基於Spring Boot的執行緒池監控方案
- 2022 年 3 月 14 日
- 筆記
- Learn Java
前言
這篇是推動大家非同步編程的思想的執行緒池的準備篇,要做好監控,讓大家使用無後顧之憂,敬畏生產。
為什麼需要對執行緒池進行監控
Java執行緒池作為最常使用到的並發工具,相信大家都不陌生,但是你真的確定使用對了嗎?大名鼎鼎的阿里Java程式碼規範要求我們不使用 Executors來快速創建執行緒池,但是拋棄Executors,使用其它方式創建執行緒池就一定不會出現問題嗎?本質上對於我們來說執行緒池本身的運行過程是一個黑盒,我們沒辦法了解執行緒池中的運行狀態時,出現問題沒有辦法及時判斷和預警。面對這種黑盒操作必須通過監控方式讓其透明化,這樣對我們來說才能更好的使用好執行緒池。因此必須對執行緒池做監控。
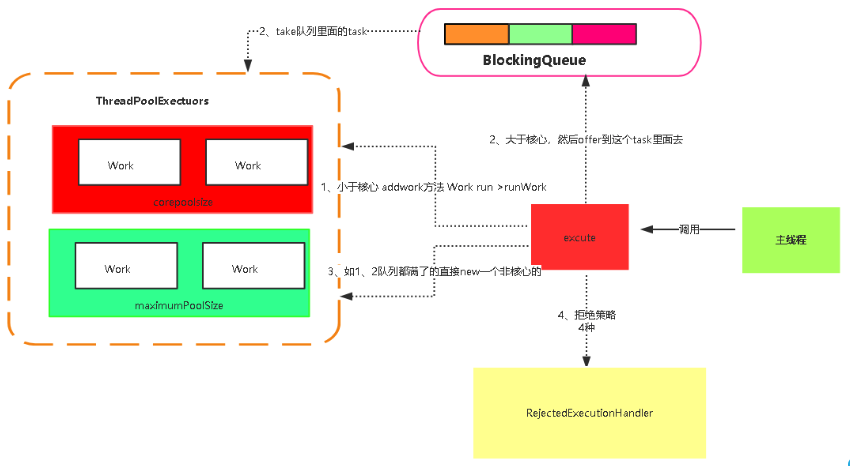
如何做執行緒池的監控
對於如何做監控,本質就是涉及三點,分別是數據採集、數據存儲以及大盤的展示,接下來我們分說下這三點;
數據採集
採集什麼數據,對於我們來說需要採集就是黑盒的數據,什麼又是執行緒池的黑盒數據,其實也就是整個執行緒處理的整個流程,在整個流程中,我們可以通過ThreadPoolExecutor中的七個方法獲取數據,通過這七個方法採集到的數據就可以使執行緒池的執行過程透明化。
-
getCorePoolSize():獲取核心執行緒數; -
getMaximumPoolSize:獲取最大執行緒數; -
getQueue():獲取執行緒池中的阻塞隊列,並通過阻塞隊列中的方法獲取隊列長度、元素個數等; -
getPoolSize():獲取執行緒池中的工作執行緒數(包括核心執行緒和非核心執行緒); -
getActiveCount():獲取活躍執行緒數,也就是正在執行任務的執行緒; -
getLargestPoolSize():獲取執行緒池曾經到過的最大工作執行緒數; -
getTaskCount():獲取歷史已完成以及正在執行的總的任務數量;
除了我們了解的這些流程以外,ThreadPoolExecutor中還提供了三種鉤子函數,
-
beforeExecute():Worker執行緒執行任務之前會調用的方法; -
afterExecute():在Worker執行緒執行任務之後會調用的方法; -
terminated():當執行緒池從運行狀態變更到TERMINATED狀態之前調用的方法;
對於beforeExecute和afterExecute可以理解為使用Aop監聽執行緒執行的時間,這樣子我們可以對每個執行緒運行的時間整體做監控,terminated可以理解為執行緒關閉時候的監控,這樣我們就可以整體獲取採集到執行緒池生命周期的所有數據了。
數據存儲以及大盤的展示
對於存儲我們這個比較適合採用時序性資料庫,此外現在很多成熟的監控產品都可以滿足我們大屏展示的訴求,這裡推薦下美團Cat和Prometheus,這裡不展開進行講解,大家可以根據自己公司的監控產品進行選擇,對於不同的方案採取的存儲形式會有些差異,甚至自己都可以自定義實現一個功能,反正難度不大。
進一步擴展以及思考
在實際的項目開發中我們會遇到以下場景:
-
不同的業務採用同一個執行緒池,這樣如果某個服務阻塞,會影響到整體共用執行緒池的所有服務,會觸發執行緒池的拒絕策略; -
流量突然增加,需要動態調整執行緒池的參數,這個時候又不能重啟;
針對這兩種場景,我們對執行緒池再次進行了深入的思考:
-
如何合理配置執行緒池參數; -
如何動態調整執行緒池參數; -
如何給不同的服務之間做執行緒池的隔離;
如何合理配置執行緒池參數
關於這個問題面試的時候也是經常被問到,我只能說這個問題開始就是一個坑,針對與CPU密集型和I/O密集型,執行緒池的參數是有不同設計的,也不是遵守幾個公式就可以搞定,當然可以參考,我認為對於執行緒池合理的參數的配置是經過多次調整得到的,甚至增加和減少業務都會影響一些參數,我不太建議大家每天背書式的CPU密集型就是N+1,非CPU密集型就是2N,因此我們更希望看到執行緒池動態配置。
如何動態調整執行緒池參數
關於如何動態調整執行緒池,還是回到我們場景問題的解決上,對於流量突增核心就是提升執行緒池的處理速度,那如何提升執行緒池的處理速度,有兩種方式,一種是加快業務的處理,也就是消費的快,顯然這種在運行的業務中我們想改變還是比較困難,這個可以作為復盤的重點;還有一種就是增加消費者,增加消費者的重點就是調整核心執行緒數以及非核心執行緒數的數量。
居於這種思考,這個時候我們需要看下ThreadPoolExecutor執行緒池源碼,首先看下開始定義的變數,通過變數的設計我們就會發現大師就是大師,大師通過AtomicInteger修飾的ctl變數,高3位存儲了執行緒池的狀態,低29存儲執行緒的個數,通過一個變數完成兩件事情,完成狀態判斷以及限制執行緒最大個數。使用一個HashSet存儲Worker的引用,而Worker繼承了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,實現一個一個不可沖入的獨佔鎖保證執行緒的安全性。
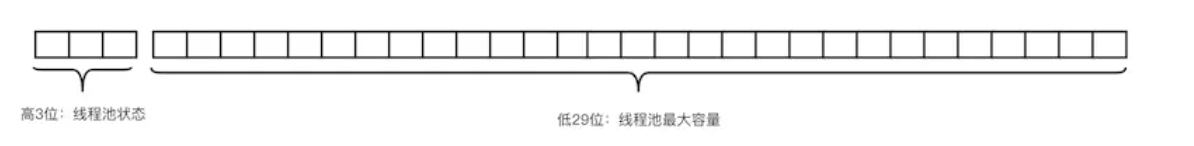
//用來標記執行緒池狀態(高3位),執行緒個數(低29位)
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
//工作狀態存儲在高3位中
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
//執行緒個數所能表達的最大數值
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
//執行緒池狀態
//RUNNING -1 能夠接收新任務,也可以處理阻塞隊列中的任務
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
//SHUTDOWN 0 不可以接受新任務,繼續處理阻塞隊列中的任務
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
//STOP 1 不接收新任務,不處理阻塞隊列中的任務,並且會中斷正在處理的任務
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
//TIDYING 2 所有任務已經中止,且工作執行緒數量為0,最後變遷到這個狀態的執行緒將要執行terminated()鉤子方法,只會有一個執行緒執行這個方法;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
//TERMINATED 3 中止狀態,已經執行完terminated()鉤子方法
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
