SpringMvc啟動源碼解析
- 2019 年 10 月 26 日
- 筆記
1. 前言
上篇文章介紹了Spring容器的初始化https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaobingblog/p/11738747.html,接下來介紹SpringMvc容器的初始化
2. 初始化化過程
上文講過一個Web項目的啟動在載入listener、fliter初始化後,再進行servlet初始化。那SpringMvc如何與Servlet聯繫起來?看web.xml配置文件,有一個專門配置SpringMvc的servlet,就是DispatcherServlet。看下DispatcherServlet類繼承關係
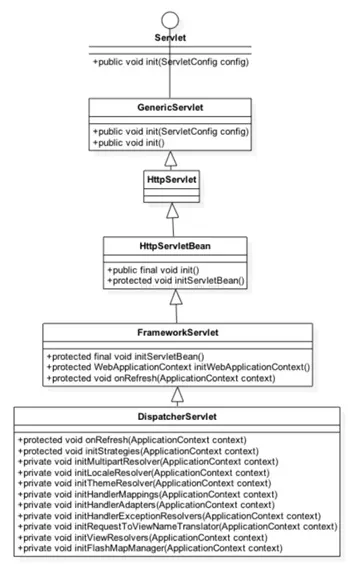
如上圖,DispatcherServlet本質上是一個Servlet。DispatcherServlet類的設計很巧妙,上層父類不同程度的實現了相關介面的部分方法,並留出了相關方法用於子類覆蓋,將不變的部分統一實現,將變化的部分預留方法用於子類實現。對Servlet有一定了解的,Servlet初始化會首先調用init()方法。子類最後重寫init()的是HttpServletBean,所以最開始對HttpServletBean的init()方法進行分析
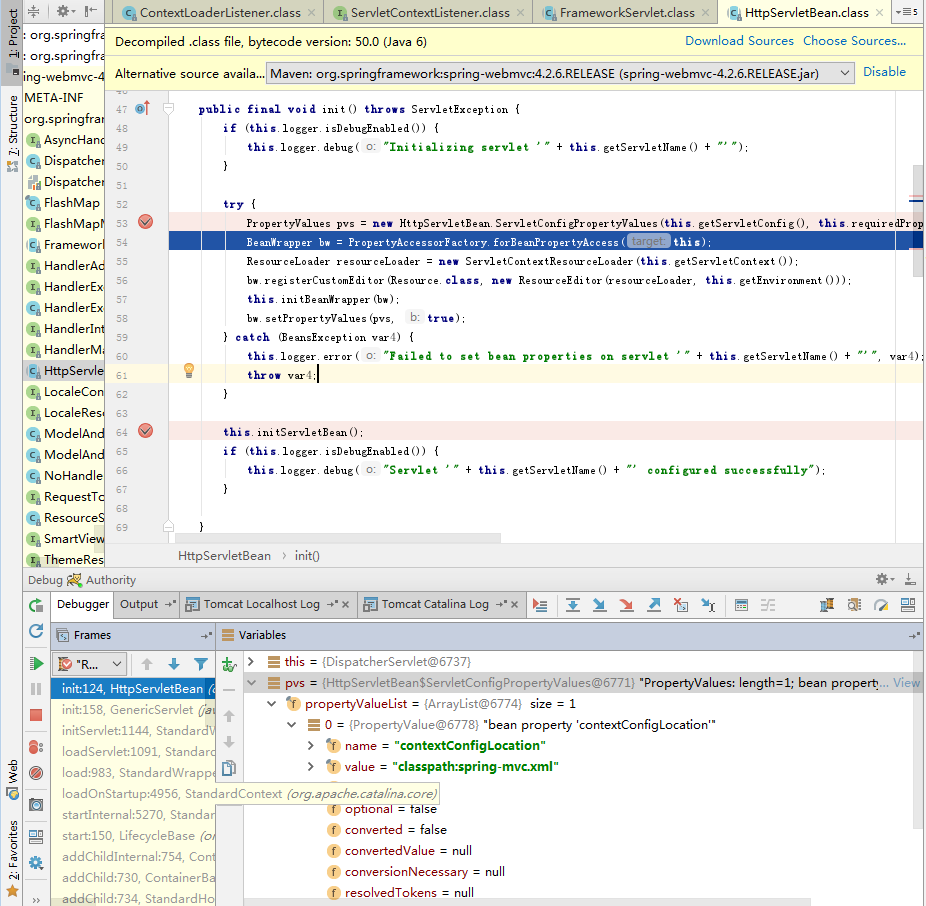
PropertyValues主要解析web.xml定義中<servlet>元素的子元素<init-param>中的參數值。見上圖,有一個鍵值對就是SpringMvc的配置文件。bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true) 將上一步解析的servlet初始化參數值綁定到DispatcherServlet對應的欄位上;
接著就是執行initServletBean方法,因為HttpServletBean中的initServletBean就是個空方法,通過觀察上述類圖,發現子類FrameworkServlet重寫了其initServletBean。於是對FrameworkServle的initServletBean進行分析
@Override protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } }
該方法中比較重要的就是initWebApplicationContext()方法的調用,該方法仍由FrameworkServlet抽象類實現,繼續查看其源碼如下所示:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { /* 獲取由ContextLoaderListener創建的根IoC容器 獲取根IoC容器有兩種方法,還可通過key直接獲取 */ WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent /*如果當前Servelt存在一個WebApplicationContext即子IoC容器並且上文獲取的根IoC容器存在,則將根IoC容器作為子IoC容器的父容器 */ cwac.setParent(rootContext); } //配置並刷新當前的子IoC容器,功能與前文講解根IoC容器時的配置刷新一致,用於構建相關Bean configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id //如果當前Servlet不存在一個子IoC容器則去查找一下 wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one //如果仍舊沒有查找到子IoC容器則創建一個子IoC容器 wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. //調用子類覆蓋的onRefresh方法完成“可變”的初始化過程 onRefresh(wac); } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); } } return wac; }
