Mybaits 源碼解析 (四)—– SqlSession的創建過程(看懂框架源碼再也不用死記硬背面試題)
- 2019 年 10 月 30 日
- 筆記
SqlSession是mybatis的核心介面之一,是myabtis介面層的主要組成部分,對外提供了mybatis常用的api。myabtis提供了兩個SqlSesion介面的實現,常用的實現類是DefaultSqlSession。它相當於一個資料庫連接對象,在一個SqlSession中可以執行多條SQL語句。
創建SqlSession
前面的兩篇文章我們已經得到了SqlSessionFactory,那麼SqlSession將由SqlSessionFactory進行創建。
SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
我們就來看看這個SqlSessionFactory的 openSession方法是如何創建SqlSession對象的。根據上面的分析,這裡的SqlSessionFactory類型對象其實是一個DefaultSqlSessionFactory對象,因此,需要到DefaultSqlSessionFactory類中去看openSession方法。
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); }
調用了openSessionFromDataSource方法,並且第一個參數獲取了默認的執行器類型,第二個參數為null,第三個參數為false,看看這個默認的執行器類型是啥
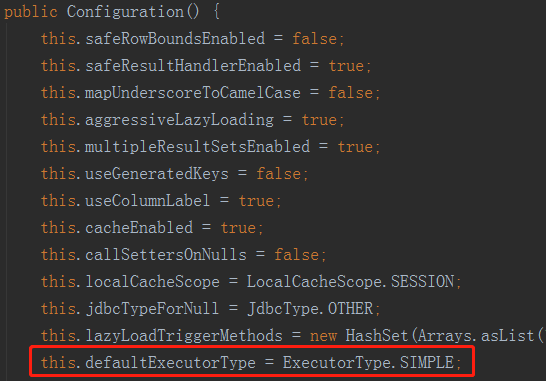
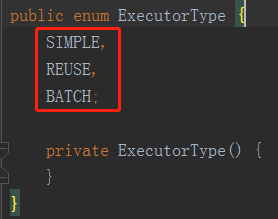
默認的執行器類型SIMPLE,我們跟進openSessionFromDataSource方法
/** * ExecutorType 指定Executor的類型,分為三種:SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH,默認使用的是SIMPLE * TransactionIsolationLevel 指定事務隔離級別,使用null,則表示使用資料庫默認的事務隔離界別 * autoCommit 是否自動提交,傳過來的參數為false,表示不自動提交 */ private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { // 獲取配置中的環境資訊,包括了數據源資訊、事務等 final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 創建事務工廠 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); // 創建事務,配置事務屬性 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 創建Executor,即執行器 // 它是真正用來Java和資料庫交互操作的類,後面會展開說。 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); // 創建DefaultSqlSession對象返回,其實現了SqlSession介面 return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
主要包含以下幾個步驟:
- 首先從configuration獲取Environment對象,裡面主要包含了DataSource和TransactionFactory對象
- 創建TransactionFactory
- 創建Transaction
- 從configuration獲取Executor
- 構造DefaultSqlSession對象
我們先來看看常規的environment配置
//配置environment環境 <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> /** 事務配置 type= JDBC、MANAGED * 1.JDBC:這個配置直接簡單使用了JDBC的提交和回滾設置。它依賴於從數據源得到的連接來管理事務範圍。 * 2.MANAGED:這個配置幾乎沒做什麼。它從來不提交或回滾一個連接。 */ <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> /** 數據源類型:type = UNPOOLED、POOLED、JNDI * 1.UNPOOLED:這個數據源的實現是每次被請求時簡單打開和關閉連接。 * 2.POOLED:這是JDBC連接對象的數據源連接池的實現。 * 3.JNDI:這個數據源的實現是為了使用如Spring或應用伺服器這類的容器 */ <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xhm" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="root" /> //默認連接事務隔離級別 <property name="defaultTransactionIsolationLevel" value=""/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
還記得前面文章是怎麼解析environments的嗎,Mybaits 源碼解析 (二)—– 根據配置文件創建SqlSessionFactory(Configuration的創建過程),我們簡單的回顧一下
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { if (environment == null) { // 獲取 default 屬性 environment = context.getStringAttribute("default"); } for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) { // 獲取 id 屬性 String id = child.getStringAttribute("id"); /* * 檢測當前 environment 節點的 id 與其父節點 environments 的屬性 default * 內容是否一致,一致則返回 true,否則返回 false * 將其default屬性值與子元素environment的id屬性值相等的子元素設置為當前使用的Environment對象 */ if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) { // 將environment中的transactionManager標籤轉換為TransactionFactory對象 TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager")); // 將environment中的dataSource標籤轉換為DataSourceFactory對象 DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource")); // 創建 DataSource 對象 DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource(); Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id) .transactionFactory(txFactory) .dataSource(dataSource); // 構建 Environment 對象,並設置到 configuration 中 configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build()); } } } } private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type"); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); //通過別名獲取Class,並實例化 TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory)this.resolveClass(type).newInstance(); factory.setProperties(props); return factory; } else { throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory."); } } private DataSourceFactory dataSourceElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type"); //通過別名獲取Class,並實例化 Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); DataSourceFactory factory = (DataSourceFactory)this.resolveClass(type).newInstance(); factory.setProperties(props); return factory; } else { throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a DataSourceFactory."); } }
獲取TransactionFactory
我們的environment配置中transactionManager type=”JDBC”和dataSource type=”POOLED”,則生成的transactionManager為JdbcTransactionFactory,DataSourceFactory為PooledDataSourceFactory
我們回到openSessionFromDataSource,接著看看getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment方法
private TransactionFactory getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environment environment) { return (TransactionFactory)(environment != null && environment.getTransactionFactory() != null ? environment.getTransactionFactory() : new ManagedTransactionFactory()); }
