直接在x86硬體上顯示圖片(無os)
1 任務
為了學習電腦底層和os,我給自己布置了一個任務:在x86硬體上,使用c和nasm來顯示一張bmp圖片。完成這個任務,前後估計花了2個月的業餘時間。
這個任務涉及了很多知識點,包括:啟動區、保護模式、nasm彙編、c和nasm彙編互調、ld鏈接、硬碟io讀取、顯示卡調色板模式、bmp圖片格式、bios中斷指令、c指針操作記憶體、borch虛擬機、binutils工具集、makefile等。
2 環境
ubuntu
borchs
nasm和 c
PS:c程式碼遵循google的C++ 風格指南,使用gnu99標準。
3步驟
3.1 生成一個10M的硬碟鏡像
bximage是borchs軟體包的一個小工具,可以用於生成硬碟或軟盤鏡像。打開終端,輸入:bximage。按照如下圖所示的,一步一步地操作。

最終會在當前目錄下,生成一個名為10M.img的文件。
3.2 準備一張320*200的bmp圖片
為簡單起見,螢幕的解析度使用320*200。因此我們的bmp圖片的大小320*200。我準備了一張圖片,如下,這是我家主子的靚照。
將文件命名為cat-666.bmp,然後寫入到#201扇區
dd if=src/cat-ham.bmp of=10M.img bs=512 seek=201 conv=notrunc
3.3 引導區
引導區位於啟動盤的#0扇區,為電腦啟動後首次執行的程式碼。為簡單起見,我們的引導區僅完成以下功能:
- 設置vga模式設置顯示模式為320*200。
- 配置了配置了5個gdt表項,用作程式運行的記憶體空間。
- 跳入32位保護模式。
- 讀取內核至記憶體0x100000
- 跳至內核入口。
具體程式碼如下:boot.asm
1 ;設置堆棧段和棧指針 2 mov eax, cs 3 mov ss, eax 4 mov sp, 0x7c00 5 6 7 set_vga: 8 mov ax, 0x0013 ;;0x0013為 320*200*8bit 9 int 0x10 ;int 0x10 10 11 set_gdt: 12 ;GDT 開始於 0x7e00 13 mov ax, 0x7e00 14 mov bx, ax; 15 16 ; null_descriptor,這是處理器的要求 17 mov dword [bx + 0x00], 0x00000000 18 mov dword [bx + 0x04], 0x00000000 19 20 ; code 啟動區 21 mov dword [bx + 0x08], 0x7c0001ff ;base:0x7c00,limit: 1ff,512B 22 mov dword [bx + 0x0c], 0x00409A00 ;粒度為1B, 23 24 ; code kernel 25 mov dword [bx + 0x10], 0x000000ff ; base: 0x10_0000, limit:0xff,1MB 26 mov dword [bx + 0x14], 0x00c09a10 ; 粒度為4KB, 27 28 ; data 29 mov dword [bx + 0x18], 0x0000ffff ;base: 0, limit:0xf_ffff, 4GB 30 mov dword [bx + 0x1c], 0x00cf9200 ;粒度為4KB, 31 32 ; stack 33 mov dword [bx + 0x20], 0x7a00fffe ; base: 0x7a00, limit:0xfffe 34 mov dword [bx + 0x24], 0x00cf9600 ; 粒度為4KB, 35 36 ;初始化描述符表暫存器 GDTR 37 mov word [cs: gdt_desc + 0x7c00], 39 ;描述符表的界限 38 lgdt [cs: gdt_desc + 0x7c00] 39 40 in al, 0x92 ;南橋晶片內的埠 41 or al, 0000_0010B 42 out 0x92, al ;打開A20 43 44 cli ;中斷機制尚未工作 45 46 mov eax, cr0 47 or eax, 1 48 mov cr0, eax ;設置PE位 49 50 ;以下進入保護模式 ... 51 jmp dword 0x0008: mode32_start ;16位的描述符選擇子:32位偏移 52 53 54 55 [bits 32] 56 mode32_start: 57 mov eax, 0x0018 ;載入數據段選擇子 58 mov es, eax; 59 mov ds, eax; 60 61 62 ; 讀取內核,並且跳入。