曹工说Redis源码(8)–面试时,redis 内存淘汰总被问,但是总答不好
文章导航
Redis源码系列的初衷,是帮助我们更好地理解Redis,更懂Redis,而怎么才能懂,光看是不够的,建议跟着下面的这一篇,把环境搭建起来,后续可以自己阅读源码,或者跟着我这边一起阅读。由于我用c也是好几年以前了,些许错误在所难免,希望读者能不吝指出。
曹工说Redis源码(1)– redis debug环境搭建,使用clion,达到和调试java一样的效果
曹工说Redis源码(2)– redis server 启动过程解析及简单c语言基础知识补充
曹工说Redis源码(3)– redis server 启动过程完整解析(中)
曹工说Redis源码(4)– 通过redis server源码来理解 listen 函数中的 backlog 参数
曹工说Redis源码(5)– redis server 启动过程解析,以及EventLoop每次处理事件前的前置工作解析(下)
曹工说Redis源码(6)– redis server 主循环大体流程解析
曹工说Redis源码(7)– redis server 的周期执行任务,到底要做些啥
什么是内存淘汰
内存淘汰,和平时我们设置redis key的过期时间,不是一回事;内存淘汰是说,假设我们限定redis只能使用8g内存,现在已经使用了这么多了(包括设置了过期时间的key和没设过期时间的key),那,后续的set操作,还怎么办呢?
是不是只能报错了?
那不行啊,不科学吧,因为有的key,可能已经很久没人用了,可能以后也不会再用到了,那我们是不是可以把这类key给干掉呢?
干掉key的过程,就是内存淘汰。
内存淘汰什么时候启用
当我们在配置文件里设置了如下属性时:
# maxmemory <bytes>
默认,该属性是被注释掉的。
其实,这个配置项的注释,相当有价值,我们来看看:
# Don't use more memory than the specified amount of bytes.
# When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys
# according to the eviction policy selected (see maxmemory-policy).
#
# If Redis can't remove keys according to the policy, or if the policy is
# set to 'noeviction', Redis will start to reply with errors to commands
# that would use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue
# to reply to read-only commands like GET.
#
# This option is usually useful when using Redis as an LRU cache, or to set
# a hard memory limit for an instance (using the 'noeviction' policy).
#
# WARNING: If you have slaves attached to an instance with maxmemory on,
# the size of the output buffers needed to feed the slaves are subtracted
# from the used memory count, so that network problems / resyncs will
# not trigger a loop where keys are evicted, and in turn the output
# buffer of slaves is full with DELs of keys evicted triggering the deletion
# of more keys, and so forth until the database is completely emptied.
#
# In short... if you have slaves attached it is suggested that you set a lower
# limit for maxmemory so that there is some free RAM on the system for slave
# output buffers (but this is not needed if the policy is 'noeviction').
#
# maxmemory <bytes>
渣翻译如下:
不能使用超过指定数量bytes的内存。当该内存限制被达到时,redis会根据过期策略(eviction policy,通过参数 maxmemory-policy来指定)来驱逐key。
如果redis根据指定的策略,或者策略被设置为“noeviction”,redis会开始针对如下这种命令,回复错误。什么命令呢?会使用更多内存的那类命令,比如set、lpush;只读命令还是不受影响,可以正常响应。
该选项通常在redis使用LRU缓存时有用,或者在使用noeviction策略时,设置一个进程级别的内存limit。
内存淘汰策略
所谓策略,意思是,当我们要删除部分key的时候,删哪些,不删哪些?是不是需要一个策略?比如是随机删,就像灭霸一样?还是按照lru时间来删,lru的策略意思就是,最近最少使用的key,将被优先删除。
总之,我们需要定一个规则。
redis默认支持以下策略:
# MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory
# is reached. You can select among five behaviors:
#
# volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm
# allkeys-lru -> remove any key accordingly to the LRU algorithm
# volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set
# allkeys-random -> remove a random key, any key
# volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL)
# noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations
#
# Note: with any of the above policies, Redis will return an error on write
# operations, when there are not suitable keys for eviction.
#
# At the date of writing this commands are: set setnx setex append
# incr decr rpush lpush rpushx lpushx linsert lset rpoplpush sadd
# sinter sinterstore sunion sunionstore sdiff sdiffstore zadd zincrby
# zunionstore zinterstore hset hsetnx hmset hincrby incrby decrby
# getset mset msetnx exec sort
#
# The default is:
#
# maxmemory-policy noeviction
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
针对设置了过期时间的,使用lru算法
# volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm
针对全部key,使用lru算法
# allkeys-lru -> remove any key accordingly to the LRU algorithm
针对设置了过期时间的,随机删
# volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set
针对全部key,随机删
# allkeys-random -> remove a random key, any key
针对设置了过期时间的,马上要过期的,删掉
# volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL)
不过期,不能写了,就报错
# noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations
一般呢,我们会设置为:
allkeys-lru,即,针对全部key,进行lru。
源码实现
配置读取
在如下结构体中,定义了如下字段:
struct redisServer {
...
unsigned long long maxmemory; /* Max number of memory bytes to use */
int maxmemory_policy; /* Policy for key eviction */
int maxmemory_samples; /* Pricision of random sampling */
...
}
当我们在配置文件中,进入如下配置时,该结构体中几个字段的值如下:
maxmemory 3mb
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
# maxmemory-samples 5 这个取了默认值
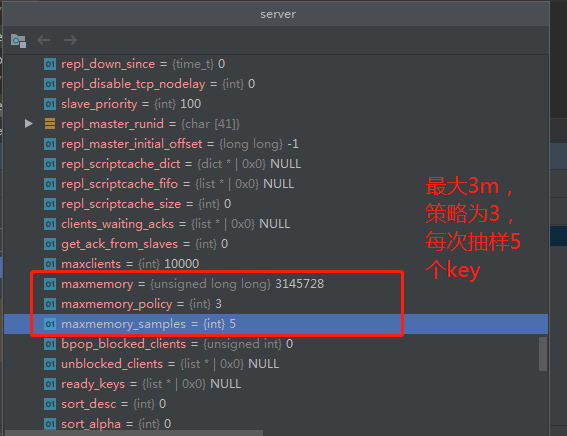
maxmemory_policy为3,是因为枚举值为3:
#define REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU 0
#define REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL 1
#define REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM 2
#define REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU 3
#define REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM 4
#define REDIS_MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION 5
#define REDIS_DEFAULT_MAXMEMORY_POLICY REDIS_MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION
处理命令时,判断是否进行内存淘汰
在处理命令的时候,会调用中的
redis.c processCommand
int processCommand(redisClient *c) {
/* The QUIT command is handled separately. Normal command procs will
* go through checking for replication and QUIT will cause trouble
* when FORCE_REPLICATION is enabled and would be implemented in
* a regular command proc. */
// 特别处理 quit 命令
void *commandName = c->argv[0]->ptr;
redisLog(REDIS_NOTICE, "The server is now processing %s", commandName);
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr, "quit")) {
addReply(c, shared.ok);
c->flags |= REDIS_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
return REDIS_ERR;
}
/* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions
* such as wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */
// 1 查找命令,并进行命令合法性检查,以及命令参数个数检查
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
if (!c->cmd) {
// 没找到指定的命令
flagTransaction(c);
addReplyErrorFormat(c, "unknown command '%s'",
(char *) c->argv[0]->ptr);
return REDIS_OK;
}
/* Check if the user is authenticated */
//2 检查认证信息
if (server.requirepass && !c->authenticated && c->cmd->proc != authCommand) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.noautherr);
return REDIS_OK;
}
/* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here.
*
* 3 如果开启了集群模式,那么在这里进行转向操作。
*
* However we don't perform the redirection if:
*
* 不过,如果有以下情况出现,那么节点不进行转向:
*
* 1) The sender of this command is our master.
* 命令的发送者是本节点的主节点
*
* 2) The command has no key arguments.
