canvas基礎[一]探究出初中數學知識
- 2020 年 11 月 11 日
- 筆記

何時用SVG何時用canvas
SVG
矢量圖,視覺清晰,文件小
<svg viewBox="0 0 100 100">
<circle cx="50" cy="50" r="50" />
<style>
circle { fill: blue; animation: pulse 2s alternate infinite; }
@keyframes pulse {
100% {
r: 30;
}
}
</style>
<script>
document.querySelector('circle').addEventListener('click', e => {
e.target.style.fill = "red";
});
</script>
</svg>
關鍵可以放在一起玩
Canvas
是javascript繪圖API
大佬提出來的想法是:
SVG是默認選擇,畫布是備份,簡單的說當你不能使用SVG時候才使用canvas
canvas 元素
<canvas id="tutorial" width="150" height="150"></canvas>
渲染上下文
var canvas = document.getElementById('tutorial');
var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
編寫一個基本骨架
<style>
#canvas{
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
</style>
<canvas id="canvas" width="150" height="150"></canvas>
繪製矩形
fillRect(x, y, width, height)
繪製一個填充的矩形
strokeRect(x, y, width, height)
繪製一個矩形的邊框
clearRect(x, y, width, height)
清除指定矩形區域,讓清除部分完全透明。
案例

let canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas')
let ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
// 填充
ctx.fillRect(10,10,80,80)
// 刪除部分
ctx.clearRect(10,10,20,20)
// 填充邊框的矩形
ctx.strokeRect(10,10,10,10)
繪製路徑
- 創建路徑起始點
- 畫圖命令繪製路徑
- 路徑閉合
- 路徑生成後,通過描邊或填充路徑來渲染圖形
deginpath()
新建一條路徑
closePath()
閉合路徑
stroke()
通過線條繪製圖形輪廓
fill()
通過填充路徑繪製成實心的圖形
案例
繪製一個三角形
let ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.moveTo(50, 50)// 點
ctx.lineTo(50, 100)// 直線
ctx.lineTo(130, 100)//
ctx.fill()
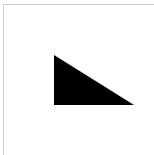
MoveTo(x,y)
將筆觸移動到指定的坐標x以及y上
lineTo(x, y)
繪製一條從當前位置到指定x以及y位置的直線。
// 描邊三角形
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.moveTo(50, 50)// 點
ctx.lineTo(50, 100)// 直線
ctx.lineTo(130, 100)//
ctx.closePath()
ctx.stroke()

lineWidth 行寬
strokeStyle 邊框的顏色
ctx.lineWidth=5
ctx.strokeStyle='red'
lineCap 線頭
- butt 默認
- round 半圓形
- square 移動到末端

