【晶片手冊開發】Sil9136音頻開發詳細分析+源碼實戰
- 2020 年 11 月 20 日
- 筆記
- /label/lzm, /label/manual, 晶片手冊
前言
- 默認在開發了影片方面後
- 這方面的工作本來可以找技術支援拿個常式參考下,很快就可以的寫出來的,以為自己對HDMI協議不太了解,但是技術支援說沒有,所以沒辦法,只能自己搞了
- 看手冊不難,難得找是資料
- 記錄一下,也分享一下
參考
- sil9136暫存器手冊:《Sil-PR-1060-C》
- HDMI協議手冊:《HDMI_1.4》
- CEA標準手冊:《CEA-861-D[安全]》
- 使用參考常式(無音頻功能)
手冊使用+實戰
- 以 I2S 介面為例開發
- 直接看手冊配置相關暫存器
- 記得輸入與輸出配對
- 如編碼類型
- 取樣長度
- 取樣頻率
- 等等
配置
-
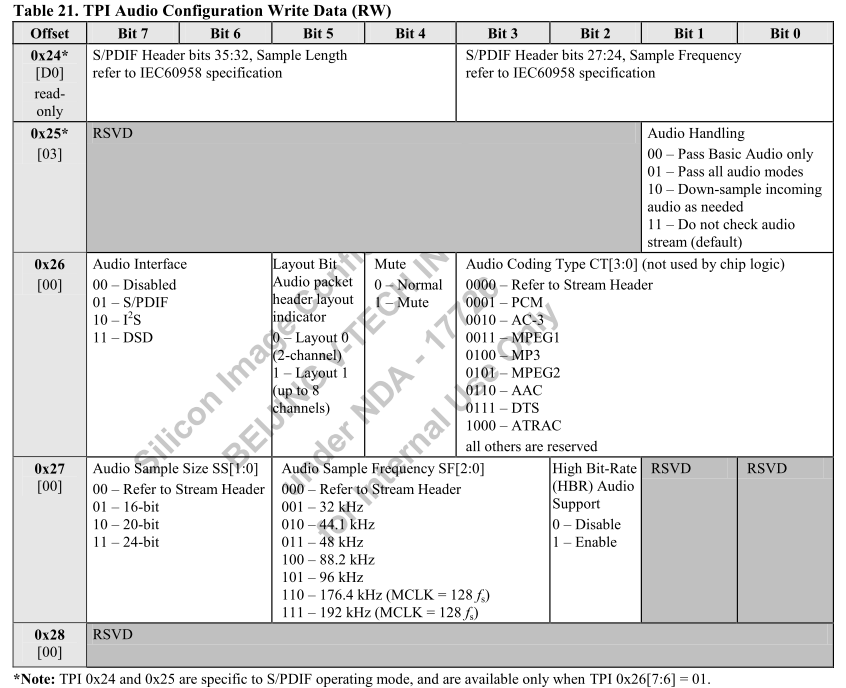
《Sil-PR-1060-C》手冊,28頁起
-
圖中說明 sil9136 支援 S/PDIF, I2S or DSD模式,主機可以通過配置TPI選擇不同的模式
-
這個暫存器表比較重要,說明了sil9136的暫存器配置
-
0x26 暫存器
- [7:6]
- 選擇模式,支援
- none
- S/PDIF
- I2S
- DSD
- 選擇模式,支援
- [5]
- 通道數,支援
- 雙通道
- 8 通道
- 通道數,支援
- [4]
- 靜音配置
- [3:0]
- 編碼類型,有
- Refer to Stream Header
- PCM (本次使用 PCM)
- AC-3
- MPEG1
- MP3
- MPEG2
- AAC
- DTS
- ATRAC
- 編碼類型,有
- [7:6]
-
0x27 暫存器
- [7:6]
- 音頻取樣比特位長度 SS
- Refer to Stream Header
- 16 bit
- 20 bit
- 24 bit
- 音頻取樣比特位長度 SS
- [5:3]
- 音頻取樣頻率 SF
- Refer to Stream Header
- 32 kHz
- 44.1 kHz
- 48 kHz
- 88.2 kHz
- 96 kHz
- 176.4 kHz
- 192 kHz
- 音頻取樣頻率 SF
- [2]
- 是否支援高比特率
- [7:6]
-
注意:圖中說明的 0x24 和 0x25 暫存器只有在 S/PDIF 模式下有效,即是 0x26[7:6]=01 時。
Configuring Audio Using I2S
-
直接跳到配置 I2S 流程,實現配置邏輯
-

- 上圖已經很明顯地顯示出了配置出 I2S 的流程了
- 步驟:
- 確保有有效的 I2S 訊號進入 sil9136
- 設置 0x26[4] 為靜音模式
- 直接調用常式介面:
SetAudioMute(AUDIO_MUTE_MUTED);
- 直接調用常式介面:
- 通過 0x20 來配置進來的 SD 格式
-

- 配置要和輸入的音頻配置搭配
- 以下為個人選擇
- SCK Sample Edge :Rising
- MCLK Multiplier:256
- WS Polarity – Left when:WS is Low
- SD Justify Data is justified:Left
- SD Direction Byte shifted first:MSB
- WS to SD First Bit Shift:Yes
- 程式為:
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_IN_CFG, (0x80x10));
-
- 通過多次設置 0x1F 來配置每一個 SD 輸入映射
-
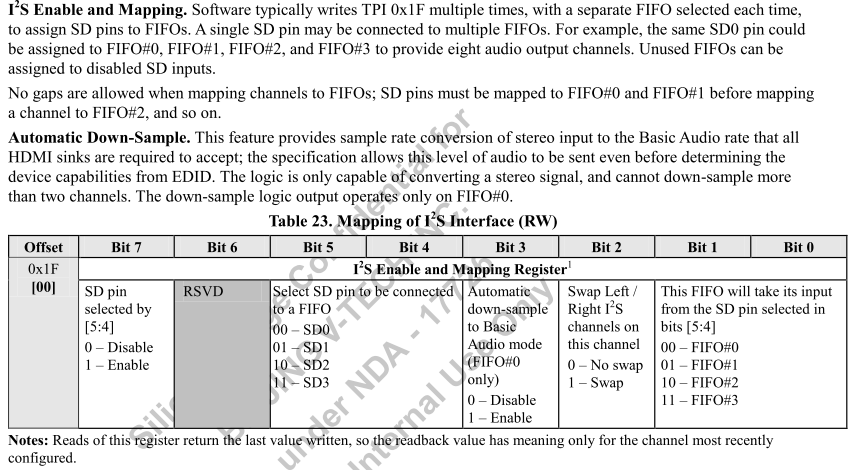
- SDx與FIFOn的映射
