ArrayList源碼分析–jdk1.8
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
JDK1.8
ArrayList源碼分析–jdk1.8
LinkedList源碼分析–jdk1.8
HashMap源碼分析–jdk1.8
AQS源碼分析–jdk1.8
ReentrantLock源碼分析–jdk1.8
ArrayList概述
1. ArrayList是可以動態擴容和動態刪除冗餘容量的索引序列,基於數組實現的集合。
2. ArrayList支援隨機訪問、克隆、序列化,元素有序且可以重複。
3. ArrayList初始默認長度10,超出擴容1.5倍,使用Object[]存儲各種數據類型。
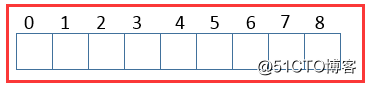
ArrayList數據結構
數據結構是集合的精華所在,數據結構往往也限制了集合的作用和側重點,了解各種數據結構是我們分析源碼的必經之路。
ArrayList的數據結構如下:
ArrayList源碼分析
/* * 用數組實現的集合,支援隨機訪問,元素有序且可以重複 * RandomAccess(ArrayList) 支援快速隨機訪問,使用for循環更加快速 * LinkedList 使用 iterator迭代器更加 快速 * RandomAccess 這是一個標記介面,一般此標記介面用於 List 實現,以表明它們支援快速(通常是恆定時間)的隨機訪問。 * 該介面的主要目的是允許通用演算法改變其行為,以便在應用於隨機或順序訪問列表時提供良好的性能 * 包含類中的基礎屬性和3個構造方法 */ public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { /** * 默認長度 10 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * 默認空的數組 */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * ArrayList中的元素 是Object[]類型的數組 */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * 動態數組的實際大小 ,默認為0 * @serial */ private int size; /** * 最大數組容量2147483639 */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * 集合長度構造函數 */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } /** * 無參構造函數,設置元素數組為空 注意此時初始容量是0,而不是大家以為的 10 */ public ArrayList() { super(); this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } /** * 集合參數構造函數 */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); // 轉化為數組 size = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) //是否成功轉化為Object類型數組 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); //不為Object數組的話就進行複製 } ArrayList繼承和實現分析
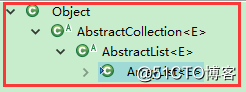
ArrayList extends AbstractList
AbstractList extends AbstractCollection
java中所有類都繼承Object,所以ArrayList的繼承結構如上圖。
1. AbstractList是一個抽象類,實現了List<E>介面,List<E>定義了一些List通用方法,而AbstractList抽象類中可以有抽象方法,還可以有具體的實現方法,AbstractList實現介面中一些通用的方法,實現了基礎的add/get/indexOf/iterator/subList/RandomAccessSubList方法,ArrayList再繼承AbstractList,拿到通用基礎的方法,然後自己在實現一些自己特有的方法,這樣的好處是:讓程式碼更簡潔,繼承結構最底層的類中通用的方法,減少重複程式碼。
2.ArrayList實現了List<E>、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable介面
1)List<E>介面,ArrayList既然繼承自AbstractList抽象類,而AbstractList已 經實現了List介面,那麼ArrayList類為何還要再實現List介面呢?我們帶著疑問往下看:
public class Demo1 extends ArrayList { public static void main(String[] args) { //返回[] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Demo1.class.getInterfaces())); } public class Demo2 implements Serializable { public static void main(String[] args) { //返回[interface java.io.Serializable] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Demo2.class.getInterfaces())); } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Serializable c1 = new Demo1();//未顯示實現介面 Serializable c2 = new Demo2();//顯示實現介面 Serializable proxy2 = createProxy(c2); proxy2.foo(); Serializable proxy1 = createProxy(c1); proxy1.foo(); } private static <T> T createProxy(final T obj) { final InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { return method.invoke(obj, args); } }; //實現介面代理,Demo1報錯,Demo2成功 //java.lang.ClassCastException: $Proxy1 cannot be cast to //example.Test$Serializable return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj .getClass().getInterfaces(), handler); }可以看出這樣這樣設計是有道理的,因此,這並不是一個錯誤,很可能是作者Josh Bloch為了便於實現代理而精心設計的。
參考與:開發collection 的作者Josh說
2)RandomAccess介面,這是一個標記介面,一般此標記介面用於 List 實現,以表明它們支援快速(通常是恆定時間)的隨機訪問,該介面的主要目的是允許通用演算法改變其行為,以便在應用於隨機或順序訪問列表時提供良好的性能,實現了該介面的話使用普通的for循環來遍歷,性能更高,而沒有實現該介面的話,使用Iterator來迭代,這樣性能更高,例如linkedList。所以這個標記性只是為了讓我們知道我們用什麼樣的方式去獲取數據性能更好
3)Cloneable介面,可以使用Object.Clone()方法。
4)Serializable介面,序列化介面,表明該類可以被序列化,什麼是序列化?簡單的說,就是能夠從類變成位元組流傳輸,反序列化,就是從位元組流變成原來的類
