SpringBoot系列之快取使用教程
- 2020 年 4 月 3 日
- 筆記
介紹SpringBoot項目中使用快取,之前先介紹一下Spring的快取抽象和JSR107,本部落格是我在學習尚矽谷影片和參考其它部落格之後做的筆記,僅供學習參考
@
一、Spring的快取抽象
1.1、快取抽象定義
Spring從3.1開始定義了org.springframework.cache.Cache
和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager介面來統一不同的快取技術;並支援使用Java Caching(JSR-107)註解簡化我們進行快取開發。Spring Cache 只負責維護抽象層,具體的實現由你的技術選型來決定。將快取處理和快取技術解除耦合。
1.2、重要介面
- Cache:快取抽象的規範介面,快取實現有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等
- CacheManager:快取管理器,管理Cache的生命周期
二、JSR107
2.1、JSR107核心介面
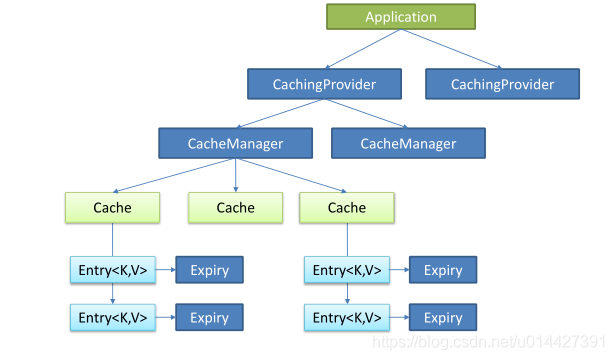
Java Caching(JSR-107)定義了5個核心介面,分別是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry和 Expiry。
- CachingProvider:創建、配置、獲取、管理和控制多個CacheManager
- CacheManager:創建、配置、獲取、管理和控制多個唯一命名的Cache,Cache存在於CacheManager的上下文中。一個CacheManager僅對應一個CachingProvider
- Cache:是由CacheManager管理的,CacheManager管理Cache的生命周期,Cache存在於CacheManager的上下文中,是一個類似map的數據結構,並臨時存儲以key為索引的值。一個Cache僅被一個CacheManager所擁有
- Entry:是一個存儲在Cache中的key-value對
- Expiry:每一個存儲在Cache中的條目都有一個定義的有效期。一旦超過這個時間,條目就自動過期,過期後,條目將不可以訪問、更新和刪除操作。快取有效期可以通過ExpiryPolicy設置
2.2、JSR107圖示
引用尚矽谷影片課件中的圖示:
三、Spring快取使用
3.1、重要註解簡介
例子實踐之前,先簡單介紹Spring提供的重要快取註解
- @Cacheable:針對方法配置,能夠根據方法的請求參數對其結果進行快取
- @CacheEvict:清空快取
- @CachePut:既調用方法,又更新快取數據
- @EnableCaching:開啟基於註解的快取
- @Caching:定義複雜的快取規則
3.2、環境準備
ok,本部落格以尚矽谷影片例子進行改寫,用這個比較經典的例子進行說明
環境準備:
- maven環境
- IntelliJ IDEA
新建兩張表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`; CREATE TABLE `employee` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `lastName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `gender` int(2) DEFAULT NULL, `d_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`; CREATE TABLE `department` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `departmentName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; 3.3、引入spring-boot-starter-cache模組
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency> 3.4、主要註解例子實踐
3.4.1、@EnableCaching
@EnableCaching開啟基於註解的快取
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; @SpringBootApplication @EnableCaching public class SpringbootCacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args); } } 3.4.2、@Cacheable註解
@Cacheable註解的作用,前面也簡介了,主要是針對方法配置,能夠根據方法的請求參數對其結果進行快取,介紹一下注解的主要屬性
- cacheNames/value:指定快取組件的名字,數組形式
- key:快取數據使用的key,確定快取可以用唯一key進行指定;eg:編寫SpEL; #id,參數id的值 ,,#a0(第一個參數), #p0(和a0的一樣的意義) ,#root.args[0]
- keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的組件id(注意: key/keyGenerator:二選一使用;不能同時使用)
- cacheManager:指定快取管理器;或者cacheResolver指定獲取解析器