- 支援一對多
- 注意:必須順序映射,如如果要映射FIFO2,就必須先完成FIFO0和FIFO1的映射
- 我的程式碼段:SD0-FIFO0; SD1-FIFO1; SD2-FIFO2; SD3-FIFO3;
do{ WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0x80); Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN); }while(Tmp != 0x80); do{ WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0x91); Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN); }while(Tmp != 0x91); do{ WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0xA2); Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN); }while(Tmp != 0xA2); do{ WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0xB3); Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN); }while(Tmp != 0xB3);
-
- 通過設置 0x27[5:3] 來配置音頻取樣頻率
- 配置為48kHz:
ReadModifyWriteTPI(TPI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_CTRL, 0x38, 0x18);
- 配置為48kHz:
- 設置 0x21-0x25 來配置發送到HDMI的頭資訊
-
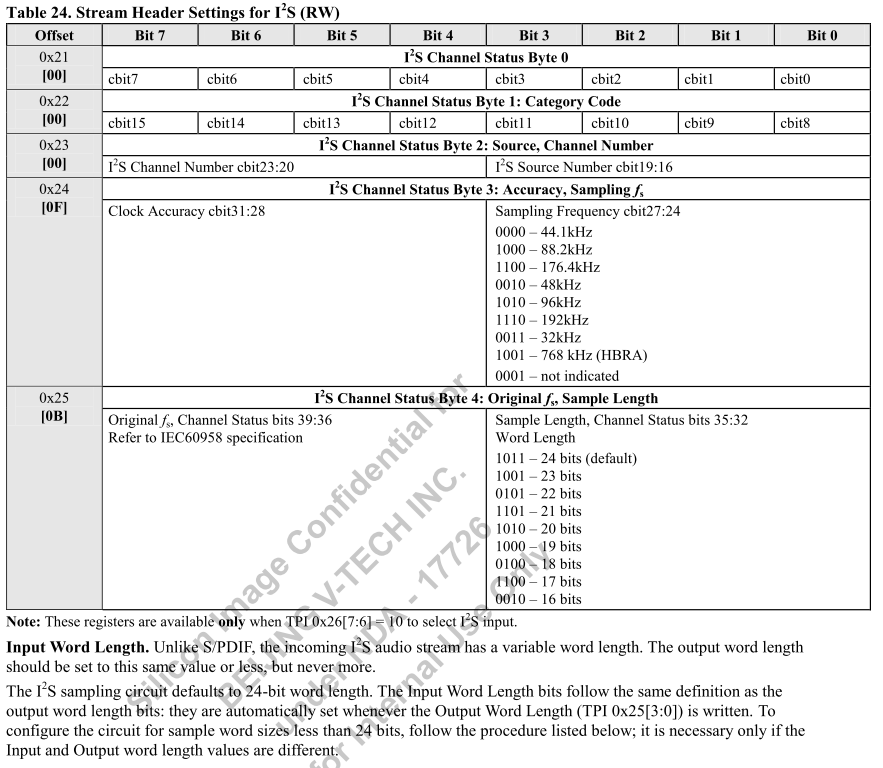
- 上圖 0x21-0x25 的描述在 I2S 模式有效,即是 0x26[7:6] = 0x10
- 主要配置兩個參數
- 取樣頻率:48 kHz
- 取樣長度:24 bits
- 程式碼段
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_0, 0x00); WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_1, 0x00); WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_2, 0x00); WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_3, 0x02); WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_4, 0x0B);
-
- 設置 0xBF-0xCD 來配置 audio infoframe
-
這步驟先給出最終程式碼再分析:
SetAudioInfoFrames(TWO_CHANNELS, 0x00, 0x00, 0x18, 0x00); -

-
說明了配置 audio infoframe 的必要性和需要參考的文件 HDMI Specification,根據本文件說明,了解到sil9136 支援 HDMI1.4 協議,所以準備好文件《HDMI_1.4》,並找到關於 audio infoframe 的說明。
-
圖A
-
圖B
-
圖C
-
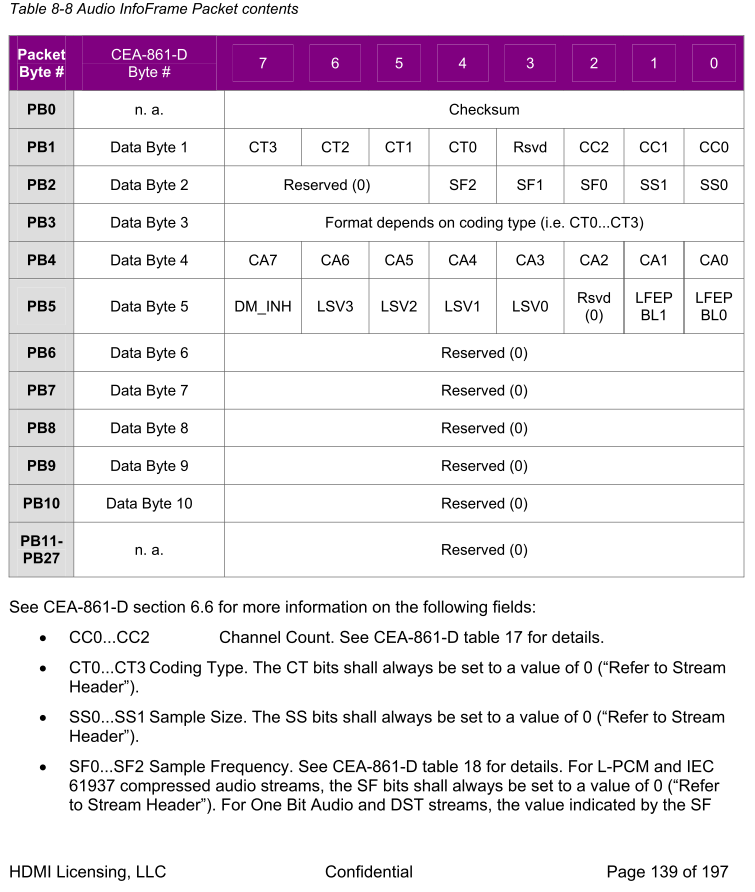
-
圖Cc1,《CEA-861-D安全》
-
圖Cc2,《CEA-861-D安全》
-
-
圖D
-
結合常式源碼
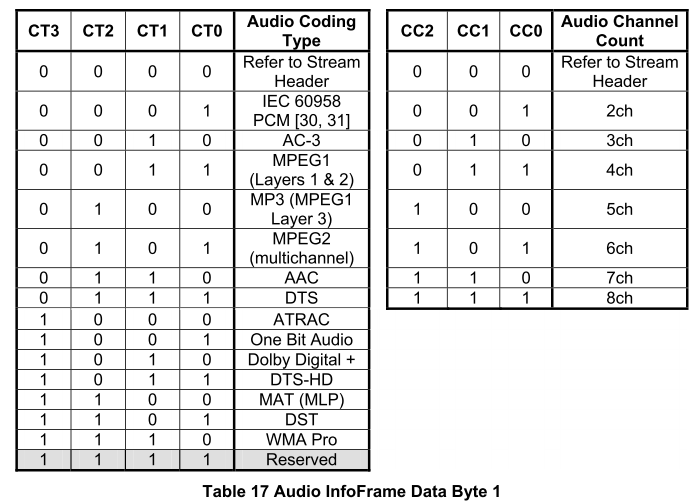
