事务注解 TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod); if (txAttr != null) { return txAttr; } //第二:去目标对象上找事务注解 txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass()); if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) { return txAttr; } if (specificMethod != method) { //第三:去我们的实现类的接口上的方法去找事务注解 txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method); if (txAttr != null) { return txAttr; } //第四:去我们的实现类的接口上去找事务注解 txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) { return txAttr; } } return null; }
进入到找@Transactional注解,findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod)方法:

进入determineTransactionAttribute(method)方法:
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement element) { //获取我们的注解解析器 for (TransactionAnnotationParser annotationParser : this.annotationParsers) { //通过注解解析器去解析我们的元素(方法或者类)上的注解 TransactionAttribute attr = annotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element); if (attr != null) { return attr; } } return null; }
进入annotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element)方法:
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element) { //从element对象中获取@Transactional注解 然后把注解属性封装到了AnnotationAttributes AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes( element, Transactional.class, false, false); if (attributes != null) { //解析出真正的事务属性对象 return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes); } else { return null; } }
进入到解析出真正的事务属性对象,parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes)方法:
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) { //创建一个基础规则的事务属性对象 RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute(); //解析@Transactionl上的传播行为 Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation"); rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value()); //解析@Transactionl上的隔离级别 Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation"); rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value()); //解析@Transactionl上的事务超时事件 rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue()); rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly")); //解析@Transactionl上的事务管理器的名称 rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value")); //解析针对哪种异常回滚 List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<>(); for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) { rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } //对哪种异常进行回滚 for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) { rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } //对哪种异常不回滚 for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) { rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } //对哪种类型不回滚 for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) { rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule)); } rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules); return rbta; }
至此computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass)方法执行完毕!!!
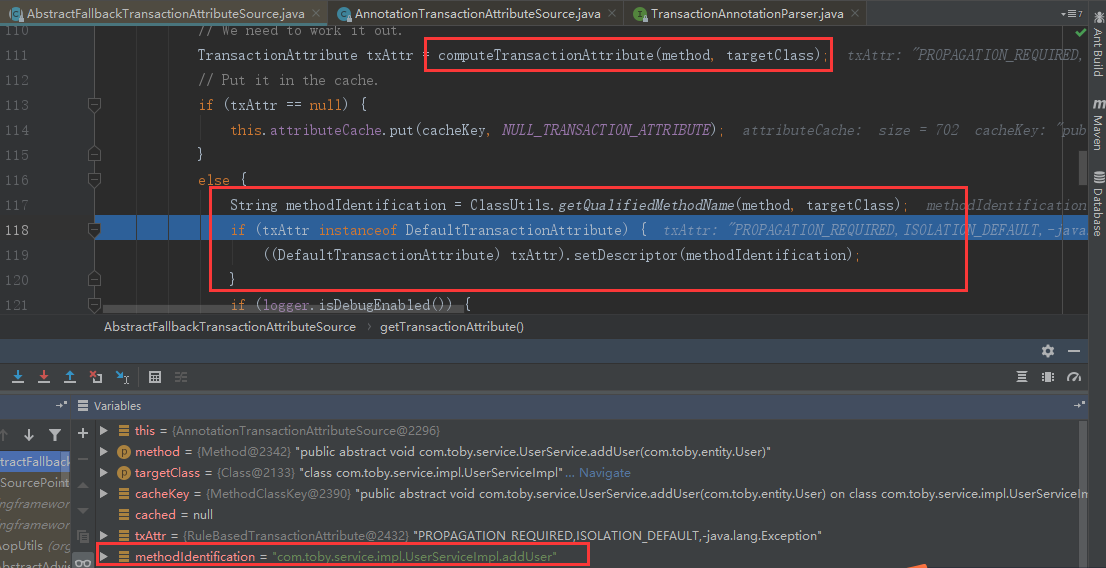
然后把我们执行方法的描述符设置到TransactionAttribute事务属性中,表示该方法需要执行Spring事务,并把事务注解属性加入到缓存attributeCache中,至此获取事务注解属性tas.getTransactionAttribute完毕!!!