* 命令没有 key 参数
*/
if (server.cluster_enabled &&
!(c->flags & REDIS_MASTER) &&
!(c->cmd->getkeys_proc == NULL && c->cmd->firstkey == 0)) {
int hashslot;
// 集群已下线
if (server.cluster->state != REDIS_CLUSTER_OK) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReplySds(c, sdsnew("-CLUSTERDOWN The cluster is down. Use CLUSTER INFO for more information\r\n"));
return REDIS_OK;
// 集群运作正常
} else {
int error_code;
clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c, c->cmd, c->argv, c->argc, &hashslot, &error_code);
// 不能执行多键处理命令
if (n == NULL) {
flagTransaction(c);
if (error_code == REDIS_CLUSTER_REDIR_CROSS_SLOT) {
addReplySds(c, sdsnew("-CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slot\r\n"));
} else if (error_code == REDIS_CLUSTER_REDIR_UNSTABLE) {
/* The request spawns mutliple keys in the same slot,
* but the slot is not "stable" currently as there is
* a migration or import in progress. */
addReplySds(c, sdsnew("-TRYAGAIN Multiple keys request during rehashing of slot\r\n"));
} else {
redisPanic("getNodeByQuery() unknown error.");
}
return REDIS_OK;
//3.1 命令针对的槽和键不是本节点处理的,进行转向
} else if (n != server.cluster->myself) {
flagTransaction(c);
// -<ASK or MOVED> <slot> <ip>:<port>
// 例如 -ASK 10086 127.0.0.1:12345
addReplySds(c, sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),
"-%s %d %s:%d\r\n",
(error_code == REDIS_CLUSTER_REDIR_ASK) ? "ASK" : "MOVED",
hashslot, n->ip, n->port));
return REDIS_OK;
}
// 如果执行到这里,说明键 key 所在的槽由本节点处理
// 或者客户端执行的是无参数命令
}
}
/* Handle the maxmemory directive.
*
* First we try to free some memory if possible (if there are volatile
* keys in the dataset). If there are not the only thing we can do
* is returning an error. */
//4 如果设置了最大内存,那么检查内存是否超过限制,并做相应的操作
if (server.maxmemory) {
//4.1 如果内存已超过限制,那么尝试通过删除过期键来释放内存
int retval = freeMemoryIfNeeded();
// 如果即将要执行的命令可能占用大量内存(REDIS_CMD_DENYOOM)
// 并且前面的内存释放失败的话
// 那么向客户端返回内存错误
if ((c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_DENYOOM) && retval == REDIS_ERR) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.oomerr);
return REDIS_OK;
}
}
....
- 1处,查找命令,对应的函数指针(类似于java里的策略模式,根据命令,找对应的策略)
- 2处,检查,是否密码正确
- 3处,集群相关操作;
- 3.1处,不是本节点处理,直接返回ask,指示客户端转向
- 4处,判断是否设置了maxMemory,这里就是本文重点:设置了maxMemory时,内存淘汰策略
- 4.1处,调用了下方的 freeMemoryIfNeeded
接下来,深入4.1处:
int freeMemoryIfNeeded(void) {
size_t mem_used, mem_tofree, mem_freed;
int slaves = listLength(server.slaves);
/* Remove the size of slaves output buffers and AOF buffer from the
* count of used memory. */
// 计算出 Redis 目前占用的内存总数,但有两个方面的内存不会计算在内:
// 1)从服务器的输出缓冲区的内存
// 2)AOF 缓冲区的内存
mem_used = zmalloc_used_memory();
if (slaves) {
...
