Mybaits 源碼解析 (二)—– 根據配置文件創建SqlSessionFactory(Configuration的創建過程)
- 2019 年 10 月 28 日
- 筆記
我們使用mybatis操作資料庫都是通過SqlSession的API調用,而創建SqlSession是通過SqlSessionFactory。下面我們就看看SqlSessionFactory的創建過程。
配置文件解析入口
我們看看第一篇文章中的測試方法
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; 3 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); 4 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); 5 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); 6 try { 7 Employee employeeMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Employee.class); 8 List<Employee> all = employeeMapper.getAll(); 9 for (Employee item : all) 10 System.out.println(item); 11 } finally { 12 sqlSession.close(); 13 } 14 }
首先,我們使用 MyBatis 提供的工具類 Resources 載入配置文件,得到一個輸入流。然後再通過 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 對象的build方法構建 SqlSessionFactory 對象。所以這裡的 build 方法是我們分析配置文件解析過程的入口方法。我們看看build裡面是程式碼:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { // 調用重載方法 return build(inputStream, null, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { try { // 創建配置文件解析器 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); // 調用 parser.parse() 方法解析配置文件,生成 Configuration 對象 return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } } public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { // 創建 DefaultSqlSessionFactory,將解析配置文件後生成的Configuration傳入 return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }
SqlSessionFactory是通過SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法創建的,build方法內部是通過一個XMLConfigBuilder對象解析mybatis-config.xml文件生成一個Configuration對象。XMLConfigBuilder從名字可以看出是解析Mybatis配置文件的,其實它是繼承了一個父類BaseBuilder,其每一個子類多是以XMLXXXXXBuilder命名的,也就是其子類都對應解析一種xml文件或xml文件中一種元素。
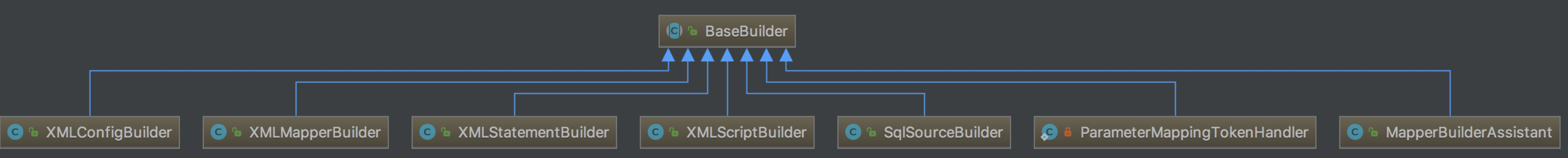
我們看看XMLConfigBuilder的構造方法:
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) { super(new Configuration()); ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration"); this.configuration.setVariables(props); this.parsed = false; this.environment = environment; this.parser = parser; }
可以看到調用了父類的構造方法,並傳入一個new Configuration()對象,這個對象也就是最終的Mybatis配置對象
我們先來看看其基類BaseBuilder
public abstract class BaseBuilder { protected final Configuration configuration; protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry; protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry; public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry(); this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); } .... }
BaseBuilder中只有三個成員變數,而typeAliasRegistry和typeHandlerRegistry都是直接從Configuration的成員變數獲得的,接著我們看看Configuration這個類
Configuration類位於mybatis包的org.apache.ibatis.session目錄下,其屬性就是對應於mybatis的全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml的配置,將XML配置中的內容解析賦值到Configuration對象中。
由於XML配置項有很多,所以Configuration類的屬性也很多。先來看下Configuration對於的XML配置文件示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <!-- 全局配置頂級節點 --> <configuration> <!-- 屬性配置,讀取properties中的配置文件 --> <properties resource="db.propertis"> <property name="XXX" value="XXX"/> </properties> <!-- 類型別名 --> <typeAliases> <!-- 在用到User類型的時候,可以直接使用別名,不需要輸入User類的全部路徑 --> <typeAlias type="com.luck.codehelp.entity.User" alias="user"/> </typeAliases> <!-- 類型處理器 --> <typeHandlers> <!-- 類型處理器的作用是完成JDBC類型和java類型的轉換,mybatis默認已經由了很多類型處理器,正常無需自定義--> </typeHandlers> <!-- 對象工廠 --> <!-- mybatis創建結果對象的新實例時,會通過對象工廠來完成,mybatis有默認的對象工廠,正常無需配置 --> <objectFactory type=""></objectFactory> <!-- 插件 --> <plugins> <!-- 可以自定義攔截器通過plugin標籤加入 --> <plugin interceptor="com.lucky.interceptor.MyPlugin"></plugin> </plugins> <!-- 全局配置參數 --> <settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="false" /> <setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true" /><!-- 是否自動生成主鍵 --> <setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="REUSE" /> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/><!-- 延遲載入標識 --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="true"/><!--有延遲載入屬性的對象是否延遲載入 --> <setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/><!-- 是否允許單個語句返回多個結果集 --> <setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/><!-- 使用列標籤而不是列名 --> <setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/><!-- 指定mybatis如何自動映射列到欄位屬性;NONE:自動映射;PARTIAL:只會映射結果沒有嵌套的結果;FULL:可以映射任何複雜的結果 --> <setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/><!-- 默認執行器類型 --> <setting name="defaultFetchSize" value=""/> <setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="5"/><!-- 驅動等待資料庫相應的超時時間 ,單位是秒--> <setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/><!-- 是否允許使用嵌套語句RowBounds --> <setting name="safeResultHandlerEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/><!