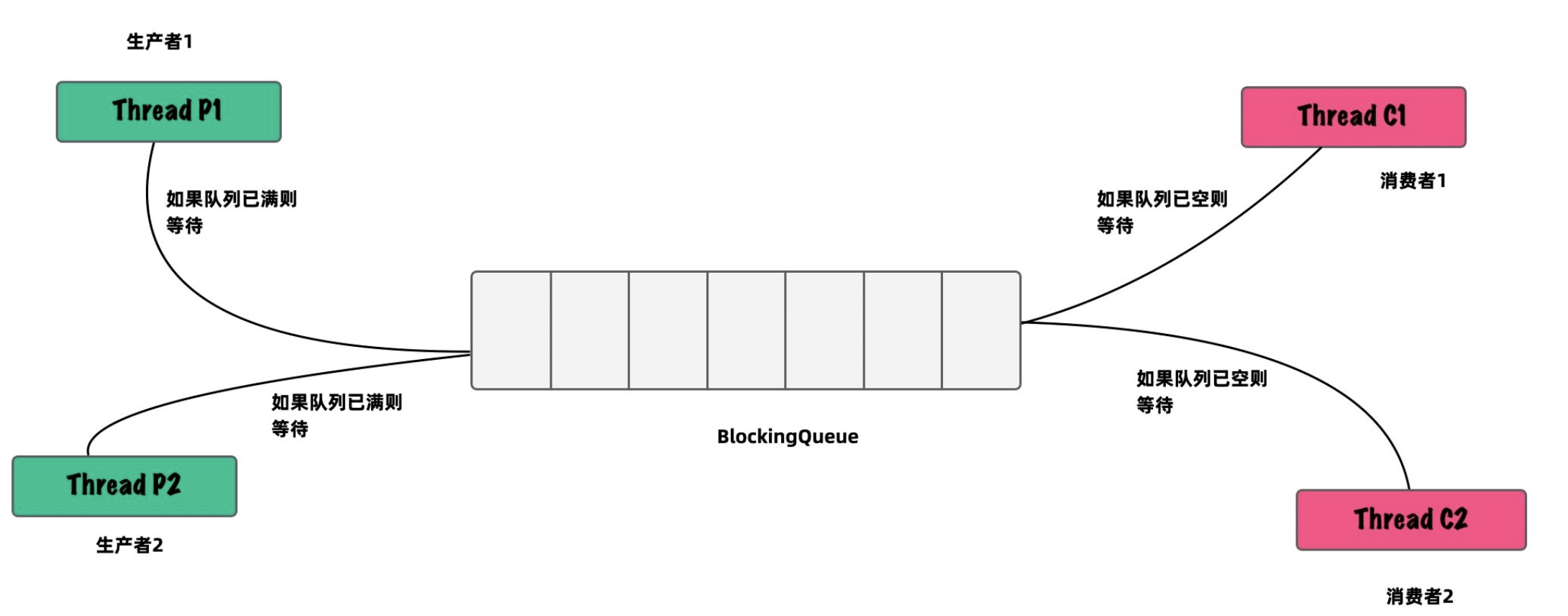
//任務隊列,當執行緒池中的執行緒達到核心執行緒數量時,再提交任務 就會直接提交到 workQueue
private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue;
//執行緒池全局鎖,增加worker減少worker時需要持有mainLock,修改執行緒池運行狀態時,也需要
private final ReentrantLock mainLock = new ReentrantLock();
//執行緒池中真正存放worker的地方。
private final HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<Worker>();
private final Condition termination = mainLock.newCondition();
//記錄執行緒池生命周期內 執行緒數最大值
private int largestPoolSize;
//記錄執行緒池所完成任務總數
private long completedTaskCount;
//創建執行緒會使用執行緒工廠
private volatile ThreadFactory threadFactory;
//拒絕策略
private volatile RejectedExecutionHandler handler;
//存活時間
private volatile long keepAliveTime;
//控制核心執行緒數量內的執行緒 是否可以被回收。true 可以,false不可以。
private volatile boolean allowCoreThreadTimeOut;
//核心執行緒池數量
private volatile int corePoolSize;
//執行緒池最大數量
private volatile int maximumPoolSize;
我們的重點看的是volatile修飾的corePoolSize、maximumPoolSize以及keepAliveTime,當然threadFactory和handler也可以看下,不過這兩個不是我們解決動態調整執行緒池的關鍵。對於這些volatile修飾的關鍵的變數,從並發角度思考的,必然是有並發讀寫的操作才使用volatile修飾的,在指標採集中我們看到其get的方法,對於寫的操作我們可以猜測肯定提供了set的方式,這個時候我們可以搜索下setCorePoolSize,果不其然我們真的搜索到了。
public void setCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize) {
if (corePoolSize < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int delta = corePoolSize - this.corePoolSize;
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
//新設置的corePoolSize小於當前核心執行緒數的時候
//會調用interruptIdleWorkers方法來中斷空閑的工作執行緒
if (workerCountOf(ctl.get()) > corePoolSize)
interruptIdleWorkers();
else if (delta > 0) {
//當設置的值大於當前值的時候核心執行緒數的時候
//按照等待隊列中的任務數量來創建新的工作執行緒
int k = Math.min(delta, workQueue.size());
while (k-- > 0 && addWorker(null, true)) {
if (workQueue.isEmpty())
break;
}
}
}
接下來我們看下interruptIdleWorkers的源碼,此處源碼使用ReentrantLock可重入鎖,因為Worker的是通過一個全局的HashSer存儲,這裡通過ReentrantLock保證執行緒安全。
private void interruptIdleWorkers(boolean onlyOne) {
//可重入鎖
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
for (Worker w : workers) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (!t.isInterrupted() && w.tryLock()) {
try {
//中斷當前執行緒
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
if (onlyOne)
break;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
接下來我們在驗證一下是否存在其他相關的參數設置,如下:
public void setMaximumPoolSize(int maximumPoolSize) {
if (maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
if (workerCountOf(ctl.get()) > maximumPoolSize)
interruptIdleWorkers();
}
public void setKeepAliveTime(long time, TimeUnit unit) {
if (time < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (time == 0 && allowsCoreThreadTimeOut())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Core threads must have nonzero keep alive times");
long keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(time);
long delta = keepAliveTime - this.keepAliveTime;
this.keepAliveTime = keepAliveTime;
if (delta < 0)
interruptIdleWorkers();
}
public void setRejectedExecutionHandler(RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.handler = handler;