ArrayList核心方法分析
1. add方法(4種重載實現)–增

1)add(E);//默認直接在末尾添加元素
/** * 新增元素 */ public boolean add(E e) { //賦值初始長度 或者擴容,新增元素,當前實際size+1的長度 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //添加元素 elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * 確保elemenData數組有合適的大小 * 如果元素為空,則複製長度默認為10 或者更大 * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 */ private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {//如果數組為空,則從size+1的值和默認值10中取最大的 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } /** * 確保elemenData數組有合適的大小 * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 * 如果長度大於元素長度則擴容 */ private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { //記錄修改次數,迭代中不一致會觸發fail-fast機制,因此在遍歷中刪除元素的正確做法應該是使用Iterator.remove() modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); //擴容 } /** * 擴容 */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 舊容量 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 新容量為舊容量的1.5倍 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 新容量小於參數指定容量,修改新容量 newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 新容量大於最大容量 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 指定新容量 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 拷貝擴容 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //如果小於0 就報錯,如果大於最大值 則取最大值 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }2)add(int index, E element);//給指定下標,添加元素
/** * 給指定下標,添加元素 */ public void add(int index, E element) { //判斷下標是否越界 rangeCheckForAdd(index); //賦值初始長度 或者擴容 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //將源數組中從index位置開始後的size-index個元素統一後移一位 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); //賦值 elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * 判斷下標是否越界 */ private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } /** * src:源數組 * srcPos:源數組要複製的起始位置 * dest:目的數組 * destPos:目的數組放置的起始位置 * length:複製的長度 * 注意:src 和 dest都必須是同類型或者可以進行轉換類型的數組 */ public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);3)addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);//添加Collection類型元素
/** * 按照指定collection的迭代器所返回的元素順序,將該collection中的所有元素添加到此列表的尾部 */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount //將數組a[0,...,numNew-1]複製到數組elementData[size,...,size+numNew-1] System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }4)addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);//指定位置,添加Collection類型元素
/** * 從指定的位置開始,將指定collection中的所有元素插入到此列表中,新元素的順序為指定collection的迭代器所返回的元素順序 */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //判斷下標是否越界 rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; //先將數組elementData[index,...,index+numMoved-1]複製到elementData[index+numMoved,...,index+2*numMoved-1] //即,將源數組中從index位置開始的後numMoved個元素統一後移numNew位 if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }總結:
正常情況下會擴容1.5倍,特殊情況下(新擴展數組大小已經達到了最大值)則只取最大值。
2.remove方法(4種重載實現)–刪

1)remove(int index); //根據指定下標 刪除元素
/** * 根據指定下標 刪除元素 */ public E remove(int index) { //判斷索引是否越界 rangeCheck(index); modCount++; //獲取舊元素 E oldValue = elementData(index); //將數組elementData中index位置之後的所有元素向前移一位 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); //將原數組最後一個位置置為null,由GC清理 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } 2)remove(Object o); //根據指定元素 刪除元素
/** * 移除ArrayList中首次出現的指定元素(如果存在),ArrayList中允許存放重複的元素 */ public boolean remove(Object o) { // 由於ArrayList中允許存放null,因此下面通過兩種情況來分別處理。 if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { //私有的移除方法,跳過index參數的邊界檢查以及不返回任何值 fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /* * 根據下標快速刪除元素 */ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; //將數組elementData中index位置之後的所有元素向前移一位 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work } /** * 清空ArrayList,將全部的元素設為null,等待垃圾回收將這個給回收掉,所以叫clear */ public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; }