-- 下劃線列名是否自動映射到駝峰屬性:如user_id映射到userId --> <setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/><!-- 本地快取(session是會話級別) --> <setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/><!-- 數據為空值時,沒有特定的JDBC類型的參數的JDBC類型 --> <setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/><!-- 指定觸發延遲載入的對象的方法 --> <setting name="callSettersOnNulls" value="false"/><!--如果setter方法或map的put方法,如果檢索到的值為null時,數據是否有用 --> <setting name="logPrefix" value="XXXX"/><!-- mybatis日誌文件前綴字元串 --> <setting name="logImpl" value="SLF4J"/><!-- mybatis日誌的實現類 --> <setting name="proxyFactory" value="CGLIB"/><!-- mybatis代理工具 --> </settings> <!-- 環境配置集合 --> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/><!-- 事務管理器 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"><!-- 資料庫連接池 --> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="root" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!-- mapper文件映射配置 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/luck/codehelp/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
而對於XML的配置,Configuration類的屬性是和XML配置對應的。Configuration類屬性如下:
public class Configuration { protected Environment environment;//運行環境 protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled = false; protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true; protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase = false; protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading = true; //true:有延遲載入屬性的對象被調用時完全載入任意屬性;false:每個屬性按需要載入 protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;//是否允許多種結果集從一個單獨的語句中返回 protected boolean useGeneratedKeys = false;//是否支援自動生成主鍵 protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;//是否使用列標籤 protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;//是否使用快取標識 protected boolean callSettersOnNulls = false;// protected boolean useActualParamName = true; protected String logPrefix; protected Class <? extends Log> logImpl; protected Class <? extends VFS> vfsImpl; protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION; protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER; protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" })); protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout; protected Integer defaultFetchSize; protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE; protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;//指定mybatis如果自動映射列到欄位和屬性,PARTIAL會自動映射簡單的沒有嵌套的結果,FULL會自動映射任意複雜的結果 protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE; protected Properties variables = new Properties(); protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory(); protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory(); protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory(); protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;//是否延時載入,false則表示所有關聯對象即使載入,true表示延時載入 protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); // #224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL protected String databaseId; protected Class<?> configurationFactory; protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this); protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain(); protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry(); protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry(); protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry(); protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection"); protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<Cache>("Caches collection"); protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection"); protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<ParameterMap>("Parameter Maps collection"); protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<KeyGenerator>("Key Generators collection"); protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<String>(); //已經載入過的resource(mapper) protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<XNode>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers"); protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<XMLStatementBuilder>(); protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<CacheRefResolver>(); protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<ResultMapResolver>(); protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<MethodResolver>(); protected final Map<String, String> cacheRefMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); //其他方法略 }
載入的過程是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder根據xml配置的文件流,通過XMLConfigBuilder的parse方法進行解析得到一個Configuration對象,我們再看看其構造函數
