c++中的类型识别
- 2020 年 3 月 13 日
- 筆記
1、类型识别的相关概念
(1)类型识别的作用
类型识别是面向对象中引入的一个新概念,主要用来判断赋值兼容性原则中的类型问题,即此时的数据类型到底是基类类型还是派生类类型?
当基类指针指向子类对象 或者 基类引用成为子类对象的别名 时,就需要使用类型识别;
1 Base *p = new Derived(); 2 Base &r = *p
对于上面的语句,我们可以这样认识,指针p是Base类型,但是P 又指向了一个新的Derived类型,此时很难判断指针P 的数据类型;同理,引用r 本来作为父类的别名而存在,但由于赋值兼容性,引用r也可以作为子类的别名,同样此时 引用 r 的数据类型也不能确定;
注:1)由之前所学知识,若没有虚函数重写,编译器为了安全起见,会将指针p 当作 Base 类型;(编译期间)
2)若有虚函数重写,就会发生动态多态特性,此时就会根据指针p 所指向的具体数据类型来确定指针p 的数据类型。(运行期间)
(2)类型识别的分类
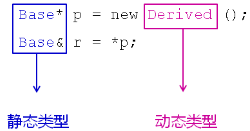
1)静态类型:变量(对象)自身的类型;在编译阶段就能确定所使用变量的数据类型。
2)动态类型:指针(引用)所指向对象的实际类型;在运行阶段根据指针所指向的具体数据类型来确定所使用的数据类型。

Base *b 所指向的实际对象无法确定,若指针b 指向的是子类对象,则程序正常运行;若指针b 指向的是父类对象,则程序有可能出现 Bug;
注:在 g++ 编译器下上述情况均可正常运行,但后者不建议使用;
在赋值兼容原则中,基类指针是否可以强制类型转换为子类指针取决于动态类型;(很重要!!!)— 只有动态类型是子类对象才能进行合法转换
2、如何得到动态类型
(1)利用多态
1)必须从基类开始提供类型虚函数;
2)所有的派生类都必须重写类型虚函数;
3)每个派生类的类型 ID必须唯一;
结果:调用类型虚函数就可以知道当前的对象究竟是什么类型,这样就可以得到动态类型,达到动态类型识别效果;

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Base 7 { 8 public: 9 enum { ID = 0 }; 10 11 virtual int type() // 类型虚函数 12 { 13 return ID; 14 } 15 }; 16 17 class Derived : public Base 18 { 19 public: 20 enum { ID = 1 }; 21 22 int type() 23 { 24 return ID; 25 } 26 27 void print() 28 { 29 cout << "I'm a Derived. " << endl; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 class Child : public Base 34 { 35 public: 36 enum { ID = 2 }; 37 38 int type() 39 { 40 return ID; 41 } 42 }; 43 44 void test(Base* pb) 45 { 46 if( pb->type() == Child::ID ) 47 { 48 Child* pc = static_cast<Child*>(pb); 49 //Child* pc = dynamic_cast<Child*>(pb); // 同上 50 51 cout << "& = " << pc << endl; 52 cout << "I'm a Child. " << endl; 53 } 54 55 if( pb->type() == Derived::ID ) 56 { 57 Derived* pd = static_cast<Derived*>(pb); 58 //Derived* pd = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(pb); // 同上 59 60 cout << "& = " << pd << endl; 61 pd->print(); 62 } 63 64 if( pb->type() == Base::ID ) 65 { 66 cout << "& = " << pb << endl; 67 cout << "I'm a Base. " << endl; 68 } 69 } 70 71 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 72 { 73 Base b; 74 Derived d; 75 Child c; 76 77 test(&b); 78 test(&d); 79 test(&c); 80 81 return 0; 82 } 83 /** 84 * 运行结果: 85 * & = 0x7ffccf0dd850 86 * I'm a Base. 87 * & = 0x7ffccf0dd860 88 * I'm a Derived. 89 * & = 0x7ffccf0dd870 90 * I'm a Child. 91 */
利用类型虚函数实现类型识别
(2)利用 dynamic_cast
1)dynamic_cast这个关键字如果要转换的实际类型和指定的类型不一样,则会返回NULL。例如当指定类型为子类对象时,如果父类指针的动态类型是这个子类对象时,转换成功,而动态类型是父类对象或者其他子类对象时,转换失败;
2)dynamic_cast 要求使用的目标对象类型必须是多态,即:所在类族至少有一个虚函数;
3)只能用于指针和引用之间的转换
1. 用于指针转换时,转换失败,返回空指针;
2. 用于引用转换时,转换失败,将引发 bad_cast异常。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Base 7 { 8 public: 9 virtual ~Base() 10 { 11 12 } 13 }; 14 15 class Derived : public Base 16 { 17 public: 18 void print() 19 { 20 cout << "I'm a Derived. " << endl; 21 } 22 }; 23 24 class Child : public Base 25 { 26 27 }; 28 29 void test(Base* pb) 30 { 31 // dynamic_cast 只能确定最终的转化结果,无法获取动态类型的原型 32 Derived* pd = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(pb); 33 34 if(pd != NULL) 35 { 36 // Derived 类类型, 可以使用指针pd访问Derived类的成员 37 cout << "& = " << pd << endl; 38 pd->print(); 39 } 40 else 41 { 42 Child* pc = dynamic_cast<Child*>(pb); 43 44 if(pc != NULL) 45 { 46 // Child 类类型, 可以使用指针pc访问Child类的成员 47 cout << "& = " << pc << endl; 48 cout << "I'm a Child. " << endl; 49 } 50 else 51 { 52 // Base 类类型, 可以使用指针pb访问Base类的成员 53 cout << "& = " << pc << endl; 54 cout << "I'm a Base. " << endl; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 60 { 61 Base b; 62 Derived d; 63 Child c; 64 65 test(&b); 66 test(&d); 67 test(&c); 68 69 return 0; 70 } 71 /** 72 * 运行结果: 73 * & = 0 74 * I'm a Base. 75 * & = 0x7ffccf0dd860 76 * I'm a Derived. 77 * & = 0x7ffccf0dd870 78 * I'm a Child. 79 */
利用 dynamic_cast 实现类型识别
(3)利用 typeid(推荐这种方法)
1)typeid 是一个关键字,专门用于动态类型识别;
2)typeid 关键字返回对应参数的类型信息,此类型信息是一个type_info类对象;
1. 当参数为类型时,返回静态类型信息;
2. 当参数为变量时:1> 参数变量内部不存在虚函数表时,返回静态类型信息; 2> 参数变量内部存在虚函数表时,返回动态类型信息;
3. 当参数为 NULL 时,将抛出异常;
3)typeid 使用时需要包含头文件<typeinfo>;
4)typeid 使用时直接指定对象或者类型。
5)typeid 在不同的编译器内部实现是不同的;
1 int i = 0; 2 3 const type_info& tiv = typeid(i); // 将 i 的类型信息放到 type_info 中去; 4 const type_info& tii = typeid(int); 5 6 cout << (tiv == tii) << endl; // 1

