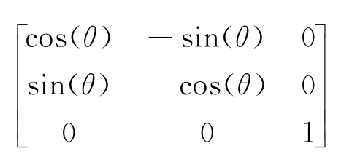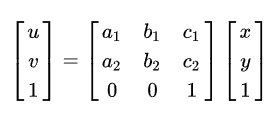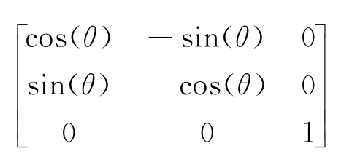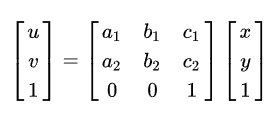[原创]一种自动化九点标定工具原理(包涵部分源码)
-
什么是标定?
- 工业应用中相机拍到一个mark点的坐标为C1(Cx,Cy),C1点对应的龙门架/机械手等执行端对应的坐标是多少?
- 标定就是解决这个问题,如相机拍到一个点坐标C1(Cx,Cy),通过标定公式的计算得到点R1(Rx,Ry),R1就是龙门架/机械手坐标系的真实点位
- C1与R1之间存在一种固定的关系,求解这个关系的过程叫做标定
-
为什么是9点标定?
- C1与R1之间的关系只有三种平移、缩放、旋转
- 矩阵中有对三种关系的公式如下:
- 平移矩阵公式
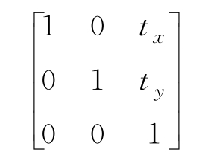
- 缩放矩阵公式
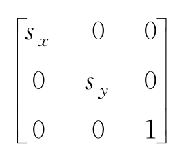
- 旋转矩阵公式
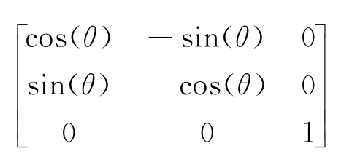
- 上面三种矩阵相乘合成一个矩阵就是仿射变换矩阵
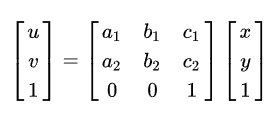
- 最后一个矩阵是根据前3个矩阵相乘得到,故为得到最终的放射变换矩阵,需要知道 Tx,Ty,Sx,Sy,θ这5个参数。为得到5个参数至少需要5个不同等式。
- 故此我们得出结论最少5个点我们就可以推到出最终的放射变换矩阵。
- 那为什么是9点标定呢?答案是为了提高精度,通过9个点我们可以有N种组合算出结果,基于这些结果我们求类似于平均值的东西提高精度
- 那为什么不是10个,11个或更多点呢?答案是9个点的计算已经基本满足大家对精度的要求了,如π=3.1415926已经满足计算精度了,就没必要再把π计算到小数点后100位了
-
怎么实现9点标定呢?
- 拿到9个相机点位[C1,C2…C9],同时拿到这9个点对应的机械手或龙门架真实坐标[R1,R2…R9]
- 把上面数据套入halcon的vector_to_hom_mat2d算子,就可以得到放射变换矩阵了
*像素坐标
Row1:=[1,2,3,4,5,6,1,2,3,4,5,6,1,2,3,4,5,6]
Column1:=[1,1,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,3,3,3]
*机械坐标
Row2:=[50,51.999,54.999,56.999,59.999,62.996,-4.999,-3,0,1.999,4.999,7.995,-59.998,-57.001,-55.001,-52.001,-49.003,-45.005]
Column2:=[-93.3,-47.299,0.002,45.499,91.498,135.493,-92.301,-44.3,0,46.999,91.497,135.494,-90.297,-44.297,1.003,46.999,91.497,134.494]
*求解放射变换矩阵
vector_to_hom_mat2d (Row1, Column1, Row2, Column2, HomMat2D)
*保存变换矩阵到HomMat2D.mat中
serialize_hom_mat2d (HomMat2D, SerializedItemHandle)
open_file ('HomMat2D.mat', 'output_binary', FileHandle)
fwrite_serialized_item (FileHandle, SerializedItemHandle)
close_file (FileHandle)
-
传统的9点标定工具怎么做?
- 求解9点工具的难点在于怎么得到相机拍照点C1对应的真实坐标R1?
