Java 樹結構的基礎部分(一)
二叉樹
1.1 為什麼需要樹這種數據結構
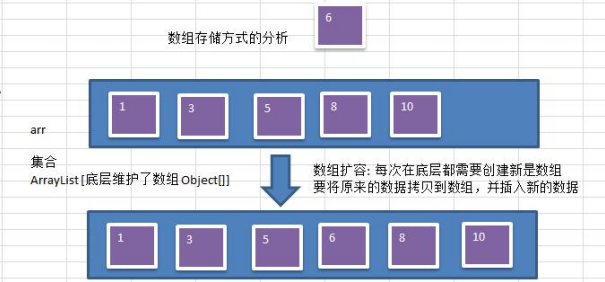
1) 數組存儲方式的分析
優點:通過下標方式訪問元素,速度快。對於有序數組,還可使用二分查找提高檢索速度。
缺點:如果要檢索具體某個值,或者插入值(按一定順序)會整體移動,效率較低 [示意圖]
畫出操作示意圖:
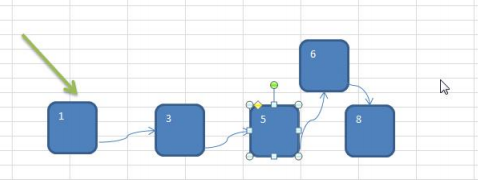
2) 鏈式存儲方式的分析
優點:在一定程度上對數組存儲方式有優化(比如:插入一個數值節點,只需要將插入節點,鏈接到鏈表中即可,
刪除效率也很好)。
缺點:在進行檢索時,效率仍然較低,比如(檢索某個值,需要從頭節點開始遍歷) 【示意圖】
操作示意圖:
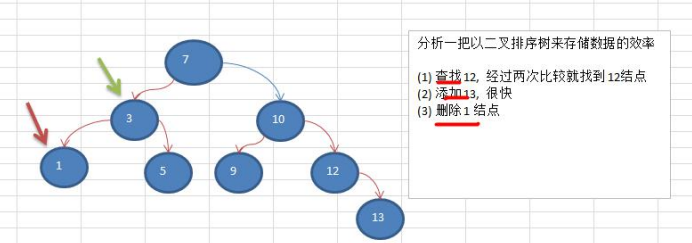
3) 樹存儲方式的分析
能提高數據存儲,讀取的效率, 比如利用 二叉排序樹(Binary Sort Tree),既可以保證數據的檢索速度,同時也
可以保證數據的插入,刪除,修改的速度。【示意圖,後面詳講】
案例: [7, 3, 10, 1, 5, 9, 12]
1.2 樹示意圖
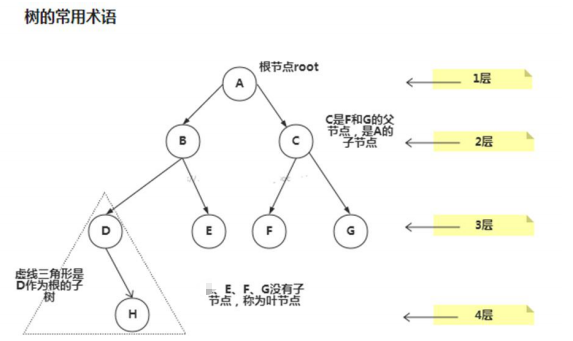
樹的常用術語(結合示意圖理解):
1) 節點
2) 根節點
3) 父節點
4) 子節點
5) 葉子節點 (沒有子節點的節點)
6) 節點的權(節點值)
7) 路徑(從 root 節點找到該節點的路線)
8) 層
9) 子樹
10) 樹的高度(最大層數)
11) 森林 :多顆子樹構成森林
1.3 二叉樹的概念
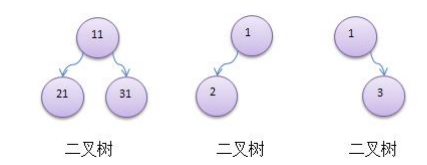
1) 樹有很多種,每個節點最多只能有兩個子節點的一種形式稱為二叉樹。
2) 二叉樹的子節點分為左節點和右節點
3) 示意圖
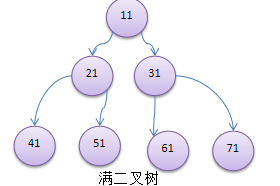
4) 如果該二叉樹的所有葉子節點都在最後一層,並且結點總數= 2^n -1 , n 為層數,則我們稱為滿二叉樹。
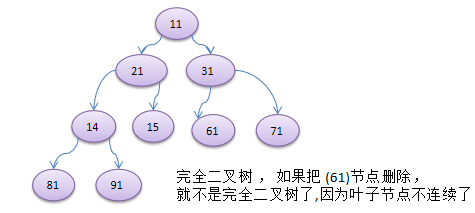
5) 如果該二叉樹的所有葉子節點都在最後一層或者倒數第二層,而且最後一層的葉子節點在左邊連續,倒數第二
層的葉子節點在右邊連續,我們稱為完全二叉樹
1.4 二叉樹遍歷的說明
使用前序,中序和後序對下面的二叉樹進行遍歷.
