生產者-消費者問題
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
目錄
1. 概述
定義
生產者消費者問題是執行緒同步的經典問題,也稱為有界緩衝區問題,問題描述大致如下:
- 生產者和消費者之間共享一個有界數據緩衝區
- 一個或多個生產者(執行緒或進程)向緩衝區放置數據
- 一個或多個消費者(執行緒或進程)從緩衝區取出數據
緩衝區
生產者消費者問題中的緩衝區,包括隊列緩衝區和環形緩衝區,它們都按照先進先出的順序處理數據,我們現在只考慮隊列緩衝區:
- 隊列緩衝區通常使用普通的隊列數據結構
- 隊列內部實現可以是鏈表或數組
緩衝區有兩個極端狀態:緩衝區空,緩衝區滿。鏈表隊列和數組隊列緩衝區空的含義相同,都是隊列中沒有一個元素的情形,但兩者緩衝區滿的含義不同:
- 數組隊列在初始化時就必須指定最大容量,緩衝區滿的條件很清晰
- 鏈表隊列沒有最大容量的概念,需要人為指定
此外,Posix消息隊列也可以作為隊列緩衝區,Posix當以無優先順序消息的方式使用時,也是按照先進先出的順序進行處理的。
本文只討論第一種數據結構隊列緩衝區,基於Posix消息隊列緩衝區的生產者消費者問題,會在後續Posix消息隊列中單獨講解。
2. 典型模型
生產者消費者個數的多少、緩衝區的類型都會影響生產者消費者問題模型的複雜度,本文選取兩種常見典型模型進行分析。
模型一
- 單個生產者 + 單個消費者
- 生產者執行緒啟動後,立即創建消費者執行緒
- 緩衝區容量有限,且小於數據條目數量
該模型只需要處理生產者和消費者之間的同步問題,在實際工程很常見,具體的同步詳情為:
- 當緩衝區為空時,消費者不能從其中取出數據
- 當緩衝區為滿時,生產者不能向其中寫入數據
模型二
- 多個生產者 + 單個消費者
- 生產者執行緒啟動後,立即創建消費者執行緒
- 緩衝區容量有限,且小於數據條目數量
模型二與模型一相比,既需要處理生產者之間的同步問題,又需要處理生產者和消費者之間的同步問題,在實際工程也比較常見,具體的同步詳情為:
- 同時只能有一個生產者向緩衝區寫入數據
- 當緩衝區為空時,消費者不能從其中取出數據
- 當緩衝區為滿時,生產者不能向其中寫入數據
可選需求
模型一和模型二所列均為必須處理的同步問題,還有一個根據實際情況、可能會存在的同步需求:
- 共享數據中包含描述緩衝區當前狀態的變數,如下標、計數、鏈表等
- 生產者和消費者在讀寫緩衝區後都需要更新緩衝區狀態變數
- 若滿足上述兩個條件,則同時只能有一個生產者或消費者可以進行緩衝區操作與狀態變數更新
隊列緩衝區,不管是數組實現還是鏈表實現,其內部都符合上述條件,都需要處理該可選同步需求。
3. 數據結構隊列C語言實現
網上找了份數據結構隊列C語言實現的程式碼,稍微改了下,可正常使用,本節後續的生產者消費者問題示例程式碼就是用它作為緩衝區。
#ifndef _LINK_QUEUE_H_ #define _LINK_QUEUE_H_ typedef enum { false = 0, true } bool; typedef int data_t; typedef struct LinkNode { data_t data; struct LinkNode *next; } LinkNode, *LinkQueue; typedef struct { LinkQueue front; LinkQueue rear; } HeadQueue; HeadQueue *CreateEmptyQueue(); bool EmptyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue); void EnQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t value); void DeQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t *value); void PrintQueue(HeadQueue *queue); bool ClearLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue); bool DestroyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue); int GetCurItemsNum(HeadQueue *queue); #endif#include "linkqueue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> static int nitems; //創建空鏈表隊列 HeadQueue *CreateEmptyQueue(void) { HeadQueue *queue = (HeadQueue *)malloc(sizeof(HeadQueue)); if (queue == NULL) { perror("Create empty queue failed"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } queue->rear = queue->front = NULL; nitems = 0; return queue; } //判斷是否為空鏈表隊列 bool EmptyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue) { if (queue == NULL) { printf("Empty link queue error!n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } return queue->front == NULL ? true : false; } //增加隊列元素 void EnQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t value) { LinkQueue new; if (queue == NULL) { printf("EnQueue Error!n"); return; } new = (LinkQueue)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode)); if (new == NULL) { perror("Insert value failed"); return; } new->data = value; new->next = NULL; if (EmptyLinkQueue(queue)) { queue->front = queue->rear = new; } else { queue->rear->next = new; queue->rear = new; } nitems++; } //刪除隊列元素 void DeQueue(HeadQueue *queue, data_t *value) { *value = 0; LinkQueue remove; if (queue == NULL) { printf("DeQueue error!n"); return; } if (EmptyLinkQueue(queue)) { printf("queue is empty!n"); return; } remove = queue->front; queue->front = remove->next; if (queue->front == NULL) queue->rear = NULL; *value = remove->data; free(remove); nitems--; } //遍歷隊列元素 void PrintQueue(HeadQueue *queue) { LinkQueue node; printf("queue = {"); node = queue->front; if (node == NULL) { printf("}n"); return ; } while (node != NULL) { printf("%d,", node->data); node = node->next; } printf("b}n"); } //清空隊列元素 bool ClearLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue) { LinkQueue remove = queue->front; while (remove != NULL) { queue->front = queue->front->next; free(remove); remove = queue->front; } queue->front = NULL; queue->rear = NULL; nitems = 0; return true; } //銷毀隊列 bool DestroyLinkQueue(HeadQueue *queue) { if (queue != NULL) { ClearLinkQueue(queue); free(queue); nitems = 0; return true; } else { printf("DestroyLinkQueue error!n"); return false; } } //獲得當前隊列元素個數 int GetCurItemsNum(HeadQueue *queue) { return nitems; }4. 程式碼實現——互斥鎖 + 條件變數
#include "linkqueue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <pthread.h> #define MAX_THREADS 10 #define MAX_ITEMS 1000000 #define MAX_BUFFER 10 /* * 編程技巧:盡量把共享數據和它們的同步變數(互斥鎖、條件變數、訊號量)收集到同一個結構體中 */ struct Shared { pthread_cond_t cond_nempty; //條件變數:緩衝區不滿 pthread_cond_t cond_nstored; //條件變數:緩衝區不空 pthread_mutex_t cond_mutex; //保護條件的鎖,用於確保同時只有一個執行緒可以訪問緩衝區 pthread_mutex_t mutex; //同步多個生產者的鎖,僅在有多個生產者時使用 HeadQueue *queue; //隊列緩衝區 int nput; int nval; }; struct Shared shared; void shared_init() { shared.queue = CreateEmptyQueue(); pthread_mutex_init(&shared.mutex, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&shared.cond_mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&shared.cond_nempty, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&shared.cond_nstored, NULL); } void shared_destroy() { DestroyLinkQueue(shared.queue); pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.mutex); pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.cond_mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&shared.cond_nempty); pthread_cond_destroy(&shared.cond_nstored); } void *produce(void *arg) { int nthreads = *((int *)arg); while (1) { if (shared.nput >= MAX_ITEMS) { pthread_exit(NULL); } if (nthreads > 