}
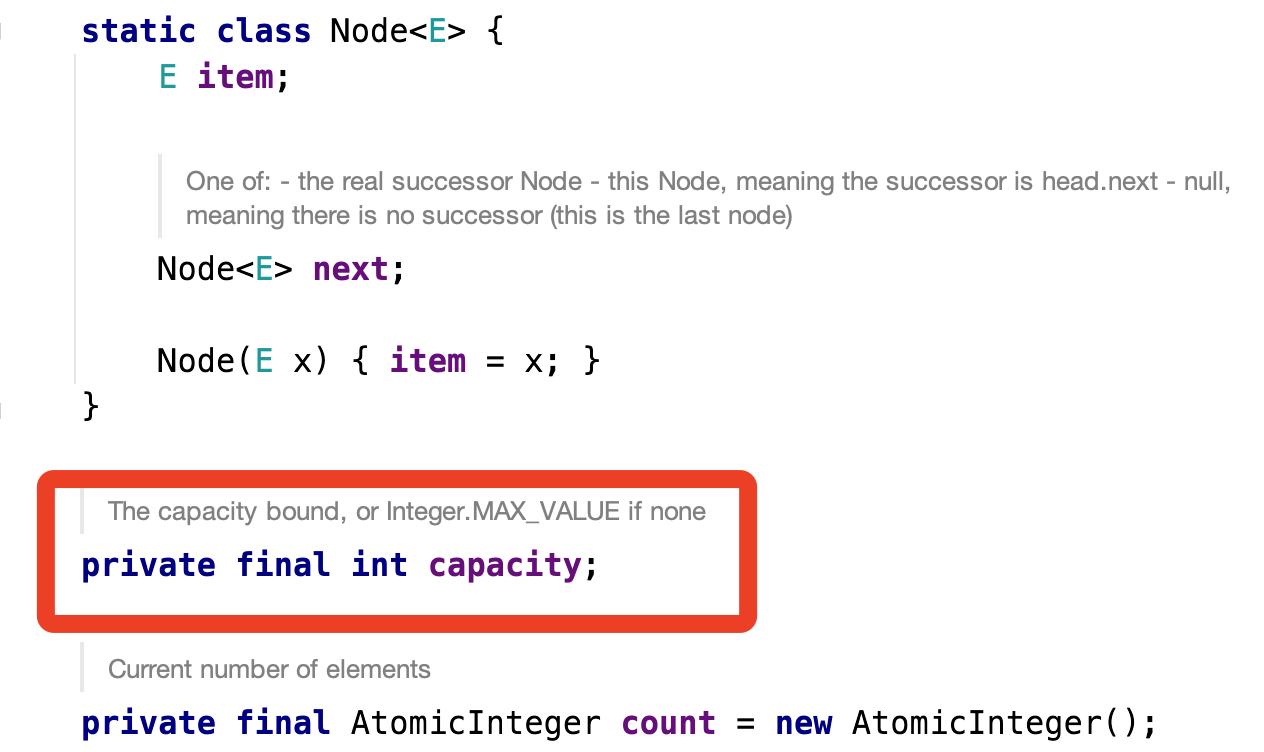
這裡我們會發現一個問題BlockingQueue的隊列容量不能修改,看到美團的文章提供的一個可修改的隊列ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue,於是乎去看了一下LinkedBlockingQueue的源碼,發現了關於capacity是一個final修飾的,這個時候我就思考一番,這個地方採用volatile修飾,對外暴露可修改,這樣就實現了動態修改阻塞隊列的大小。
如何給不同的服務之間做執行緒池的隔離
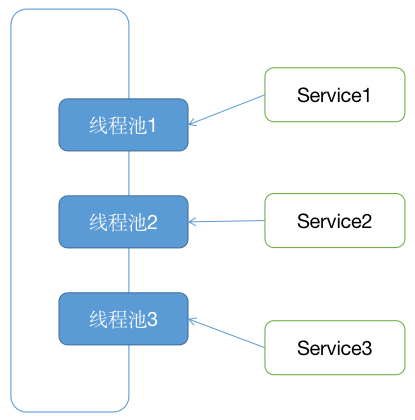
關於如何給不同服務之間做執行緒池的隔離,這裡我們可以採用Hystrix的艙壁模式,也就是說針對不同服務類型的服務單獨創建執行緒池,這樣就可以實現服務之間不相互影響,不會因為某個服務導致整體的服務影響都阻塞。
實現方案
聊了這麼多前置的知識儲備,接下來我們來聊聊實現方案,整體的實現方案我們建立在Spring Boot的基礎實現,採用Spring Cloud刷新動態配置,採用該方式比較合適單體應用,對於有Appllo和Nacos可以通過監聽配置方式的來動態刷新。
-
Maven依賴如下;
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR7</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
-
配置資訊如下:
monitor.threadpool.executors[0].thread-pool-name=first-monitor-thread-pool
monitor.threadpool.executors[0].core-pool-size=4
monitor.threadpool.executors[0].max-pool-size=8
monitor.threadpool.executors[0].queue-capacity=100
monitor.threadpool.executors[1].thread-pool-name=second-monitor-thread-pool
monitor.threadpool.executors[1].core-pool-size=2
monitor.threadpool.executors[1].max-pool-size=4
monitor.threadpool.executors[1].queue-capacity=40
/**
* 執行緒池配置
*
* @author wangtongzhou
* @since 2022-03-11 21:41
*/
@Data
public class ThreadPoolProperties {
/**
* 執行緒池名稱
*/
private String threadPoolName;
/**
* 核心執行緒數
*/
private Integer corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* 最大執行緒數
*/
private Integer maxPoolSize;
/**
* 隊列最大數量
*/
private Integer queueCapacity;
/**
* 拒絕策略
*/
private String rejectedExecutionType = "AbortPolicy";
/**
* 空閑執行緒存活時間
*/
private Long keepAliveTime = 1L;
/**
* 空閑執行緒存活時間單位
*/
private TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;
}
/**
* 動態刷新執行緒池配置
*
* @author wangtongzhou
* @since 2022-03-13 14:09
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "monitor.threadpool")
@Data
@Component
public class DynamicThreadPoolProperties {
private List<ThreadPoolProperties> executors;
}
-
自定可修改阻塞隊列大小的方式如下:
/**
* 可重新設定隊列大小的阻塞隊列
*
* @author wangtongzhou
* @since 2022-03-13 11:54
*/
public class ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingDeque<E>, java.io.Serializable {
/*
* Implemented as a simple doubly-linked list protected by a
* single lock and using conditions to manage blocking.
*
* To implement weakly consistent iterators, it appears we need to
* keep all Nodes GC-reachable from a predecessor dequeued Node.
* That would cause two problems:
* - allow a rogue Iterator to cause unbounded memory retention
* - cause cross-generational linking of old Nodes to new Nodes if
* a Node was tenured while live, which generational GCs have a
* hard time dealing with, causing repeated major collections.
* However, only non-deleted Nodes need to be reachable from
* dequeued Nodes, and reachability does not necessarily have to
* be of the kind understood by the GC. We use the trick of
* linking a Node that has just been dequeued to itself. Such a
* self-link implicitly means to jump to "first" (for next links)