3)removeAll(Collection<?> c); //刪除包含在指定容器c中的所有元素
/** * 刪除ArrayList中包含在指定容器c中的所有元素 */ public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { //檢查指定的對象c是否為空 Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false); } /** * 刪除全部 * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 */ private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; int r = 0, w = 0; //讀寫雙指針 boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) //判斷指定容器c中是否含有elementData[r]元素 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; }4)removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter); //按照一定規則過濾(刪除)集合中的元素
/** * 按照一定規則過濾(刪除)集合中的元素 * 如:idList.removeIf(id -> id == nul); * 去掉 List idList 集合中id 為 null 的 * @param filter * @return */ @Override public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) { Objects.requireNonNull(filter); // figure out which elements are to be removed // any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage // will leave the collection unmodified int removeCount = 0; final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size); final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this.size; for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E element = (E) elementData[i]; if (filter.test(element)) { removeSet.set(i); removeCount++; } } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } // shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0; if (anyToRemove) { final int newSize = size - removeCount; for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) { i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i); elementData[j] = elementData[i]; } for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) { elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work } this.size = newSize; if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } return anyToRemove; }總結:
remove函數用戶移除指定下標的元素,此時會把指定下標到數組末尾的元素向前移動一個單位,並且會把數組最後一個元素設置為null,這樣是為了方便之後將整個數組不被使用時,會被GC,可以作為小的技巧使用。
3.set方法–改
/** * 覆蓋指定下標元素 */ public E set(int index, E element) { //判斷索引是否越界 rangeCheck(index); //獲取舊元素 E oldValue = elementData(index); //覆蓋為新元素 elementData[index] = element; //返回舊元素 return oldValue; } /** * 判斷下標是否越界 */ private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }4.get方法–查
/** * 返回指定索引的值 */ public E get(int index) { //判斷索引是否越界 rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 * 返回下標元素的 值 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; }5.indexOf方法–查找下標
/** * 查找下標, 如果為null,直接和null比較,返回下標 */ public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * 查找最後出現的下標,從大往下循環查找 */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }6.clone方法–克隆
/** * 複製,返回此ArrayList 的淺拷貝 */ public Object clone() { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable throw new InternalError(e); } }7.trimToSize方法–刪除冗餘容量
/** * 判斷數據實際容量大小,刪除自動增長後冗餘的容量 * 該方法用於回收多餘的記憶體。也就是說一旦我們確定集合不在添加多餘的元素之後,調用 trimToSize() 方法會將實現集合的數組大小剛好調整為集合元素的大小。 * 注意:該方法會花時間來複制數組元素,所以應該在確定不會添加元素之後在調用 */ public void trimToSize() { modCount++; if (size < elementData.length) { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } }ArrayList總結
1)arrayList可以存放null,本質是Object[]類型的數組。 2)arrayList區別於數組的地方在於能夠自動擴展大小,其中關鍵的方法就是gorw()方法。 3)arrayList由於本質是數組,所以它在數據的查詢方面會很快,而在插入刪除這些方面,性能下降很多,有移動很多數據才能達到應有的效果,而LinkedList則相反。 4)arrayList實現了RandomAccess,所以在遍歷它的時候推薦使用for循環。 5)初始化數組時推薦給初始長度,反覆擴容會增加時耗,影響性能效率。