1 public Configuration() { 2 this.safeRowBoundsEnabled = false; 3 this.safeResultHandlerEnabled = true; 4 this.mapUnderscoreToCamelCase = false; 5 this.aggressiveLazyLoading = true; 6 this.multipleResultSetsEnabled = true; 7 this.useGeneratedKeys = false; 8 this.useColumnLabel = true; 9 this.cacheEnabled = true; 10 this.callSettersOnNulls = false; 11 this.localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION; 12 this.jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER; 13 this.lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet(Arrays.asList("equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString")); 14 this.defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE; 15 this.autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL; 16 this.autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE; 17 this.variables = new Properties(); 18 this.reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory(); 19 this.objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory(); 20 this.objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory(); 21 this.mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this); 22 this.lazyLoadingEnabled = false; 23 this.proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); 24 this.interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain(); 25 this.typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry(); 26 this.typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry(); 27 this.languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry(); 28 this.mappedStatements = new Configuration.StrictMap("Mapped Statements collection"); 29 this.caches = new Configuration.StrictMap("Caches collection"); 30 this.resultMaps = new Configuration.StrictMap("Result Maps collection"); 31 this.parameterMaps = new Configuration.StrictMap("Parameter Maps collection"); 32 this.keyGenerators = new Configuration.StrictMap("Key Generators collection"); 33 this.loadedResources = new HashSet(); 34 this.sqlFragments = new Configuration.StrictMap("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers"); 35 this.incompleteStatements = new LinkedList(); 36 this.incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList(); 37 this.incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList(); 38 this.incompleteMethods = new LinkedList(); 39 this.cacheRefMap = new HashMap(); 40 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class); 41 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class); 42 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class); 43 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class); 44 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class); 45 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class); 46 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class); 47 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class); 48 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class); 49 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class); 50 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class); 51 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class); 52 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class); 53 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class); 54 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class); 55 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class); 56 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class); 57 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class); 58 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class); 59 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class); 60 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class); 61 this.typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class); 62 this.languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class); 63 this.languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class); 64 }
我們看到第26行this.typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();,並且第40到61行向 typeAliasRegistry 註冊了很多別名,我們看看TypeAliasRegistry