* or "last" (for prev links).
*/
/*
* We have "diamond" multiple interface/abstract class inheritance
* here, and that introduces ambiguities. Often we want the
* BlockingDeque javadoc combined with the AbstractQueue
* implementation, so a lot of method specs are duplicated here.
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -387911632671998426L;
/**
* Doubly-linked list node class
*/
static final class Node<E> {
/**
* The item, or null if this node has been removed.
*/
E item;
/**
* One of:
* - the real predecessor Node
* - this Node, meaning the predecessor is tail
* - null, meaning there is no predecessor
*/
Node<E> prev;
/**
* One of:
* - the real successor Node
* - this Node, meaning the successor is head
* - null, meaning there is no successor
*/
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) {
item = x;
}
}
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
/**
* Number of items in the deque
*/
private transient int count;
/**
* Maximum number of items in the deque
*/
private volatile int capacity;
public int getCapacity() {
return capacity;
}
public void setCapacity(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/**
* Main lock guarding all access
*/
final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* Condition for waiting takes
*/
private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
/**
* Condition for waiting puts
*/
private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
/**
* Creates a {@code ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockIngQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.
*/
public ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockIngQueue} with the given (fixed) capacity.
*
* @param capacity the capacity of this deque
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is less than 1
*/
public ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/**
* Creates a {@code ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockIngQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}, initially containing the elements of
* the given collection, added in traversal order of the
* collection's iterator.
*
* @param c the collection of elements to initially contain
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
* of its elements are null
*/
public ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility
try {
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (!linkLast(new Node<E>(e))) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// Basic linking and unlinking operations, called only while holding lock
/**
* Links node as first element, or returns false if full.
*/
private boolean linkFirst(Node<E> node) {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
if (count >= capacity) {
return false;
}
Node<E> f = first;
node.next = f;
first = node;
if (last == null) {
last = node;
} else {
f.prev = node;
}
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
/**
* Links node as last element, or returns false if full.