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <typeinfo> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Base 8 { 9 public: 10 virtual ~Base() 11 { 12 } 13 }; 14 15 class Derived : public Base 16 { 17 public: 18 void print() 19 { 20 cout << "I'm a Derived." << endl; 21 } 22 }; 23 24 class Child : public Base 25 { 26 public: 27 void print() 28 { 29 cout << "I'm a Child." << endl; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 void test(Base* pb) 34 { 35 const type_info& tb = typeid(*pb); 36 37 if( tb == typeid(Derived) ) 38 { 39 Derived* pd = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(pb); 40 41 cout << "& = " << pd << endl; 42 pd->print(); 43 } 44 else if( tb == typeid(Child) ) 45 { 46 Child* pc = dynamic_cast<Child*>(pb); 47 48 cout << "& = " << pc << endl; 49 pc->print(); 50 51 } 52 else if( tb == typeid(Base) ) 53 { 54 cout << "& = " << pb << endl; 55 cout << "I'm a Base. " << endl; 56 } 57 58 cout << tb.name() << endl; 59 } 60 61 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 62 { 63 Base b; 64 Derived d; 65 Child c; 66 int index; 67 char ch; 68 69 const type_info& tp = typeid(b); 70 const type_info& tc = typeid(d); 71 const type_info& tn = typeid(c); 72 const type_info& ti = typeid(index); 73 const type_info& tch = typeid(ch); 74 75 cout<<tp.name()<<endl; 76 cout<<tc.name()<<endl; 77 cout<<tn.name()<<endl; 78 cout<<ti.name()<<endl; 79 cout<<tch.name()<<endl; 80 81 test(&b); 82 test(&d); 83 test(&c); 84 85 return 0; 86 } 87 /** 88 * 运行结果: 89 * 4Base 90 * 7Derived 91 * 5Child 92 * i 93 * c 94 * & = 0x7ffcbd4d6280 95 * I'm a Base. 96 * 4Base 97 * & = 0x7ffcbd4d6290 98 * I'm a Derived. 99 * 7Derived 100 * & = 0x7ffcbd4d62a0 101 * I'm a Child. 102 * 5Child 103 */
利用 typeid 实现类型识别
3 种动态类型的实现方法 建议选 第3种 (typeid)。
对于多态实现,存在以下缺陷:
1)必须从基类开始提供类型虚函数;
2)所有的派生类都必须重写类型虚函数;
3)每个派生类的类型名必须唯一;
对于 dynamic_cast 实现,只能得到类型转换的结果,不能获取真正的动态类型,同时 dynamic_cast 必须多态实现。