public class TypeAliasRegistry { private final Map<String, Class<?>> TYPE_ALIASES = new HashMap(); public TypeAliasRegistry() { this.registerAlias("string", String.class); this.registerAlias("byte", Byte.class); this.registerAlias("long", Long.class); this.registerAlias("short", Short.class); this.registerAlias("int", Integer.class); this.registerAlias("integer", Integer.class); this.registerAlias("double", Double.class); this.registerAlias("float", Float.class); this.registerAlias("boolean", Boolean.class); this.registerAlias("byte[]", Byte[].class); this.registerAlias("long[]", Long[].class); this.registerAlias("short[]", Short[].class); this.registerAlias("int[]", Integer[].class); this.registerAlias("integer[]", Integer[].class); this.registerAlias("double[]", Double[].class); this.registerAlias("float[]", Float[].class); this.registerAlias("boolean[]", Boolean[].class); this.registerAlias("_byte", Byte.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_long", Long.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_short", Short.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_int", Integer.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_integer", Integer.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_double", Double.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_float", Float.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_boolean", Boolean.TYPE); this.registerAlias("_byte[]", byte[].class); this.registerAlias("_long[]", long[].class); this.registerAlias("_short[]", short[].class); this.registerAlias("_int[]", int[].class); this.registerAlias("_integer[]", int[].class); this.registerAlias("_double[]", double[].class); this.registerAlias("_float[]", float[].class); this.registerAlias("_boolean[]", boolean[].class); this.registerAlias("date", Date.class); this.registerAlias("decimal", BigDecimal.class); this.registerAlias("bigdecimal", BigDecimal.class); this.registerAlias("biginteger", BigInteger.class); this.registerAlias("object", Object.class); this.registerAlias("date[]", Date[].class); this.registerAlias("decimal[]", BigDecimal[].class); this.registerAlias("bigdecimal[]", BigDecimal[].class); this.registerAlias("biginteger[]", BigInteger[].class); this.registerAlias("object[]", Object[].class); this.registerAlias("map", Map.class); this.registerAlias("hashmap", HashMap.class); this.registerAlias("list", List.class); this.registerAlias("arraylist", ArrayList.class); this.registerAlias("collection", Collection.class); this.registerAlias("iterator", Iterator.class); this.registerAlias("ResultSet", ResultSet.class); } public void registerAliases(String packageName) { this.registerAliases(packageName, Object.class); } //略 }
其實TypeAliasRegistry裡面有一個HashMap,並且在TypeAliasRegistry的構造器中註冊很多別名到這個hashMap中,好了,到現在我們只是創建了一個 XMLConfigBuilder,在其構造器中我們創建了一個 Configuration 對象,接下來我們看看將mybatis-config.xml解析成Configuration中對應的屬性,也就是parser.parse()方法:
XMLConfigBuilder
1 public Configuration parse() { 2 if (parsed) { 3 throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); 4 } 5 parsed = true; 6 // 解析配置 7 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); 8 return configuration; 9 }
我們看看第7行,注意一個 xpath 表達式 – /configuration。這個表達式代表的是 MyBatis 的<configuration/>標籤,這裡選中這個標籤,並傳遞給parseConfiguration方法。我們繼續跟下去。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { // 解析 properties 配置 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); // 解析 settings 配置,並將其轉換為 Properties 對象 Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); // 載入 vfs loadCustomVfs(settings); // 解析 typeAliases 配置 typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); // 解析 plugins 配置 pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); // 解析 objectFactory 配置 objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); // 解析 objectWrapperFactory 配置 objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); // 解析 reflectorFactory 配置 reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); // settings 中的資訊設置到 Configuration 對象中 settingsElement(settings); // 解析 environments 配置 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); // 解析 databaseIdProvider,獲取並設置 databaseId 到 Configuration 對象 databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); // 解析 typeHandlers 配置 typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); // 解析 mappers 配置 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
解析 properties 配置
先來看一下 properties 節點的配置內容。如下:
<properties resource="db.properties"> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123456"/> </properties>
我為 properties 節點配置了一個 resource 屬性,以及兩個子節點。接著我們看看propertiesElement的邏輯