bool SetAudioInfoFrames函數,得出只需要了解幾個參數配置即可。- byte ChannelCount
- 參照圖C和圖Cc1,C0…C2,選擇雙通道,得出值為 0x01
- byte CodingType
- CT0…CT3: The CT bits shall always be set to a value of 0 (「Refer to Stream Header」).即是置為0即可
- SS
- The SS bits shall always be set to a value of 0 (「Refer to Stream Header」). 即是置為0即可
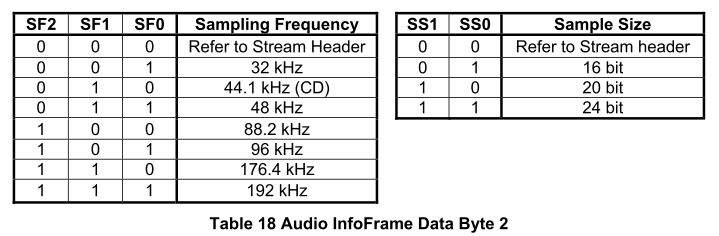
- Fs
- 參考源碼、0x27暫存器、圖C和圖Cc2
- 推測
Fs就是取樣頻率 SF0…SF2 B_Data[6] = (Fs >> 1) | (SS >> 6);- Fs在圖C中的PB2[4:2],而上述程式碼中右移一位,所以 Fs 的值佔用[5:3],參考0x27。
- 取樣頻率為 48kHz,得出 Fs=x018
- SpeakerConfig
- 參考源碼
B_Data[8] = SpeakerConfig;得出 SpeakerConfig 為 圖C中的PB4 - 這裡為 LPCM ,所以 SpeakerConfig = 0;
- 參考源碼
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // // FUNCTION : SetAudioInfoFrames() // // PURPOSE : Load Audio InfoFrame data into registers and send to sink // // INPUT PARAMS : (1) Channel count (2) speaker configuration per CEA-861D // Tables 19, 20 (3) Coding type: 0x09 for DSD Audio. 0 (refer // to stream header) for all the rest (4) Sample Frequency. Non // zero for HBR only (5) Audio Sample Length. Non zero for HBR // only. // // OUTPUT PARAMS : None // // GLOBALS USED : None // // RETURNS : TRUE // ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// bool SetAudioInfoFrames(byte ChannelCount, byte CodingType, byte SS, byte Fs, byte SpeakerConfig) { byte B_Data[SIZE_AUDIO_INFOFRAME]; // 14 byte i; TPI_TRACE_PRINT((">>SetAudioInfoFrames()\n")); for (i = 0; i < SIZE_AUDIO_INFOFRAME +1; i++) B_Data[i] = 0; B_Data[0] = EN_AUDIO_INFOFRAMES; // 0xC2 B_Data[1] = TYPE_AUDIO_INFOFRAMES; // 0x84 B_Data[2] = AUDIO_INFOFRAMES_VERSION; // 0x01 B_Data[3] = AUDIO_INFOFRAMES_LENGTH; // 0x0A B_Data[5] = ChannelCount; // 0 for "Refer to Stream Header" or for 2 Channels. 