【原創】(五)Linux進程調度-CFS調度器
- 2020 年 3 月 15 日
- 筆記
背景
Read the fucking source code!–By 魯迅A picture is worth a thousand words.–By 高爾基
說明:
- Kernel版本:4.14
- ARM64處理器,Contex-A53,雙核
- 使用工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio
1. 概述
Completely Fair Scheduler,完全公平調度器,用於Linux系統中普通進程的調度。CFS採用了紅黑樹演算法來管理所有的調度實體sched_entity,演算法效率為O(log(n))。CFS跟蹤調度實體sched_entity的虛擬運行時間vruntime,平等對待運行隊列中的調度實體sched_entity,將執行時間少的調度實體sched_entity排列到紅黑樹的左邊。- 調度實體
sched_entity通過enqueue_entity()和dequeue_entity()來進行紅黑樹的出隊入隊。
老規矩,先上張圖片來直觀了解一下原理:
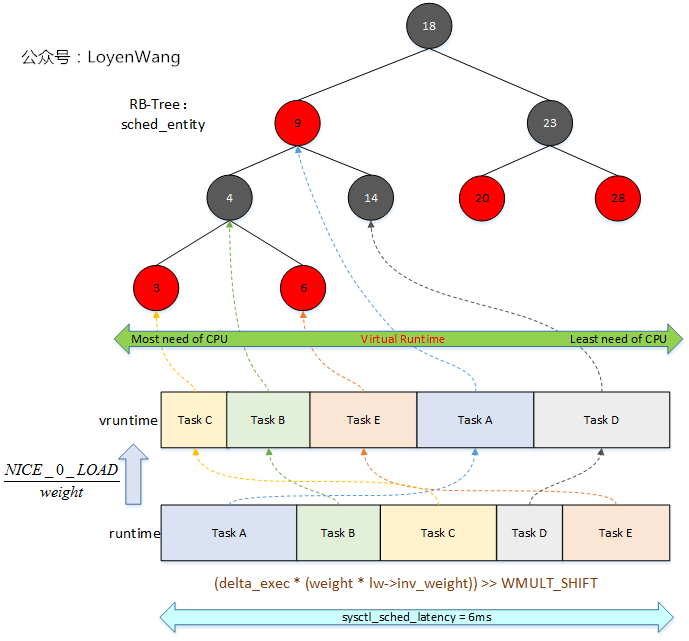
- 每個
sched_latency周期內,根據各個任務的權重值,可以計算出運行時間runtime; - 運行時間
runtime可以轉換成虛擬運行時間vruntime; - 根據虛擬運行時間的大小,插入到CFS紅黑樹中,虛擬運行時間少的調度實體放置到左邊;
- 在下一次任務調度的時候,選擇虛擬運行時間少的調度實體來運行;
在開始本文之前,建議先閱讀下(一)Linux進程調度器-基礎。
開始探索之旅!
2. 數據結構
2.1 調度類
Linux內核抽象了一個調度類struct sched_class,這是一種典型的面向對象的設計思想,將共性的特徵抽象出來封裝成類,在實例化各個調度器的時候,可以根據具體的調度演算法來實現。這種方式做到了高內聚低耦合,同時又很容易擴展新的調度器。
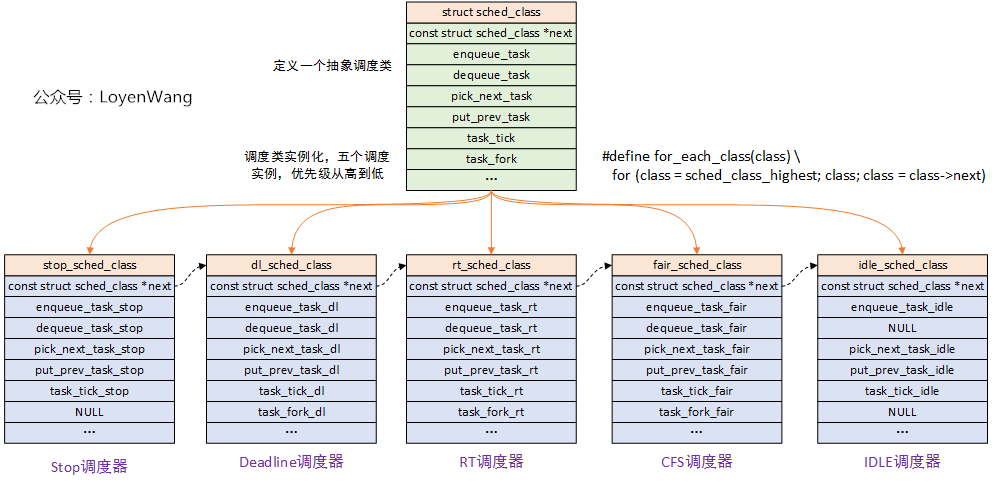
- 在調度核心程式碼
kernel/sched/core.c中,使用的方式是task->sched_class->xxx_func,其中task表示的是描述任務的結構體struct task_struck,在該結構體中包含了任務所使用的調度器,進而能找到對應的函數指針來完成調用執行,有點類似於C++中的多態機制。
2.2 rq/cfs_rq/task_struct/task_group/sched_entity
struct rq:每個CPU都有一個對應的運行隊列;struct cfs_rq:CFS運行隊列,該結構中包含了struct rb_root_cached紅黑樹,用於鏈接調度實體struct sched_entity。rq運行隊列中對應了一個CFS運行隊列,此外,在task_group結構中也會為每個CPU再維護一個CFS運行隊列;struct task_struct:任務的描述符,包含了進程的所有資訊,該結構中的struct sched_entity,用於參與CFS的調度;struct task_group:組調度(參考前文),Linux支援將任務分組來對CPU資源進行分配管理,該結構中為系統中的每個CPU都分配了struct sched_entity調度實體和struct cfs_rq運行隊列,其中struct sched_entity用於參與CFS的調度;struct sched_entity:調度實體,這個也是CFS調度管理的對象了;
來一張圖看看它們之間的組織關係:

struct sched_entity結構體欄位注釋如下:
struct sched_entity { /* For load-balancing: */ struct load_weight load; //調度實體的負載權重值 struct rb_node run_node; //用於連接到CFS運行隊列的紅黑樹中的節點 struct list_head group_node; //用於連接到CFS運行隊列的cfs_tasks鏈表中的節點 unsigned int on_rq; //用於表示是否在運行隊列中 u64 exec_start; //當前調度實體的開始執行時間 u64 sum_exec_runtime; //調度實體執行的總時間 u64 vruntime; //虛擬運行時間,這個時間用於在CFS運行隊列中排隊 u64 prev_sum_exec_runtime; //上一個調度實體運行的總時間 u64 nr_migrations; //負載均衡 struct sched_statistics statistics; //統計資訊 #ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED int depth; //任務組的深度,其中根任務組的深度為0,逐級往下增加 struct sched_entity *parent; //指向調度實體的父對象 /* rq on which this entity is (to be) queued: */ struct cfs_rq *cfs_rq; //指向調度實體歸屬的CFS隊列,也就是需要入列的CFS隊列 /* rq "owned" by this entity/group: */ struct cfs_rq *my_q; //指向歸屬於當前調度實體的CFS隊列,用於包含子任務或子的任務組 #endif #ifdef CONFIG_SMP /* * Per entity load average tracking. * * Put into separate cache line so it does not * collide with read-mostly values above. */ struct sched_avg avg ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; //用於調度實體的負載計算(`PELT`) #endif };- struct cfs_rq結構體的關鍵欄位注釋如下:
/* CFS-related fields in a runqueue */ struct cfs_rq { struct load_weight load; //CFS運行隊列的負載權重值 unsigned int nr_running, h_nr_running; //nr_running:運行的調度實體數(參與時間片計算) u64 exec_clock; //運行時間 u64 min_vruntime; //最少的虛擬運行時間,調度實體入隊出隊時需要進行增減處理 #ifndef CONFIG_64BIT u64 min_vruntime_copy; #endif struct rb_root_cached tasks_timeline; //紅黑樹,用於存放調度實體 /* * 'curr' points to currently running entity on this cfs_rq. * It is set to NULL otherwise (i.e when none are currently running). */ struct sched_entity *curr, *next, *last, *skip; //分別指向當前運行的調度實體、下一個調度的調度實體、CFS運行隊列中排最後的調度實體、跳過運行的調度實體 #ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_DEBUG unsigned int nr_spread_over; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_SMP /* * CFS load tracking */ struct sched_avg avg; //計算負載相關 u64 runnable_load_sum; unsigned long runnable_load_avg; //基於PELT的可運行平均負載 #ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED unsigned long tg_load_avg_contrib; //任務組的負載貢獻 unsigned long propagate_avg; #endif atomic_long_t removed_load_avg, removed_util_avg; #ifndef CONFIG_64BIT u64 load_last_update_time_copy; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED /* * h_load = weight * f(tg) * * Where f(tg) is the recursive weight fraction assigned to * this group. */ unsigned long h_load; u64 last_h_load_update; struct sched_entity *h_load_next; #endif /* CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED */ #endif /* CONFIG_SMP */ #ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED struct rq *rq; /* cpu runqueue to which this cfs_rq is attached */ //指向CFS運行隊列所屬的CPU RQ運行隊列 /* * leaf cfs_rqs are those