創建Transaction
很明顯 environment.getTransactionFactory() 就是JdbcTransactionFactory,看看這個工廠是如何創建Transaction的
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit); }
直接通過工廠方法創建了一個JdbcTransaction對象,並傳參DataSource ,事務隔離級別null,自動提交false三個參數,我們來看看JdbcTransaction
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction { //資料庫連接對象 protected Connection connection; //資料庫DataSource protected DataSource dataSource; //資料庫隔離級別 protected TransactionIsolationLevel level; //是否自動提交 protected boolean autoCommmit; public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) { //設置dataSource和隔離級別,是否自動提交屬性 //這裡隔離級別傳過來的是null,表示使用資料庫默認隔離級別,自動提交為false,表示不自動提交 this.dataSource = ds; this.level = desiredLevel; this.autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit; } public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { if (this.connection == null) { this.openConnection(); } return this.connection; } //提交功能是通過Connection去完成的 public void commit() throws SQLException { if (this.connection != null && !this.connection.getAutoCommit()) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]"); } this.connection.commit(); } } //回滾功能是通過Connection去完成的 public void rollback() throws SQLException { if (this.connection != null && !this.connection.getAutoCommit()) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]"); } this.connection.rollback(); } } //關閉功能是通過Connection去完成的 public void close() throws SQLException { if (this.connection != null) { this.resetAutoCommit(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]"); } this.connection.close(); } } //獲取連接是通過dataSource來完成的 protected void openConnection() throws SQLException { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection"); } this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection(); if (this.level != null) { this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel()); } this.setDesiredAutoCommit(this.autoCommmit); } }
JdbcTransaction主要維護了一個默認autoCommit為false的Connection對象,對事物的提交,回滾,關閉等都是接見通過Connection完成的。
創建Executor
//創建一個執行器,默認是SIMPLE public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; //根據executorType來創建相應的執行器,Configuration默認是SIMPLE if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { //創建SimpleExecutor實例,並且包含Configuration和transaction屬性 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } //如果要求快取,生成另一種CachingExecutor,裝飾者模式,默認都是返回CachingExecutor /** * 二級快取開關配置示例 * <settings> * <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> * </settings> */ if (cacheEnabled) { //CachingExecutor使用裝飾器模式,將executor的功能添加上了二級快取的功能,二級快取會單獨文章來講 executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } //此處調用插件,通過插件可以改變Executor行為,此處我們後面單獨文章講 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
executor包含了Configuration和剛剛創建的Transaction,默認的執行器為SimpleExecutor,如果開啟了二級快取(默認開啟),則CachingExecutor會包裝SimpleExecutor,然後依次調用攔截器的plugin方法返回一個被代理過的Executor對象。
CachingExecutor 對象裡面包含了剛創建的SimpleExecutor,後面文章我們會及具體講這個類
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor { private Executor delegate; private TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager(); public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) { this.delegate = delegate; delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this); } //略 }
構造DefaultSqlSession對象
new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
傳參configuration和剛生成的executor,我們來簡單看看
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession { /** * mybatis全局配置新 */ private final Configuration configuration; /** * SQL執行器 */ private final Executor executor; /** * 是否自動提交 */ private final boolean autoCommit; private List<Cursor<?>> cursorList; public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) { this.configuration = configuration; this.executor = executor; this.dirty = false; this.autoCommit = autoCommit; } @Override public <T> T selectOne(String statement) { return this.<T>selectOne(statement, null); } @Override public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) { // Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many. List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter); if (list.size() == 1) { return list.get(0); } else if (list.size() > 1) { throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size()); } else { return null; } } @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) { return this.selectList(statement, null); } @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) { return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT); } @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } //略....update等方法 }
SqlSession的所有查詢介面最後都歸結位Exector的方法調用。後面文章我們來分析其調用流程


