利用 esp8266 搭建簡單物聯網項目
接上一篇部落格,這次還是關於 esp8266 –> 物聯網
一、雲端數據監控:DHT11 + NodeMcu +Dweet.io
- 接上一篇部落格的接線及相關配置不變( DHT11 + NodeMcu )
- 配置 Dweet.io
Dweet.io 是一個可以通過非常簡易的方式為物聯網設備提供通訊服務(包括報警等)的雲端平台。它不需要任何的設置或註冊步驟,只要終端設備連接上互聯網,即可直接發布或訂閱數據。
通過 Dweet.io 提供的雲端服務,可以很方便的將感測器數據發布到在線平台並實時地進行遠程監控。
-
Dweeting(發送數據到雲端)
- 調用URL:
//dweet.io/dweet/for/my-thing-name?hello=world&foo=bar
- 調用URL:
-
Get Dweeting
- 獲取最新發布的 dweet :
//dweet.io/get/latest/dweet/for/my-thing-name - 獲取某個名字下所有的 dweets :
//dweet.io/get/dweets/for/my-thing-name
- 獲取最新發布的 dweet :
$ http -b "//dweet.io/get/dweets/for/rollingstarky"
{
"by": "getting",
"the": "dweets",
"this": "succeeded",
"with": [
{
"content": {
"foo": "bar",
"hello": "world"
},
"created": "2020-09-25T16:30:34.524Z",
"thing": "rollingstarky"
},
{
"content": {
"foo": "bar",
"hello": "world"
},
"created": "2020-09-25T16:10:46.694Z",
"thing": "rollingstarky"
}
]
}
- 項目程式碼
把上篇部落格的數據傳送到 Dweet.io 雲端平台
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include "DHT.h"
// WiFi parameters
const char* ssid = "wifi-name";
const char* password = "wifi-password";
#define DHTPIN 5
#define DHTTYPE DHT11
// Initialize DHT sensor
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE, 15);
const char* host = "dweet.io";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(10);
dht.begin();
// Connecting to a WiFi network
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(host);
// Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections
WiFiClient client;
const int httpPort = 80;
if (!client.connect(host, httpPort)) {
Serial.println("connection failed");
return;
}
// Reading temperature and humidity
float h = dht.readHumidity();
float t = dht.readTemperature();
while (isnan(h) || isnan(t)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
delay(2000);
// Get the measurements once more
h = dht.readHumidity();
t = dht.readTemperature();
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("The temperature and humidity are:");
Serial.println(t);
Serial.println(h);
// Send the request to the server
