畸變矯正、透視變換加速(OpenCV C++)
前兩周,同事和我說檢測時間超時,其中對影像做畸變矯正和投影變換就要花費25ms(3000×3000的圖)。而此時我們已經用上了文章opencv影像畸變矯正加速、透視變換加速方法總結中的方法。突然我想到了我去年筆記OpenCV筆記(10) 相機模型與標定中的一個函數cv::undistortPoints(),對感興趣點進行畸變矯正。在應用之前,需要測試下兩種方法計算出來的點的差值,即remap和undistortPoints的不同。結論:對全圖進行畸變矯正,再找點 VS 找點後,對點進行畸變矯正,兩者的差值小於0.1個像素,可行!同樣的方法可以運用在投影變換上。在尺寸測量方面,這樣可以節省掉畸變矯正和投影變換的時間。
1 只對感興趣的點進行畸變矯正
// 讀取相機參數文件
FileStorage fs("D:/distortionLens.xml", FileStorage::READ);
Mat intrinsic_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));
Mat distortion_coeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));
fs["intrinsic_matrix"] >> intrinsic_matrix;
fs["distortion_coeffs"] >> distortion_coeffs;
Mat mapx = Mat(s, CV_32FC1);
Mat mapy = Mat(s, CV_32FC1);
// 根據內參和畸變係數,建立查找表
//intrinsic_matrix = getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, s, 1, s, 0);
initUndistortRectifyMap(intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, Mat(),
intrinsic_matrix, s, CV_32FC1, mapx, mapy);
// 方法1:畸變矯正後找角點
Mat distortionMat;
remap(src, distortionMat, mapx, mapy, INTER_CUBIC);
vector<Point2f> distortPoints;
findChessboardCornersSB(src, Size(21, 21), distortPoints, 64);
// 方法2:找角點後畸變矯正
vector<Point2f> oriPoints, sparsePoints;
findChessboardCornersSB(src, Size(21, 21), oriPoints, 64);
undistortPoints(oriPoints, sparsePoints, intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, Mat(), intrinsic_matrix);
// 列印比較
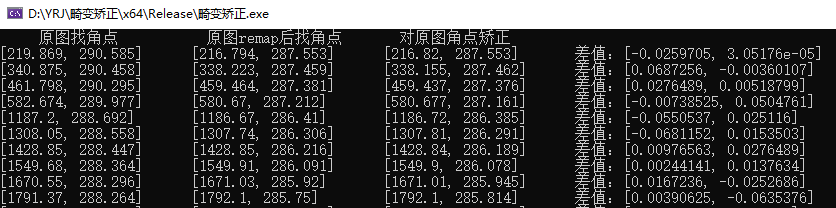
cout << " 原圖找角點 " << "\t" << " 原圖remap後找角點 " << "\t" << " 對原圖角點矯正 " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < sparsePoints.size(); i++) {
cout << oriPoints[i] << "\t" << distortPoints[i] << "\t" << sparsePoints[i] << "\t" << "差值:" << distortPoints[i] - sparsePoints[i] << endl;
}
部分數據如下所示,可以看出,兩者差值小於0.1個像素,加速10ms完成,接下來再對投影變換加速一下。
2 只對感興趣的點進行投影變換
// 讀取變換矩陣
fs = FileStorage("D:/transMat.txt", FileStorage::READ);
Mat transMat = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));
fs["transMat"] >> transMat;
// 方法1:進行透視變換後找角點
Mat warpMat;
warpPerspective(src, warpMat, transMat, s, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar(255));
vector<Point2f> warpPoints;
findChessboardCornersSB(warpMat,Size(21, 21), warpPoints, 64);
// 方法2:找角點後進行透視變換
vector<Point2f> outPoints;
for (int i = 0; i < oriPoints.size(); i++) {
Mat_<double> oriPoint(3, 1);
oriPoint(0, 0) = oriPoints[i].x;
oriPoint(1, 0) = oriPoints[i].y;
oriPoint(2, 0) = 1;
Mat dstPoints = transMat * oriPoint;
double a1 = dstPoints.at<double>(0, 0);
double a2 = dstPoints.at<double>(1, 0);
double a3 = dstPoints.at<double>(2, 0);
outPoints.push_back(Point2f(a1 * 1.0 / a3, a2 * 1.0 / a3));
}
//列印
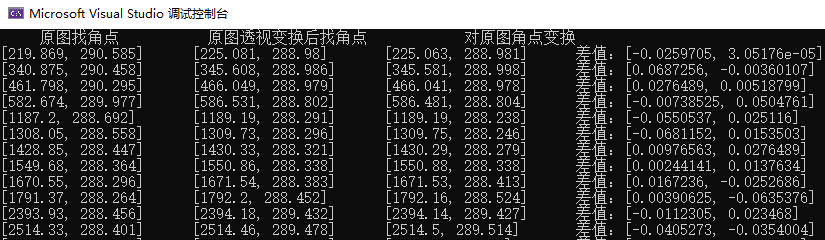
cout << " 原圖找角點 " << "\t" << " 原圖透視變換後找角點 " << "\t" << " 對原圖角點變換 " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < sparsePoints.size(); i++) {
cout << oriPoints[i] << "\t" << warpPoints[i] << "\t" << outPoints[i] << "\t" << "差值:" << distortPoints[i] - sparsePoints[i] << endl;
}
3 合併
3.1 讀取文件
void GetMap()
{
FileStorage fs(path+"distortionLens.xml", FileStorage::READ);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
intrinsic_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1, Scalar::all(0));
distortion_coeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_64FC1, Scalar::all(0));
fs["intrinsic_matrix"] >> intrinsic_matrix;
fs["distortion_coeffs"] >> distortion_coeffs;
}
fs = FileStorage(path+"transMat.txt", FileStorage::READ);
if (fs.isOpened())
{
transMat = Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1, Scalar::all(0));
fs["transMat"] >> transMat;
}
}
3.2 變換感興趣點
void remapPoints(vector<Point2f>& points) {
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
Mat_<double> oriPoint(3, 1);
oriPoint(0, 0) = points[i].x;
oriPoint(1, 0) = points[i].y;
oriPoint(2, 0) = 1;
Mat dstPoint = transMat * oriPoint;
double a1 = dstPoint.at<double>(0, 0);
double a2 = dstPoint.at<double>(1, 0);
double a3 = dstPoint.at<double>(2, 0);
points[i] = Point2f(a1 * 1.0 / a3, a2 * 1.0 / a3);
}
undistortPoints(points, points, intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, Mat(), intrinsic_matrix);
}