*/
private boolean linkLast(Node<E> node) {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
if (count >= capacity) {
return false;
}
Node<E> l = last;
node.prev = l;
last = node;
if (first == null) {
first = node;
} else {
l.next = node;
}
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
/**
* Removes and returns first element, or null if empty.
*/
private E unlinkFirst() {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null) {
return null;
}
Node<E> n = f.next;
E item = f.item;
f.item = null;
f.next = f; // help GC
first = n;
if (n == null) {
last = null;
} else {
n.prev = null;
}
--count;
notFull.signal();
return item;
}
/**
* Removes and returns last element, or null if empty.
*/
private E unlinkLast() {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null) {
return null;
}
Node<E> p = l.prev;
E item = l.item;
l.item = null;
l.prev = l; // help GC
last = p;
if (p == null) {
first = null;
} else {
p.next = null;
}
--count;
notFull.signal();
return item;
}
/**
* Unlinks x.
*/
void unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
Node<E> p = x.prev;
Node<E> n = x.next;
if (p == null) {
unlinkFirst();
} else if (n == null) {
unlinkLast();
} else {
p.next = n;
n.prev = p;
x.item = null;
// Don't mess with x's links. They may still be in use by
// an iterator.
--count;
notFull.signal();
}
}
// BlockingDeque methods
/**
* @throws IllegalStateException if this deque is full
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (!offerFirst(e)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
}
/**
* @throws IllegalStateException if this deque is full
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void addLast(E e) {
if (!offerLast(e)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return linkFirst(node);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return linkLast(node);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void putFirst(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkFirst(node)) {
notFull.await();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void putLast(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkLast(node)) {
notFull.await();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean offerFirst(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (!linkFirst(node)) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return false;
}
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean offerLast(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (!linkLast(node)) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return false;
}
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return x;
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return x;
}
@Override
public E pollFirst() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkFirst();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E pollLast() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkLast();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E takeFirst() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ((x = unlinkFirst()) == null) {
notEmpty.await();
}
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E takeLast() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ((x = unlinkLast()) == null) {
notEmpty.await();
}
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E pollFirst(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
E x;
while ((x = unlinkFirst()) == null) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E pollLast(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
E x;
while ((x = unlinkLast()) == null) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public E getFirst() {
E x = peekFirst();
if (x == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return x;
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public E getLast() {
E x = peekLast();
if (x == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return x;
}
@Override
public E peekFirst() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (first == null) ? null : first.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public E peekLast() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (last == null) ? null : last.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
return false;
}
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
return false;
}
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = last; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// BlockingQueue methods
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque unless it would
* violate capacity restrictions. When using a capacity-restricted deque,
* it is generally preferable to use method {@link #offer(Object) offer}.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if this deque is full
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
@Override
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
@Override
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
putLast(e);
}
/**
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return offerLast(e, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of the queue represented by this deque.
* This method differs from {@link #poll poll} only in that it throws an
* exception if this deque is empty.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst() removeFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this deque is empty
*/
@Override
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
@Override
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
@Override
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
return takeFirst();
}
@Override
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return pollFirst(timeout, unit);
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue represented by
* this deque. This method differs from {@link #peek peek} only in that
* it throws an exception if this deque is empty.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #getFirst() getFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this deque is empty
*/
@Override
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
@Override
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
/**
* Returns the number of additional elements that this deque can ideally
* (in the absence of memory or resource constraints) accept without
* blocking. This is always equal to the initial capacity of this deque
* less the current {@code size} of this deque.
*
* <p>Note that you <em>cannot</em> always tell if an attempt to insert
* an element will succeed by inspecting {@code remainingCapacity}
* because it may be the case that another thread is about to
* insert or remove an element.
*/
@Override
public int remainingCapacity() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return capacity - count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/**
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
if (c == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (c == this) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if (maxElements <= 0) {
return 0;
}
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int n = Math.min(maxElements, count);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
c.add(first.item); // In this order, in case add() throws.
unlinkFirst();
}
return n;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// Stack methods
/**
* @throws IllegalStateException if this deque is full
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
// Collection methods
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this deque.
* If the deque does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
* More formally, removes the first element {@code e} such that
* {@code o.equals(e)} (if such an element exists).
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contained the specified element
* (or equivalently, if this deque changed as a result of the call).
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to
* {@link #removeFirstOccurrence(Object) removeFirstOccurrence}.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if this deque changed as a result of the call
*/
@Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this deque.
*
* @return the number of elements in this deque
*/
@Override
public int size() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this deque contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}.
*
* @param o object to be checked for containment in this deque
* @return {@code true} if this deque contains the specified element
*/
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
return false;
}
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/*
* TODO: Add support for more efficient bulk operations.
*
* We don't want to acquire the lock for every iteration, but we
* also want other threads a chance to interact with the
* collection, especially when count is close to capacity.
*/
// /**
// * Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this
// * queue. Attempts to addAll of a queue to itself result in
// * {@code IllegalArgumentException}. Further, the behavior of
// * this operation is undefined if the specified collection is
// * modified while the operation is in progress.
// *
// * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this queue
// * @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
// * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
// * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
// * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
// * @throws IllegalStateException if this deque is full
// * @see #add(Object)
// */
// public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// if (c == null)
// throw new NullPointerException();
// if (c == this)
// throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// lock.lock();
// try {
// boolean modified = false;
// for (E e : c)
// if (linkLast(e))
// modified = true;
// return modified;
// } finally {
// lock.unlock();
// }
// }
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this deque, in
* proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this deque. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this deque
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[] toArray() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] a = new Object[count];
int k = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
a[k++] = p.item;
}
return a;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this deque, in
* proper sequence; the runtime type of the returned array is that of
* the specified array. If the deque fits in the specified array, it
* is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the
* runtime type of the specified array and the size of this deque.
*
* <p>If this deque fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than this deque), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the deque is set to
* {@code null}.