}
if (server.aof_state != REDIS_AOF_OFF) {
mem_used -= sdslen(server.aof_buf);
mem_used -= aofRewriteBufferSize();
}
/* Check if we are over the memory limit. */
//1 如果目前使用的内存大小比设置的 maxmemory 要小,那么无须执行进一步操作
if (mem_used <= server.maxmemory) return REDIS_OK;
//2 如果占用内存比 maxmemory 要大,但是 maxmemory 策略为不淘汰,那么直接返回
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION)
return REDIS_ERR; /* We need to free memory, but policy forbids. */
/* Compute how much memory we need to free. */
// 3 计算需要释放多少字节的内存
mem_tofree = mem_used - server.maxmemory;
// 初始化已释放内存的字节数为 0
mem_freed = 0;
// 根据 maxmemory 策略,
//4 遍历字典,释放内存并记录被释放内存的字节数
while (mem_freed < mem_tofree) {
int j, k, keys_freed = 0;
// 遍历所有字典
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
long bestval = 0; /* just to prevent warning */
sds bestkey = NULL;
dictEntry *de;
redisDb *db = server.db + j;
dict *dict;
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM) {
// 如果策略是 allkeys-lru 或者 allkeys-random
//5 那么淘汰的目标为所有数据库键
dict = server.db[j].dict;
} else {
// 如果策略是 volatile-lru 、 volatile-random 或者 volatile-ttl
//6 那么淘汰的目标为带过期时间的数据库键
dict = server.db[j].expires;
}
/* volatile-random and allkeys-random policy */
// 如果使用的是随机策略,那么从目标字典中随机选出键
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM) {
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict);
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
}
/* volatile-lru and allkeys-lru policy */
//7
else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU) {
struct evictionPoolEntry *pool = db->eviction_pool;
while (bestkey == NULL) {
// 8
evictionPoolPopulate(dict, db->dict, db->eviction_pool);
/* Go backward from best to worst element to evict. */
for (k = REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (pool[k].key == NULL) continue;
// 8.1
de = dictFind(dict, pool[k].key);
/* 8.2 Remove the entry from the pool. */
sdsfree(pool[k].key);
/* Shift all elements on its right to left. */
memmove(pool + k, pool + k + 1,
sizeof(pool[0]) * (REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE - k - 1));
/* Clear the element on the right which is empty
* since we shifted one position to the left. */
pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE - 1].key = NULL;
pool[REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE - 1].idle = 0;
/* If the key exists, is our pick. Otherwise it is
* a ghost and we need to try the next element. */
// 8.3
if (de) {
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
break;
} else {
/* Ghost... */
continue;
}
}
}
}
/* volatile-ttl */
// 策略为 volatile-ttl ,从一集 sample 键中选出过期时间距离当前时间最接近的键
else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
...
}
/* Finally remove the selected key. */
// 8.4 删除被选中的键
if (bestkey) {
long long delta;
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(bestkey, sdslen(bestkey));
propagateExpire(db, keyobj);
/* We compute the amount of memory freed by dbDelete() alone.
* It is possible that actually the memory needed to propagate
* the DEL in AOF and replication link is greater than the one
* we are freeing removing the key, but we can't account for
* that otherwise we would never exit the loop.
*
* AOF and Output buffer memory will be freed eventually so
* we only care about memory used by the key space. */
// 计算删除键所释放的内存数量
delta = (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
dbDelete(db, keyobj);
delta -= (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
mem_freed += delta;
// 对淘汰键的计数器增一
server.stat_evictedkeys++;
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_EVICTED, "evicted",
keyobj, db->id);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
keys_freed++;
...
}
}
if (!keys_freed) return REDIS_ERR; /* nothing to free... */
}
return REDIS_OK;
}
-
1处,如果目前使用的内存大小比设置的 maxmemory 要小,那么无须执行进一步操作
-
2处,如果占用内存比 maxmemory 要大,但是 maxmemory 策略为不淘汰,那么直接返回
-
3处,计算需要释放多少字节的内存
-
4处,遍历字典,释放内存并记录被释放内存的字节数
-
5处,如果策略是 allkeys-lru 或者 allkeys-random 那么淘汰的目标为所有数据库键