如果canApply方法返回true表示找到真正能用的增强器了,然后就把合适的增强器加入到eligibleAdvisors中:

至此findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName)执行完毕!!!
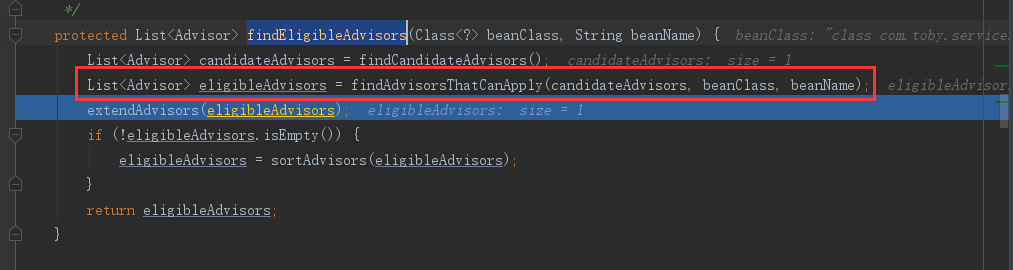
③ extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors) 扩展增强器
④ sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors) 排序
其中③,④ 略 具体参考Spring系列(五):Spring AOP源码解析,其实事务找增强器相对Aop简单很多,到此findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName)执行完毕!!!

到此Spring事务创建代理对象完毕!!!
四、Spring事务代理调用过程
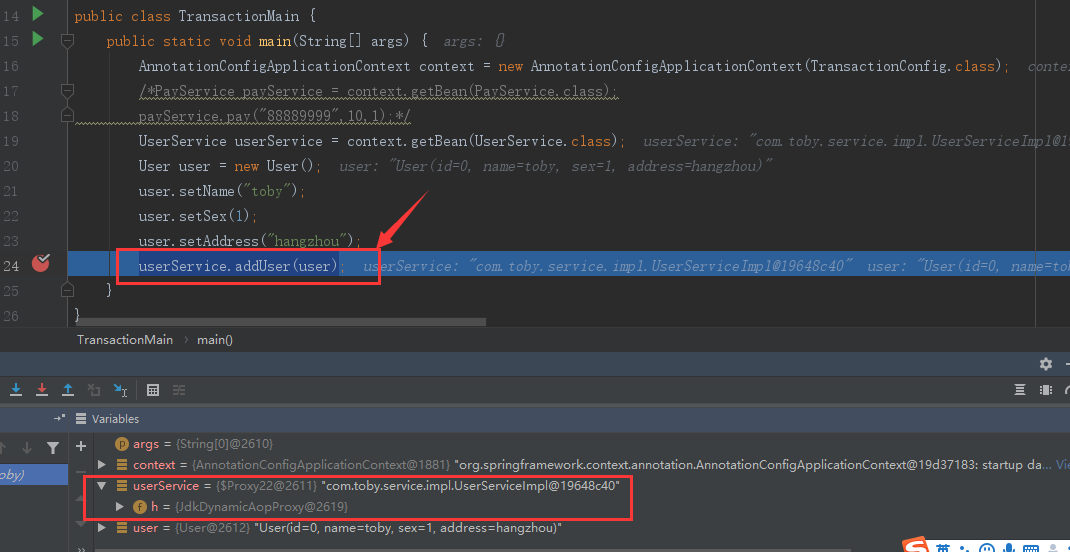
第一步:执行addUser(user)方法
其实就是调用org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; //获取到我们的目标对象 TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null; try { //若是equals方法不需要代理 if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself. return equals(args[0]); } //若是hashCode方法不需要代理 else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself. return hashCode(); } //若是DecoratingProxy也不要拦截器执行 else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) { // There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config. return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised); } else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config... return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); } Object retVal; /** * 这个配置是暴露我们的代理对象到线程变量中,需要搭配@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)一起使用 * 比如在目标对象方法中再次获取代理对象可以使用这个AopContext.currentProxy() * 还有的就是事务方法调用事务方法的时候也是用到这个 */ if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { //把我们的代理对象暴露到线程变量中 oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } //获取我们的目标对象 target = targetSource.getTarget(); //获取我们目标对象的class Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); //把aop的advisor转化为拦截器链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); //如果拦截器链为空 if (chain.isEmpty()) { //通过反射直接调用执行 Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { //创建一个方法调用对象 MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); //调用执行 retVal = invocation.proceed(); } // Massage return value if necessary. Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method // is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets // a reference to itself in another returned object. retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // Must have come from TargetSource. targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
进入到invocation.proceed()方法,该方法的调用用到了递归和责任链设计模式:
public Object proceed() throws Throwable { //从-1开始,下标=拦截器的长度-1的条件满足表示执行到了最后一个拦截器的时候,此时执行目标方法 if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint(); } //获取第一个方法拦截器使用的是前++ Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have // been evaluated and found to match. InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) { return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); } else { // Dynamic matching failed. // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain. return proceed(); } } else { return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } }
进入到((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this)方法:
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { //获取我们的代理对象的class属性 Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); /** * 以事务的方式调用目标方法 * 在这埋了一个钩子函数 用来回调目标方法的 */ return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed); }
调用invokeWithinTransaction方法
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable { //获取我们的事务属源对象 TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); //通过事务属性源对象获取到我们的事务属性信息 final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null); //获取我们配置的事务管理器对象 final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); //从tx属性对象中获取出标注了@Transactionl的方法描述符 final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr); //处理声明式事务 if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { //有没有必要创建事务 TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); Object retVal; try { //调用钩子函数进行回调目标方法 retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { //抛出异常进行回滚处理 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); throw ex; } finally { //清空我们的线程变量中transactionInfo的值 cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } //提交事务 commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); return retVal; } //编程式事务 else { final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder(); // It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in. try { Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> { TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); try { return invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) { // A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback. if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) ex; } else { throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex); } } else { // A normal return value: will lead to a commit. throwableHolder.throwable = ex; return null; } } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } }); // Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow. if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { throw throwableHolder.throwable; } return result; } catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) { throw ex.getCause(); } catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) { if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable); ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable); } throw ex2; } catch (Throwable ex2) { if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable); } throw ex2; } } }
1 createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification)方法:
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm, @Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) { // 把我们的方法描述符作为一个事务名称 if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) { txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) { @Override public String getName() { return joinpointIdentification; } }; } TransactionStatus status = null; if (txAttr != null) { if (tm != null) { //获取一个事务状态 status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr); } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification + "] because no transaction manager has been configured"); } } } //把事务状态和事务属性等信息封装成一个TransactionInfo对象 return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); }
1.1 进入获取一个事务状态,tm.getTransaction(txAttr)方法:
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException { //尝试获取一个事务对象 Object transaction = doGetTransaction(); // Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks. boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled(); /** * 判断从上一个方法传递进来的事务属性是不是为空 */ if (definition == null) { //为空的话,执行非事务方法 definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); } /** * 判断是不是已经存在了事务对象 */ if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) { //处理存在的事务 return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled); } //检查事务设置的超时时间 if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout()); } /** * 若当前的事务属性式 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY 表示必须运行在事务中,若当前没有事务就抛出异常 * 由于isExistingTransaction(transaction)跳过了这里,说明当前是不存在事务的,那么就会抛出异常 */ if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException( "No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'"); } /** * PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 当前存在事务就加入到当前的事务,没有就新开一个 * PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:新开一个事务,若当前存在事务就挂起当前事务 * PROPAGATION_NESTED: PROPAGATION_NESTED 表示如果当前正有一个事务在运行中,则该方法应该运行在 一个嵌套的事务中, 被嵌套的事务可以独立于封装事务进行提交或者回滚(保存点), 如果封装事务不存在,行为就像 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW */ else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW || definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) { /** * 挂起当前事务,在这里为啥传入null? * 因为逻辑走到这里了,经过了上面的isExistingTransaction(transaction) 判断当前是不存在事务的 * 所有再这里是挂起当前事务传递一个null进去 */ SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null); if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition); } try { boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); //新创建一个事务状态 DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); //开启一个新的事物 doBegin(transaction, definition); //把当前的事务信息绑定到线程变量去 prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) { resume(null, suspendedResources); throw ex; } } else { //创建一个空的事务 // Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization. if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " + "isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition); } boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS); return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); } }
