spring源碼解析之前置知識點
- 2020 年 5 月 17 日
- 筆記
- Spring Framework
本文是作者原創,版權歸作者所有.若要轉載,請註明出處.
最近在看spring源碼,但是spring的體系太龐大了,在這裡記錄一下閱讀源碼中遇到知識點
@PostConstruct
被註解的方法,在對象載入完依賴注入後執行
看個demo
package com.day01.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.day01") public class SpringConfig { }
IndexDao
package com.day01.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class IndexDao { public IndexDao(){ System.out.println("IndexDao 構造方法"); } }
IndexService
@Service public class IndexService { @Autowired private IndexDao indexDao; public IndexService(){ System.out.println("IndexService 構造方法"); } @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("IndexService init方法"); } public void hello(){ System.out.println("IndexService"); } }
Testday01
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService"); indexService.hello(); }
看結果
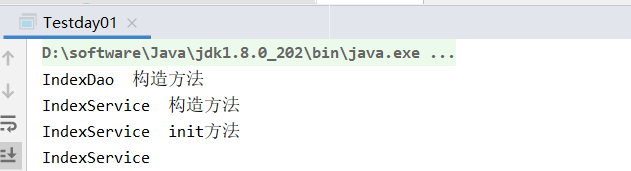
可以看出在spring項目中,在一個bean的初始化過程中,方法執行先後順序為Constructor > @Autowired > @PostConstruct
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是Spring框架的提供的一個擴展點,通過實現BeanPostProcessor介面,程式設計師就可插手bean實例化的過程
看demo
@Component public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { /** * 在bean初始化之前執行 */ @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("indexService")){ System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization"); } //這裡也可以產生代理對象 Proxy.newProxyInstance(),也是aop實現的原理 return bean; } /** * 初始化之後 */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("indexService")){ System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization"); } return bean; } }
運行上文的Testday01,看下結果
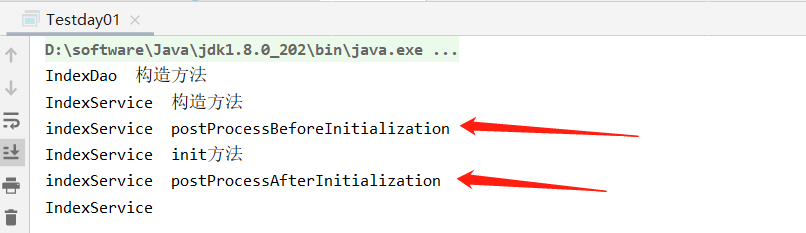
可以看出
===Spring IOC容器實例化Bean===
===調用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法===
===調用bean實例的初始化方法===
===調用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法===
值得說明的是這個介面可以設置多個,會形成一個列表,那麼如何確定他們的執行順序呢?
Ordered和PriorityOrdered
Spring提供了Ordered和PriorityOrdered介面,來處理相同介面實現類的優先順序問題
看個demo
TestBeanPostProcessor
@Component public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor , PriorityOrdered { /** * 在bean初始化之前執行 */ @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("indexService")){ System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization"); } //這裡也可以產生代理對象 Proxy.newProxyInstance(),也是aop實現的原理 return bean; } /** * 在bean初始化之前執行 */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("indexService")){ System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization"); } return bean; } @Override public int getOrder() { return 100;//注意這裡 } }
TestBeanPostProcessor2
@Component public class TestBeanPostProcessor2 implements BeanPostProcessor , PriorityOrdered { /** * 在bean初始化之前執行 */ @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("indexService")){ System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization2"); } //這裡也可以產生代理對象 Proxy.newProxyInstance(),也是aop實現的原理 return bean; } /** * 在bean初始化之前執行 */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (beanName.equals("indexService")){ System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization2"); } return bean; } @Override public int getOrder() { return 99; } }
運行test類,看結果
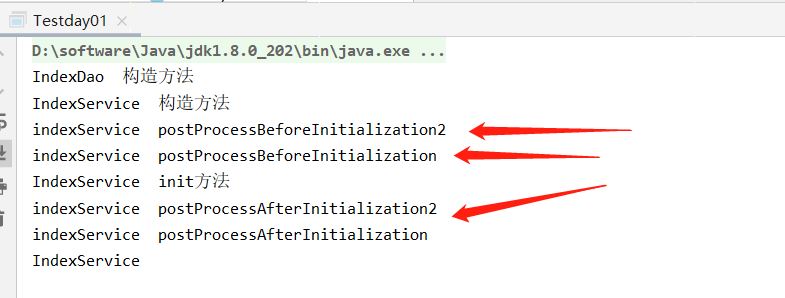
這段程式碼的邏輯:
1. 若對象o1是Ordered介面類型,o2是PriorityOrdered介面類型,那麼o2的優先順序高於o1
2. 若對象o1是PriorityOrdered介面類型,o2是Ordered介面類型,那麼o1的優先順序高於o2
3. 其他情況,若兩者都是Ordered介面類型或兩者都是PriorityOrdered介面類型,調用Ordered介面的getOrder方法得到order值,order值越大,優先順序越小
若2個對象中有一個對象實現了PriorityOrdered介面,那麼這個對象的優先順序更高。
若2個對象都是PriorityOrdered或Ordered介面的實現類,那麼比較Ordered介面的getOrder方法得到order值,值越低,優先順序越高
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
spring的擴展點之一:實現該介面,可以在spring的bean創建之前修改beandefinitions屬性。
例如可以把bean的scope從singleton改為prototype,也可以把property的值給修改掉。
可以同時配置多個BeanFactoryPostProcessor,並通過設置’order’屬性來控制各個BeanFactoryPostProcessor的執行次序
看個demo
@Component public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("===============TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor============"); } }
測試類
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class); IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService"); indexService.hello(); IndexService indexService2 = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService"); System.out.println(indexService); System.out.println(indexService2); }