- condition:指定符合條件的情況下才快取;使用SpEl表達式,eg:condition = "#a0>1":第一個參數的值>1的時候才進行快取
- unless:否定快取;當unless指定的條件為true,方法的返回值就不會被快取;eg:unless = "#a0!=2":如果第一個參數的值不是2,結果不快取;
- sync:是否使用非同步模式
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}, /*keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",*/key = "#id",condition = "#a0>=1",unless = "#a0!=2") public Employee getEmp(Integer id) { Employee employee = this.employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); LOG.info("查詢{}號員工數據",id); return employee; } 這裡也可以使用自定義的keyGenerator,使用屬性keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator
定義一個@Bean類,將KeyGenerator添加到Spring容器
@Configuration public class CacheConfig { @Bean(value = {"myKeyGenerator"}) public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){ return new KeyGenerator() { @Override public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) { return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(params).toString()+"]"; } }; } } 3.4.3、@CachePut註解
@CachePut註解也是一個用來快取的註解,不過快取和@Cacheable有明顯的區別是即調用方法,又更新快取數據,也就是執行方法操作之後再來同步更新快取,所以這個主鍵常用於更新操作,也可以用於查詢,主鍵屬性和@Cacheable有很多類似的,詳情參看@link @CachePut源碼
/** * @CachePut:既調用方法,又更新快取數據;同步更新快取 * 修改了數據,同時更新快取 */ @CachePut(value = {"emp"}, key = "#result.id") public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){ employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee); LOG.info("更新{}號員工數據",employee.getId()); return employee; } 3.4.4、 @CacheEvic註解
主要屬性:
- key:指定要清除的數據
- allEntries = true:指定清除這個快取中所有的數據
- beforeInvocation = false:默認代表快取清除操作是在方法執行之後執行
- beforeInvocation = true:代表清除快取操作是在方法運行之前執行
@CacheEvict(value = {"emp"}, beforeInvocation = true,key="#id") public void deleteEmp(Integer id){ employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id); //int i = 10/0; } 3.4.5、@Caching註解
@Caching 用於定義複雜的快取規則,可以集成@Cacheable和 @CachePut
// @Caching 定義複雜的快取規則 @Caching( cacheable = { @Cacheable(/*value={"emp"},*/key = "#lastName") }, put = { @CachePut(/*value={"emp"},*/key = "#result.id"), @CachePut(/*value={"emp"},*/key = "#result.email") } ) public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){ return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName); } 3.4.6、 @CacheConfig註解
@CacheConfig註解可以用於抽取快取的公共配置,然後在類加上就可以,eg:@CacheConfig(cacheNames = {"emp"},cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager")
附錄拓展:SpEL表達式用法
Cache SpEL available metadata
| 名稱 | 位置 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodName | root對象 | 當前被調用的方法名 | #root.methodname |