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { // 解析 propertis 的子節點,並將這些節點內容轉換為屬性對象 Properties Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 獲取 propertis 節點中的 resource 和 url 屬性值 String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = context.getStringAttribute("url"); // 兩者都不用空,則拋出異常 if (resource != null && url != null) { throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other."); } if (resource != null) { // 從文件系統中載入並解析屬性文件 defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource)); } else if (url != null) { // 通過 url 載入並解析屬性文件 defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url)); } Properties vars = configuration.getVariables(); if (vars != null) { defaults.putAll(vars); } parser.setVariables(defaults); // 將屬性值設置到 configuration 中 configuration.setVariables(defaults); } } public Properties getChildrenAsProperties() { //創建一個Properties對象 Properties properties = new Properties(); // 獲取並遍歷子節點 for (XNode child : getChildren()) { // 獲取 property 節點的 name 和 value 屬性 String name = child.getStringAttribute("name"); String value = child.getStringAttribute("value"); if (name != null && value != null) { // 設置屬性到屬性對象中 properties.setProperty(name, value); } } return properties; } // -☆- XNode public List<XNode> getChildren() { List<XNode> children = new ArrayList<XNode>(); // 獲取子節點列表 NodeList nodeList = node.getChildNodes(); if (nodeList != null) { for (int i = 0, n = nodeList.getLength(); i < n; i++) { Node node = nodeList.item(i); if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { children.add(new XNode(xpathParser, node, variables)); } } } return children; }
解析properties主要分三個步驟:
- 解析 properties 節點的子節點,並將解析結果設置到 Properties 對象中。
- 從文件系統或通過網路讀取屬性配置,這取決於 properties 節點的 resource 和 url 是否為空。
- 將解析出的屬性對象設置到 XPathParser 和 Configuration 對象中。
需要注意的是,propertiesElement 方法是先解析 properties 節點的子節點內容,後再從文件系統或者網路讀取屬性配置,並將所有的屬性及屬性值都放入到 defaults 屬性對象中。這就會存在同名屬性覆蓋的問題,也就是從文件系統,或者網路上讀取到的屬性及屬性值會覆蓋掉 properties 子節點中同名的屬性和及值。
解析 settings 配置
settings 節點的解析過程
下面先來看一個settings比較簡單的配置,如下:
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/> </settings>
接著來看看settingsAsProperties
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) { if (context == null) { return new Properties(); } // 獲取 settings 子節點中的內容,解析成Properties,getChildrenAsProperties 方法前面已分析過 Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 創建 Configuration 類的“元資訊”對象 MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory); for (Object key : props.keySet()) { // 檢測 Configuration 中是否存在相關屬性,不存在則拋出異常 if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) { throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive)."); } } return props; }
設置 settings 配置到 Configuration 中
接著我們看看將 settings 配置設置到 Configuration 對象中的過程。如下:
private void settingsElement(Properties props) throws Exception { // 設置 autoMappingBehavior 屬性,默認值為 PARTIAL configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL"))); configuration.setAutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior(AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior", "NONE"))); // 設置 cacheEnabled 屬性,默認值為 true configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true)); // 省略部分程式碼 // 解析默認的枚舉處理器 Class<? extends TypeHandler> typeHandler = (Class<? extends TypeHandler>)resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultEnumTypeHandler")); // 設置默認枚舉處理器 configuration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(typeHandler); configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false)); configuration.setUseActualParamName(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useActualParamName"), true)); // 省略部分程式碼 }
上面程式碼處理調用 Configuration 的 setter 方法
解析 typeAliases 配置
在 MyBatis 中,可以為我們自己寫的有些類定義一個別名。這樣在使用的時候,我們只需要輸入別名即可,無需再把全限定的類名寫出來。在 MyBatis 中,我們有兩種方式進行別名配置。第一種是僅配置包名,讓 MyBatis 去掃描包中的類型,並根據類型得到相應的別名
<typeAliases> <package name="com.mybatis.model"/> </typeAliases>
第二種方式是通過手動的方式,明確為某個類型配置別名。這種方式的配置如下:
<typeAliases> <typeAlias alias="employe" type="com.mybatis.model.Employe" /> <typeAlias type="com.mybatis.model.User" /> </typeAliases>
下面我們來看一下兩種不同的別名配置是怎樣解析的。程式碼如下:
XMLConfigBuilder
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { // 從指定的包中解析別名和類型的映射 if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage); // 從 typeAlias 節點中解析別名和類型的映射 } else { // 獲取 alias 和 type 屬性值,alias 不是必填項,可為空 String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias"); String type = child.getStringAttribute("type"); try { // 載入 type 對應的類型 Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type); // 註冊別名到類型的映射 if (alias == null) { typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz); } else { typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e); } } } } }
我們看到通過包掃描和手動註冊時通過子節點名稱是否package來判斷的
從 typeAlias 節點中解析並註冊別名
在別名的配置中,type屬性是必須要配置的,而alias屬性則不是必須的。