client.print(String("GET /dweet/for/rollingstarkyesp8266?temperature=") + String(t) + "&humidity=" + String(h) + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" +
"Host: " + host + "\r\n" +
"Connection: close\r\n\r\n");
unsigned long timeout = millis();
while (client.available() == 0) {
if (millis() - timeout > 5000) {
Serial.println(">>> Client Timeout !");
client.stop();
return;
}
}
// Read all the lines of the reply from server and print them to Serial
while(client.available()){
String line = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.print(line);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("closing connection");
Serial.println();
// Repeat every 10 seconds
delay(10000);
}
- 訪問最新更新的數據:
//dweet.io/get/latest/dweet/for/rollingstarkyesp8266
{“this”:”succeeded”,”by”:”getting”,”the”:”dweets”,”with”:[{“thing”:”rollingstarkyesp8266″,”created”:”2020-09-25T09:27:22.823Z”,”content”:{“temperature”:28,”humidity”:61}}]}
- 訪問全部數據:
//dweet.io/get/dweets/for/rollingstarkyesp8266
{“this”:”succeeded”,”by”:”getting”,”the”:”dweets”,”with”:[{“thing”:”rollingstarkyesp8266″,”created”:”2020-09-25T09:17:04.292Z”,”content”:{“temperature”:27.9,”humidity”:58}},{“thing”:”rollingstarkyesp8266″,”created”:”2020-09-25T09:15:08.961Z”,”content”:{“temperature”:27.9,”humidity”:59}},{“thing”:”rollingstarkyesp8266″,”created”:”2020-09-25T09:13:16.383Z”,”content”:{“temperature”:27.9,”humidity”:58}},{“thing”:”rollingstarkyesp8266″,”created”:”2020-09-25T09:11:30.363Z”,”content”:{“temperature”:27.9,”humidity”:57}},{“thing”:”rollingstarkyesp8266″,”created”:”2020-09-25T09:09:43.309Z”,”content”:{“temperature”:27.9,”humidity”:57}}]}
- 訪問可視化圖表:
//dweet.io/follow/rollingstarkyesp8266- 這裡有點見鬼,出不來,單數據應該是都到雲端了,可以查到 Json 數據(假裝有圖有真相)
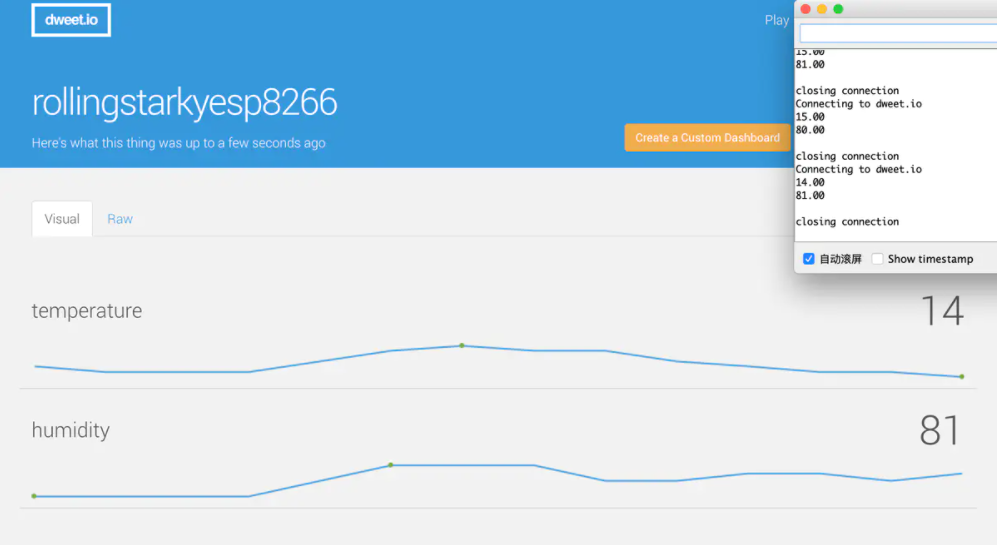
- 這裡有點見鬼,出不來,單數據應該是都到雲端了,可以查到 Json 數據(假裝有圖有真相)
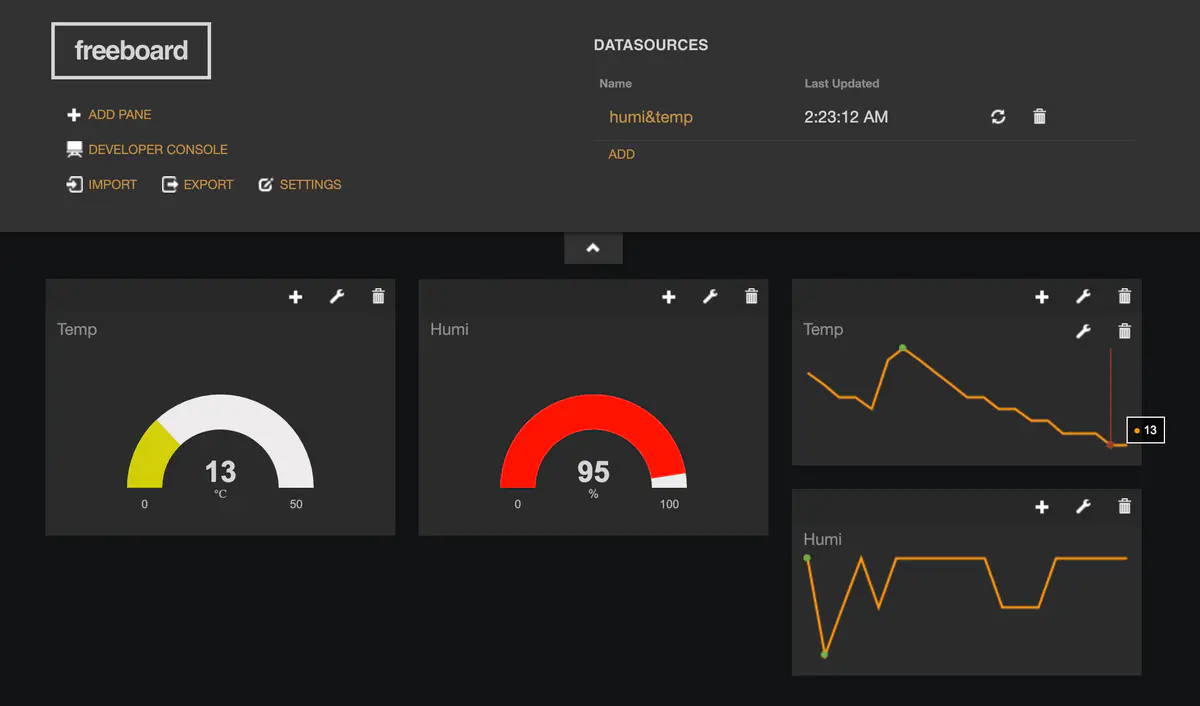
- 鏈接 freeboard 平台(儀錶盤)
- 註冊
- 懂點英語,稍微摸索一下
二、遠程控制物聯網設備:NodeMcu + PubSubClient + aREST
1.準備工具
- aREST 庫
aREST 框架可以為一些常見的嵌入式開發板提供 RESTful 介面,支援通過串口、Wi-Fi、乙太網、藍牙等硬體發送命令至開發板,激發特定的操作,並將數據以 JSON 的格式返回給控制端用戶
- PubSubClient 庫
- 源程式碼
// Import required libraries