運行一下,看結果

可以看到,spring管理的bean默認是單例的,我們把indexService改成prototype試一下
@Component public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("===============TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor============"); BeanDefinition indexService = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("indexService"); String scope = indexService.getScope(); System.out.println(scope);//singleton //indexService.setScope("singleton"); indexService.setScope("prototype");//設置為原型 System.out.println(scope);//singleton } }
看下結果

BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor繼承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor介面,並可以註冊bean到spring容器中,一共要實現以下兩個方法:
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException: 該方法的實現中,主要用來對bean定義做一些改變。 void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException: 該方法用來註冊更多的bean到spring容器中,詳細觀察入參BeanDefinitionRegistry介面,看看這個參數能帶給我們什麼能力。
看個demo
public class IndexService2 { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public IndexService2(){ System.out.println("IndexService2 構造方法"); } @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("IndexService2 init方法"); } public void hello(){ System.out.println("IndexService2 hello"); } }
注意:IndexService2並沒有@Component註解,說明這個類並沒有交給spring管理,繼續
@Component public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException { GenericBeanDefinition genericBeanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition(); genericBeanDefinition.setScope("singleton"); genericBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(IndexService2.class);//將IndexService2交給spring管理 registry.registerBeanDefinition("indexService2",genericBeanDefinition); } @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("===============MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor============"); } }
注意上述程式碼中通過BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 將IndexService2手動註冊交給spring管理
運行test類
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class); IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService"); indexService.hello(); IndexService2 indexService2 = (IndexService2) applicationContext.getBean("indexService2"); System.out.println(indexService); System.out.println(indexService2); }
看結果
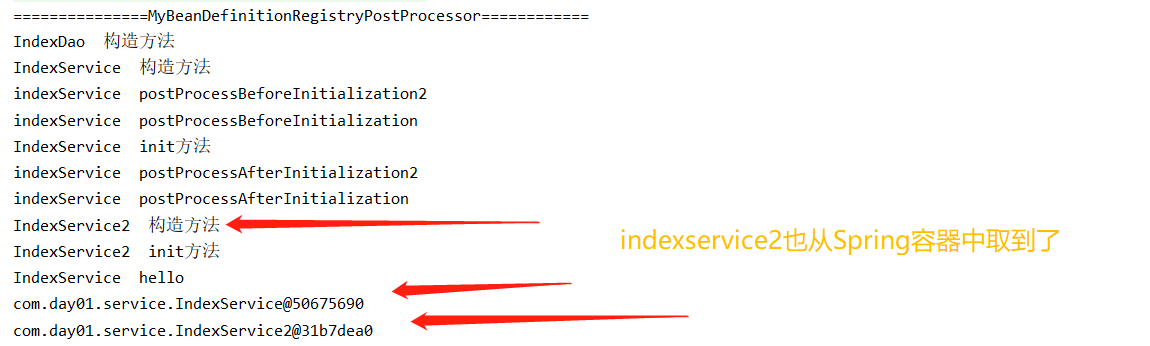
ApplicationContextAware
我們可以通過註解@Autowired 很簡單方便獲取bean,雖然這種方法很簡單方便,但是有些特殊場景用不了,比如靜態方法中不能使用
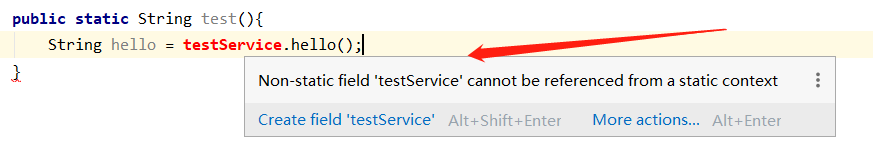
此時可以藉助ApplicationContextAware獲取bean
看個demo
@Service public class TestServiceImpl { public String hello(){ return "hello world"; } }
這裡無法注入TestServiceImpl 無法使用,看demo
@Component public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null; @Autowired private TestServiceImpl testService; /** * 實現ApplicationContextAware介面, 注入Context到靜態變數中. */ @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { ApplicationContextUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext; } /** * 獲取靜態變數中的ApplicationContext. */ public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { return applicationContext; } /** * 從靜態變數applicationContext中得到Bean, 自動轉型為所賦值對象的類型. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static <T> T getBean(String name) { return (T) applicationContext.getBean(name); } /** * 從靜態變數applicationContext中得到Bean, 自動轉型為所賦值對象的類型. */ public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) { return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType); } /*public static String test(){ String hello = testService.hello(); }*/ }
看測試類
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class); IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService"); indexService.hello(); System.out.println(indexService); /*IndexService2 indexService2 = (IndexService2) applicationContext.getBean("indexService2"); System.out.println(indexService2);*/ String testServiceImpl = ((TestServiceImpl) ApplicationContextUtil.getBean("testServiceImpl")).hello(); System.out.println(testServiceImpl); }
看結果
ok,今天就先到這裡,以後有新的內容隨時補充吧