1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex); } pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.cond_mutex); while (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) == MAX_BUFFER) pthread_cond_wait(&shared.cond_nempty, &shared.cond_mutex); EnQueue(shared.queue, shared.nval); shared.nput++; shared.nval++; pthread_cond_signal(&shared.cond_nstored); if (nthreads > 1) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.cond_mutex); } pthread_exit(NULL); } void *consume(void *arg) { int nval; int i; for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.cond_mutex); while (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) == 0) pthread_cond_wait(&shared.cond_nstored, &shared.cond_mutex); DeQueue(shared.queue, &nval); pthread_cond_signal(&shared.cond_nempty); pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.cond_mutex); if (nval != i) { printf("error: buff[%d] = %dn", i, nval); } } pthread_exit(NULL); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { pthread_t tid_produce[MAX_THREADS]; pthread_t tid_consume; int nthreads; struct timeval start_time; struct timeval end_time; float time_sec; int i; nthreads = (atoi(argv[1]) > MAX_THREADS) ? MAX_THREADS : atoi(argv[1]); shared_init(); gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &nthreads); } pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL); } pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL); gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL); time_sec = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec) + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec) / 1000000.0; printf("%d produce and %d consume total spend %.2f secondn", nthreads, 1, time_sec); shared_destroy(); return 0; }運行時通過命令行參數指定生產者個數,來選擇模型一或模型二,其中,在produce()中,第57-56行、第74-77行會根據生產者個數,選擇是否使用第二把鎖。
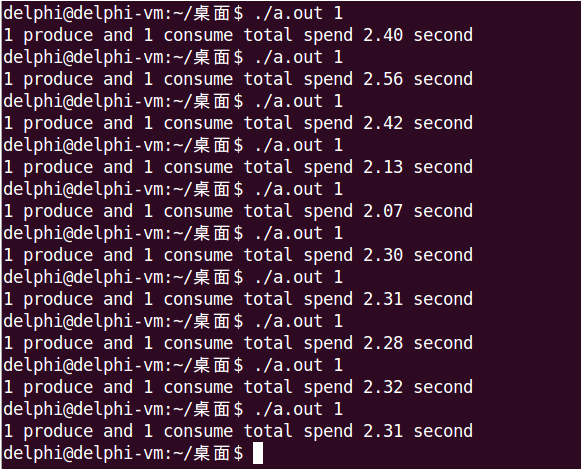
下面分別是模型一和模型二的運行結果。
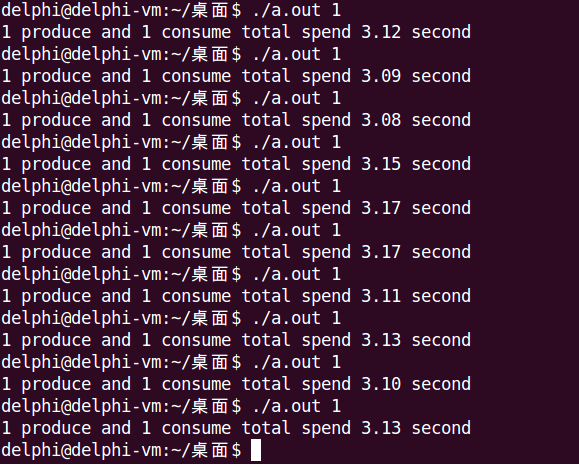
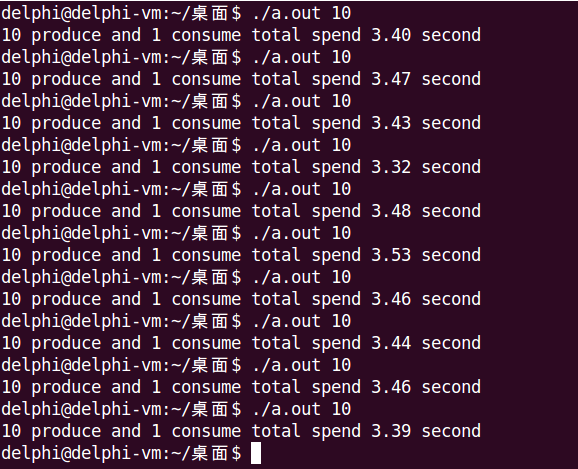
5. 程式碼實現——互斥鎖 + Posix有名訊號量
#include "linkqueue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <semaphore.h> #define SEM_NEMPTY "/sem_nempty" #define SEM_NSTROED "/sem_nstored" #define MAX_THREADS 10 #define MAX_ITEMS 1000000 #define MAX_BUFFER 10 /* * 編程技巧:把共享數據和它們的同步變數(互斥鎖、條件變數、訊號量)收集到同一個結構體中 */ struct Shared { pthread_mutex_t mutex; sem_t *nempty; sem_t *nstored; HeadQueue *queue; int nput; int nval; }; struct Shared shared; void shared_init() { shared.queue = CreateEmptyQueue(); pthread_mutex_init(&shared.mutex, NULL); shared.nempty = sem_open(SEM_NEMPTY, O_CREAT, 0666, MAX_BUFFER); shared.nstored = sem_open(SEM_NSTROED, O_CREAT, 0666, 0); } void