-
6处,如果策略是 volatile-lru 、 volatile-random 或者 volatile-ttl ,那么淘汰的目标为带过期时间的数据库键
-
7处,如果使用的是 LRU 策略, 那么从 sample 键中选出 IDLE 时间最长的那个键
-
8处,调用evictionPoolPopulate,该函数在下面讲解,该函数的功能是,传入一个链表,即这里的db->eviction_pool,然后在函数内部,随机找出n个key,放入传入的链表中,并按照空闲时间排序,空闲最久的,放到最后。
当该函数,返回后,db->eviction_pool这个链表里就存放了我们要淘汰的key。
-
8.1处,找到这个key,这个key,在后边会被删除
-
8.2处,下面这一段,从db->eviction_pool将这个已经处理了的key删掉
-
8.3处,如果这个key,是存在的,则跳出循环,在后面8.4处,会被删除
-
8.4处,删除这个key
选择哪些key作为被淘汰的key
前面我们看到,在7处,如果为lru策略,则会进入8处的函数:
evictionPoolPopulate。
该函数的名称为:填充(populate)驱逐(eviction)对象池(pool)。驱逐的意思,就是现在达到了maxmemory,没办法,只能开始删除掉一部分元素,来腾空间了,不然新的put类型的命令,根本没办法执行。
该方法的大概思路是,使用lru的时候,随机找n个key,类似于抽样,然后放到一个链表,根据空闲时间排序。
具体看看该方法的实现:
void evictionPoolPopulate(dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) {
其中,传入的第三个参数,是要被填充的对象,在c语言中,习惯传入一个入参,然后在函数内部填充或者修改入参对象的属性。
该属性,就是前面说的那个链表,用来存放收集的随机的元素,该链表中节点的结构如下:
struct evictionPoolEntry {
unsigned long long idle; /* Object idle time. */
sds key; /* Key name. */
};
该结构共2个字段,一个存储key,一个存储空闲时间。
该链表中,共maxmemory-samples个元素,会按照idle时间长短排序,idle时间长的在链表尾部,(假设头在左,尾在右)。
void evictionPoolPopulate(dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) {
int j, k, count;
dictEntry *_samples[EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE];
dictEntry **samples;
/* Try to use a static buffer: this function is a big hit...
* Note: it was actually measured that this helps. */
if (server.maxmemory_samples <= EVICTION_SAMPLES_ARRAY_SIZE) {
samples = _samples;
} else {
samples = zmalloc(sizeof(samples[0]) * server.maxmemory_samples);
}
/* 1 Use bulk get by default. */
count = dictGetRandomKeys(sampledict, samples, server.maxmemory_samples);
// 2
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
unsigned long long idle;
sds key;
robj *o;
dictEntry *de;
de = samples[j];
key = dictGetKey(de);
/* If the dictionary we are sampling from is not the main
* dictionary (but the expires one) we need to lookup the key
* again in the key dictionary to obtain the value object. */
if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key);
// 3
o = dictGetVal(de);
// 4
idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o);
/* 5 Insert the element inside the pool.
* First, find the first empty bucket or the first populated
* bucket that has an idle time smaller than our idle time. */
k = 0;
while (k < REDIS_EVICTION_POOL_SIZE &&
pool[k].key &&
pool[k].idle < idle)
k++;
...
// 6
pool[k].key = sdsdup(key);
pool[k].idle = idle;
}
if (samples != _samples) zfree(samples);
}
-
1处,获取
server.maxmemory_samples个key,这里是随机获取的,(dictGetRandomKeys),这个值,默认值为5,放到samples中 -
2处,遍历返回来的samples
-
3处,调用如下宏,获取val
he的类型为dictEntry:
/* * 哈希表节点 */ typedef struct dictEntry { // 键 void *key; // 值 union { // 1 void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; } v; // 指向下个哈希表节点,形成链表 struct dictEntry *next; } dictEntry;所以,这里去
robj *o; o = dictGetVal(de);实际就是获取其v属性中的val,(1处):
#define dictGetVal(he) ((he)->v.val) -
4处,准备计算该val的空闲时间
我们上面3处,看到,获取的o的类型为robj。我们现在看看怎么计算对象的空闲时长:
/* Given an object returns the min number of milliseconds the object was never * requested, using an approximated LRU algorithm. */ unsigned long long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) { //4.1 获取系统的当前时间 unsigned long long lruclock = LRU_CLOCK(); // 4.2 if (lruclock >= o->lru) { // 4.3 return (lruclock - o->lru) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION; } else { return (lruclock + (REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru)) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION; } }这里,4.1处,获取系统的当前时间;
4.2处,如果系统时间,大于对象的lru时间
4.3处,则用系统时间减去对象的lru时间,再乘以单位,换算为毫秒,最终返回的单位,为毫秒(可以看注释。)
#define REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION 1000 /* LRU clock resolution in ms */ -
5处,这里拿当前元素,和pool中已经放进去的元素,从第0个开始比较,如果当前元素的idle时长,大于pool中指针0指向的元素,则和pool中索引1的元素比较;直到条件不满足为止。
这句话意思就是,类似于冒泡,把当前元素一直往后冒,直到idle时长小于被比较的元素为止。
-
6处,把当前元素放进pool中。
经过上面的处理后,链表中存放了全部的抽样元素,且ide时间最长的,在最右边。
对象还有字段存储空闲时间?