1) 前序遍歷: 先輸出父節點,再遍歷左子樹和右子樹
2) 中序遍歷: 先遍歷左子樹,再輸出父節點,再遍歷右子樹
3) 後序遍歷: 先遍歷左子樹,再遍歷右子樹,最後輸出父節點
4) 小結: 看輸出父節點的順序,就確定是前序,中序還是後序
1.5 二叉樹遍歷應用實例(前序,中序,後序)
應用實例的說明和思路

程式碼實現
在最後面
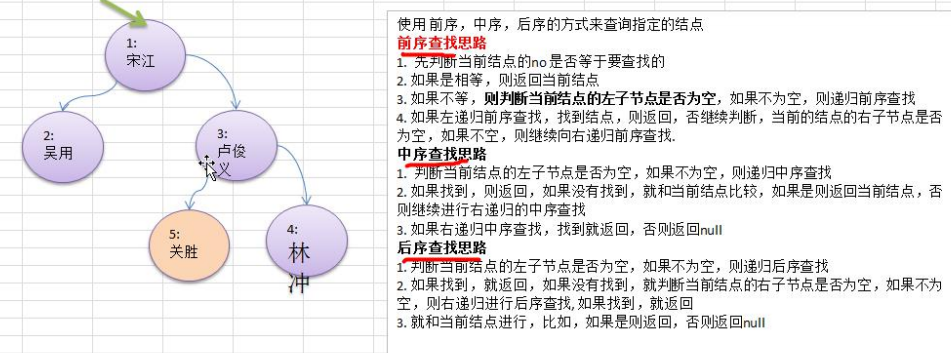
1.6 二叉樹-查找指定節點
要求
1) 請編寫前序查找,中序查找和後序查找的方法。
2) 並分別使用三種查找方式,查找 heroNO = 5 的節點
3) 並分析各種查找方式,分別比較了多少次
4) 思路分析圖解
5) 程式碼實現
在最後面
1.7 二叉樹-刪除節點
要求
1) 如果刪除的節點是葉子節點,則刪除該節點
2) 如果刪除的節點是非葉子節點,則刪除該子樹
3) 測試,刪除掉 5 號葉子節點 和 3 號子樹.
4) 完成刪除思路分析

5) 程式碼實現
package com.lin.tree_0308;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
HeroNode heroNode1 = new HeroNode(1, "伍六七");
HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2, "梅花十一");
HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3, "梅花十三");
HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4, "江主任");
HeroNode heroNode5 = new HeroNode(5, "希義");
heroNode1.setLeft(heroNode2);
heroNode1.setRight(heroNode3);
heroNode3.setRight(heroNode4);
heroNode3.setLeft(heroNode5);
binaryTree.setRoot(heroNode1);
// System.out.println("前序遍歷:");
// binaryTree.preOrder();
// System.out.println("中序遍歷:");
// binaryTree.infixOrder();
//
// System.out.println("後序遍歷");
// binaryTree.postOrder();
// System.out.println("前序查找:");
// HeroNode preOrderSearch = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5);
// if(preOrderSearch != null) {
// System.out.println(preOrderSearch);
// } else {
// System.out.println("沒有找到");
// }
// System.out.println("中序查找:");
// HeroNode infixOrderSearch = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(5);
// if(infixOrderSearch != null) {
// System.out.println(infixOrderSearch);
// } else {
// System.out.println("沒有找到");
// }
//
// System.out.println("後序查找:");
// HeroNode postOrderSearch = binaryTree.postOrderSearch(5);
// if(postOrderSearch != null) {
// System.out.println(postOrderSearch);
// } else {
// System.out.println("沒有找到");
// }
System.out.println("刪除前");
binaryTree.preOrder();
binaryTree.delNode(2);
System.out.println("刪除後");
binaryTree.preOrder();
}
}
class BinaryTree{
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
// 刪除節點
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一個root
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空樹!");
}
}
// 前序遍歷
public void preOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉樹為空!");
}
}
// 中序遍歷
public void infixOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉樹為空!");
}
}
// 後序遍歷
public void postOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉樹為空!");
}
}
// 前序查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if(root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 後序查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
class HeroNode{
private String name;
private int no;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode [name=" + name + ", no=" + no + "]";
}
// 前序遍歷
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 輸出父節點
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍歷
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this); // 輸出父節點
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 前序遍歷
public void postOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
System.out.println(this); // 輸出父節點
}
// 前序查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("1");
// 比較當前節點是不是
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 1 判斷當前節點的左節點是否為空,如果不為空,則遞歸前序查找
// 2 如果左遞歸前序查找,找到節點,則返回
HeroNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {// 說明左子樹找到了
return resNode;
}
// 1 左遞歸如果沒有找到,則繼續判斷
// 2 當前節點的右節點是否為空,如果不為空,則繼續向右遞歸前序查找
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
// 這時候不管有沒有找到都要返回resNode
return resNode;
}
// 中序查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("1");
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 後序查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("1");
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 如果都沒有找到
return resNode;
}
/**
*
* @Description:1 因為我們的二叉樹是單向,所以我們是判斷當前節點的子節點是否需要刪除節點,而不是直接去判斷當前節點是否需要刪除節點。<br>
* 2 如果當前節點的左子節點不為空,並且左子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.left = null;並且就返回(結束遞歸刪除) <br>
* 3 如果當前節點的右子節點不為空,並且右子節點就是要刪除節點,就將this.right = null;並且就返回(結束遞歸刪除) <br>
* 4 如果第2和第3都沒有刪除節點,那麼我們就需要向左子樹進行遞歸刪除<br>
* 5 如果第4補也沒有刪除節點,則向右子樹進行遞歸刪除<br>
* @author LinZM
* @date 2021-3-8 15:17:32
* @version V1.8
*/
public void delNode(int no) {
if(this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
if(this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
}
僅供參考,有錯誤還請指出!
有什麼想法,評論區留言,互相指教指教。
覺得不錯的可以點一下右邊的推薦喲