shared_destroy() { DestroyLinkQueue(shared.queue); pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.mutex); sem_close(shared.nempty); sem_close(shared.nstored); sem_unlink(SEM_NEMPTY); sem_unlink(SEM_NSTROED); } void *produce(void *arg) { while (1) { if (shared.nput >= MAX_ITEMS) { pthread_exit(NULL); } /* * produce和consume都必須先sem_wait,確保sem_wait返回後再上鎖; * 防止先上鎖後sem_wait阻塞,導致另一方二次上鎖而死鎖. */ sem_wait(shared.nempty); pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex); EnQueue(shared.queue, shared.nval); /* 如果隊列緩衝區中的元素個數超過了MAX_BUFFER,就輸出提示資訊 */ if (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) > MAX_BUFFER) { printf("notice: queue buffer capacity > %dn", MAX_BUFFER); } shared.nput++; shared.nval++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex); sem_post(shared.nstored); } pthread_exit(NULL); } void *consume(void *arg) { int nval; int i; for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++) { /* * produce和consume都必須先sem_wait,確保sem_wait返回後再上鎖; * 防止先上鎖後sem_wait阻塞,導致另一方二次上鎖而死鎖. */ sem_wait(shared.nstored); pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex); DeQueue(shared.queue, &nval); if (nval != i) { printf("error: buff[%d] = %dn", i, nval); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex); sem_post(shared.nempty); } pthread_exit(NULL); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { pthread_t tid_produce[MAX_THREADS]; pthread_t tid_consume; int nthreads; struct timeval start_time; struct timeval end_time; float time_sec; int i; nthreads = (atoi(argv[1]) > MAX_THREADS) ? MAX_THREADS : atoi(argv[1]); shared_init(); gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &nthreads); } pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL); } pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL); gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL); time_sec = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec) + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec) / 1000000.0; printf("%d produce and %d consume total spend %.2f secondn", nthreads, 1, time_sec); shared_destroy(); return 0; }運行時通過命令行參數指定生產者個數,來選擇模型一或模型二。
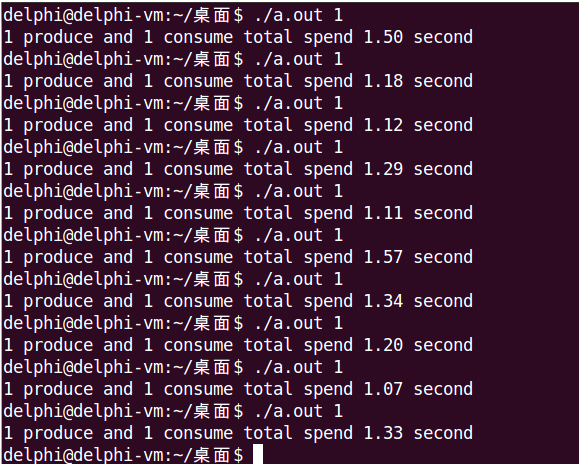
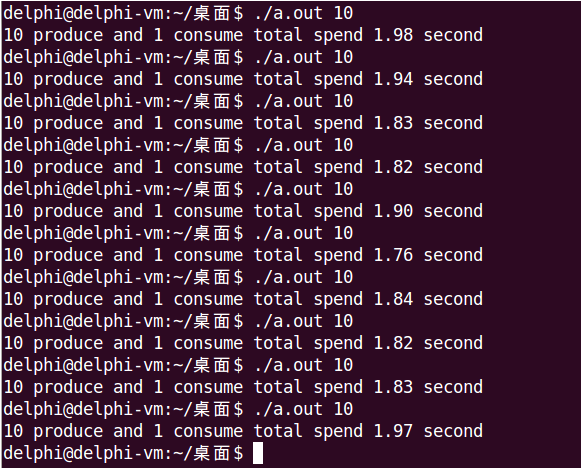
6. 程式碼實現——互斥鎖 + Posix無名訊號量
#include "linkqueue.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <semaphore.h> #define MAX_THREADS 10 #define MAX_ITEMS 1000000 #define MAX_BUFFER 10 /* * 編程技巧:把共享數據和它們的同步變數(互斥鎖、條件變數、訊號量)收集到同一個結構體中 */ struct Shared { pthread_mutex_t mutex; sem_t nempty; sem_t nstored; HeadQueue *queue; int nput; int nval; }; struct Shared shared; void shared_init() { shared.queue = CreateEmptyQueue(); pthread_mutex_init(&shared.mutex, NULL); sem_init(&shared.nempty, 0, MAX_BUFFER); sem_init(&shared.nstored, 0, 0); } void