*
* <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
* <p>Suppose {@code x} is a deque known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the deque into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
* <pre> {@code String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);}</pre>
* <p>
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the deque are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this deque
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this deque
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (a.length < count) {
a = (T[]) java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance
(a.getClass().getComponentType(), count);
}
int k = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
a[k++] = (T) p.item;
}
if (a.length > k) {
a[k] = null;
}
return a;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Node<E> p = first;
if (p == null) {
return "[]";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (; ; ) {
E e = p.item;
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
p = p.next;
if (p == null) {
return sb.append(']').toString();
}
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Atomically removes all of the elements from this deque.
* The deque will be empty after this call returns.
*/
@Override
public void clear() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> f = first; f != null; ) {
f.item = null;
Node<E> n = f.next;
f.prev = null;
f.next = null;
f = n;
}
first = last = null;
count = 0;
notFull.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this deque in proper sequence.
* The elements will be returned in order from first (head) to last (tail).
*
* <p>The returned iterator is
* <a href="package-summary.html#Weakly"><i>weakly consistent</i></a>.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this deque in proper sequence
*/
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this deque in reverse
* sequential order. The elements will be returned in order from
* last (tail) to first (head).
*
* <p>The returned iterator is
* <a href="package-summary.html#Weakly"><i>weakly consistent</i></a>.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this deque in reverse order
*/
@Override
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingItr();
}
/**
* Base class for Iterators for ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockIngQueue
*/
private abstract class AbstractItr implements Iterator<E> {
/**
* The next node to return in next()
*/
Node<E> next;
/**
* nextItem holds on to item fields because once we claim that
* an element exists in hasNext(), we must return item read
* under lock (in advance()) even if it was in the process of
* being removed when hasNext() was called.
*/
E nextItem;
/**
* Node returned by most recent call to next. Needed by remove.
* Reset to null if this element is deleted by a call to remove.
*/
private Node<E> lastRet;
abstract Node<E> firstNode();
abstract Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> n);
AbstractItr() {
// set to initial position
final ReentrantLock lock = ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
next = firstNode();
nextItem = (next == null) ? null : next.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns the successor node of the given non-null, but
* possibly previously deleted, node.
*/
private Node<E> succ(Node<E> n) {
// Chains of deleted nodes ending in null or self-links
// are possible if multiple interior nodes are removed.
for (; ; ) {
Node<E> s = nextNode(n);
if (s == null) {
return null;
} else if (s.item != null) {
return s;
} else if (s == n) {
return firstNode();
} else {
n = s;
}
}
}
/**
* Advances next.
*/
void advance() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// assert next != null;
next = succ(next);
nextItem = (next == null) ? null : next.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
@Override
public E next() {
if (next == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
lastRet = next;
E x = nextItem;
advance();
return x;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
Node<E> n = lastRet;
if (n == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
lastRet = null;
final ReentrantLock lock = ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (n.item != null) {
unlink(n);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* Forward iterator
*/
private class Itr extends AbstractItr {
@Override
Node<E> firstNode() {
return first;
}
@Override
Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> n) {
return n.next;
}
}
/**
* Descending iterator
*/
private class DescendingItr extends AbstractItr {
@Override
Node<E> firstNode() {
return last;
}
@Override
Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> n) {
return n.prev;
}
}
/**
* A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator
*/
static final class LBDSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> queue;
Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized
int batch; // batch size for splits
boolean exhausted; // true when no more nodes
long est; // size estimate
LBDSpliterator(ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
this.est = queue.size();
}
@Override
public long estimateSize() {
return est;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
Node<E> h;
final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;
int b = batch;
int n = (b <= 0) ? 1 : (b >= MAX_BATCH) ? MAX_BATCH : b + 1;
if (!exhausted &&
((h = current) != null || (h = q.first) != null) &&
h.next != null) {
Object[] a = new Object[n];
final ReentrantLock lock = q.lock;
int i = 0;
Node<E> p = current;
lock.lock();
try {
if (p != null || (p = q.first) != null) {
do {
if ((a[i] = p.item) != null) {
++i;
}
} while ((p = p.next) != null && i < n);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if ((current = p) == null) {
est = 0L;
exhausted = true;
} else if ((est -= i) < 0L) {
est = 0L;
}
if (i > 0) {
batch = i;
return Spliterators.spliterator
(a, 0, i, Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL |
Spliterator.CONCURRENT);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;
final ReentrantLock lock = q.lock;
if (!exhausted) {
exhausted = true;
Node<E> p = current;
do {
E e = null;
lock.lock();
try {
if (p == null) {
p = q.first;
}
while (p != null) {
e = p.item;
p = p.next;
if (e != null) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (e != null) {
action.accept(e);
}
} while (p != null);
}
}
@Override
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;
final ReentrantLock lock = q.lock;
if (!exhausted) {
E e = null;
lock.lock();
try {
if (current == null) {
current = q.first;
}
while (current != null) {
e = current.item;
current = current.next;
if (e != null) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (current == null) {
exhausted = true;
}
if (e != null) {
action.accept(e);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL |
Spliterator.CONCURRENT;
}
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this deque.
*
* <p>The returned spliterator is
* <a href="package-summary.html#Weakly"><i>weakly consistent</i></a>.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#CONCURRENT},
* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}, and {@link Spliterator#NONNULL}.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this deque
* @implNote The {@code Spliterator} implements {@code trySplit} to permit limited
* parallelism.
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new LBDSpliterator<E>(this);
}
/**
* Saves this deque to a stream (that is, serializes it).
*
* @param s the stream
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
* @serialData The capacity (int), followed by elements (each an
* {@code Object}) in the proper order, followed by a null
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// Write out capacity and any hidden stuff
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
s.writeObject(p.item);
}
// Use trailing null as sentinel
s.writeObject(null);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Reconstitutes this deque from a stream (that is, deserializes it).