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#include <aREST.h>
// Clients
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient client(espClient);
// Create aREST instance
aREST rest = aREST(client);
// Unique ID to identify the device for cloud.arest.io
char* device_id = "wuwu380";
// WiFi parameters
const char* ssid = "wifi-name";
const char* password = "wifi-password";
// Callback functions
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length);
void setup(void)
{
// Start Serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// Set callback
client.setCallback(callback);
// Give name and ID to device
rest.set_id(device_id);
rest.set_name("devices_control");
// Connect to WiFi
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
// Set output topic
char* out_topic = rest.get_topic();
}
void loop() {
// Connect to the cloud
rest.handle(client);
}
// Handles message arrived on subscribed topic(s)
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
rest.handle_callback(client, topic, payload, length);
}
- 運行結果
$ http -b //cloud.arest.io/wuwu380/name
{
“connected”: true,
“hardware”: “esp8266”,
“id”: “wuwu380”,
“name”: “devices_control”,
“variables”: {}
}
$ http -b //cloud.arest.io/wuwu380/mode/5/o
{
“connected”: true,
“hardware”: “esp8266”,
“id”: “wuwu380”,
“message”: “Pin D5 set to output”,
“name”: “devices_control”
}
$ http -b //cloud.arest.io/wuwu380/digital/5/1
{
“connected”: true,
“hardware”: “esp8266”,
“id”: “wuwu380”,
“message”: “Pin D5 set to 1”,
“name”: “devices_control”
}
三、 esp8266 連接 OLED 屏,製作天氣時鐘
我一開始就想做這個了,一開始當成終極目標,現在看看,九折水瓶 😃
- 必要組件
- U8G2 螢幕驅動庫
- 可以去 Ardunio 下載,也可以把 U8g2.rar 解壓到 libraries 文件夾
- 接線
| OLED | NodeMcu |
| : – : | : – : |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3V3/5V |
| SCL | D1 |
| SDA | D2 |
- 載入程式
文件 – 示例 – U8G2 – full_buffer – 任意打開一個,去除下行程式碼的注釋
U8G2_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_F_SW_I2C u8g2(U8G2_R0, /* clock=*/ SCL, /* data=*/ SDA, /* reset=*/ U8X8_PIN_NONE); // All Boards without Reset of the Display
寫入程式

一切的學習,都是從 hello world 開始的[Doge]