that hold tasks (lowest schedulable entity in * a hierarchy). Non-leaf lrqs hold other higher schedulable entities * (like users, containers etc.) * * leaf_cfs_rq_list ties together list of leaf cfs_rq's in a cpu. This * list is used during load balance. */ int on_list; struct list_head leaf_cfs_rq_list; struct task_group *tg; /* group that "owns" this runqueue */ //CFS運行隊列所屬的任務組 #ifdef CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH int runtime_enabled; //CFS運行隊列中使用CFS頻寬控制 u64 runtime_expires; //到期的運行時間 s64 runtime_remaining; //剩餘的運行時間 u64 throttled_clock, throttled_clock_task; //限流時間相關 u64 throttled_clock_task_time; int throttled, throttle_count; //throttled:限流,throttle_count:CFS運行隊列限流次數 struct list_head throttled_list; //運行隊列限流鏈表節點,用於添加到cfs_bandwidth結構中的cfttle_cfs_rq鏈表中 #endif /* CONFIG_CFS_BANDWIDTH */ #endif /* CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED */ };3. 流程分析
整個流程分析,圍繞著CFS調度類實體:fair_sched_class中的關鍵函數來展開。
先來看看fair_sched_class都包含了哪些函數:
/* * All the scheduling class methods: */ const struct sched_class fair_sched_class = { .next = &idle_sched_class, .enqueue_task = enqueue_task_fair, .dequeue_task = dequeue_task_fair, .yield_task = yield_task_fair, .yield_to_task = yield_to_task_fair, .check_preempt_curr = check_preempt_wakeup, .pick_next_task = pick_next_task_fair, .put_prev_task = put_prev_task_fair, #ifdef CONFIG_SMP .select_task_rq = select_task_rq_fair, .migrate_task_rq = migrate_task_rq_fair, .rq_online = rq_online_fair, .rq_offline = rq_offline_fair, .task_dead = task_dead_fair, .set_cpus_allowed = set_cpus_allowed_common, #endif .set_curr_task = set_curr_task_fair, .task_tick = task_tick_fair, .task_fork = task_fork_fair, .prio_changed = prio_changed_fair, .switched_from = switched_from_fair, .switched_to = switched_to_fair, .get_rr_interval = get_rr_interval_fair, .update_curr = update_curr_fair, #ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED .task_change_group = task_change_group_fair, #endif };3.1 runtime與vruntime
CFS調度器沒有時間片的概念了,而是根據實際的運行時間和虛擬運行時間來對任務進行排序,從而選擇調度。
那麼,運行時間和虛擬運行時間是怎麼計算的呢?看一下流程調用:

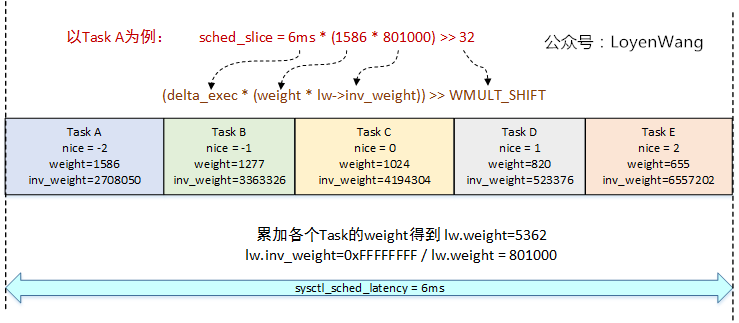
- Linux內核默認的