context.lineCap = 'butt';
context.lineCap = 'round';
context.lineCap = 'square';
lineJoin 線連接
- bevel 斜角
- round 圓角
- square 默認
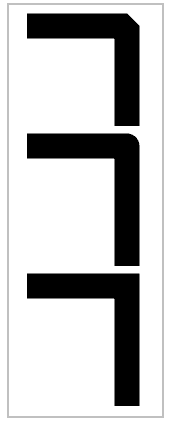
ctx.lineJoin = "bevel";
ctx.lineJoin = "round";
默認 "square"
圓弧
arc()
度數轉為弧度公式
度數*Math.PI/180
方法
arc(x,y,radius,startAngle,endAngle,direction)
畫一個以(x,y)為圓心的以radius為半徑的圓弧(圓),從startAngle開始到endAngle結束,direction方向true順時針,false逆時針,默認順時針true
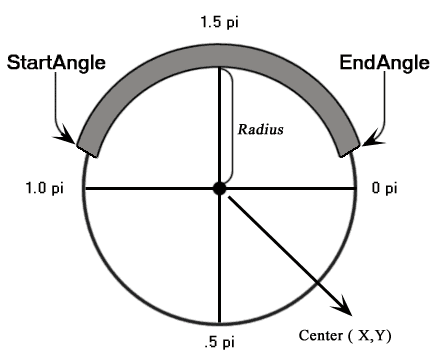
用弧度畫一個圓
let ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.moveTo(250, 250)// 點
ctx.arc(250,250,100,0,2 * Math.PI,)
ctx.closePath()
ctx.stroke()
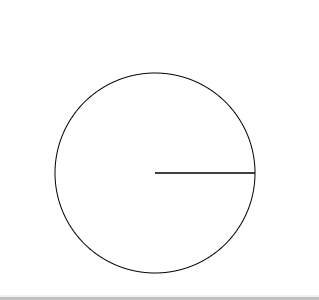
我們要記住開始的弧度和結束的弧度記住上面的公式,一個圓是2*Math.PI
所以半圓是Math.PI
ctx.arc(250,250,100,1/3*Math.PI,2 * Math.PI,)
開始位置是1/3,結束位置是終點位置
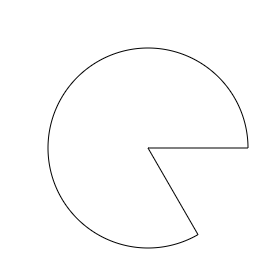
arcTo
arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,radius)
畫曲線,要想明白它們之間的關係需要畫輔助線
let x0 = 100,
y0 = 100,
x1 = 400,
y1 = 100,
x2 = 350,
y2 = 150;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(x0, y0);
ctx.strokeStyle = "#f00";
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.arcTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, 20);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.strokeStyle = "rgba(0,0,0,0.5)";
ctx.lineWidth = 1;
ctx.moveTo(x0, y0);
ctx.lineTo(x1, y1);
ctx.fillText('x1,y1', x1 + 10, y1 + 10)
ctx.lineTo(x2, y2);
ctx.fillText('x2,y2', x2 + 10, y2)
ctx.stroke();
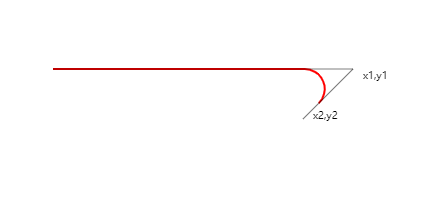
說明一下,x0,y0 起點坐標,x1,y1 第一個點坐標,x2,y2 第二個坐標
arcTo的規律: 他其實是通過起點,第1點,第2點的兩條直線,組成了一個夾角,而這兩條線,也是參數圓的切線。其中圓的半徑決定了圓會在什麼位置與線條發生切邊。
讓我們把球球變大吧!
ctx.arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,50); //半徑改成50

我們發現他們還是相切的,因為切線可以無限延長
為了方便計算,我先把兩條線的夾角改成90度。
var x0=100,
y0=400,
x1 = 500,
y1 = 400,
x2 = 500,
y2 = 450;
更改後就是90度張開了喲!我們保持球的半徑不變。刷新後:

我們把y2變大,也就是延長了一條切線,把他變成550,刷新後:

切線是延長了,但arcTo畫出的紅線沒有任何變化。
寫一個可行的案例吧
-
繪製一個背景網格
// 繪製網格 grid for (let x = 0.5; x < 500; x += 10) { ctx.moveTo(x, 0); ctx.lineTo(x, 500) } for (let y = 0; y < 500; y += 10) { ctx.moveTo(0, y) ctx.lineTo(500, y) } ctx.strokeStyle = '#eee'; ctx.stroke(); -
畫兩條直線相交
// lines ctx.strokeStyle = 'gray'; ctx.lineWidth = 1; ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(51, 24) ctx.lineTo(314, 540) ctx.moveTo(477, 34) ctx.lineTo(86, 484) ctx.stroke(); -
繪製兩條線上的點
問題來了兩點確定一條直線怎麼知道線上的點的位置關係
兩點式公式
(y-y2)/(y1-y2) = (x-x2)/(x1-x2) -
求兩條直線上面的交點
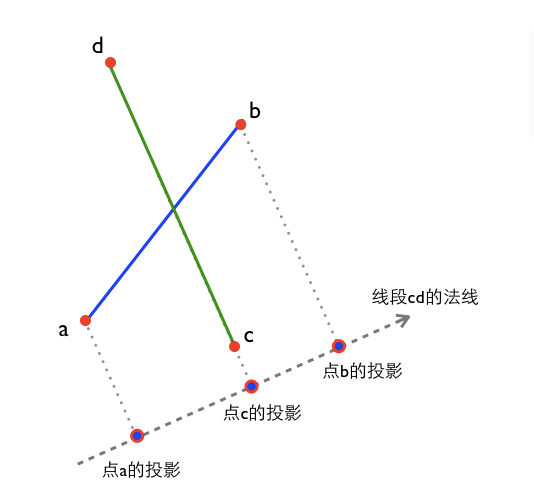
function segmentsIntr(a, b, c, d){ //線段ab的法線N1 let nx1 = (b.y - a.y), ny1 = (a.x - b.x); //線段cd的法線N2 let nx2 = (d.y - c.y), ny2 = (c.x - d.x); //兩條法線做叉乘, 如果結果為0, 說明線段ab和線段cd平行或共線,不相交 let denominator = nx1*ny2 - ny1*nx2; if (denominator==0) { return false; } //在法線N2上的投影 let distC_N2=nx2 * c.x + ny2 * c.y; let distA_N2=nx2 * a.x + ny2 * a.y-distC_N2; let distB_N2=nx2 * b.x + ny2 * b.y-distC_N2; // 點a投影和點b投影在點c投影同側 (對點在線段上的情況,本例當作不相交處理); if ( distA_N2*distB_N2>=0 ) { return false; } // //判斷點c點d 和線段ab的關係, 原理同上 // //在法線N1上的投影 let distA_N1=nx1 * a.x + ny1 * a.y; let distC_N1=nx1 * c.x + ny1 * c.y-distA_N1; let distD_N1=nx1 * d.x + ny1 * d.y-distA_N1; if ( distC_N1*distD_N1>=0 ) { return false; } //計算交點坐標 let fraction= distA_N2 / denominator; let dx= fraction * ny1, dy= -fraction * nx1; return { x: a.x + dx , y: a.y + dy }; } console.log(segmentsIntr({x: 51, y: 24}, {x: 314, y: 540}, {x: 477, y: 34}, {x: 86, y: 484}));上demo程式碼
// 兩點式公式 // (y-y2)/(y1-y2) = (x-x2)/(x1-x2)。 // 我們設y=200,可以求出x=140.7 ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(140.7,200) ctx.arc(140.7,200,5,0,2*Math.PI) // 設x=350,求右邊直線的y點 180.16 ctx.moveTo(350,180.16) ctx.arc(350,180.16,5,0,2*Math.PI) // 求原點坐標 ctx.moveTo(211.713,339.3166) ctx.arc(211.713,339.3166,5,0,2*Math.PI) ctx.fillStyle = 'red'; ctx.fill();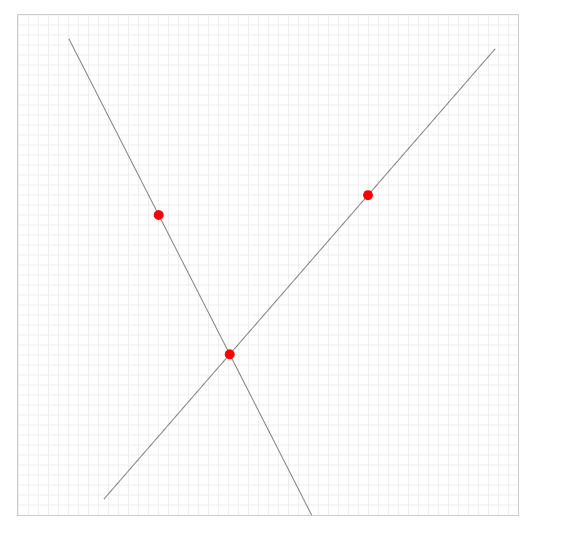
-
標記點的位置
ctx.font='14px Arial' ctx.beginPath() ctx.fillText("(x0,y0)",140.7+5,200+5) ctx.fillText("(x1,y1)",350+5,180.16+5) ctx.fillText("(x2,y2)",211.713+5,339.3166+5) -
畫
arcTo曲線// 編寫arcTo ctx.beginPath() ctx.lineWidth=3; ctx.moveTo(140.7,200) ctx.arcTo(211.713,339.3166,350,180.16,100) ctx.stroke()