*
* @param s the stream
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the class of a serialized object
* could not be found
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
count = 0;
first = null;
last = null;
// Read in all elements and place in queue
for (; ; ) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E item = (E) s.readObject();
if (item == null) {
break;
}
add(item);
}
}
}
-
自定義執行緒池,增加每個執行緒處理的耗時,以及平均耗時、最大耗時、最小耗時,以及輸出監控日誌資訊等等;
/**
* 執行緒池監控類
*
* @author wangtongzhou
* @since 2022-02-23 07:27
*/
public class ThreadPoolMonitor extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ThreadPoolMonitor.class);
/**
* 默認拒絕策略
*/
private static final RejectedExecutionHandler defaultHandler = new AbortPolicy();
/**
* 執行緒池名稱,一般以業務名稱命名,方便區分
*/
private String poolName;
/**
* 最短執行時間
*/
private Long minCostTime;
/**
* 最長執行時間
*/
private Long maxCostTime;
/**
* 總的耗時
*/
private AtomicLong totalCostTime = new AtomicLong();
private ThreadLocal<Long> startTimeThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 調用父類的構造方法,並初始化HashMap和執行緒池名稱
*
* @param corePoolSize 執行緒池核心執行緒數
* @param maximumPoolSize 執行緒池最大執行緒數
* @param keepAliveTime 執行緒的最大空閑時間
* @param unit 空閑時間的單位
* @param workQueue 保存被提交任務的隊列
* @param poolName 執行緒池名稱
*/
public ThreadPoolMonitor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, String poolName) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), poolName);
}
/**
* 調用父類的構造方法,並初始化HashMap和執行緒池名稱
*
* @param corePoolSize 執行緒池核心執行緒數
* @param maximumPoolSize 執行緒池最大執行緒數
* @param keepAliveTime 執行緒的最大空閑時間
* @param unit 空閑時間的單位
* @param workQueue 保存被提交任務的隊列
* @param
* @param poolName 執行緒池名稱
*/
public ThreadPoolMonitor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler, String poolName) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler, poolName);
}
/**
* 調用父類的構造方法,並初始化HashMap和執行緒池名稱
*
* @param corePoolSize 執行緒池核心執行緒數
* @param maximumPoolSize 執行緒池最大執行緒數
* @param keepAliveTime 執行緒的最大空閑時間
* @param unit 空閑時間的單位
* @param workQueue 保存被提交任務的隊列
* @param threadFactory 執行緒工廠
* @param poolName 執行緒池名稱
*/
public ThreadPoolMonitor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory, String poolName) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, defaultHandler);
this.poolName = poolName;
}
/**
* 調用父類的構造方法,並初始化HashMap和執行緒池名稱
*
* @param corePoolSize 執行緒池核心執行緒數
* @param maximumPoolSize 執行緒池最大執行緒數
* @param keepAliveTime 執行緒的最大空閑時間
* @param unit 空閑時間的單位
* @param workQueue 保存被提交任務的隊列
* @param threadFactory 執行緒工廠
* @param handler 拒絕策略
* @param poolName 執行緒池名稱
*/
public ThreadPoolMonitor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler, String poolName) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
this.poolName = poolName;
}
/**
* 執行緒池延遲關閉時(等待執行緒池裡的任務都執行完畢),統計執行緒池情況
*/
@Override
public void shutdown() {
// 統計已執行任務、正在執行任務、未執行任務數量
LOGGER.info("{} 關閉執行緒池, 已執行任務: {}, 正在執行任務: {}, 未執行任務數量: {}",
this.poolName, this.getCompletedTaskCount(), this.getActiveCount(), this.getQueue().size());
super.shutdown();
}
/**
* 執行緒池立即關閉時,統計執行緒池情況
*/
@Override
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
// 統計已執行任務、正在執行任務、未執行任務數量
LOGGER.info("{} 立即關閉執行緒池,已執行任務: {}, 正在執行任務: {}, 未執行任務數量: {}",
this.poolName, this.getCompletedTaskCount(), this.getActiveCount(), this.getQueue().size());
return super.shutdownNow();
}
/**
* 任務執行之前,記錄任務開始時間
*/
@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
startTimeThreadLocal.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
/**
* 任務執行之後,計算任務結束時間
*/
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeThreadLocal.get();
startTimeThreadLocal.remove();
maxCostTime = maxCostTime > costTime ? maxCostTime : costTime;
if (getCompletedTaskCount() == 0) {
minCostTime = costTime;
}
minCostTime = minCostTime < costTime ? minCostTime : costTime;
totalCostTime.addAndGet(costTime);
LOGGER.info("{}-pool-monitor: " +
"任務耗時: {} ms, 初始執行緒數: {}, 核心執行緒數: {}, 執行的任務數量: {}, " +
"已完成任務數量: {}, 任務總數: {}, 隊列里快取的任務數量: {}, 池中存在的最大執行緒數: {}, " +
"最大允許的執行緒數: {}, 執行緒空閑時間: {}, 執行緒池是否關閉: {}, 執行緒池是否終止: {}",
this.poolName,
costTime, this.getPoolSize(), this.getCorePoolSize(), this.getActiveCount(),
this.getCompletedTaskCount(), this.getTaskCount(), this.getQueue().size(), this.getLargestPoolSize(),
this.getMaximumPoolSize(), this.getKeepAliveTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS), this.isShutdown(), this.isTerminated());
}
public Long getMinCostTime() {
return minCostTime;
}
public Long getMaxCostTime() {
return maxCostTime;
}
public long getAverageCostTime(){
if(getCompletedTaskCount()==0||totalCostTime.get()==0){
return 0;
}
return totalCostTime.get()/getCompletedTaskCount();
}
/**
* 生成執行緒池所用的執行緒,改寫了執行緒池默認的執行緒工廠,傳入執行緒池名稱,便於問題追蹤
*/
static class MonitorThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
/**
* 初始化執行緒工廠
*
* @param poolName 執行緒池名稱
*/
MonitorThreadFactory(String poolName) {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = Objects.nonNull(s) ? s.getThreadGroup() : Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = poolName + "-pool-" + poolNumber.getAndIncrement() + "-thread-";
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r, namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(), 0);
if (t.isDaemon()) {
t.setDaemon(false);
}
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY) {
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
}
return t;
}
}
}
-
動態修改執行緒池的類,通過Spring的監聽器監控配置刷新方法,實現動態更新執行緒池的參數;