① 进入到doGetTransaction()方法:
protected Object doGetTransaction() { //创建一个数据源事务对象 DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject(); //是否允许当前事务设置保持点 txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed()); /** * TransactionSynchronizationManager 事务同步管理器对象(该类中都是局部线程变量) * 用来保存当前事务的信息,我们第一次从这里去线程变量中获取 事务连接持有器对象 通过数据源为key去获取 * 由于第一次进来开始事务 我们的事务同步管理器中没有被存放.所以此时获取出来的conHolder为null */ ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource()); txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false); //返回事务对象 return txObject; }
② 进入isExistingTransaction(transaction)方法:
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction; //若第一次进来开始事务,txObject.hasConnectionHolder() 返回的null 那么表示不存在事务 return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive()); }
③ 由于事务传播机制是TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,所以走下面分支
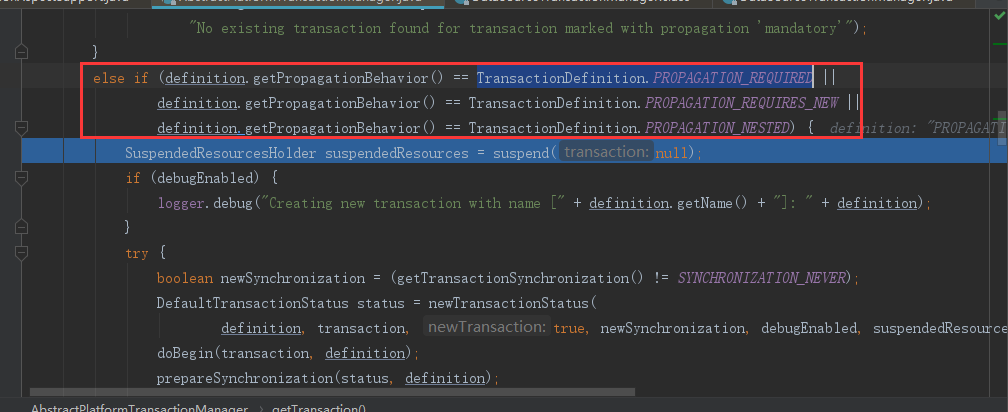
④ 进入挂起事务,suspend(null)方法:
protected final SuspendedResourcesHolder suspend(@Nullable Object transaction) throws TransactionException { //判断当前的线程变量中 有没有激活的事物,有需要清空线程变量 if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) { List<TransactionSynchronization> suspendedSynchronizations = doSuspendSynchronization(); try { Object suspendedResources = null; if (transaction != null) { suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction); } //获取已存在的事务的名称 String name = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionName(); //清空线程变量的 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(null); //获取出只读事务的名称 boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly(); //清空线程变量的 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false); //获取已存在事务的隔离级别 Integer isolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(); //清空隔离级别 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(null); //获取激活标志 boolean wasActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive(); //清空标记 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(false); //把上诉从线程变量中获取出来的存在事务属性封装为挂起的事务属性返回出去 return new SuspendedResourcesHolder( suspendedResources, suspendedSynchronizations, name, readOnly, isolationLevel, wasActive); } catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) { // doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active... doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations); throw ex; } } else if (transaction != null) { // Transaction active but no synchronization active. Object suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction); return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(suspendedResources); } else { // Neither transaction nor synchronization active. return null; } }
⑤ 进入到事务开始,doBegin(transaction, definition)方法:
