Java流中的map運算元和flatMap運算元的區別
- 2020 年 3 月 28 日
- 筆記
map運算元和flatMap運算元
map和flatMap都是映射(轉換),那麼他們之間究竟有什麼區別呢?
1.我們先簡單了解下map運算元:
@org.junit.Test public void test1(){ List<String> words = Arrays.asList("hello","world"); words.stream() .map(String::length) //使用了方法引用,將String類型轉換為int類型 .forEach(System.out::println); } //輸出:5 5 map是流的中間操作,
傳入一個Function函數式介面,返回一個流。關於函數式介面和lambda表達式可以看我之前的隨筆。
2.再看個例子,來簡單了解下兩者間的區別,先著重思考一下下面的案例用map會有什麼問題?
需求:傳入一個集合 list = Arrays.asList("hello","Hello")
要求:輸出:h,e,l,o,H (單詞裡面的每一個字母去重 ,並且進行列印)
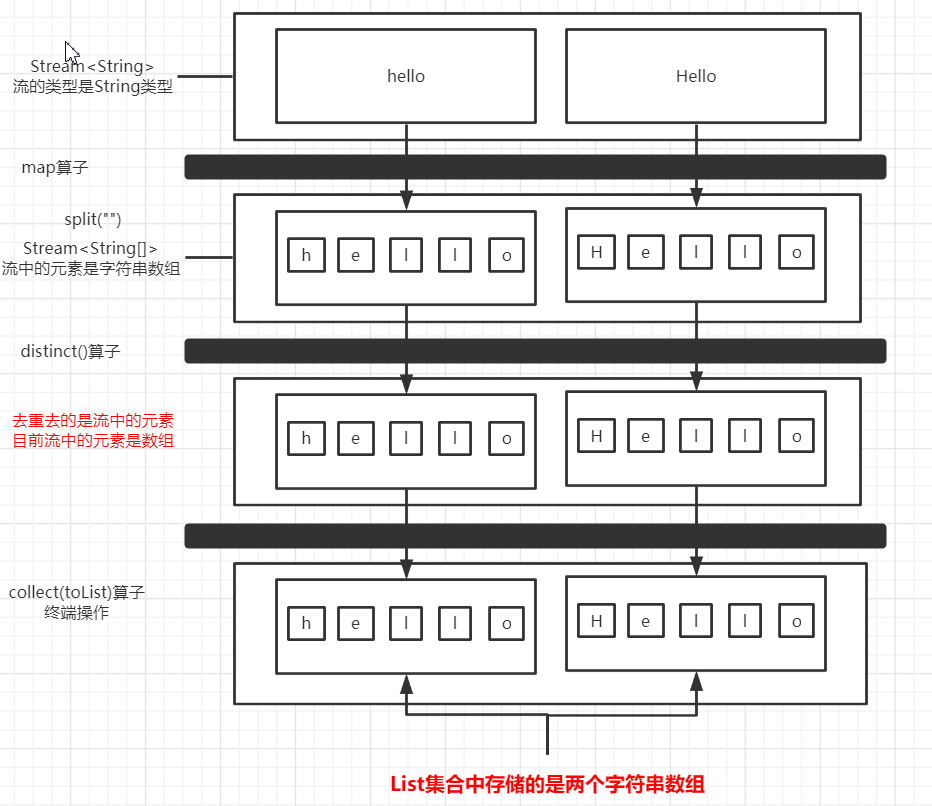
@org.junit.Test public void test2(){ //錯誤演示 List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello","Hello");//h,e,l,o,H list.stream() .map(m->m.split("")) .distinct() .collect(toList()) .stream() .forEach(System.out::println); } 那麼輸出結果符合我們的需求嗎?
