coco標註資訊與labelme標註資訊的詳解、相互轉換及可視化
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
引言
在做實例分割或語義分割的時候,我們通常要用labelme進行標註,labelme標註的json文件與coco數據集已經標註好的json文件的格式和內容有差異。如果要用coco數據集的資訊,就要對json文件進行修改和轉換。本部落格提供兩種格式的具體內容及含義以及兩種格式相互轉換的程式碼,並對兩種格式的json標註資訊進行可視化。
1.coco格式的json標註資訊詳解及可視化
從coco官網下載coco的數據集裡面,關於實例的標註資訊在“annotations_trainval2017.zip”壓縮文件裡面的“instances_train2017.json”和“instances_val2017.json”裡面,分別是訓練集和驗證集的標註資訊。
下載地址:
訓練集圖片:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/train2017.zip 驗證集圖片:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/val2017.zip 測試集圖片:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/test2017.zip 訓練集、驗證集標註資訊:http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/annotations_trainval2017.zip http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/stuff_annotations_trainval2017.zip http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/panoptic_annotations_trainval2017.zip
由於“instances_train2017.json”裡面把所有訓練集圖片的標註資訊整合到一個文件了,文件非常大,不太好查看內部具體內容。我從這個文件中提取出一張圖片的資訊保存成一個新的json文件。
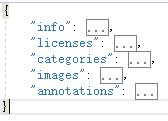
json文件內主要欄位:
程式碼如下:

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from __future__ import print_function """ Created on Thu Aug 15 13:58:40 2019 @author: Taoting """ ''' 從coco的標註文件里提取一張圖片對應的json資訊,並保存成新的json文件(以instance為例,其他的類似)。 ''' import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import os, sys, zipfile import urllib.request import shutil import numpy as np import skimage.io as io import pylab import json from pycocotools.coco import COCO pylab.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8.0, 10.0) json_file='../../../coco dataset/annotations_trainval2017/instances_val2017.json' # # Object Instance 類型的標註 # json_file='./annotations/person_keypoints_val2017.json' # Object Keypoint 類型的標註格式 # json_file='./annotations/captions_val2017.json' # Image Caption的標註格式 data=json.load(open(json_file,'r')) data_2={} data_2['info']=data['info'] data_2['licenses']=data['licenses'] data_2['images']=[data['images'][0]] # 只提取第一張圖片 data_2['categories']=data['categories'] annotation=[] # 通過imgID 找到其所有instance imgID=data_2['images'][0]['id'] #print(imgID)#397133 # initialize COCO api for instance annotations coco=COCO(json_file) img = coco.loadImgs([imgID]) #print(img)#[{'license': 4, 'file_name': '000000397133.jpg', 'coco_url': 'http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000397133.jpg', # 'height': 427, 'width': 640, 'date_captured': '2013-11-14 17:02:52', 'flickr_url': 'http://farm7.staticflickr.com/6116/6255196340_da26cf2c9e_z.jpg', 'id': 397133}] #print(img['file_name']) # load and display image I = io.imread('../../../coco dataset/val2017/%s' % img[0]['file_name']) # use url to load image #I = io.imread(img['coco_url']) #plt.axis('off') #plt.imshow(I) #plt.show() for ann in data['annotations']: if ann['image_id']==imgID: annotation.append(ann) data_2['annotations']=annotation # 保存到新的json json.dump(data_2,open('./{}.json'.format(str(img[0]['file_name']).split('.')[0]),'w'),indent=4)
從coco標註json中提取單張圖片的標註資訊
得到一張圖片的標註資訊如下,包含5大部分的欄位資訊。
“info”的value是一個dict,存儲數據集的一些基本資訊,我們不需要關注;