shared_destroy() { DestroyLinkQueue(shared.queue); pthread_mutex_destroy(&shared.mutex); sem_destroy(&shared.nempty); sem_destroy(&shared.nstored); } void *produce(void *arg) { while (1) { if (shared.nput >= MAX_ITEMS) { pthread_exit(NULL); } /* * produce和consume都必須先sem_wait,確保sem_wait返回後再上鎖; * 防止先上鎖後sem_wait阻塞,導致另一方二次上鎖而死鎖. */ sem_wait(&shared.nempty); pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex); EnQueue(shared.queue, shared.nval); /* 如果隊列緩衝區中的元素個數超過了MAX_BUFFER,就輸出提示資訊 */ if (GetCurItemsNum(shared.queue) > MAX_BUFFER) { printf("notice: queue buffer capacity > %dn", MAX_BUFFER); } shared.nput++; shared.nval++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex); sem_post(&shared.nstored); } pthread_exit(NULL); } void *consume(void *arg) { int nval; int i; for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++) { /* * produce和consume都必須先sem_wait,確保sem_wait返回後再上鎖; * 防止先上鎖後sem_wait阻塞,導致另一方二次上鎖而死鎖. */ sem_wait(&shared.nstored); pthread_mutex_lock(&shared.mutex); DeQueue(shared.queue, &nval); if (nval != i) { printf("error: buff[%d] = %dn", i, nval); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&shared.mutex); sem_post(&shared.nempty); } pthread_exit(NULL); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { pthread_t tid_produce[MAX_THREADS]; pthread_t tid_consume; int nthreads; struct timeval start_time; struct timeval end_time; float time_sec; int i; nthreads = (atoi(argv[1]) > MAX_THREADS) ? MAX_THREADS : atoi(argv[1]); shared_init(); gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { pthread_create(&tid_produce[i], NULL, produce, &nthreads); } pthread_create(&tid_consume, NULL, consume, NULL); for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { pthread_join(tid_produce[i], NULL); } pthread_join(tid_consume, NULL); gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL); time_sec = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec) + (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec) / 1000000.0; printf("%d produce and %d consume total spend %.2f secondn", nthreads, 1, time_sec); shared_destroy(); return 0; }運行時通過命令行參數指定生產者個數,來選擇模型一或模型二。

7. 效率對比
結論
- 只有Posix無名訊號量使用多生產者獲得了效率正提升,其餘都是負提升
- 單生產者效率,Posix有名訊號量 > Posix無名訊號量 > 條件變數
- 多生產者效率,Posix無名訊號量 > Posix有名訊號量 > 條件變數
該結論僅限於本文使用的示例程式碼,僅作結果陳述,不代表具有普適性,也沒有進行深層原因分析。
奇怪的問題
在使用條件變數的示例程式碼中,當有多個生產者時用了兩把鎖:
- mutex同步多個生產者,確保多個生產者不會同時訪問緩衝區
- cond_mutex確保生產者消費者不會同時訪問緩衝區
實際上,只需要一個cond_mutex就夠了,但經過測試發現這樣運行時間會明顯增加,如下圖所示:
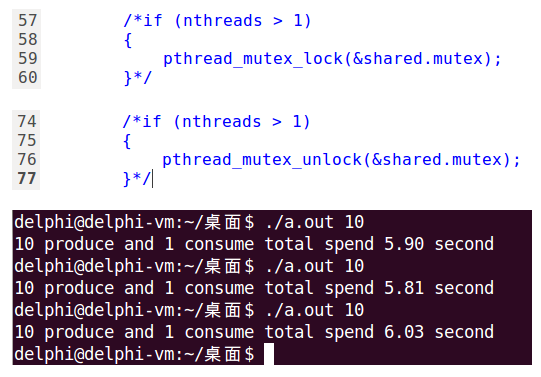
先從理論上分析下,10個生產者1個消費者:
- 只能同時有一個生產者訪問緩衝區
- 只能同時有一個生產者或消費者訪問緩衝區
總結起來就是:只能同時有一個執行緒訪問緩衝區。從這個結論來看,確實不需要第二把鎖,在一把鎖就夠用的情況下,再加第二把鎖反而多了不必要的開銷。
經過測試,Posix有名和無名訊號量都符合這個理論,運行時間明顯增加了,有名訊號量從1.9s增加到2.3s,無名訊號量從1.4s增加到2.5s。
但邪門就邪門在,條件變數卻相反,一把鎖效率低,兩把鎖反而效率有大幅提升,想不通為什麼!
