CUDA編程入門
- 2020 年 4 月 4 日
- 筆記
CUDA是一個並行計算框架.用於計算加速.是nvidia家的產品.廣泛地應用於現在的深度學習加速.
一句話描述就是:cuda幫助我們把運算從cpu放到gpu上做,gpu多執行緒同時處理運算,達到加速效果.
從一個簡單例子說起:
#include <iostream> #include <math.h> // function to add the elements of two arrays void add(int n, float *x, float *y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) y[i] = x[i] + y[i]; } int main(void) { int N = 1<<20; // 1M elements float *x = new float[N]; float *y = new float[N]; // initialize x and y arrays on the host for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { x[i] = 1.0f; y[i] = 2.0f; } // Run kernel on 1M elements on the CPU add(N, x, y); // Check for errors (all values should be 3.0f) float maxError = 0.0f; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(y[i]-3.0f)); std::cout << "Max error: " << maxError << std::endl; // Free memory delete [] x; delete [] y; return 0; } 這段程式碼很簡單,對兩個數組對應位置元素相加.數組很大,有100萬個元素.
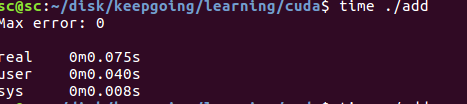
程式碼運行時間在0.075s.
改寫程式碼使之運行於gpu
gpu上能夠運算的函數,在cuda中我們稱之為kernel.由nvcc將其編譯為可以在GPU上運行的格式.
#include <iostream> #include <math.h> // Kernel function to add the elements of two arrays __global__ void add(int n, float *x, float *y) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) y[i] = x[i] + y[i]; } int main(void) { int N = 1<<20; float *x, *y; // Allocate Unified Memory – accessible from CPU or GPU cudaMallocManaged(&x, N*sizeof(float)); cudaMallocManaged(&y, N*sizeof(float)); // initialize x and y arrays on the host for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { x[i] = 1.0f; y[i] = 2.0f; } // Run kernel on 1M elements on the GPU add<<<1, 1>>>(N, x, y); // Wait for GPU to finish before accessing on host cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // Check for errors (all values should be 3.0f) float maxError = 0.0f; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(y[i]-3.0f)); std::cout << "Max error: " << maxError << std::endl; // Free memory cudaFree(x); cudaFree(y); return 0; } nvcc編譯的文件的後綴為.cu
- cuda中定義kernel在函數前加上
__global聲明就可以了. - 在顯示記憶體上分配記憶體使用cudaMallocManaged
- 調用一個函數使用<<< >>>符號.比如對add的函數的調用使用`add<<<1, 1>>>(N, x, y);`,關於其中參數的意義,後文再做解釋.
- 需要cudaDeviceSynchronize()讓cpu等待gpu上的計算做完再執行cpu上的操作
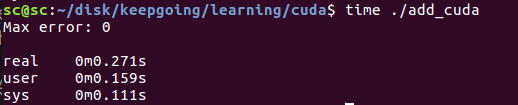
可以用nvprof做更詳細的性能分析.
注意用sudo 否則可能報錯. sudo /usr/local/cuda/bin/nvprof ./add_cuda 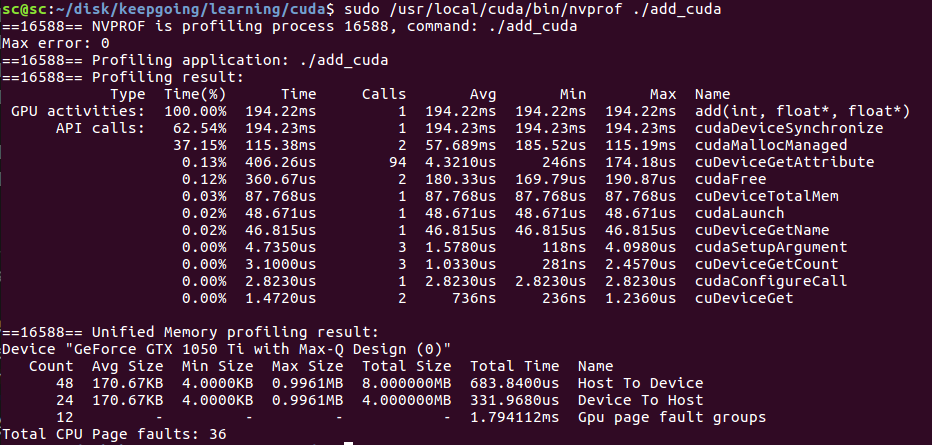
gpu上add用了194ms.
這裡,我們注意到,跑在gpu反而比cpu更慢了.因為我們這段程式碼里`add<<<1, 1>>>(N, x, y);`並沒有發揮gpu並行運算的優勢,反而因為多了一些cpu與gpu的交互使得程式變慢了.
用GPU threads加速運算
重點來了
CUDA GPUS有多組Streaming Multiprocessor(SM).每個SM可以運行多個thread block. 每一個thread block有多個thread.