“licenses”的value是一個list,存儲license資訊,我們不需要關注;
“categories”的value是一個list,存儲數據集的類別資訊,包括類別的超類、類別id、類別名稱;
“images”的value是一個list,存儲這張圖片的基本資訊,包括圖片名、長、寬、id等重要資訊;
“annotations”的value是一個list,存儲這張圖片的標註資訊,非常重要,list中的每一個元素是一個dict,也即一個標註對象(instance)的資訊。包括的欄位有”segmentation”:標註點的坐標,從第一個的x,y坐標一直到最後一個點的x,y坐標;”area”是標註的閉合多邊形的面積; “iscrowd”表示對象之間是否有重疊;”image_id”是圖片的id;“bbox”是instance的邊界框的左上角的x,y,邊界框的寬和高;”category_id”是這個instance對應的類別id;”id”表示此instance標註資訊在所有instance標註資訊中的id。
{ "info": { "description": "COCO 2017 Dataset", "url": "http://cocodataset.org", "version": "1.0", "year": 2017, "contributor": "COCO Consortium", "date_created": "2017/09/01" }, "licenses": [ { "url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/", "id": 1, "name": "Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License" }, { "url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0/", "id": 2, "name": "Attribution-NonCommercial License" }, ...(太長,省略) ],
"categories": [
{
"supercategory": "person",
"id": 1,
"name": "person"
},
...(太長,省略)
], "images": [ { "license": 2, "file_name": "000000000049.jpg", "coco_url": "http://images.cocodataset.org/train2017/000000000049.jpg", "height": 500, "width": 381, "date_captured": "2013-11-14 20:00:23", "flickr_url": "http://farm4.staticflickr.com/3250/2883102207_bcba5527a7_z.jpg", "id": 49 } ], "annotations": [ { "segmentation": [ [ 181.59, 363.43, ...(太長,省略) ] ], "area": 8451.22405, "iscrowd": 0, "image_id": 49, "bbox": [ 162.57, 226.56, 130.41, 184.43 ], "category_id": 19, "id": 56407 }, ...(太長,省略) ] }
我們對這個新coco格式的json文件進行可視化:

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Thu Aug 15 14:48:12 2019 @author: Taoting """ from __future__ import print_function import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # ~ from pycocotools.coco import COCO from coco import COCO import os, sys, zipfile import urllib.request import shutil import numpy as np import skimage.io as io import pylab pylab.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8.0, 10.0) annFile='./modified_satisfied_json_train2017/000000000149.json'#json文件路徑 coco=COCO(annFile) cats = coco.loadCats(coco.getCatIds()) nms=[cat['name'] for cat in cats] nms = set([cat['supercategory'] for cat in cats]) imgIds = coco.getImgIds() img = coco.loadImgs(imgIds[0])[0] dataType = './satisfied_images_train2017' I = io.imread('%s/%s'%(dataType,img['file_name'])) plt.axis('off') plt.imshow(I) plt.show() # 載入和可視化instance標註資訊 catIds=[] for ann in coco.dataset['annotations']: if ann['image_id']==imgIds[0]: catIds.append(ann['category_id']) plt.imshow(I); plt.axis('off') annIds = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id'], catIds=catIds, iscrowd=None) anns = coco.loadAnns(annIds) coco.showAnns(anns) plt.show()
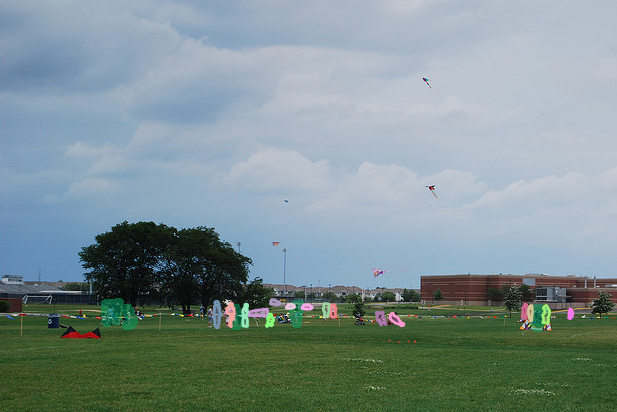
coco格式的json文件可視化instance的mask
可視化結果如下:

2.labelme格式的json標註資訊詳解及可視化
labelme標註工具標註的json格式與coco的格式有差異:
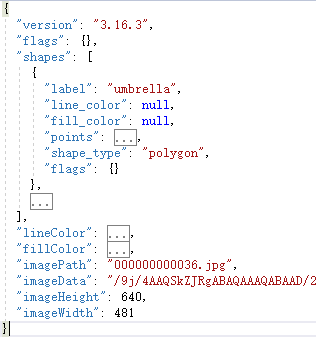
重點關注的是:
“shapes”:存儲標註instance的閉合多邊形的資訊,重點關註:label:類別名稱;points:閉合多邊形的每個點的x,y坐標;
“line_color”:閉合多邊形的邊界線顏色;
“fill_color”:閉合多邊形的填充顏色;
“imagePath”:圖片名稱;
“imageData”:圖片路徑(加密後);
“imageHeight”:圖片高;
“imageWidth”:圖片寬;