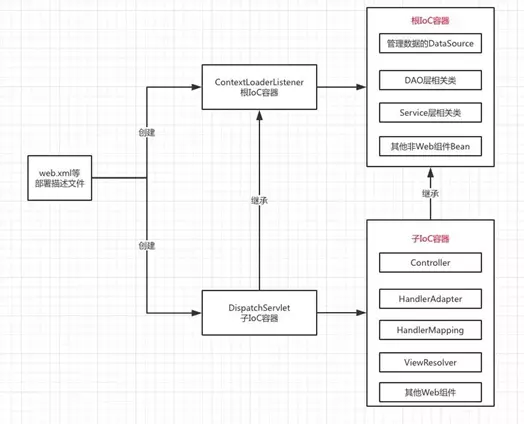
該方法的主要作用同樣是創建一個WebApplicationContext對象,即Ioc容器,上文我們已經創建過一個根Ioc容器,即Spring容器。Web第一次啟動時,通過Debug,會執行wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);將根IOC容器作為參數,調用createWebApplicationContex創建一個子IOC容器
這裡簡單提一下父子IOC容器,父子容器類似於類的繼承關係,子類可以訪問父類中的成員變數,而父類不可訪問子類的成員變數,同樣的,子容器可以訪問父容器中定義的Bean,但父容器無法訪問子容器定義的Bean。在一個SpringMvc項目中,父容器通常就是我們所說的Spring容器,它是載入Spring.xml配置文件,來管理Spring.xml中的Bean,這些Bean是全局共享的,即在任何當前容器或子容器中都能使用,我們一般配置Service,dao等bean。Service類中可以調用其他Service,dao。子容器通常是我們所說的SpringMvc容器,它所配置的Bean只能被當前子容器使用,但可以使用父容器的Bean。我們一般在子容器配置Controller、Interceptor等重要組件。這也就說明了我們為什麼可以在Controller中使用service或dao,而反過來不行
接下來繼續看createWebApplicationContex源碼:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" + contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]"); } if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"); } ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); wac.setParent(parent); wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation()); configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; }
該方法用於創建一個子IoC容器並將根IoC容器做為其父容器,接著進行配置和刷新操作用於構造相關的Bean。至此,根IoC容器以及相關Servlet的子IoC容器已經配置完成。子IOC容器配置完成後,調用onRefresh(wac)方法,通過類圖可知,onRefresh具體實現是由DispatcherServlet類實現
@Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } /** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
摘抄一段評論:onRefresh()方法直接調用了initStrategies()方法,源碼如上,通過函數名可以判斷,該方法用於初始化創建multipartResovle來支援圖片等文件的上傳、本地化解析器、主題解析器、HandlerMapping處理器映射器、HandlerAdapter處理器適配器、異常解析器、視圖解析器、flashMap管理器等,這些組件都是SpringMVC開發中的重要組件,相關組件的初始化創建過程均在此完成。
3. 總結
在Debug源碼中,涉及到了很多設計模式,想起校招面試時面試官問我,你知道Spring源碼中有哪些設計模式嗎,哈哈哈,一臉懵逼,不過現在也是。看來以後得好好學習設計模式了。
至此,對Tomcat啟動一個Spring項目已有了大概認知,還是很開心。小白進階之路任重而道遠。