如下圖所示:
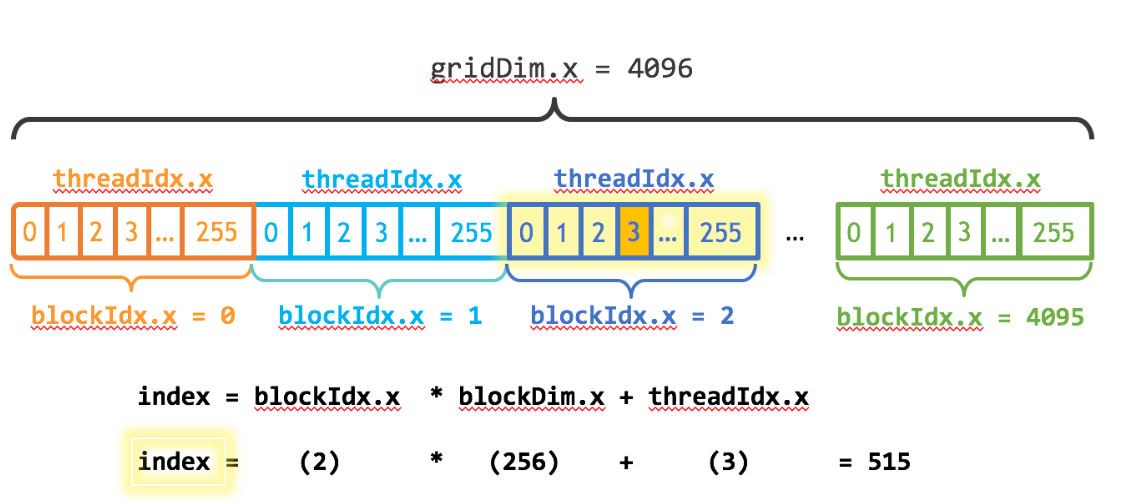
注意幾個關鍵變數:
- blockDim.x 表明了一個thread block內含有多少個thread
- threadIdx.x 表明了當前thread在該thread blcok內的index
- blockIdx.x 表明了當前是第幾個thread block
我們要做的就是把計算分配到所有的thread上去.這些thread上並行地做運算,從而達到加速的目的.
前面我們說到在cuda內調用一個函數(稱之為kernel)的用法為<<<p1,p2>>>,比如`add<<<1, 1>>>(N, x, y);` 第一個參數的含義即為thread block的數量,第二個參數的含義為block內參與運算的thread數量.
現在來改寫一下程式碼:
#include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> // Kernel function to add the elements of two arrays __global__ void add(int n, float *x, float *y) { int index = threadIdx.x; int stride = blockDim.x; printf("index=%d,stride=%dn",index,stride); for (int i = index; i < n; i+=stride) { y[i] = x[i] + y[i]; if(index == 0) { printf("i=%d,blockIdx.x=%d,thread.x=%dn",i,blockIdx.x,threadIdx.x); } } } int main(void) { int N = 1<<20; float *x, *y; // Allocate Unified Memory – accessible from CPU or GPU cudaMallocManaged(&x, N*sizeof(float)); cudaMallocManaged(&y, N*sizeof(float)); // initialize x and y arrays on the host for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { x[i] = 1.0f; y[i] = 2.0f; } // Run kernel on 1M elements on the GPU add<<<1, 256>>>(N, x, y); // Wait for GPU to finish before accessing on host cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // Check for errors (all values should be 3.0f) float maxError = 0.0f; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(y[i]-3.0f)); std::cout << "Max error: " << maxError << std::endl; // Free memory cudaFree(x); cudaFree(y); return 0; } 注意add的寫法,我們把0,256,512…放到thread1計算,把1,257,…放到thread2計算,依次類推.調用的時候,add<<<1, 256>>>(N, x, y);表明我們只把計算分配到了thread block1內的256個thread去做.
編譯這個程式(注意把程式碼里的printf注釋掉,因為要統計程式運行時間):nvcc add_block.cu -o add_cuda_blcok -I/usr/local/cuda-9.0/include/ -L/usr/local/cuda-9.0/lib64

可以看到add的gpu時間僅僅用了2.87ms
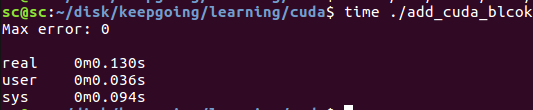
程式的整體運行時間為0.13s,主要是cudaMallocManaged,cudaDeviceSynchronize之類的操作耗費了比較多的時間.
再一次改寫程式碼
這一次我們用更多的thread block.
int blockSize = 256; int numBlocks = (N + blockSize - 1) / blockSize; add<<<numBlocks, blockSize>>>(N, x, y); // Kernel function to add the elements of two arrays __global__ void add(int n, float *x, float *y) { int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x; for (int i = index; i < n; i+=stride) { y[i] = x[i] + y[i]; //printf("i=%d,blockIdx.x=%dn",i,blockIdx.x); } } 編譯:nvcc add_grid.cu -o add_cuda_grid -I/usr/local/cuda-9.0/include/ -L/usr/local/cuda-9.0/lib64
統計性能:

可以看出來,gpu上add所用的時間進一步縮小到1.8ms
參考:https://devblogs.nvidia.com/even-easier-introduction-cuda/


