深度优先遍历,广度优先遍历实现对象的深拷贝
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
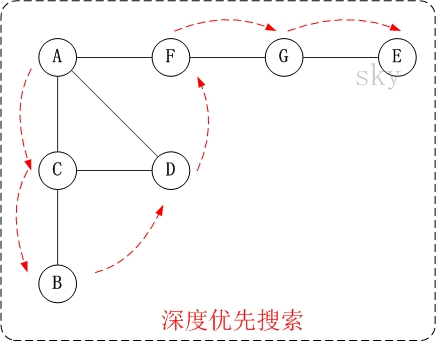
深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历(Depth-First-Search),是搜索算法的一种,它沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深地搜索树的分支。当节点v的所有边都已被探寻过,将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。这一过程一直进行到已探寻源节点到其他所有节点为止,如果还有未被发现的节点,则选择其中一个未被发现的节点为源节点并重复以上操作,直到所有节点都被探寻完成。
简单的说,DFS就是从图中的一个节点开始追溯,直到最后一个节点,然后回溯,继续追溯下一条路径,直到到达所有的节点,如此往复,直到没有路径为止。
DFS和BFS一般是用来解决图的遍历的,但是在这里,既然是前端,我是用DFS和BFS来遍历DOM树。
下面采用栈的形式或者递归的形式实现:
DOM节点
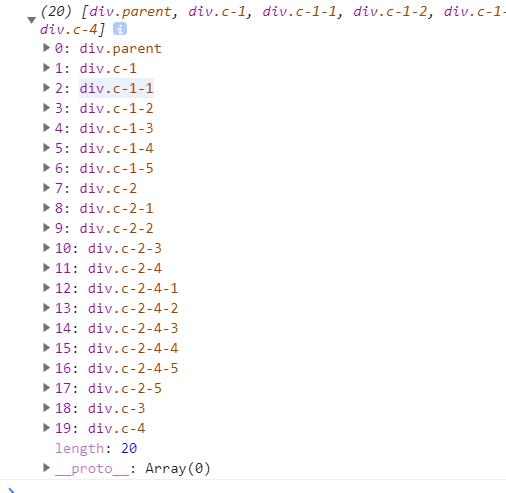
<div class="parent"> <div class="c-1"> <div class="c-1-1"> </div> <div class="c-1-2"> </div> <div class="c-1-3"> </div> <div class="c-1-4"> </div> <div class="c-1-5"> </div> </div> <div class="c-2"> <div class="c-2-1"> </div> <div class="c-2-2"> </div> <div class="c-2-3"> </div> <div class="c-2-4"> <div class="c-2-4-1"> </div> <div class="c-2-4-2"> </div> <div class="c-2-4-3"> </div> <div class="c-2-4-4"> </div> <div class="c-2-4-5"> </div> </div> <div class="c-2-5"> </div> </div> <div class="c-3"> </div> <div class="c-4"> </div> </div>DFS实现
var node = document.querySelectorAll('.parent')[0]; //递归写法 function DFS1 (node, nodeList = []){ if (node != null){ nodeList.push(node); let children = node.children for(let i = 0; i < children.length; i++){ DFS1(children[i], nodeList) } } return nodeList } let nodeList = DFS1(node); console.log(nodeList); //栈写法 function DFS2(node){ let nodeList = []; if (node){ //栈 后进先出 let stack = []; stack.push(node); while (stack.length) { let _node = stack.pop(); nodeList.push(_node); let children = _node.children; //这样写是从右向左 // for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { // stack.push(children[i]); // } //从左向右 for (let i = children.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { stack.push(children[i]); } } } return nodeList; } let nodeList2 = DFS2(node); console.log(nodeList2);运行结果,上面DFS1和DFS2的结果是一样的
广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历(Breadth-First-Search)是从根节点开始,沿着图的宽度遍历节点,如果所有节点均被访问过,则算法终止,BFS 同样属于盲目搜索,一般用队列数据结构来辅助实现BFS。
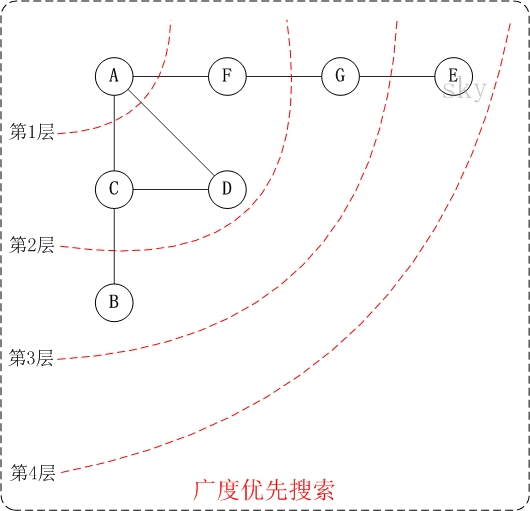
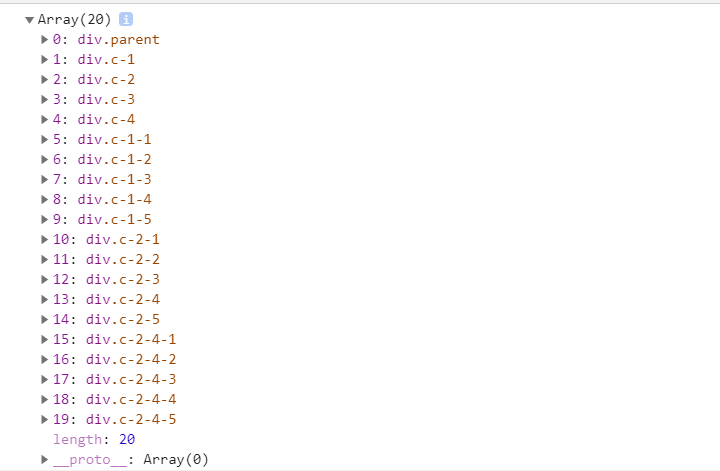
还是采用上面的DOM节点。BFS的写法如下。
代码采用队列的形式实现。
var node = document.querySelectorAll('.parent')[0]; function BFS1(node, nodeList = []) { if (!node){ return; } //队列 先进先出 var sequeue = []; sequeue.push(node); while (sequeue.length){ var _node = sequeue.shift(); nodeList.push(_node) for(var i = 0; i < _node.children.length; i++){ sequeue.push(_node.children[i]) } } return nodeList } let nodeList = BFS1(node); console.log(nodeList);结果如下
下面采用两种方式来实现对象深度克隆的实现。
DFS深度克隆
深度克隆要注意两个问题
1、环状数据问题:如果一个对象具有环状对象,比如obj.a.b.c === obj.a,就会使递归进入死循环,从而导致爆栈错误。
2、边界处理: 对象中不止原始类型,还存在如函数、Set等数据类型,我们需要一一做处理。下面代码只是解决了对函数的复制。