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) { //强制转化事务对象 DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction; Connection con = null; try { //判断事务对象没有数据库连接持有器 if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() || txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) { //通过数据源获取一个数据库连接对象 Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction"); } //把我们的数据库连接包装成一个ConnectionHolder对象 然后设置到我们的txObject对象中去 txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true); } //标记当前的连接是一个同步事务 txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true); con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection(); //为当前的事务设置隔离级别 Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition); txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel); //关闭自动提交 if (con.getAutoCommit()) { txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit"); } con.setAutoCommit(false); } //判断事务为只读事务 prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition); //设置事务激活 txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true); //设置事务超时时间 int timeout = determineTimeout(definition); if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout); } // 绑定我们的数据源和连接到我们的同步管理器上 把数据源作为key,数据库连接作为value 设置到线程变量中 if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder()); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { //释放数据库连接 DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource()); txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false); } throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex); } }
⑥ 进入到prepareSynchronization(status, definition)方法:
protected void prepareSynchronization(DefaultTransactionStatus status, TransactionDefinition definition) { if (status.isNewSynchronization()) { //绑定事务激活 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(status.hasTransaction()); //当前事务的隔离级别 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel( definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT ? definition.getIsolationLevel() : null); //是否为只读事务 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly()); //事务的名称 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(definition.getName()); TransactionSynchronizationManager.initSynchronization(); } }
1.2 把事务状态和事务属性等信息封装成一个TransactionInfo对象,prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status)方法:
protected TransactionInfo prepareTransactionInfo(PlatformTransactionManager tm, TransactionAttribute txAttr, String joinpointIdentification, TransactionStatus status) { TransactionInfo txInfo = new TransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); if (txAttr != null) { // We need a transaction for this method... if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Getting transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() + "]"); } // The transaction manager will flag an error if an incompatible tx already exists. txInfo.newTransactionStatus(status); } else { // The TransactionInfo.hasTransaction() method will return false. We created it only // to preserve the integrity of the ThreadLocal stack maintained in this class. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) logger.trace("Don't need to create transaction for [" + joinpointIdentification + "]: This method isn't transactional."); } // We always bind the TransactionInfo to the thread, even if we didn't create // a new transaction here. This guarantees that the TransactionInfo stack // will be managed correctly even if no transaction was created by this aspect. txInfo.bindToThread(); return txInfo; }
2 调用钩子函数进行回调目标方法,invocation.proceedWithInvocation()方法最终会调用到目标方法里面:
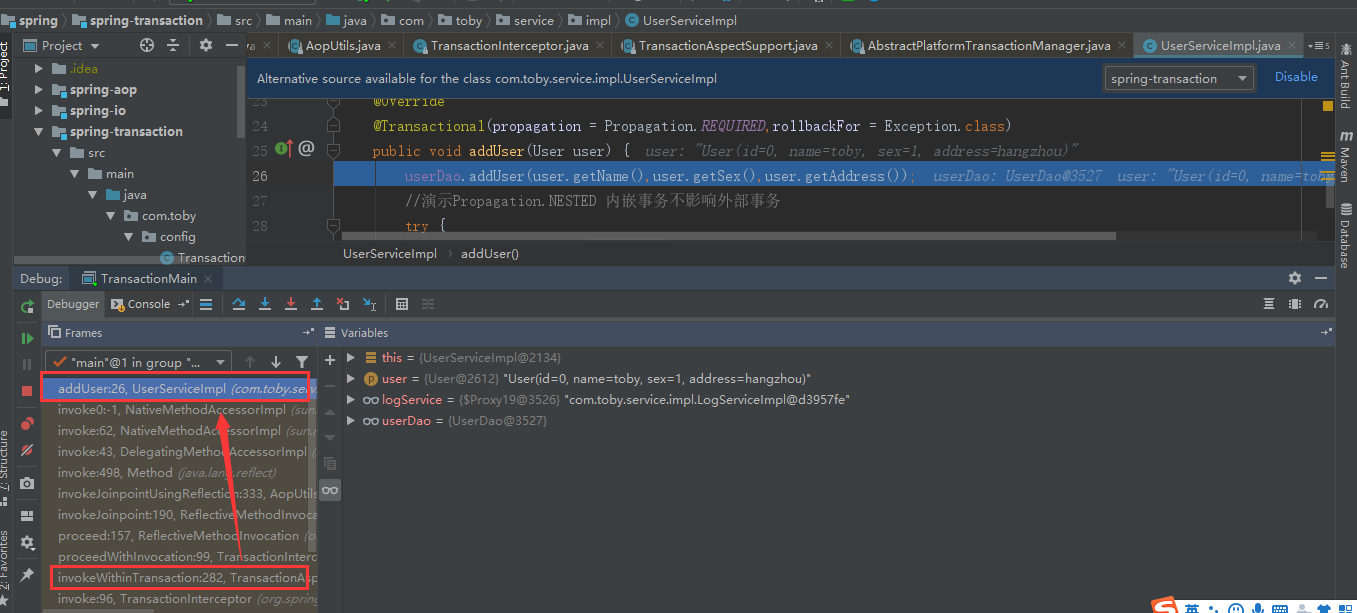
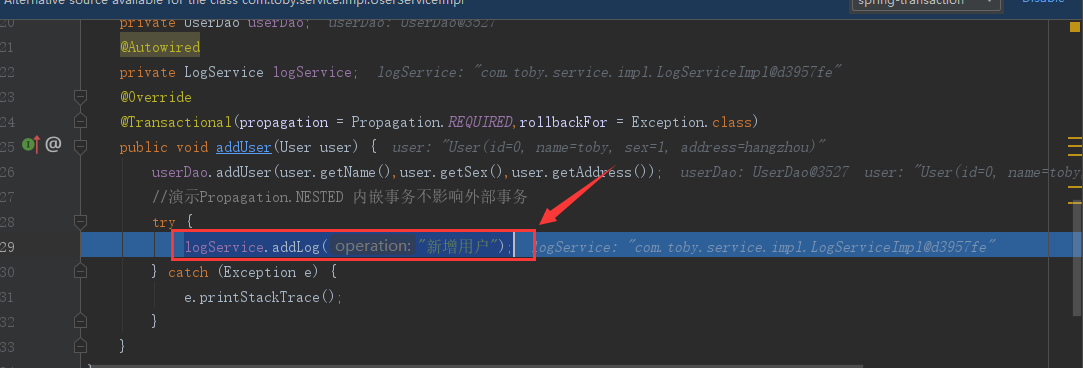
第二步:addLog(“新增用户”) 其中事务注解上的传播机制是propagation = Propagation.NESTED
执行流程参考前面的addUser流程,区别是到AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#getTransaction里面的isExistingTransaction (transaction),这个时候是返回true的,所以执行handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled)方法:
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction( TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled) throws TransactionException { /** * 判断当前的事务行为是不是PROPAGATION_NEVER的 * 表示为不支持事务,但是当前又存在一个事务,所以抛出异常 */ if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException( "Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'"); } /** * 判断当前的事务属性不支持事务,PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED,所以需要先挂起已经存在的事务 */ if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Suspending current transaction"); } //挂起存在的事务 Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction); boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS); //创建一个新的非事务状态(保存了上一个存在事务状态的属性) return prepareTransactionStatus( definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); } /** * 当前的事务属性状态是PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW表示需要新开启一个事务状态 */ if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]"); } //挂起已经存在的事务 SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction); try { boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); //创建一个新的事务状态(包含了挂起的事务的属性) DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources); //开启新的事务 doBegin(transaction, definition); //把新的事务状态设置到当前的线程变量中去 prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) { resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx); throw beginEx; } } if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) { if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) { throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException( "Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " + "specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'"); } if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]"); } //嵌套事务的处理 if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) { //开启一个新的事务 DefaultTransactionStatus status = prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null); //为事务设置一个回退点 status.createAndHoldSavepoint(); return status; } else {// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls. // Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here // in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction. boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus( definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); doBegin(transaction, definition); prepareSynchronization(status, definition); return status; } } // Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED. if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction"); } if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) { if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) { Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(); if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) { Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants; throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" + definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " + (currentIsolationLevel != null ? isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) : "(unknown)")); } } if (!definition.isReadOnly()) { if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) { throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" + definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is"); } } } boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER); return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null); }
由于addLog上面的事务注解的传播机制是TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED,所以执行下面分支

可以看出内嵌事务设置保存点,也就是说内嵌事务的异常回滚是回滚到该保存点的,只要外层封装事务捕获了内嵌事务的异常,内嵌事务的回滚是不会影响外层封装事务的。从demo的例子就能体现这点。接下来又回到addUser方法:
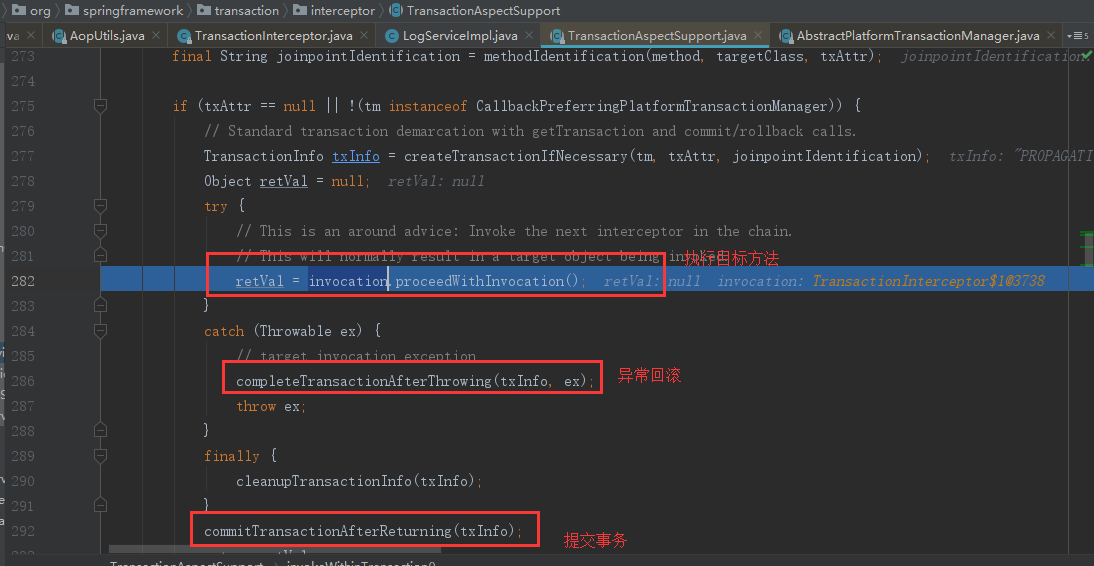
示例demo中的目标方法如下:
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NESTED,rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void addLog(String operation) { logDao.addLog(operation); System.out.println(1/0); }
1/0会报java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero异常,所以被catch捕获到,从而进行回滚,此时由于前面内嵌事务设置了保存点,所以内嵌事务值回滚到保存点,对外面没有影响。内嵌事务执行完了之后,继续外层addUser的方法执行
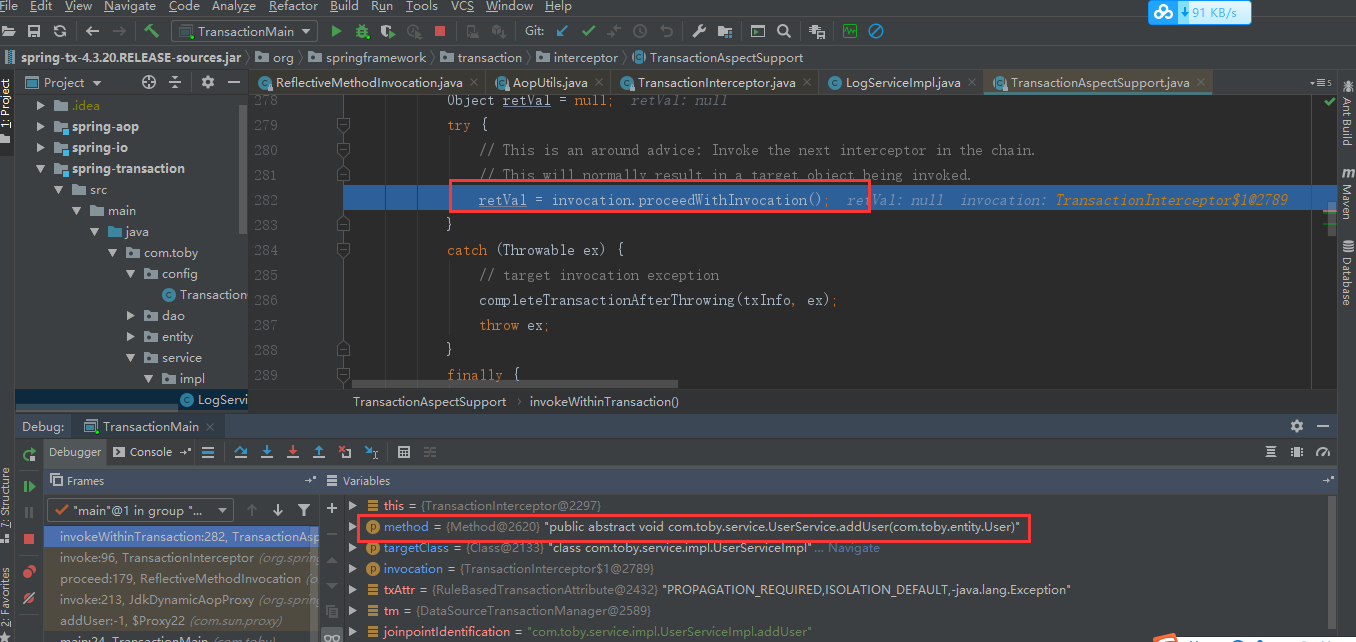
addUser方法捕获了logService.addLog(“新增用户”)异常如下:
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void addUser(User user) { userDao.addUser(user.getName(),user.getSex(),user.getAddress()); //演示Propagation.NESTED 内嵌事务不影响外部事务 try { logService.addLog("新增用户"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
所以外层事务的还是能正常提交事务
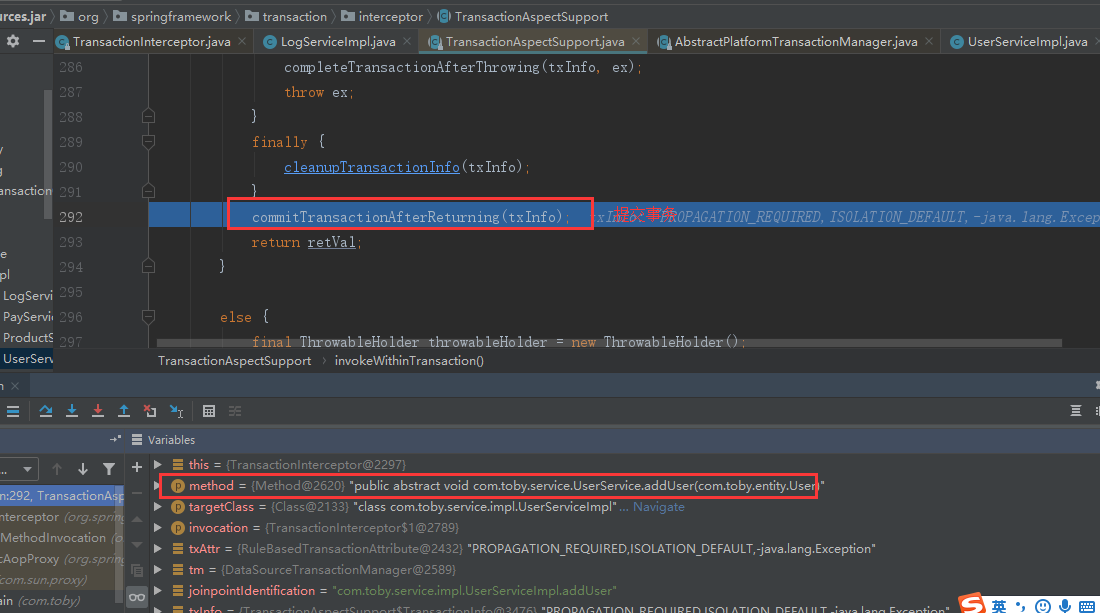
至此整个addUser方法执行完毕!!!!
总结:首先通过事务概述,对事务的ACID特性,事务的隔离级别,Spring事务的传播机制有了一定的认识,然后分析了@Enable TransactionManagement注解开启Spring事务的支持功能,该注解为我们Spring容器中注册了InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxy Creator组件,Spring事务代理创建都在这个组件中完成,然后通过一个较为复杂的嵌套事务的调用过程分析,进一步加深对Spring事务的传播机制理解。Spring系列完整代码在码云:spring系列