//輸出結果:這倆行是個什麼鬼? [Ljava.lang.String;@51e2adc7 [Ljava.lang.String;@1a8a8f7c 這顯然不符合我們的要求,那究竟是哪裡出錯了呢?我們一步一步分析一下:
1.Stream
2.Stream<String[]> mapRDD= baseRDD.map(w->w.split("")); 調用map運算元,轉換
3.Stream<String[]> distinctRDD= mapRDD.distinct(); 調用distinct運算元,去重
4.List<String[]> collectRDD = distinctRDD.collect(toList()); 流轉換為集合,最後輸出
我們一步一步分析下來,看起來是不是還是沒問題呢?接下來讓我們再改寫一下:
@org.junit.Test public void test3(){ List<String> words = Arrays.asList("hello","Hello");//h,e,l,o,H Stream<String[]> mapRDD = words.stream() .map(word->word.split("")); mapRDD.map(Arrays::stream) .distinct() .collect(toList()) .stream() .forEach(System.out::println); } //輸出:這又是個什麼鬼???是不是越來越迷糊了,不要著急 java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@2353b3e6 java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@631330c 再來一步一步分析一下:
Stream<String[]> map1RDD = words.stream().map(word->word.split("")); 轉換
Stream<Stream
Stream<Stream
List<Stream
這裡我們需要注意的是:map轉化(輸入一個類型,返回另外一個類型)
輸入類型的值(值的類型是上一個數據集的泛型)
輸出數據的類型會作為下一個數據集的泛型
還是不理解?沒關係,等會我們通過圖來深刻理解一下。
那flatMap運算元呢?
@org.junit.Test public void test4(){ List<String> words = Arrays.asList("hello","Hello");//h,e,l,o,H words.stream() .map(word->word.split("")) .flatMap(d->{ Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(d); return Arrays.stream(d); }) .distinct() .forEach(System.out::println); } //輸出 heloH 居然成功實現了需求,這兩者究竟有什麼區別呢?我們通過圖畫來更加生動形象的了解下(畫圖不易,值得一贊)
對比一下flatMap運算元:
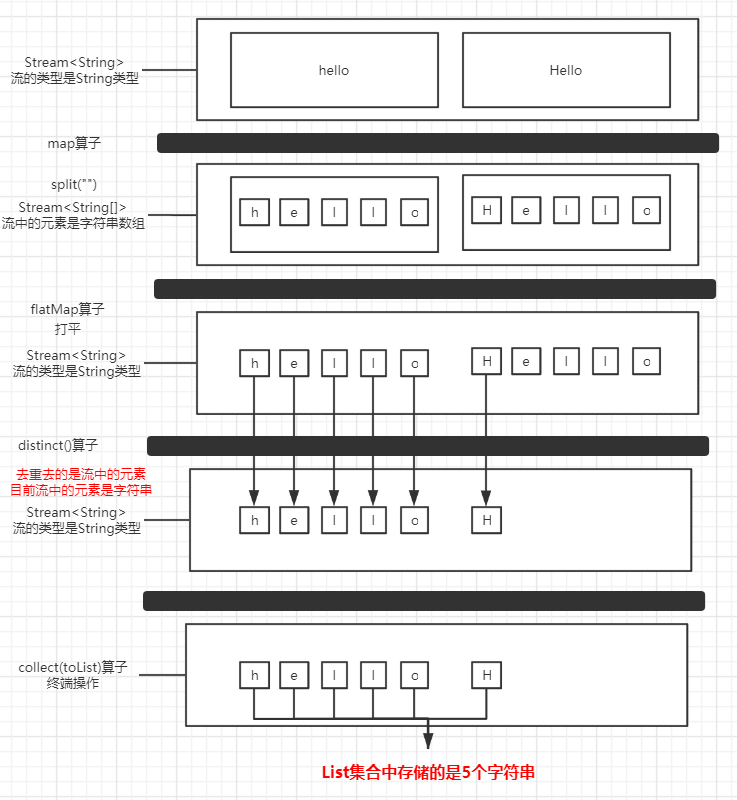
這樣就一目了然了!!!
總結一下:
map運算元:map返回值類型就是新的數據集的泛型
flatMap運算元: flatMap運算元返回類型就是新的數據集的類型
最後再看個案例:
需求:輸入:【1,2,3】【3,4】
輸出:【(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4),(3,3),(3,4)】
@org.junit.Test public void test7(){ //集合(.stream()) List<Integer> number1 = Arrays.asList(1,2,3); List<Integer> number2 = Arrays.asList(4,5); /** * 倒著推理一下 : * 最終的結果(終端): List<int[]> * 終端操作的上一個操作:Stream<int[]> * */ List<int[]> pairs = number1.stream() .flatMap(i->{ // Stream<int[]> stream = // number2.stream().map(j->new int[]{i,j}); return number2.stream().map(j->new int[]{i,j}); }) .collect(toList()); Stream<int[]> intArrayRDD = pairs.stream(); intArrayRDD.forEach(arr->{ for(int i : arr){ System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); }); }//OK 至此,map運算元和flatMap運算元就介紹完畢了!