/**
* 動態刷新執行緒池
*
* @author wangtongzhou
* @since 2022-03-13 14:13
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DynamicThreadPoolManager {
@Autowired
private DynamicThreadPoolProperties dynamicThreadPoolProperties;
/**
* 存儲執行緒池對象
*/
public Map<String, ThreadPoolMonitor> threadPoolExecutorMap = new HashMap<>();
public Map<String, ThreadPoolMonitor> getThreadPoolExecutorMap() {
return threadPoolExecutorMap;
}
/**
* 初始化執行緒池
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
createThreadPools(dynamicThreadPoolProperties);
}
/**
* 初始化執行緒池的創建
*
* @param dynamicThreadPoolProperties
*/
private void createThreadPools(DynamicThreadPoolProperties dynamicThreadPoolProperties) {
dynamicThreadPoolProperties.getExecutors().forEach(config -> {
if (!threadPoolExecutorMap.containsKey(config.getThreadPoolName())) {
ThreadPoolMonitor threadPoolMonitor = new ThreadPoolMonitor(
config.getCorePoolSize(),
config.getMaxPoolSize(),
config.getKeepAliveTime(),
config.getUnit(),
new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<>(config.getQueueCapacity()),
RejectedExecutionHandlerEnum.getRejectedExecutionHandler(config.getRejectedExecutionType()),
config.getThreadPoolName()
);
threadPoolExecutorMap.put(config.getThreadPoolName(),
threadPoolMonitor);
}
});
}
/**
* 調整執行緒池
*
* @param dynamicThreadPoolProperties
*/
private void changeThreadPools(DynamicThreadPoolProperties dynamicThreadPoolProperties) {
dynamicThreadPoolProperties.getExecutors().forEach(config -> {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = threadPoolExecutorMap.get(config.getThreadPoolName());
if (Objects.nonNull(threadPoolExecutor)) {
threadPoolExecutor.setCorePoolSize(config.getCorePoolSize());
threadPoolExecutor.setMaximumPoolSize(config.getMaxPoolSize());
threadPoolExecutor.setKeepAliveTime(config.getKeepAliveTime(), config.getUnit());
threadPoolExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(RejectedExecutionHandlerEnum.getRejectedExecutionHandler(config.getRejectedExecutionType()));
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = threadPoolExecutor.getQueue();
if (queue instanceof ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue) {
((ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>) queue).setCapacity(config.getQueueCapacity());
}
}
});
}
@EventListener
public void envListener(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) {
log.info("配置發生變更" + event);
changeThreadPools(dynamicThreadPoolProperties);
}
}
-
DynamicThreadPoolPropertiesController對外暴露兩個方法,第一個通過ContextRefresher提供對外刷新配置的介面,實現及時更新配置資訊,第二提供一個查詢介面的方法,
/**
* 動態修改執行緒池參數
*
* @author wangtongzhou
* @since 2022-03-13 17:27
*/
@RestController
public class DynamicThreadPoolPropertiesController {
@Autowired
private ContextRefresher contextRefresher;
@Autowired
private DynamicThreadPoolProperties dynamicThreadPoolProperties;
@Autowired
private DynamicThreadPoolManager dynamicThreadPoolManager;
@PostMapping("/threadPool/properties")
public void update() {
ThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties =
dynamicThreadPoolProperties.getExecutors().get(0);
threadPoolProperties.setCorePoolSize(20);
threadPoolProperties.setMaxPoolSize(50);
threadPoolProperties.setQueueCapacity(200);
threadPoolProperties.setRejectedExecutionType("CallerRunsPolicy");
contextRefresher.refresh();
}
@GetMapping("/threadPool/properties")
public Map<String, Object> queryThreadPoolProperties() {
Map<String, Object> metricMap = new HashMap<>();
List<Map> threadPools = new ArrayList<>();
dynamicThreadPoolManager.getThreadPoolExecutorMap().forEach((k, v) -> {
ThreadPoolMonitor threadPoolMonitor = (ThreadPoolMonitor) v;
Map<String, Object> poolInfo = new HashMap<>();
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.name", k);
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.core.size", threadPoolMonitor.getCorePoolSize());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.largest.size", threadPoolMonitor.getLargestPoolSize());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.max.size", threadPoolMonitor.getMaximumPoolSize());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.thread.count", threadPoolMonitor.getPoolSize());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.max.costTime", threadPoolMonitor.getMaxCostTime());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.average.costTime", threadPoolMonitor.getAverageCostTime());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.min.costTime", threadPoolMonitor.getMinCostTime());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.active.count", threadPoolMonitor.getActiveCount());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.completed.taskCount", threadPoolMonitor.getCompletedTaskCount());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.queue.name", threadPoolMonitor.getQueue().getClass().getName());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.rejected.name", threadPoolMonitor.getRejectedExecutionHandler().getClass().getName());
poolInfo.put("thread.pool.task.count", threadPoolMonitor.getTaskCount());
threadPools.add(poolInfo);
});
metricMap.put("threadPools", threadPools);
return metricMap;
}
}
整體上的流程到這裡就完成了,算是一個Demo版,對於該組件更深入的思考我認為還可以做以下三件事情:
-
應該以starter的形式嵌入到應用,通過判斷啟動類載入的Appllo、Nacos還是默認實現; -
對外可以Push、也可以是日誌,還可以支援各種庫,提供豐富的輸出形式,這個樣子的話更加通用化; -
提供統一查詢介面、修改介面、增加許可權校驗、增加預警規則配置;
參考以下內容:
結束
歡迎大家點點關注,點點贊!