- 传统的作法是在机械手或龙门架的执行端下挂一个针尖。让龙门架/机械手到达标定板的点位1使针尖与点位1中心重合,记录真实位置,同时通过拍照得出点位1的相机坐标
-
还有没有更方便的9点标定工具?其原理是什么?
- 有,其核心原理是取消针尖,通过旋转180度方式求解出相机坐标点C1
- 如机械手在物理点位R1(Rx,Ry)拍照的到此mark点对应的相机坐标C1(Cx1,Cy1),然后让机械手旋转180度再次拍照的到mark点对应相机坐标C2(Cx2,Cy2)。那么物理点R1(Rx,Ry)对应的相机的点位未C1,C2的中心点。 因为物料点围绕自己旋转真实点位并未发生变化。
- 通过这种方法就可以实现自动化的9点标定工具
-
此工具适用范围
- 此工具只适用于固定相机(眼在手外)的标定,如底部相机,顶部固定相机。
- 对于相机随龙门架/机械手移动(眼在手上)的标定请听下回分解
-
源码
private Position updatePoiMatrix(Position pcbPoi, Position dstPoi)
{
//到上一个放pcb的点位
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(pcbPoi);
this.currentCylinder.Open();
//到达待测量的点位
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(dstPoi);
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(dstPoi);
//放板
this.currentCylinder.Close();
Thread.Sleep(600);
Position pUp = dstPoi.Copy();
pUp.Z = this.currentRobot.GetSafeZ();
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(pUp);
//到达安全点位
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(safePoi);
//拍照获取mark点
Position poi1 = this.getMarkPoi();
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(dstPoi);
//打开
this.currentCylinder.Open();
//先上升一定的高度再旋转
Position dstPoi2 = dstPoi.Copy();
dstPoi2.Z = this.currentRobot.GetSafeZ();
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(dstPoi2);
//旋转180度
if (dstPoi2.U > 90)
{
dstPoi2.U -= 180;
}
else if (dstPoi2.U < -90)
{
dstPoi2.U += 180;
}
else
{
dstPoi2.U += 180;
}
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(dstPoi2);
dstPoi2.Z = dstPoi.Z;
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(dstPoi2);
//放板
this.currentCylinder.Close();
Thread.Sleep(600);
//到达安全点位
this.currentRobot.GoToPosition(safePoi);
//拍照获取mark2点
Position poi2 = this.getMarkPoi();
//更新对应的数组
imagePoiList.Add(new Position() { X = (poi1.X + poi2.X) / 2, Y = (poi1.Y + poi2.Y) / 2 });
robotPoiList.Add(dstPoi2.Copy());
//返回取PCB的最新位置
return dstPoi2;
}
public void SaveMat(List<Position> imageList, List<Position> robotPoiList, string path)
{
HTuple imageXList = new HTuple(), imageYList = new HTuple();
HTuple robotXList = new HTuple(), robotYList = new HTuple();
for (int i = 0; i < imageList.Count; i++)
{
imageXList[i] = imageList[i].X;
imageYList[i] = imageList[i].Y;
robotXList[i] = robotPoiList[i].X;
robotYList[i] = robotPoiList[i].Y;
}
HTuple hv_HomMat2D = new HTuple(), hv_SerializedItemHandle = new HTuple();
HTuple hv_FileHandle = new HTuple();
////标定
hv_HomMat2D.Dispose();
HOperatorSet.VectorToHomMat2d(imageXList, imageYList, robotXList, robotYList, out hv_HomMat2D);
//保存变换矩阵
hv_SerializedItemHandle.Dispose();
HOperatorSet.SerializeHomMat2d(hv_HomMat2D, out hv_SerializedItemHandle);
hv_FileHandle.Dispose();
HOperatorSet.OpenFile(path, "output_binary", out hv_FileHandle);
HOperatorSet.FwriteSerializedItem(hv_FileHandle, hv_SerializedItemHandle);
HOperatorSet.CloseFile(hv_FileHandle);
imageXList.Dispose();
imageYList.Dispose();
robotXList.Dispose();
robotYList.Dispose();
hv_HomMat2D.Dispose();
hv_SerializedItemHandle.Dispose();
hv_FileHandle.Dispose();
}