let _toString = Object.prototype.toString; let map = { array: 'Array', object: 'Object', function: 'Function', string: 'String', null: 'Null', undefined: 'Undefined', boolean: 'Boolean', number: 'Number' } function getType(obj){ return _toString.call(obj).slice(8, -1) } function isTypeOf(obj, type){ return map[type] && map[type] === getType(obj) } //深度克隆 //深度优先遍历 /** * * 解决三个问题 递归问题 环状数据问题 边界处理(比如函数,Set等) */ const DFSdeepClone = function (obj, visitedArr = []){ let _obj = {}; if (isTypeOf(obj, 'array') || isTypeOf(obj, 'object')){ let index = visitedArr.indexOf(obj); if (index > -1){ _obj = visitedArr[index] } else{ visitedArr.push(obj) for (let key in obj){ _obj[key] = DFSdeepClone(obj[key], visitedArr) } } } else if(isTypeOf(obj, 'function')){ _obj = eval( '(' + obj.toString() + ')')//处理函数 } else{ _obj = obj;//处理原始值 } return _obj; } let testObj = { a: 1, b: { c: 1, d: 2 }, circle: null, e: function() { console.log(1); } } let cloneTestObj = DFSdeepClone(testObj); let cloneTestObj2 = testObj; console.log(cloneTestObj); console.log('经过深度克隆后的更改'); cloneTestObj.b = {};//经过深度克隆后的更改 console.log(cloneTestObj); console.log(testObj); cloneTestObj2.b = {}; //引用的更改 console.log('引用的更改'); console.log(cloneTestObj2); console.log(testObj); //环状数据 let testCircle = { a: 1, b: { c: 1, d: 2, circle: null, }, e: function() { console.log(1); } } testCircle.b.circle = testCircle.b; cloneTestCircle = DFSdeepClone(testCircle);//不处理环问题是会爆栈的 进入死循环 console.log(cloneTestCircle);BFS深度克隆
let _toString = Object.prototype.toString; let map = { array: 'Array', object: 'Object', function: 'Function', string: 'String', null: 'Null', undefined: 'Undefined', boolean: 'Boolean', number: 'Number' } function getType(obj){ return _toString.call(obj).slice(8, -1) } function isTypeOf(obj, type){ return map[type] && map[type] === getType(obj) } //广度优先深度克隆, 利用队列的方式实现 //利用copyObj建立一个与原对象相同的数据结构, 遇到可处理的值(比如原始值,函数,就处理后赋值到相应的节点下) const BFSdeepClone = function (obj, visitedArr = []){ let copyObj = {}; let sequeue = [obj];//进队列 //同时copyObj也跟着一起进队列 let copySequeue = [copyObj]; while(sequeue.length){ let _obj = sequeue.shift(); let _copyObj = copySequeue.shift(); if (isTypeOf(_obj, 'array') || isTypeOf(_obj, 'object')){ for(item in _obj){ let val = _obj[item]; if (isTypeOf(val, 'object')){ let index = visitedArr.indexOf(val) if (~index){ //是环形数据 _copyObj[item] = visitedArr[index]; } else{ //新的对象,给copyObj一个对应属性的空对象 sequeue.push(val); _copyObj[item] = {}; copySequeue.push(_copyObj[item]); visitedArr.push(val); } } else if (isTypeOf(val, 'array')){ sequeue.push(val); _copyObj[item] = []; copySequeue.push(_copyObj[item]) } else if(isTypeOf(val, 'function')){ _copyObj[item] = eval( '(' + val.toString() + ')');//处理函数 } else{ _copyObj[item] = val;//处理原始值 } } } else if(isTypeOf(obj, 'function')){ _copyObj = eval( '(' + _obj.toString() + ')');//处理函数 } else{ _copyObj = _obj;//处理原始值 } } return copyObj } let testObj = { a: 1, b: { c: 1, d: 2 }, circle: null, e: function() { console.log(1); } } let cloneTestObj = BFSdeepClone(testObj); let cloneTestObj2 = testObj; console.log(cloneTestObj); //环状数据 let testCircle = { a: 1, b: { c: 1, d: 2, circle: null, }, e: function () { console.log(1); } } testCircle.b.circle = testCircle.b; cloneTestCircle = BFSdeepClone(testCircle);//不处理环问题是会爆栈的 进入死循环 console.log(cloneTestCircle); /** * 打印如下 { a: 1, b: { c: 1, d: 2 }, circle: null, e: [Function] } { a: 1, b: { c: 1, d: 2, circle: { c: 1, d: 2, circle: [Circular] } }, e: [Function] } */