0x07 for 8 Channels B_Data[5] |= (CodingType << 4); // 0xC7[7:4] == 0b1001 for DSD Audio B_Data[4] = 0x84 + 0x01 + 0x0A; // Calculate checksum // B_Data[6] = (Fs << 2) | SS; B_Data[6] = (Fs >> 1) | (SS >> 6); //write Fs to 0x27[5:3] and SS to 0x27[7:6] to update the IForm with the current value. // ReadModifyWriteTPI(TPI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_CTRL, BITS_7_6 | BITS_5_4_3, (B_Data[6] & BITS_1_0) << 6 | (B_Data[6] & 0x1C) << 1); B_Data[8] = SpeakerConfig; for (i = 5; i < SIZE_AUDIO_INFOFRAME; i++) B_Data[4] += B_Data[i]; B_Data[4] = 0x100 - B_Data[4]; g_audio_Checksum = B_Data[4]; // Audio checksum for global use WriteBlockTPI(TPI_AUDIO_BYTE_0, SIZE_AUDIO_INFOFRAME, B_Data); #ifdef DEV_EMBEDDED EnableEmbeddedSync(); #endif return TRUE; } - byte ChannelCount
-
-
- I2S 模式, 設置音頻通道數,並關閉靜音
- 程式碼:
WriteByteTPI(TPI_AUDIO_INTERFACE_REG, AUD_IF_I2S | TWO_CHANNEL_LAYOUT | 0x01); - 注意:audio inframe中的通道數配置必須和 0x26 配置的一樣
- 程式碼:
總結實現
- 得出一下程式碼,並把一下函數放到熱插拔的插入後運行即可
/**
* @brief setPrivateAudio(void)
* @param
* @retval
* @author lzm
*/
void setPrivateAudio(void)
{
byte Tmp = 0;
/* Select I2S input mode using TPI 0x26[7:6], with Mute enabled (bit [4] = 1). */
SetAudioMute(AUDIO_MUTE_MUTED);
/* Write register TPI 0x20 to select the general incoming SD format. */
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_IN_CFG, (SCK_SAMPLE_EDGE | 0x10));
/* Write register TPI 0x1F up to four times, to program each of the SD inputs. */
do{
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0x80);
Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN);
}while(Tmp != 0x80);
do{
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0x91);
Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN);
}while(Tmp != 0x91);
do{
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0xA2);
Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN);
}while(Tmp != 0xA2);
do{
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN, 0xB3);
Tmp = ReadByteTPI(TPI_I2S_EN);
}while(Tmp != 0xB3);
// /* Program register TPI 0x27 with the correct audio about. */
// WriteByteTPI(TPI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_CTRL, AUDIO_SAMPLE_SIZE_24BIT | AUDIO_SAMPLE_FREQ_48KHZ | AUDIO_SAMPLE_HBR_DISABLE);
/* Program register TPI 0x27[5:3] with the correct audio rate */
ReadModifyWriteTPI(TPI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_CTRL, 0x38, AUDIO_SAMPLE_FREQ_48KHZ);
/* Program registers TPI 0x21-x25 with the correct header information for the stream that will be sent over HDMI. */
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_0, 0x00);
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_1, 0x00);
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_2, 0x00);
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_3, 0x02);
WriteByteTPI(TPI_I2S_CHST_4, 0x0B);
/* Write registers TPI 0xBF-xCD with the appropriate Audio InfoFrame information. */
SetAudioInfoFrames(TWO_CHANNELS, 0x00, 0x00, 0x18, 0x00);
/* Set the audio packet header layout indicator to 2-channel or multi-channel mode as needed using the sequence described below.
Note that Audio InfoFrame byte 1 must also have this same setting. */
/* Again write register TPI 0x26 with I2S selected, this time with Mute disabled (bit [4] = 0). */
WriteByteTPI(TPI_AUDIO_INTERFACE_REG, AUD_IF_I2S | TWO_CHANNEL_LAYOUT | 0x01);
SetAudioMute(AUDIO_MUTE_NORMAL);
}