QCustomplot使用分享(九) 繪製圖表-多功能游標
- 2019 年 10 月 26 日
- 筆記
目錄
原文鏈接:QCustomplot使用分享(九) 繪製圖表-多功能游標
一、概述
上一篇文章QCustomplot使用分享(八) 層(完結)講述了第一篇QCustomPlot控制項的使用,主要是展示了多維度折線圖,並且有一個簡單的游標展示效果。本篇文章是在上一篇文章的基礎上進行的功能加強,主要是針對游標進行優化,提供更加豐富的游標功能。
二、效果圖
如下圖所示,是我做的一個測試效果圖,途中包括一個簡單的折線圖和一系列游標,折線圖的顯示模式有十幾種效果,具體可以看QCustomplot使用分享(一) 能做什麼事這篇文章里的截圖,這裡我就不在貼出。
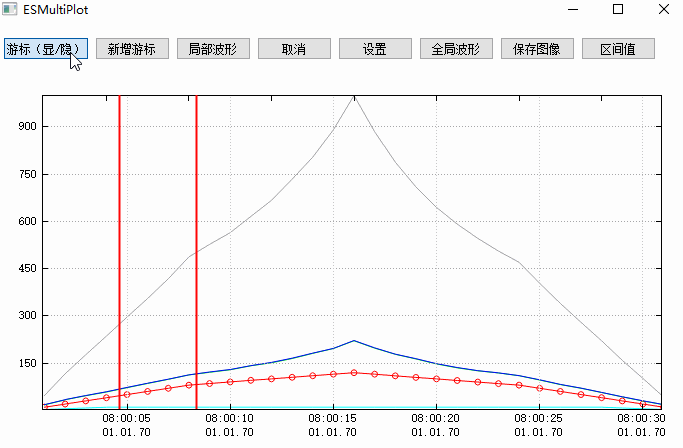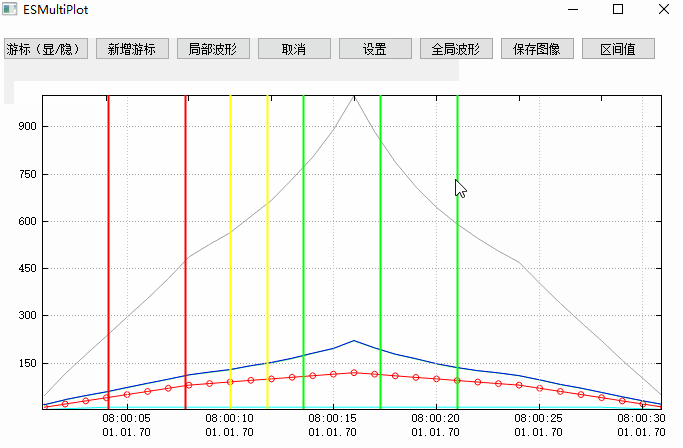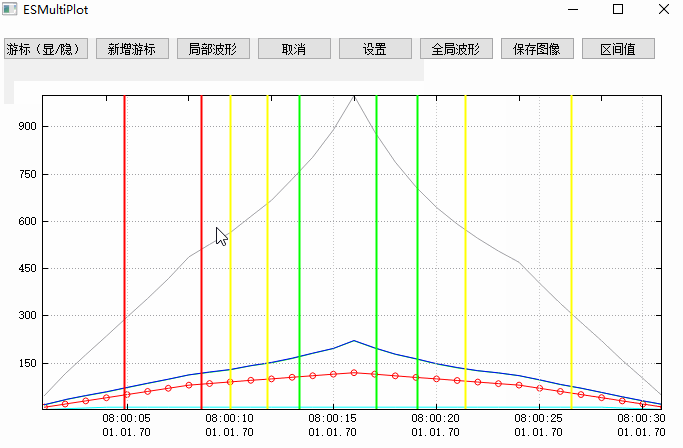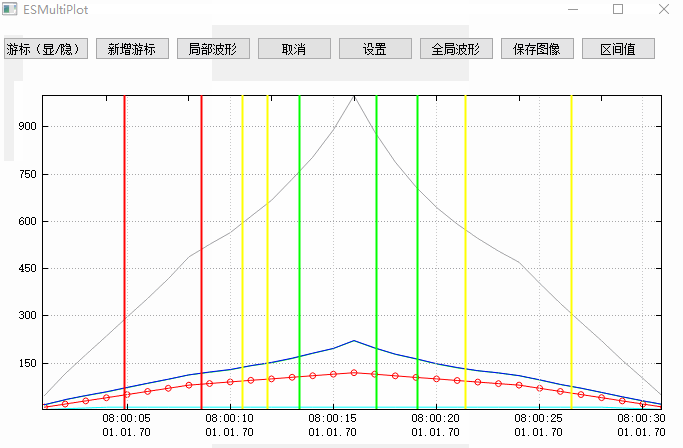
這個效果圖主要展示了游標的使用,其他相關功能可以參考之前寫的文章,本篇文章最後也會通過相關文章小節提供,感興趣的同學可以去文末查找。
演示demo中的數據是讀取於cvs文件,如果大家自己想從其他渠道獲取數據也可以,這個繪圖控制項已經添加了足夠的介面可供調用。
繪圖控制項提供的游標功能如下,比如:
- 多種類游標,單游標,雙游標
- 游標顯示、隱藏,支援移動
- 雙游標鎖定移動,非鎖定移動
- 獲取游標區間值
- 設置游標顏色
- 獲取游標區間數據
下面的文章中我會分析下主要的介面和核心功能實現
圖中的展示效果測試程式碼如下,程式碼中的關鍵節點就2個
- 構造ESCvsDBOperater類,並載入cvs文件
- 通過Set介面設置數據,並設置折線圖類型
ESCsvDBOperater * csvDBOperater = new ESCsvDBOperater(nullptr); csvDBOperater->loadCSVFile(qApp->applicationDirPath() + "\temp\test31.csv"); QStringList names = csvDBOperater->getCSVNames(); auto callback = [this, names](const QString & name, const QVector<double> & data){ int index = names.indexOf(name); if (index != -1) { if (index == 0) { ui->widget->SetGraphKey(data); } else { int l = name.indexOf("("); int r = name.indexOf(")"); if (l != -1 && r != -1) { ui->widget->SetGraphValue(index - 1, name.left(l), /*name.mid(l + 1, r - l - 1)*/"", data); ui->widget->SetGraphScatterStyle(index - 1, 4); } else { ui->widget->SetGraphValue(index - 1, name, "", data); } } }當然QCP不僅僅能顯示折線圖,他還可以顯示各種各樣的效果圖,感興趣的到QCustomplot使用分享(一) 能做什麼事文章中觀看
三、源碼講解
1、源碼結構
如圖所示,是工程的頭文件截圖,圖中的文件數量比較多,但是對外我們使用的可能只是一個ESMPMultiPlot類,這個類中提供了很多介面,足夠我們使用,當然了如果有特殊需求的話,可以進行提供訂製

2、頭文件
如下是頭文件中的介面,我只是把相關的Public介面列出來了,而這些介面也正好是我們平時使用比較多的介面,看介面名稱應該都知道介面是幹什麼的,因此不再細說
void ClearCache();//清空上一個csv繪圖數據 void SetGraphCount(int);//設置折線圖個數 void SetGraphKey(const QVector<double> &);//設置x軸數據 void SetGraphKeyRange(double, double);//設置x軸範圍,即時間範圍 void SetGraphScatterStyle(int, int);//設置折線圖樣式 void SetGraphValue(int, const QString &, const QString & , const QVector<double> &);//設置折線圖數據 void AppendGraphValue(int, double, double);//追加折線圖數據 void AppendGraphValue(int, const QVector<double> &, const QVector<double> &);//追加折線圖數據 QVector<double> GetGraphValues(int, int);//獲取折線圖 游標區間值 參數1:折線下標 參數2:游標order QString GetGraphName(int) const; void SetGraphColor(int, const QColor &);//設置折線圖顏色 QColor GetGraphColor(int);//獲取折線圖顏色 