private final Map<String, Class<?>> TYPE_ALIASES = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>(); public void registerAlias(Class<?> type) { // 獲取全路徑類名的簡稱 String alias = type.getSimpleName(); Alias aliasAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(Alias.class); if (aliasAnnotation != null) { // 從註解中取出別名 alias = aliasAnnotation.value(); } // 調用重載方法註冊別名和類型映射 registerAlias(alias, type); } public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) { if (alias == null) { throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null"); } // 將別名轉成小寫 String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH); /* * 如果 TYPE_ALIASES 中存在了某個類型映射,這裡判斷當前類型與映射中的類型是否一致, * 不一致則拋出異常,不允許一個別名對應兩種類型 */ if (TYPE_ALIASES.containsKey(key) && TYPE_ALIASES.get(key) != null && !TYPE_ALIASES.get(key).equals(value)) { throw new TypeException( "The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + TYPE_ALIASES.get(key).getName() + "'."); } // 快取別名到類型映射 TYPE_ALIASES.put(key, value); }
若用戶為明確配置 alias 屬性,MyBatis 會使用類名的小寫形式作為別名。比如,全限定類名com.mybatis.model.User的別名為user。若類中有@Alias註解,則從註解中取值作為別名。
從指定的包中解析並註冊別名
public void registerAliases(String packageName) { registerAliases(packageName, Object.class); } public void registerAliases(String packageName, Class<?> superType) { ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<Class<?>>(); /* * 查找包下的父類為 Object.class 的類。 * 查找完成後,查找結果將會被快取到resolverUtil的內部集合中。 */ resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName); // 獲取查找結果 Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> typeSet = resolverUtil.getClasses(); for (Class<?> type : typeSet) { // 忽略匿名類,介面,內部類 if (!type.isAnonymousClass() && !type.isInterface() && !type.isMemberClass()) { // 為類型註冊別名 registerAlias(type); } } }
主要分為兩個步驟:
- 查找指定包下的所有類
- 遍歷查找到的類型集合,為每個類型註冊別名
我們看看查找指定包下的所有類
private Set<Class<? extends T>> matches = new HashSet(); public ResolverUtil<T> find(ResolverUtil.Test test, String packageName) { //將包名轉換成文件路徑 String path = this.getPackagePath(packageName); try { //通過 VFS(虛擬文件系統)獲取指定包下的所有文件的路徑名,比如com/mybatis/model/Employe.class List<String> children = VFS.getInstance().list(path); Iterator i$ = children.iterator(); while(i$.hasNext()) { String child = (String)i$.next(); //以.class結尾的文件就加入到Set集合中 if (child.endsWith(".class")) { this.addIfMatching(test, child); } } } catch (IOException var7) { log.error("Could not read package: " + packageName, var7); } return this; } protected String getPackagePath(String packageName) { //將包名轉換成文件路徑 return packageName == null ? null : packageName.replace('.', '/'); } protected void addIfMatching(ResolverUtil.Test test, String fqn) { try { //將路徑名轉成全限定的類名,通過類載入器載入類名,比如com.mybatis.model.Employe.class String externalName = fqn.substring(0, fqn.indexOf(46)).replace('/', '.'); ClassLoader loader = this.getClassLoader(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Checking to see if class " + externalName + " matches criteria [" + test + "]"); } Class<?> type = loader.loadClass(externalName); if (test.matches(type)) { //加入到matches集合中 this.matches.add(type); } } catch (Throwable var6) { log.warn("Could not examine class '" + fqn + "'" + " due to a " + var6.getClass().getName() + " with message: " + var6.getMessage()); } }
主要有以下幾步:
- 通過 VFS(虛擬文件系統)獲取指定包下的所有文件的路徑名,比如 com/mybatis/model/Employe.class
- 篩選以
.class結尾的文件名 - 將路徑名轉成全限定的類名,通過類載入器載入類名
- 對類型進行匹配,若符合匹配規則,則將其放入內部集合中
這裡我們要注意,在前面我們分析Configuration對象的創建時,就已經默認註冊了很多別名,可以回到文章開頭看看。
解析 plugins 配置
插件是 MyBatis 提供的一個拓展機制,通過插件機制我們可在 SQL 執行過程中的某些點上做一些自定義操作。比喻分頁插件,在SQL執行之前動態拼接語句,我們後面會單獨來講插件機制,先來了解插件的配置。如下:
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"> <property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/> </plugin> </plugins>
解析過程分析如下:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor"); // 獲取配置資訊 Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 解析攔截器的類型,並創建攔截器 Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance(); // 設置屬性 interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); // 添加攔截器到 Configuration 中 configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); } } }
首先是獲取配置,然後再解析攔截器類型,並實例化攔截器。最後向攔截器中設置屬性,並將攔截器添加到 Configuration 中。
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor"); // 獲取配置資訊 Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 解析攔截器的類型,並實例化攔截器 Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance(); // 設置屬性 interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); // 添加攔截器到 Configuration 中 configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); } } } public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { //添加到Configuration的interceptorChain屬性中 this.interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor); }
我們來看看InterceptorChain