前面4处,说到,用系统的当前时间,减去对象的lru时间。
大家看看对象的结构体
typedef struct redisObject {
// 类型
unsigned type:4;
// 编码
unsigned encoding:4;
//1 对象最后一次被访问的时间
unsigned lru:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* lru time (relative to server.lruclock) */
// 引用计数
int refcount;
// 指向实际值的指针
void *ptr;
} robj;
上面1处,lru属性,就是用来存储这个。
创建对象时,直接使用当前系统时间创建
robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o));
o->type = type;
o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_RAW;
o->ptr = ptr;
o->refcount = 1;
/*1 Set the LRU to the current lruclock (minutes resolution). */
o->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
return o;
}
1处即是。
robj *createEmbeddedStringObject(char *ptr, size_t len) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(robj)+sizeof(struct sdshdr)+len+1);
struct sdshdr *sh = (void*)(o+1);
o->type = REDIS_STRING;
o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR;
o->ptr = sh+1;
o->refcount = 1;
// 1
o->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
sh->len = len;
sh->free = 0;
if (ptr) {
memcpy(sh->buf,ptr,len);
sh->buf[len] = '\0';
} else {
memset(sh->buf,0,len+1);
}
return o;
}
1处即是。
每次查找该key时,刷新时间
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
// 查找键空间
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
// 节点存在
if (de) {
// 取出值
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
* Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
* a copy on write madness. */
// 更新时间信息(只在不存在子进程时执行,防止破坏 copy-on-write 机制)
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1)
// 1
val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
// 返回值
return val;
} else {
// 节点不存在
return NULL;
}
}
1处即是,包括get、set等各种操作,都会刷新该时间。
仔细看下面的堆栈,set的,get同理:
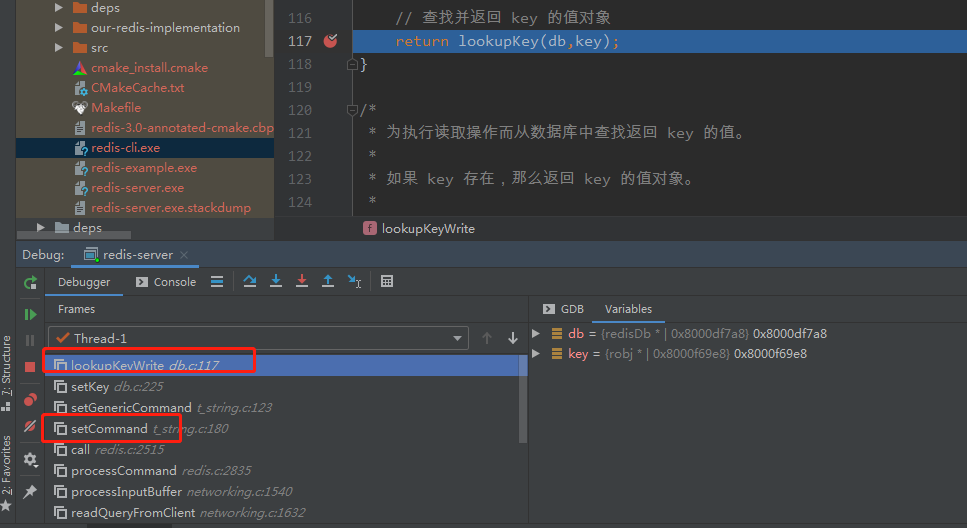
总结
大家有没有更清楚一些呢?
总的来说,就是,设置了max-memory后,达到该内存限制后,会在处理命令时,检查是否要进行内存淘汰;如果要淘汰,则根据maxmemory-policy的策略来。
随机选择maxmemory-sample个元素,按照空闲时间排序,拉链表;挨个挨个清除。