讀取200個扇區至 0x10_0000 63 read_kernel: 64 mov dx, 0x1f2; 65 mov al, 200 ; 200個扇區 66 out dx, al ; 67 68 mov dx, 0x1f3 ; 69 mov al ,0x01 ; 1號扇區(第2個扇區), zero-based 70 out dx, al; 71 72 mov dx, 0x1f4 ; 73 mov al, 0x00 ; 74 out dx, al ; 75 76 mov dx, 0x1f5 ; 77 mov al, 0x00; 78 out dx, al; 79 80 mov dx, 0x1f6 ; 81 mov al, 0xe0 ; 82 out dx, al ; 83 84 ; ask for read 85 mov dx, 0x1f7 ; 86 mov al, 0x20 ; 87 out dx, al ; 88 89 ; wait for finish 90 mov dx, 0x1f7 ; 91 _rk_wait: 92 in al,dx ; 93 and al, 0x88 ; 94 cmp al, 0x08 ; 95 jnz _rk_wait ; 96 97 ;read data to bx 98 mov ebx, 0x10_0000 ; 99 mov cx, 256 * 200 ; n * 256; 100 mov dx, 0x1f0 ; 101 102 _rk_read_loop: 103 in ax, dx; 104 mov word[ebx], ax; ; 每次讀2個位元組 105 add ebx, 2; 106 loop _rk_read_loop ; 107 108 ; jump to kernel, 段選擇子 109 jmp dword 0x0010:0 110 111 112 hlt; 113 114 115 ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 116 gdt_desc: dw 0 117 dd 0x00007e00 ; GDT的物理地址,剛好在啟動區之後 118 ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 119 times 510-($-$$) db 0 120 db 0x55, 0xaa
編譯
nasm boot.asm -f bin -o boot.bin
寫入到硬碟鏡像(寫入到#0扇區)
dd if=boot.bin of=10M.img bs=512 count=1 conv=notrunc
3.4 bmp文件的結構
BMP文件格式,又稱為Bitmap(點陣圖)或是DIB(Device-Independent Device,設備無關點陣圖),是Windows系統中廣泛使用的影像文件格式。其結構如下圖所示:

參考://www.cnblogs.com/kingmoon/archive/2011/04/18/2020097.html
參考bmp的結構定義,編寫如下頭文件:bmp.h
1 #ifndef _OS_BMP_H_ 2 #define _OS_BMP_H_ 3 4 #include <stdint.h> 5 6 typedef struct { 7 /** 8 * 文件類型, 9 */ 10 char type[2]; 11 12 /** 13 * 點陣圖大小 14 */ 15 uint32_t size; 16 17 /** 18 * 保留位 19 */ 20 uint16_t reserved1; 21 22 /** 23 * 保留位 24 */ 25 uint16_t reserved2; 26 27 /** 28 * 影像數據偏移量 29 */ 30 uint32_t off_bits; 31 32 } __attribute__ ((packed)) BitMapFileHeader; 33 34 /** 35 * 資訊頭 36 */ 37 typedef struct { 38 /** 39 * BitMapFileHeader 位元組數 40 */ 41 uint32_t size; 42 43 /** 44 * 點陣圖寬度 45 */ 46 uint32_t width; 47 48 /** 49 * 點陣圖高度,正位正向,反之為倒圖 50 */ 51 uint32_t height; 52 53 /** 54 * 為目標設備說明位面數,其值將總是被設為1 55 */ 56 uint16_t planes; 57 58 /** 59 * 說明比特數/象素,為1、4、8、16、24、或32。 60 */ 61 uint16_t bit_count; 62 63 /** 64 * 圖象數據壓縮的類型沒有壓縮的類型:BI_RGB 65 */ 66 uint32_t compression; 67 68 /** 69 * 影像數據區大小,以位元組為單位 70 */ 71 uint32_t image_size; 72 73 /** 74 * 水平解析度 75 */ 76 uint32_t x_pixel_per_meter; 77 78 /** 79 * 垂直解析度 80 */ 81 uint32_t y_pixel_per_meter; 82 83 /** 84 * 點陣圖實際使用的彩色表中的顏色索引數 85 */ 86 uint32_t color_used; 87 88 /** 89 * 對圖象顯示有重要影響的索引數,0都重要。 