利用labelme提供的介面將標註好的json進行可視化程式碼:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ @author: Taoting 將用labeime標註格式的json進行可視化 """ import json import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import skimage.io as io from labelme import utils def main(): json_path = './PATH/TO/JSON' data = json.load(open(json_path)) img = io.imread('%s/%s'%('./PATH/TO/IMAGE',data['imagePath'])) lab, lab_names = utils.labelme_shapes_to_label(img.shape, data['shapes']) captions = ['%d: %s' % (l, name) for l, name in enumerate(lab_names)] lab_ok = utils.draw_label(lab, img, captions) plt.subplot(121) plt.imshow(img) plt.subplot(122) plt.imshow(lab_ok) plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': main()
可視化結果:
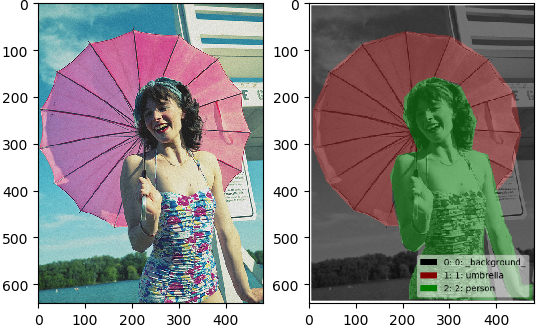
可以看到右圖中的mask的可視化效果
結合1和2中的兩種格式的json,我們只需要針對格式的差異對json文件做修改,就能將格式進行互相轉換。
3.coco格式的json轉labelme格式的json
直接上程式碼:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ @author: Taoting 將用coco格式的json轉化成labeime標註格式的json """ import json import cv2 import numpy as np import os #用一個labelme格式的json作為參考,因為很多資訊都是相同的,不需要修改。 def reference_labelme_json(): ref_json_path = 'reference_labelme.json' data=json.load(open(ref_json_path)) return data def labelme_shapes(data,data_ref): shapes = [] label_num = {'person':0,'bicycle':0,'car':0,'motorcycle':0,'bus':0,'train':0,'truck':0}#根據你的數據來修改 for ann in data['annotations']: shape = {} class_name = [i['name'] for i in data['categories'] if i['id'] == ann['category_id']] #label要對應每一類從_1開始編號 label_num[class_name[0]] += 1 shape['label'] = class_name[0] + '_' + str(label_num[class_name[0]]) shape['line_color'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['line_color'] shape['fill_color'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['fill_color'] shape['points'] = [] # ~ print(ann['segmentation']) if not type(ann['segmentation']) == list: continue else: x = ann['segmentation'][0][::2]#奇數個是x的坐標 y = ann['segmentation'][0][1::2]#偶數個是y的坐標 for j in range(len(x)): shape['points'].append([x[j], y[j]]) shape['shape_type'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['shape_type'] shape['flags'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['flags'] shapes.append(shape) return shapes def Coco2labelme(json_path,data_ref): with open(json_path,'r') as fp: data = json.load(fp) # 載入json文件 data_labelme={} data_labelme['version'] = data_ref['version'] data_labelme['flags'] = data_ref['flags'] data_labelme['shapes'] = labelme_shapes(data,data_ref) data_labelme['lineColor'] = data_ref['lineColor'] data_labelme['fillColor'] = data_ref['fillColor'] data_labelme['imagePath'] = data['images'][0]['file_name'] data_labelme['imageData'] = None # ~ data_labelme['imageData'] = data_ref['imageData'] data_labelme['imageHeight'] = data['images'][0]['height'] data_labelme['imageWidth'] = data['images'][0]['width'] return data_labelme if __name__ == '__main__': root_dir = './ROOT DIR' json_list = os.listdir(root_dir) #參考的json data_ref = reference_labelme_json() for json_path in json_list: if json_path.split('.')[-1] == 'json': print('當前文件: ', json_path) data_labelme= Coco2labelme(os.path.join(root_dir,json_path), data_ref) file_name = data_labelme['imagePath'] # 保存json文件 json.dump(data_labelme,open('./PATH/%s.json' % file_name.split('.')[0],'w'),indent=4)