sysctl_sched_latency是6ms,這個值用戶態可設。sched_period用於保證可運行任務都能至少運行一次的時間間隔; - 當可運行任務大於8個的時候,
sched_period的計算則需要根據任務個數乘以最小調度顆粒值,這個值系統默認為0.75ms; - 每個任務的運行時間計算,是用
sched_period值,去乘以該任務在整個CFS運行隊列中的權重佔比; - 虛擬運行的時間 = 實際運行時間 * NICE_0_LOAD / 該任務的權重;
還是來看一個實例吧,以5個Task為例,其中每個Task的nice值不一樣(優先順序不同),對應到的權重值在內核中提供了一個轉換數組:
const int sched_prio_to_weight[40] = { /* -20 */ 88761, 71755, 56483, 46273, 36291, /* -15 */ 29154, 23254, 18705, 14949, 11916, /* -10 */ 9548, 7620, 6100, 4904, 3906, /* -5 */ 3121, 2501, 1991, 1586, 1277, /* 0 */ 1024, 820, 655, 526, 423, /* 5 */ 335, 272, 215, 172, 137, /* 10 */ 110, 87, 70, 56, 45, /* 15 */ 36, 29, 23, 18, 15, };圖來了:
3.2 CFS調度tick
CFS調度器中的tick函數為task_tick_fair,系統中每個調度tick都會調用到,此外如果使用了hrtimer,也會調用到這個函數。
流程如下:

主要的工作包括:
- 更新運行時的各類統計資訊,比如
vruntime, 運行時間、負載值、權重值等; - 檢查是否需要搶佔,主要是比較運行時間是否耗盡,以及
vruntime的差值是否大於運行時間等;
來一張圖,感受一下update_curr函數的相關資訊更新吧:

3.3 任務出隊入隊
- 當任務進入可運行狀態時,需要將調度實體放入到紅黑樹中,完成入隊操作;
- 當任務退出可運行狀態時,需要將調度實體從紅黑樹中移除,完成出隊操作;
- CFS調度器,使用
enqueue_task_fair函數將任務入隊到CFS隊列,使用dequeue_task_fair函數將任務從CFS隊列中出隊操作。
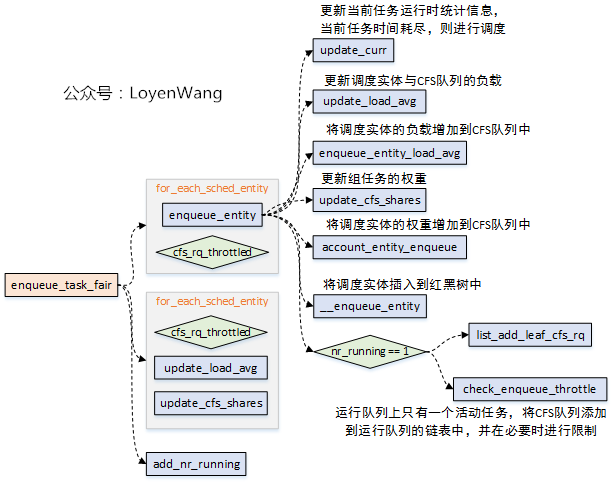
- 出隊與入隊的操作中,核心的邏輯可以分成兩部分:1)更新運行時的數據,比如負載、權重、組調度的佔比等等;2)將sched_entity插入紅黑樹,或者從紅黑樹移除;
- 由於
dequeue_task_fair大體的邏輯類似,不再深入分析; - 這個過程中,涉及到了
CPU負載計算、task_group組調度、CFS Bandwidth頻寬控制等,這些都在前邊的文章中分析過,可以結合進行理解;
3.3 任務創建
在父進程通過fork創建子進程的時候,task_fork_fair函數會被調用,這個函數的傳入參數是子進程的task_struct。該函數的主要作用,就是確定子任務的vruntime,因此也能確定子任務的調度實體在紅黑樹RB中的位置。
task_fork_fair本身比較簡單,流程如下圖:
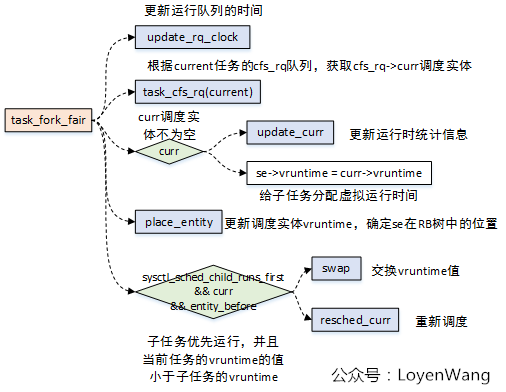
3.4 任務選擇
每當進程任務切換的時候,也就是schedule函數執行時,調度器都需要選擇下一個將要執行的任務。
在CFS調度器中,是通過pick_next_task_fair函數完成的,流程如下:

- 當需要進程任務切換的時候,
pick_next_task_fair函數的傳入參數中包含了需要被切換出去的任務,也就是pre_task; - 當
pre_task不是普通進程時,也就是調度類不是CFS,那麼它就不使用sched_entity的調度實體來參與調度,因此會執行simple分支,通過put_pre_task函數來通知系統當前的任務需要被切換,而不是通過put_prev_entity函數來完成; - 當
pre_task是普通進程時,調用pick_next_entity來選擇下一個執行的任務,這個選擇過程實際是有兩種情況:當調度實體對應task時,do while()遍歷一次,當調度實體對應task_group是,則需要遍歷任務組來選擇下一個執行的任務了。 put_prev_entity,用於切換任務前的準備工作,更新運行時的統計數據,並不進行dequeue的操作,其中需要將CFS隊列的curr指針置位成NULL;- set_next_entity,用於設置下一個要運行的調度實體,設置CFS隊列的
curr指針; - 如果使能了
hrtimer,則將hrtimer的到期時間設置為調度實體的剩餘運行時間;
暫且分析到這吧,CFS調度器涵蓋的內容還是挺多的,fair.c一個文件就有將近一萬行程式碼,相關內容的分析也分散在前邊的文章中了,感興趣的可以去看看。
打完收工,洗洗睡了。