90 */ 91 uint32_t color_important; 92 } __attribute__ ((packed)) BitMapInfoHeader; 93 94 /* 95 * 顏色結構體 96 */ 97 typedef struct { 98 /** 99 * 100 */ 101 uint8_t blue; 102 103 /** 104 * 105 */ 106 uint8_t green; 107 108 /** 109 * 110 */ 111 uint8_t red; 112 113 /** 114 * 保留值 115 */ 116 uint8_t reserved; 117 118 } __attribute__ ((packed)) RGB; 119 120 #endif //_OS_BMP_H_
程式碼說明:
- 定義了3個結構體BitMapFileHeader(文件頭)、 BitMapInfoHeader(點陣圖資訊頭)、RGB(顏色)
- 需要特別注意的是,在類型定義中加入了__attribute__ ((packed))修飾。它的作用就是告訴編譯器取消結構體在編譯過程中的優化對齊,按照實際佔用位元組數進行對齊,是GCC特有的語法。不加入這個的話,會導致程式在讀取bmp數據時發生錯位。
3.5 io操作
在這個任務中需要直接操作硬體,比如讀取硬碟扇區、埠讀寫、打開中斷、讀取eflags標誌等,這部分功能的程式碼將使用nasm來編寫,然後導出相應的方法讓c來調用。
nasm程式碼如下:x86.asm
;數據區 [section .data] ; ;程式碼區 [section .text] ; global read_sector; global io_hlt ; ; global io_in8; global io_in16; global io_in32; global io_out8; global io_out16; global io_out32; ; global io_read_eflags; global io_write_eflags; ; global io_cli; global io_sti; ; ;功能 : 讀取一個扇區 ;入口 : 無 ;出口 : 無 ;堆棧使用: 無 ;全局變數: ;函數簽名:void read_sector(int sector, int dst); read_sector: mov ecx, [esp + 4] ;參數1:sector mov ebx, [esp + 8] ;參數2:dst mov dx, 0x1f2 ; mov al, 0x01 ;1 sector out dx, al ; mov dx, 0x1f3 ; mov al, cl ;0-7 out dx, al ; mov dx, 0x1f4 ; mov al, ch ;8-15 out dx, al mov dx, 0x1f5 ; mov al, 0x00 ;16-23 out dx, al ; mov dx, 0x1f6 ; mov al, 0xe0 ; out dx, al ; ; ask for read mov dx, 0x1f7 ; mov al, 0x20 ; out dx, al ; ; wait for finish mov dx, 0x1f7 ; _rs_wait: in al, dx ; and al, 0x88 ; cmp al, 0x08 ; jnz _rs_wait ; ;read data to bx mov cx, 256 ; mov dx, 0x1f0 ; _rs_read_loop: in ax, dx ; mov word[ebx], ax ; add ebx, 2 ; loop _rs_read_loop ; ret ; ;功能 : 掛起 ;入口 : 無 ;出口 : 無 ;堆棧使用: 無 ;全局變數: ;函數簽名:void io_hlt(void); io_hlt: hlt ; ret; ;功能 : 讀取 eflags ;函數簽名: int read_eflags(void); io_read_eflags: pushfd ;將 eflags 壓入棧 pop eax ;將 eflags 彈出並保存至eax ret ;功能 : 往埠寫入1個位元組 ;函數簽名: void io_out8(int port, int value); io_out8: mov edx, [esp + 4] ;參數1: port mov al, [esp + 8] ;參數2:value out dx, al ret ;功能 : 從埠讀取1個位元組 ;函數簽名:uint8_t io_in8(int port); io_in8: mov edx, [esp + 4] ;參數1: port mov eax, 0 ;將數據置為0,防止干擾 in al, dx ; ret ;功能 : 從埠讀取2個位元組 ;函數簽名:uint16_t io_in16(int port); io_in16: mov edx, [esp + 4] ;參數1: port mov eax, 0 ;將數據置為0,防止干擾 in ax, dx ; ret ;功能 : 從埠讀取4個位元組 ;函數簽名:uint32_t io_in32(int port); io_in32: mov edx, [esp + 4] ;參數1: port mov eax, 0 ;將數據置為0,防止干擾 in eax, dx ; ret ;功能 : 往埠寫入2個位元組 ;函數簽名: void io_out16(int port, int value); io_out16: mov edx, [esp + 4] ;參數1: port mov al, [esp + 8] ;參數2:value out dx, ax ret ;功能 : 往埠寫入4個位元組 ;函數簽名: void io_out32(int port, int value); io_out32: mov edx, [esp + 4] ;參數1: port mov al, [esp + 8] ;參數2:value out dx, eax ret ;功能 : 關閉中斷 ;函數簽名: void io_cli(void); io_cli: cli ; clean interrupt flag ret ;功能 : 打開中斷 ;函數簽名: void io_sti(void); io_sti: sti ; set interrupt flag ret ;功能 : 寫入 eflags ;函數簽名: void write_eflags(int flags); io_write_eflags: mov eax, [esp + 4] ;參數1:eflags push eax ;將參數 eflags壓入棧中 popfd ;從棧中彈出eflags的值並將之寫入到 EFLAGS 暫存器 ret
程式碼說明:
- 導出函數使用global關鍵字。比如global read_sector,將導出read_sector函數。
- 函數的參數使用棧來存儲,次序為從右到左,使用esp棧指針來訪問。
- 所有的函數都放在section .text 中。
- 整型類型的返回值可以放在eax/ax/dx寄存中進行返回。
編譯
nasm -f elf -o x86.o x86.asm
為了便於c程式碼調用上面的程式碼,我們還需要創建一個頭文件:x86.h:
#ifndef _OS_X86_H_ #define _OS_X86_H_ #include <stdint.h> /** * 讀取扇區的數據 * @param sector 扇區號。 * @param dst 目標地址 */ void read_sector(int sector, uint8_t *dst); /** * 掛起 */ void io_hlt(); /** * 讀取 eflags * @return */ uint32_t io_read_eflags(); /** * 寫入 eflags * @param flags */ void io_write_eflags(uint32_t flags); /** * 從埠讀取1個位元組 * @param port 埠號 * @return 埠上的數據 */ uint8_t io_in8(uint16_t port); /** * 從埠讀取2個位元組 * @param port 埠號 * @return 埠上的數據 */ uint16_t io_in16(uint16_t port); /** * 從埠讀取4個位元組 * @param port 埠號 * @return 埠上的數據 */ uint32_t io_in32(uint16_t port); /** * 往埠寫入1個位元組 * @param port 埠號 * @param value 要寫入的值 * @return */ void io_out8(uint16_t port, uint8_t value); /** * 往埠寫入2個位元組 * @param port 埠號 * @param value 要寫入的值 * @return */ void io_out16(uint16_t port, uint16_t value); /** * 往埠寫入4個位元組 * @param port 埠號 * @param value 要寫入的值 * @return */ void io_out32(uint16_t port, uint32_t value); /** * 關閉中斷 */ void io_cli(); /** * 打開中斷 */ void io_sti(); #endif //_OS_X86_H_