用2中的可視化程式碼檢驗是否正確轉換。
4.labelme格式的json轉coco格式的json
直接上程式碼:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """Created on Thu Aug 15 15:05:56 2019 @author: Taoting 將用labeime標註的json轉化成coco格式的json """ import json import cv2 import numpy as np import os #用閉包實現計數器 def counter(): cnt = 1000000 def increce(): nonlocal cnt x = cnt cnt += 1 return x return increce def p_images(data,data_coco): images=[] image={} file_name=data['imagePath'].split('\')[-1] image['file_name']=file_name image['id']=int(file_name.split('.')[0]) image['height']=data['imageHeight'] image['width']=data['imageWidth'] img=None images.append(image) data_coco['images']=images return file_name #用一個coco格式的json做參考 def modify_categories(): ref_json_path = 'reference.json' data=json.load(open(ref_json_path)) modified_categories = [] catNms=['person','bicycle','car','motorcycle','truck','bus']#根據你的數據修改 for i,cat in enumerate(data['categories']): if cat['name'] in catNms: modified_categories.append(cat) else: pass return modified_categories,data['info'],data['licenses'] def p_annotation(data,data_coco,cnt): # annotations annotations=[] for i in range(len(data['shapes'])): annotation={} annotation['segmentation']=[list(np.asarray(data['shapes'][i]['points']).flatten())] # data['shapes'][0]['points'] annotation['iscrowd']=0 annotation['image_id']=data_coco['images'][0]['id'] #找出標註點中的外接矩形的四個點 x = annotation['segmentation'][0][::2]#奇數個是x的坐標 y = annotation['segmentation'][0][1::2]#偶數個是y的坐標 print(x,y) x_left = min(x)-1#往外擴展1個像素,也可以不擴展 y_left = min(y)-1 w = max(x) - min(x)+1 h = max(y) - min(y)+1 annotation['bbox']=[x_left,y_left,w,h] # [左上角x,y以及寬和高] cat_list_dict = [cat for cat in data_coco['categories'] if cat['name'] == data['shapes'][i]['label'].split('_')[1]]#注意這裡是跟標註時填類別的方式有關 annotation['category_id']=cat_list_dict[0]['id'] annotation['id'] = cnt() # 第一個對象 這個ID也不能重複,如果下一張圖,id不能取1,需從1 開始往下取 #print('cnt', annotation['id']) #print('annotation',annotation) annotations.append(annotation) #print('annotations',annotations) data_coco['annotations']=annotations #print(data_coco['annotations']) #return data_coco def Labelme2coco(json_path,cnt): with open(json_path,'r') as fp: data = json.load(fp) # 載入json文件 data_coco={} # images file_name = p_images(data,data_coco) # categories modified_categories, info, p_license = modify_categories() data_coco['categories'] = modified_categories #print(data_coco['categories']) # info data_coco['info'] = info # license data_coco['license'] = p_license # annotations p_annotation(data,data_coco,cnt) #print(data_coco['annotations']) return data_coco,file_name if __name__ == '__main__': root_dir = './ROOT DIR' json_list = os.listdir(root_dir) cnt = counter() for json_path in json_list: if json_path.split('.')[-1] == 'json': data_coco,file_name = Labelme2coco(os.path.join(root_dir,json_path),cnt) # 保存json文件 json.dump(data_coco,open('./PATH/%s.json' % file_name.split('.')[0],'w'),indent=4)
用1中的可視化程式碼檢驗是否正確轉換。