void SetSingleCursor(bool single);//啟動單游標 bool IsSingleCursor(int index) const;//測試游標是否是單游標 void ShowCursor(bool visible = true);//設置游標是否顯示 void AppendCursor(const QColor & color);//新增游標 void LockedCursor(int, bool);//鎖定指定游標 參數2表示是否鎖定 int CursorCount() const; bool CursorVisible() const;//游標是否顯示 void SetCursorColor(int index, const QColor &);//設置游標顏色 第二個參數指示哪個游標 double GetCursorKey(bool);//獲取游標對象x軸值 true表示左游標 false表示右游標 double GetCursorKey(int index, bool);//獲取游標對象x軸值 true表示左游標 false表示右游標 void ResizeKeyRange(bool, int index = 0);//設置x軸縮放 true時按游標縮放 false時恢復默認狀態 void ResizeValueRange();//y軸自適應 void ConfigureGraph();//設置 void ConfigureGraphAmplitude(int);//雙擊右側單位時觸發 void SavePng(const QString & = "");//保存圖片 1、分析時 自動執行並傳入路徑 2、點擊保存圖形按鈕時 傳空路徑3、添加游標
如下是模擬添加游標的程式碼,通過一個變數i來模擬不同情況,添加不同類型的游標,當前支援添加可移動單游標、可移動雙游標、可鎖定拖動雙游標
- 單游標:單挑線,可以用滑鼠進行拖拽
- 可移動雙游標:兩條線,分別移動,左邊游標永遠不會大於右邊游標
- 可鎖定拖動雙游標:兩條線,鎖定移動,也就是說不管移動那條線,另一條線會同步移動,並一直在窗口內
void ESMultiPlot::on_pushButton_add_cursor_clicked() { graphColor.append(Qt::red); graphColor.append(Qt::green); graphColor.append(Qt::blue); graphColor.append(Qt::gray); graphColor.append(Qt::cyan); graphColor.append(Qt::yellow); graphColor.append(Qt::magenta); static int i = 1; if (i % 3 == 0) { ui->widget->SetSingleCursor(true); ui->widget->AppendCursor(graphColor[rand() % 6 + 1]); } else if (i % 3 == 1) { ui->widget->SetSingleCursor(false); ui->widget->AppendCursor(graphColor[rand() % 6 + 1]); ui->widget->LockedCursor(i, false); } else { ui->widget->SetSingleCursor(false); ui->widget->AppendCursor(graphColor[rand() % 6 + 1]); ui->widget->LockedCursor(i, true); } ++i; }如上程式碼所示,SetSingleCursor設置為true時,表示接下來要添加的游標是單游標;LockedCursor可以鎖定指定雙游標,對單游標不生效。
4、監測移動
多游標模式下移動游標比一組游標複雜一些,我們需要循環監測所有的游標,並獲取一個可移動游標。
這裡獲取移動游標的邏輯為距離滑鼠按下的位置在5個像素以內的游標,並且優先響應先構造的游標,如果左右游標同時滿足的話優先響應右游標
void ESMPMultiPlot::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent * event) { if (m_bCursor) { m_bDrag = true; for (int i = 0; i < m_pCursors.size(); ++i) { QCPItemStraightLine * leftCursor = m_pCursors.at(i).leftCursor; bool ispressed = false; double distance = leftCursor->selectTest(event->pos(), false); if (distance <= 5 && axisRect()->rect().contains(event->pos())) { m_bDragType = 1; m_bLeftCursor = true; ispressed = true; m_bLock = m_pCursors.at(i).lock; m_bSingleCursor = m_pCursors.at(i).single; m_bOrder = i; } QCPItemStraightLine * rightCursor = m_pCursors.at(i).rightCursor; distance = rightCursor->selectTest(event->pos(), false); if (distance <= 5 && axisRect()->rect().contains(event->pos())) { m_bDragType = 1; m_bLeftCursor = false; ispressed = true; m_bLock = m_pCursors.at(i).lock; m_bSingleCursor = m_pCursors.at(i).single; m_bOrder = i; } if (ispressed) { break; } } } for (int i = 0; i < m_vecNames.size(); ++i) { double distance = m_vecNames[i]->selectTest(event->pos(), false); //QPointF posF = m_vecNames[i]->position->pixelPosition; if (distance <= 13 && m_vecNames[i]->visible()) { m_bDragType = 2; m_iDragIndex = i; break; } } __super::mousePressEvent(event); }5、移動游標
QCustomplot使用分享(八) 層(完結)文章講述的是一組游標移動,移動游標時需要考慮的點比較少,分別是:
- 游標時不能移出介面
- 左游標必須小於右游標
本篇文章的多組游標移動相對來說考慮的點就需要更多一些,分別是:
游標默認值游標組(一個游標、或者兩個游標);左右游標是針對兩個游標而言
基礎規則
- 游標不能移出介面
單游標
- 左側為雙游標時,與左側右游標比,反之與左游標比
- 右側直接與左游標比
雙游標非鎖定-移動左側游標
- 左側為雙游標時,與左側右游標比,反之與左游標比
- 右側直接與右游標比
雙游標非鎖定-移動右側游標
- 右側直接與右側游標左游標比
- 左側直接與左游標比
雙游標鎖定
- 右移時,直接用右游標與右側游標的左游標比
- 左移時,直接用左游標與左側游標的右游標比
如下程式碼所示,是移動游標的核心程式碼,主要的移動情況,上邊已經說了,下邊移動邏輯就不在細說,感興趣的同學可以自己查看,需要提供訂製的可以加我QQ。
void ESMPMultiPlot::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent * event) { if (m_bDragType == 1 && m_bDrag) { double pixelx = event->pos().x(); QCPRange keyRange = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->range(); double min = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(keyRange.lower); double max = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(keyRange.upper); if (min + 1 > pixelx) { pixelx = min + 1; } else if (max - 1 < pixelx) { pixelx = max - 1; } //按住左游標移動 double move_distance = 0; double rcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point1->key(); double rcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(rcursor); double lcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point1->key(); double lcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(lcursor); if (m_bLeftCursor) { //修正左邊 if (m_bOrder != 0) { double rcursor; if (m_pCursors[m_bOrder - 1].rightCursor->visible()) { rcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder - 1].rightCursor->point1->key(); } else//左側是單游標 { rcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder - 1].leftCursor->point1->key(); } double rcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(rcursor); if (pixelx <= rcursorx + 4) { pixelx = rcursorx + 4; } move_distance = rcursorx - pixelx;//可向左移動距離(向左為負) } else { if (pixelx <= min + 2) { pixelx = min + 2; } move_distance = min - pixelx;//可向左移動距離(向左為負) } //修正右邊 if (m_bLock)//鎖定移動 { move_distance = pixelx - lcursorx;//往右準備移動的距離 if (m_bOrder == m_pCursors.size() - 1) { if (rcursorx + move_distance > max - 2) { move_distance = max - 2 - rcursorx;//往右真正可移動距離 } } else { double nlcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder + 1].leftCursor->point1->key(); double nlcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(nlcursor); if (rcursorx + move_distance > nlcursorx - 4) { move_distance = nlcursorx - 4 - rcursorx;//往右真正可移動距離 } } } else { if (m_bSingleCursor) { move_distance = pixelx - lcursorx;//往右準備移動的距離 if (m_bOrder == m_pCursors.size() - 1) { if (lcursorx + move_distance > max - 2) { move_distance = max - 2 - lcursorx;//往右真正可移動距離 } } else { double nlcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder + 1].leftCursor->point1->key(); double nlcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(nlcursor); if (lcursorx + move_distance > nlcursorx - 4) { move_distance = nlcursorx - 4 - lcursorx;//往右真正可移動距離 } } } else { if (pixelx >= rcursorx - 4) { pixelx = rcursorx - 4; } move_distance = pixelx - lcursorx;//可向右移動距離(向右為正) } } } else//按住右游標移動 { //修正右邊 if (m_bOrder != m_pCursors.size() - 1) { double lcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder + 1].leftCursor->point1->key(); double lcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(lcursor); if (pixelx >= lcursorx - 4) { pixelx = lcursorx - 4; } move_distance = pixelx - lcursorx;//可向右移動距離 } else { if (pixelx >= max - 2) { pixelx = max - 2; } move_distance = pixelx - lcursorx;//可向右移動距離 } //修正左邊 if (m_bLock)//鎖定移動 { move_distance = pixelx - rcursorx;//往左準備移動的距離 if (m_bOrder == 0) { if (lcursorx + move_distance <= min + 2) { move_distance = min + 2 - lcursorx;//往左真正可移動距離 } } else { double nlcursor = m_pCursors[m_bOrder - 1].rightCursor->point1->key(); double nlcursorx = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->coordToPixel(nlcursor); if (lcursorx + move_distance <= nlcursorx + 4) { move_distance = nlcursorx + 4 - lcursorx;//往右真正可移動距離 } } } else { if (pixelx <= lcursorx + 4) { pixelx = lcursorx + 4; } move_distance = pixelx - rcursorx;//可向左移動距離(向左為負) } } double key; if (m_bLeftCursor) { key = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(lcursorx + move_distance); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point1->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point1->value()); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point2->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point2->value()); } else { key = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(rcursorx + move_distance); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point1->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point1->value()); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point2->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point2->value()); } if (m_bLock) { if (m_bLeftCursor) { key = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(rcursorx + move_distance); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point1->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point1->value()); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point2->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].rightCursor->point2->value()); } else { key = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atBottom)->pixelToCoord(lcursorx + move_distance); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point1->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point1->value()); m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point2->setCoords(key, m_pCursors[m_bOrder].leftCursor->point2->value()); } } event->accept(); replot(); emit CursorChanged(m_bLeftCursor); return; } else if (m_bDragType == 2) { double pixely = event->pos().y(); QCPRange keyRange = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->range(); double max = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->coordToPixel(keyRange.lower); double min = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->coordToPixel(keyRange.upper); if (min > pixely) { pixely = min; } else if (max < pixely) { pixely = max; } m_vecNames[m_iDragIndex]->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptPlotCoords); double coordy1 = axisRect()->axis(QCPAxis::atLeft)->pixelToCoord(pixely); double coordx = m_vecNames[m_iDragIndex]->position->coords().rx(); double coordy = m_vecNames[m_iDragIndex]->position->coords().ry(); m_vecNames[m_iDragIndex]->position->setCoords(coordx, coordy1); m_vecUnits[m_iDragIndex]->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptPlotCoords); m_vecUnits[m_iDragIndex]->position->setCoords(m_vecUnits[m_iDragIndex]->position->coords().rx(), coordy1); (*m_graphConfigure)[m_iDragIndex].position += (coordy1 - coordy); RefrushGraph(m_iDragIndex); event->accept(); replot(); return; } __super::mouseMoveEvent(event); }在ESMPPlot類中,m_mapLeftCursor和m_mapRightCursor分別是左右游標,為什麼這裡取了一個map呢?答案是:當時設計的時候是支援多個垂直擺放的游標可以進行游標同步,如果炒股的同學可能就會知道,k線和指標之間可能會有一個數值方便的線,不管在哪個繪圖區進行移動,另一個圖表裡的線也會跟著移動