程式碼說明:
- 函數的簽名要跟nasm文件中的保持一致,包括函數名,參數個數、參數類型。
- 在調用的時候跟普通的頭文件一樣,先引入x86.h,然後調用相應的方法。
3.6 內核程式碼
在內核程式碼中,執行以下操作:
- 讀取bmp文件所在的起始個扇區。從該扇區數據中取出文件大小,決定要還要繼續讀幾個扇區,接著讀完所有扇區。
- 從bmp數據中取出調色板數據,然後用它來更改顯示卡的調色板。
- 從bmp數據中取出影像數據,寫入到影像緩衝區。
程式碼如下:kernel.c
1 #include <stdint.h> 2 #include "x86.h" 3 #include "bmp.h" 4 5 // 影片緩衝區的記憶體位置 6 #define VIDEO_BUFFER_MEMORY_LOC 0x0a0000 7 // bmp文件的記憶體位置 8 #define BMP_FILE_MEMORY_LOC 0x200000 9 // bmp文件所在的起始扇區 10 #define BMP_FILE_SECTOR 201 11 12 int main(void) { 13 // 讀扇區的索引, 14 uint32_t sector_read_index = BMP_FILE_SECTOR; 15 // 讀文件的索引 16 uint8_t *file_read_index = (uint8_t *) BMP_FILE_MEMORY_LOC; 17 18 // 讀取bmp文件所在的第1個扇區 19 read_sector(sector_read_index, file_read_index); 20 file_read_index = file_read_index + 512; 21 sector_read_index++; 22 23 // 文件頭 24 BitMapFileHeader *bmp_header = (BitMapFileHeader *) BMP_FILE_MEMORY_LOC; 25 uint32_t file_size = bmp_header->size; 26 27 // 影像數據偏移 28 uint32_t off_bits = bmp_header->off_bits; 29 30 // 需要再讀取幾個扇區? 31 int more_sectors = (file_size / 512) - 1; 32 if (file_size % 512 != 0) { 33 more_sectors++; 34 } 35 36 // 讀取更多扇區 37 for (int i = 0; i < more_sectors; i++) { 38 read_sector(sector_read_index, file_read_index); 39 sector_read_index++; 40 file_read_index += 512; 41 } 42 43 //*********************調色板設置 ************* 44 // 讀取調色板數據 45 // 調色板數據開始於文件偏移 54 46 RGB *palette_index = (RGB *) (BMP_FILE_MEMORY_LOC + 54); 47 // 48 uint32_t eflags = io_read_eflags(); 49 io_cli(); 50 51 // 寫入0號調色板 52 io_out8(0x03c8, 0); 53 54 // 寫入調色板數據 55 for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) { 56 RGB rgb = *palette_index; 57 // 必須除以4,因為 vga 只能顯示64色 58 io_out8(0x03c9, rgb.red / 4); 59 io_out8(0x03c9, rgb.green / 4); 60 io_out8(0x03c9, rgb.blue / 4); 61 palette_index++; 62 } 63 64 io_write_eflags(eflags); 65 66 // 點陣圖資訊頭 67 BitMapInfoHeader *info_header = (BitMapInfoHeader *) (BMP_FILE_MEMORY_LOC + 14); 68 // 數據位數組 69 uint8_t *file_bits = (uint8_t *) (BMP_FILE_MEMORY_LOC + off_bits); 70 // 坐標點的記憶體地址 71 uint8_t *p = 0; 72 // 73 