-
問題又來了,我該怎麼求這個切點的坐標呢
唉,我這種菜雞都忘記啦…
我想出來的方法手動移動,我就不寫了,都忘光了
全部程式碼集合
let canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas') let ctx = canvas.getContext('2d'); // 繪製網格 grid for (let x = 0.5; x < 500; x += 10) { ctx.moveTo(x, 0); ctx.lineTo(x, 500) } for (let y = 0; y < 500; y += 10) { ctx.moveTo(0, y) ctx.lineTo(500, y) } ctx.strokeStyle = '#eee'; ctx.stroke(); // lines ctx.strokeStyle = 'gray'; ctx.lineWidth = 1; ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(51, 24) ctx.lineTo(314, 540) // k=(y2-y1)/(x2-x1) ctx.moveTo(477, 34) ctx.lineTo(86, 484) ctx.stroke(); // 原點 // 問題來了兩點確定一條直線怎麼知道線上的點的位置關係 // 兩點式公式 // (y-y2)/(y1-y2) = (x-x2)/(x1-x2)。 // 我們設y=200,可以求出x=140.7 ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(140.7,200) ctx.arc(140.7,200,5,0,2*Math.PI) // 設x=350,求右邊直線的y點 180.16 ctx.moveTo(350,180.16) ctx.arc(350,180.16,5,0,2*Math.PI) // 求原點坐標 ctx.moveTo(211.713,339.3166) ctx.arc(211.713,339.3166,5,0,2*Math.PI) ctx.fillStyle = 'red'; ctx.fill(); // 標記點的坐標 ctx.font='14px Arial' ctx.beginPath() ctx.fillText("(x0,y0)",140.7+5,200+5) ctx.fillText("(x1,y1)",211.713+5,339.3166+5) ctx.fillText("(x2,y2)",350+5,180.16+5) // 編寫arcTo ctx.beginPath() ctx.lineWidth=3; ctx.moveTo(140.7,200) ctx.arcTo(211.713,339.3166,350,180.16,100) ctx.stroke()這種輔助線有點複雜.那我們可以用簡單點的直線輔助線
相信大家已經很熟練了,直接上程式碼吧
ctx.strokeStyle = '#eee'; ctx.stroke(); // lines ctx.strokeStyle = 'gray'; ctx.lineWidth = 1; ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(81, 24) ctx.lineTo(81, 400) ctx.moveTo(400, 300) ctx.lineTo(40, 300) ctx.stroke(); // 原點 ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(81, 200) ctx.arc(81, 200, 5, 0, 2 * Math.PI) ctx.moveTo(220, 300) ctx.arc(220, 300, 5, 0, 2 * Math.PI) // 求原點坐標 ctx.moveTo(81, 300) ctx.arc(81, 300, 5, 0, 2 * Math.PI) ctx.fillStyle = 'red'; ctx.fill(); // 標記點的坐標 ctx.font = '14px Arial' ctx.beginPath() ctx.fillText("(x0,y0)", 81 + 5, 200 + 5) ctx.fillText("(x1,y1)", 81 + 5, 300 + 5) ctx.fillText("(x2,y2)", 220 + 5, 300 + 5) // 編寫arcTo ctx.beginPath() ctx.lineWidth = 3; ctx.moveTo(81, 200) ctx.arcTo(81, 300, 220, 300, 100) ctx.stroke()