不了解這個的同學也不要緊,我們這個控制項默認的就是一個表,因此這個map里也就只存了一個指,因此可以不關心這個問題
在ESMPMultiPlot類中,我們模擬了ESMPPlot的功能,這個時候呢?我們的坐標軸矩形只有一個了,x軸都是一樣的,表示時間,對於不同曲線的y軸我們進行了平移,以達到不同的顯示位置
這裡邊有一個很重的技巧,那就是我們對y軸數據進行了一次單位換算,讓他顯示的時候可以更好顯示在我們制定的區域內,可能像下面這樣
/* y1p=(y1-Yzero1)/Ygrid1+Xaxis1;%核心轉換公式,將原始坐標值y1轉換為新坐標值y1p y1;%原始數值 Yzero1;%零點幅值,決定曲線1零點位置的變數 Ygrid1;%單格幅值,決定曲線1每個單元格大小的量 Xaxis1;%顯示位置,決定曲線1在畫圖板中顯示位置的變數 */當然了,我們轉換後的坐標只是為了顯示方便而已,如果我們根據UI獲取原始值,我們還需要使用一個逆向公式進行轉換回去。
6、其他函數
還有一些其他的方法,比如保存圖表、獲取圖表坐標、設置圖表顏色等這裡就不細講了,文章篇幅所限,不能一一的都貼出來,有需要的夥伴可以聯繫我,提供功能訂製。
四、測試方式
1、測試工程
控制項我們將的差不多了,這裡把測試的程式碼放出來,大家參考下,首先測試工程截圖如下所示,我們的測試程式碼,大多數都是寫在了main函數中。

2、測試文件
這裡簡單說名下,我們的這個文件用途,第一列Time是代表了x軸的時間,而第二列開始的數據都是我們的折線圖,一列數據代表一條折線圖,並且列的名稱就是我們折線圖左側的名稱;列名稱括弧里的單位就是折線圖右側的單位。

3、測試程式碼
限於篇幅,這裡我還是把無關的程式碼刪減了很多,需要完整的源碼的可以聯繫我。
void ESMPMultiPlot::LoadData() { ESCsvDBOperater * csvDBOperater = new ESCsvDBOperater(nullptr); csvDBOperater->loadCSVFile(qApp->applicationDirPath() + "\temp\test31.csv"); QStringList names = csvDBOperater->getCSVNames(); auto callback = [this, names](const QString & name, const QVector<double> & data){ 添加圖表數據 }; ui->widget->SetGraphCount(names.size() - 1); for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); ++i) { csvDBOperater->receiveData(names[i], callback); } double start = csvDBOperater->getStartTime(); double end = csvDBOperater->getEndTime(); csvDBOperater->receiveData(names[2], 10.201, 10.412, callback); QVector<double> tiems = csvDBOperater->getRangeTimeDatas(10.201, 10.412); ui->widget->SetGraphKeyRange(start, end); }五、相關文章
- QCustomplot使用分享(一) 能做什麼事
- QCustomplot使用分享(二) 源碼解讀
- QCustomplot使用分享(三) 圖
- QCustomplot使用分享(四) QCPAbstractItem
- QCustomplot使用分享(五) 布局
- QCustomplot使用分享(六) 坐標軸和網格線
- QCustomplot使用分享(七) 層(完結)
- QCustomplot使用分享(八) 層(完結)
六、總結
QCustomPlot是一個非常強大的繪圖類,並且效率很高,對效率要求較高的程式都可以使用。
本篇文章是繼前7篇講解QCP後的第二篇使用案例,後續還會陸續提供更多複雜的功能。
這個控制項已經被我封裝成一個dll,如果有需要的小夥伴可以加我諮詢
七、關於美化
因為我這裡的程式都是測試程式,因此都是使用的原生效果,如果有需要美化的同學,或者客戶,我也可以提供訂製美化功能,歡迎諮詢。
 |
 |
很重要–轉載聲明
-
本站文章無特別說明,皆為原創,版權所有,轉載時請用鏈接的方式,給出原文出處。同時寫上原作者:朝十晚八 or Twowords
-
如要轉載,請原文轉載,如在轉載時修改本文,請事先告知,謝絕在轉載時通過修改本文達到有利於轉載者的目的。