| method | root對象 | 當前被調用的方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | root對象 | 當前被調用的目標對象實例 | #root.target |
| targetClass | root對象 | 當前被調用的目標對象的類 | #root.targetClass |
| args | root對象 | 當前被調用的方法的參數列表 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | root對象 | 當前方法調用使用的快取列表 | #root.caches[0].name |
| argument Name | 執行上下文(avaluation context) | 當前被調用的方法的參數,如findArtisan(Artisan artisan),可以通過#artsian.id獲得參數 | #artsian.id |
| result | 執行上下文(evaluation context) | 方法執行後的返回值(僅當方法執行後的判斷有效,如 unless cacheEvict的beforeInvocation=false) | #result |
四、集成Redis快取
4.1、環境準備
基於前面的Spring快取環境,集成redis要引入相關配置:
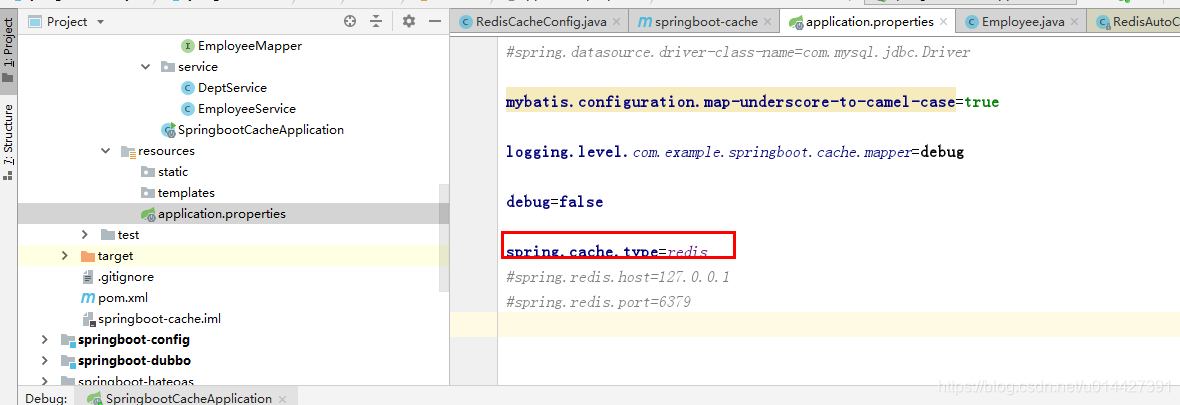
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId> </dependency> 切換快取方式為Redis:spring.cache.type=redis
4.2、Redis配置類實現
RedisTemplate配置
@Resource private LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory; @Bean @Primary public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate(){ RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(lettuceConnectionFactory); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = this.initJacksonSerializer(); // 設置value的序列化規則和 key的序列化規則 redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); return redisTemplate; } RedisCacheManager相關程式碼可以參考博文,該部落客已經對程式碼做了比較好的封裝,所以本文不複製程式碼
4.3、RestTemplate相關操作
使用RestTemplate操作redis
- 1、 redisTemplate.opsForValue();//操作字元串
- 2、redisTemplate.opsForHash();//操作hash
- 3、redisTemplate.opsForList();//操作list
- 4、redisTemplate.opsForSet();//操作set
- 5、redisTemplate.opsForZSet();//操作有序set
4.4、快取業務測試
@Autowired DepartmentMapper departmentMapper; @Qualifier("redisCacheManager") @Autowired RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager; // @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",cacheManager = "redisCacheManager") // public Department getDeptById(Integer id){ // System.out.println("查詢部門"+id); // Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); // return department; // } // 使用快取管理器得到快取,進行api調用 public Department getDeptById(Integer id){ LOG.info("查詢id為{}的員工資訊",id); //獲取某個快取 Cache deptCache = redisCacheManager.getCache("dept"); Department department = null; if(deptCache.get(id)==null){ department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); deptCache.put(id,department); } else { SimpleValueWrapper valueWrapper = (SimpleValueWrapper) deptCache.get(id); department = (Department)valueWrapper.get(); } return department; } 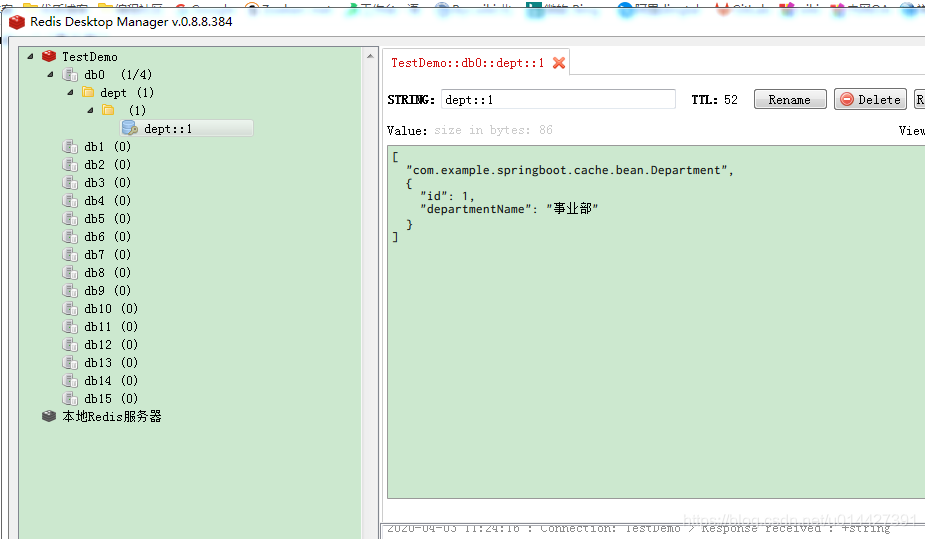
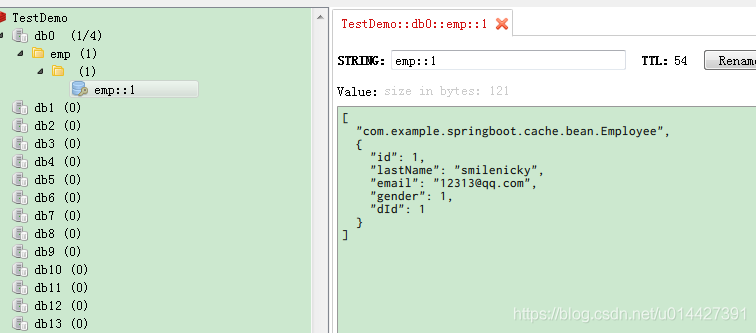
當然使用前面的Spring主鍵也是可以快取的,
參考博文:
快取抽象層Spring cache實戰操作
程式碼例子下載:github鏈接