for (int i = 0; i < info_header->image_size; i++) { 74 // x 坐標 75 int x = i % info_header->width; 76 // y 坐標 77 int y = (info_header->height - 1) - (i / info_header->width); 78 // 點(x,y)的記憶體地址 79 p = (uint8_t *) (VIDEO_BUFFER_MEMORY_LOC + x + y * info_header->width); 80 *p = *file_bits; 81 file_bits++; 82 } 83 84 // use this to avoid to reset 85 while (1) { 86 io_hlt(); 87 } 88 return 0; 89 }
關鍵程式碼說明:
- 在寫入調色板之前,eflags要先暫存,然後再回寫。
- bmp的數據是從下往上,從左往右存儲的,所以顯示的時候要反過來。
- 對影片緩衝區記憶體區域的讀寫用到了指針。定義一個指針uint8_t *p, p為坐標點的記憶體地址,然後使用*p = *file_bits來修改該記憶體的值。
編譯
gcc -c-std=gnu99 -fno-stack-protector -m32 -Wall -o kernel.o kernel.c
3.7 鏈接
鏈接腳本如下:kernel.ld
1 OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-i386") 2 OUTPUT_ARCH(i386) 3 ENTRY(main) 4 5 SECTIONS 6 { 7 . = 0x040000; 8 .text : { 9 *(.text) 10 } 11 .data : { 12 *(.data) 13 } 14 .bss : { 15 *(.bss) 16 } 17 /DISCARD/ : { 18 *(.eh_frame .note.GNU-stack) 19 } 20 } 21 22
腳本說明:
- OUTPUT_FORMAT(“elf32-i386”) 表示輸出格式為efl32 32位格式。
- ENTRY(main) 表示入口函數為main
- /DISCARD/表示忽略.eh_frame段和.note.GNU-stack
鏈接
ld -s -T kernel.ld -o kernel.out kernel.o x86.o 注意,對象文件(*.o)的次序要正確,否則運行的時候會出錯。次序的原則是被依賴的放在後面。
3.8 .text段提取
鏈接後的文件kernel.out是一個elf類型的文件,它包含了elf頭資訊、.text、.data等。通過readelf命令可以查看efl文件的結構。
readelf -a kernel.out
命令結果如下:
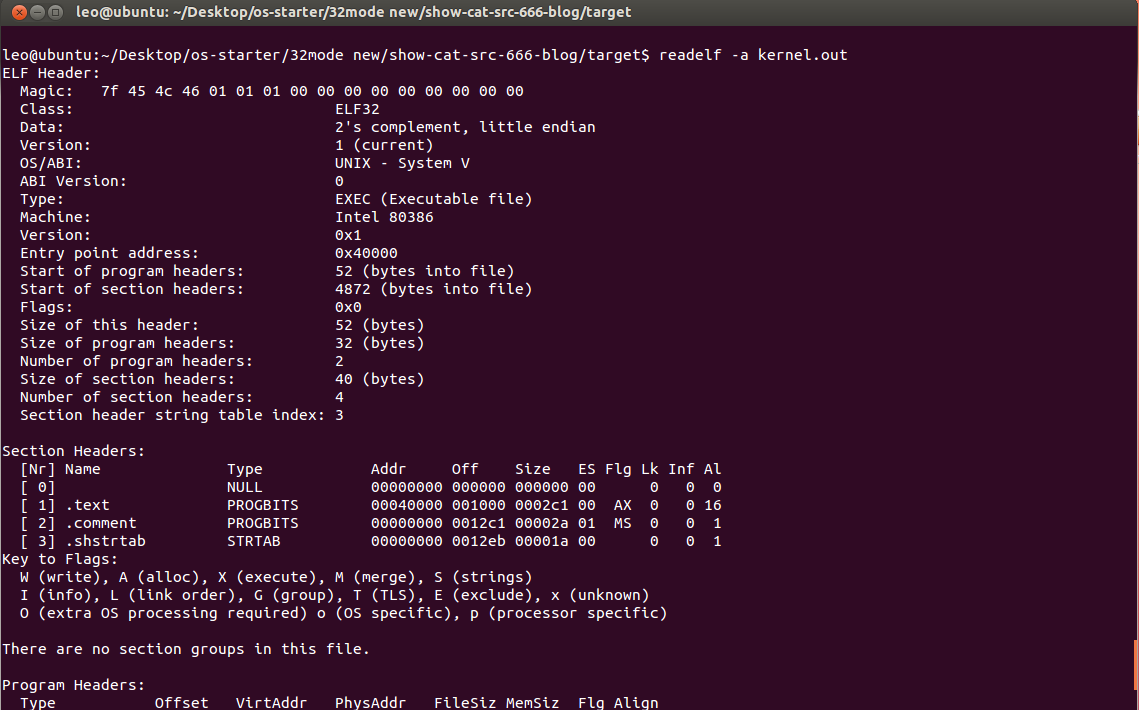
我們僅需要 .text段 。這個時候通過objcopy來提取kernel.out中的.text段,如下:
objcopy -S -O binary -j .text kernel.out kernel.bin
將kernel.bin寫入到硬碟鏡像(從#1扇區開始)
dd if=target/kernel.bin of=10M.img bs=512 seek=1 count=200 conv=notrunc
3.9 放入borch虛擬機中運行
配置一個虛擬機,配置如下,bochsrc :
1 ############################################################### 2 # Configuration file for Bochs 3 ############################################################### 4 5 # how much memory the emulated machine will have 6 megs: 32 7 8 # filename of ROM images 9 romimage: file=/usr/local/share/bochs/BIOS-bochs-latest 10 vgaromimage: file=/usr/local/share/bochs/VGABIOS-lgpl-latest 11 12 # what disk images will be used 13 #floppya: 1_44=a.img, status=inserted 14 ata0-master: type=disk, mode=flat, path="10M.img", cylinders=20, heads=16, spt=63 15 16 # choose the boot disk. 17 #boot: floppy 18 boot: disk 19 20 21 # where do we send log messages? 22 # log: bochsout.txt 23 # disable the mouse 24 mouse: enabled=0 25 26 # enable key mapping, using US layout as default. 27 keyboard_mapping: enabled=1, map=/usr/local/share/bochs/keymaps/x11-pc-us.map 28 29