public class InterceptorChain { private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList(); public InterceptorChain() { } public Object pluginAll(Object target) { Interceptor interceptor; for(Iterator i$ = this.interceptors.iterator(); i$.hasNext(); target = interceptor.plugin(target)) { interceptor = (Interceptor)i$.next(); } return target; } public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { this.interceptors.add(interceptor); } public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() { return Collections.unmodifiableList(this.interceptors); } }
實際上是一個 interceptors 集合,關於插件的原理我們後面再講。
解析 environments 配置
在 MyBatis 中,事務管理器和數據源是配置在 environments 中的。它們的配置大致如下:
<environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
我們來看看environmentsElement方法
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { if (environment == null) { // 獲取 default 屬性 environment = context.getStringAttribute("default"); } for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) { // 獲取 id 屬性 String id = child.getStringAttribute("id"); /* * 檢測當前 environment 節點的 id 與其父節點 environments 的屬性 default * 內容是否一致,一致則返回 true,否則返回 false * 將其default屬性值與子元素environment的id屬性值相等的子元素設置為當前使用的Environment對象 */ if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) { // 將environment中的transactionManager標籤轉換為TransactionFactory對象 TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager")); // 將environment中的dataSource標籤轉換為DataSourceFactory對象 DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource")); // 創建 DataSource 對象 DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource(); Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id) .transactionFactory(txFactory) .dataSource(dataSource); // 構建 Environment 對象,並設置到 configuration 中 configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build()); } } } }
看看TransactionFactory和 DataSourceFactory的獲取
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type"); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); //通過別名獲取Class,並實例化 TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory)this.resolveClass(type).newInstance(); factory.setProperties(props); return factory; } else { throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory."); } } private DataSourceFactory dataSourceElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type"); //通過別名獲取Class,並實例化 Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); DataSourceFactory factory = (DataSourceFactory)this.resolveClass(type).newInstance(); factory.setProperties(props); return factory; } else { throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a DataSourceFactory."); } }
<transactionManager type=”JDBC”/>中type有”JDBC”、”MANAGED”這兩種配置,而我們前面Configuration中默認註冊的別名中有對應的JdbcTransactionFactory.class、ManagedTransactionFactory.class這兩個TransactionFactory
<dataSource type=”POOLED”>中type有”JNDI”、”POOLED”、”UNPOOLED”這三種配置,默認註冊的別名中有對應的JndiDataSourceFactory.class、PooledDataSourceFactory.class、UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class這三個DataSourceFactory
而我們的environment配置中transactionManager type=”JDBC”和dataSource type=”POOLED”,則生成的transactionManager為JdbcTransactionFactory,DataSourceFactory為PooledDataSourceFactory
我們來看看PooledDataSourceFactory和UnpooledDataSourceFactory
public class UnpooledDataSourceFactory implements DataSourceFactory { private static final String DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX = "driver."; private static final int DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH = "driver.".length(); //創建UnpooledDataSource實例 protected DataSource dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource(); public DataSource getDataSource() { return this.dataSource; } //略 } //繼承UnpooledDataSourceFactory public class PooledDataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory { public PooledDataSourceFactory() { //創建PooledDataSource實例 this.dataSource = new PooledDataSource(); } }
我們發現 UnpooledDataSourceFactory 創建的dataSource是 UnpooledDataSource,PooledDataSourceFactory創建的 dataSource是PooledDataSource
解析 mappers 配置
mapperElement方法會將mapper標籤內的元素轉換成MapperProxyFactory產生的代理類,和與mapper.xml文件的綁定,我們下一篇文章會詳解介紹這個方法
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else { String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) { Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } } } } }
創建DefaultSqlSessionFactory
到此為止XMLConfigBuilder的parse方法中的重要步驟都過了一遍了,然後返回的就是一個完整的Configuration對象了,最後通過SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build的重載方法創建了一個SqlSessionFactory實例DefaultSqlSessionFactory,我們來看看
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { //創建DefaultSqlSessionFactory實例 return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); } public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory { private final Configuration configuration; //只是將configuration設置為其屬性 public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; } //略 }