關鍵配置說明:
- megs: 32 表示記憶體為32M
- boot: disk 表示從硬碟啟動
- ata0-master: path=”10M.img”, 設置了硬碟鏡像的路徑
- vgaromimage: file=VGABIOS-lgpl-latest 表示顯示卡的rom鏡像為VGABIOS-lgpl-latest,如果設置錯誤,顯示就會不正常。
- keyboard_mapping: enabled=1, 用於設置鍵盤布局,這裡採用美式鍵盤布局。
啟動虛擬機
bochs -q
效果如下:
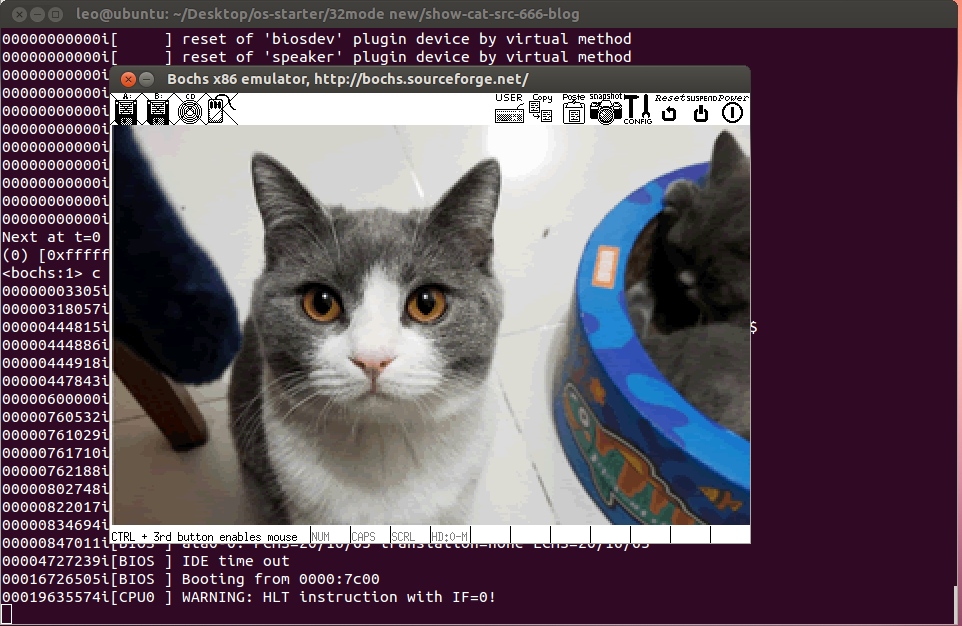
3.10 makefile
用makefile將上面零散的命令整合一下。腳本如下,Makefile:
1 .PHONY : all clean run install 2 3 CFLAGS = -std=gnu99 -fno-stack-protector -m32 -Wall 4 5 all: target/boot.bin target/kernel.bin install 6 7 target/boot.bin : src/boot.asm 8 nasm src/boot.asm -f bin -o target/boot.bin 9 10 target/kernel.bin : target/kernel.out 11 objcopy -S -O binary -j .text target/kernel.out target/kernel.bin 12 13 target/x86.o : src/x86.asm 14 nasm -f elf -o target/x86.o src/x86.asm 15 16 target/kernel.o : src/kernel.c 17 gcc -c $(CFLAGS) -o target/kernel.o src/kernel.c 18 19 # x86.o要放到最後,否則會無法運行 20 target/kernel.out : target/kernel.o target/x86.o 21 ld -s -T kernel.ld -o target/kernel.out target/kernel.o target/x86.o 22 23 24 25 install : 26 # #0扇區 27 dd if=target/boot.bin of=10M.img bs=512 count=1 conv=notrunc 28 # #1 ~ #200 扇區 29 dd if=target/kernel.bin of=10M.img bs=512 seek=1 count=200 conv=notrunc 30 # #201扇區開始 31 dd if=src/cat-666.bmp of=10M.img bs=512 seek=201 conv=notrunc 32 33 34 run : 35 make all 36 bochs -q 37 38 39 clean : 40 -rm target/*.bin 41 -rm target/*.o 42 -rm target/*.out 43 44 45 46
腳本說明:
- 將源文件放到src目錄下,將目標文件放到target目錄下。
- make run 為運行。
- make install 為安裝。
- make clean 為清理。
3.11 記憶體和硬碟布局
記憶體布局
|
物理地址 |
內容 |
|
0x7c00 ~ 0x7dff |
啟動區 |
|
0x7e00~ 0x7eff |
gdt |
|
0x100000~0x1fffff |
內核,大小1M。 |
|
0x200000開始 |
圖片。 |
|
0x0a0000-0xaf9ff |
影像緩衝區 |
硬碟布局
|
扇區 |
內容 |
|
#0 |
boot.bin |
|
#1 ~ #200 |
kernel.bin |
|
#201 |
cat-6666.bmp |
4 參考資料
- 《x86彙編語言 從實模式到保護模式》
- 《Linux0.11內核完全注釋》
- 《30天自製作業系統》
- 《一步一步學習linux彙編語言程式設計》
- 《xv6》



