重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————3种配置验证[十四]
- 2021 年 6 月 8 日
- 笔记
- .net core(web)
前言
简单整理一些配置的验证。
正文
配置的验证大概分为3类:
-
直接注册验证函数
-
实现IValidteOptions
-
使用Microsoft.Extensions.Options.DataAnnotations
直接注册验证函数
服务:
public class SelfService : ISelfService
{
IOptionsMonitor<SelfServiceOption> _options;
public SelfService(IOptionsMonitor<SelfServiceOption> options)
{
this._options = options;
_options.OnChange((selftServiceOptions) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("alter change:" + selftServiceOptions.Name);
});
}
public string ShowOptionName()
{
return _options.CurrentValue.Name;
}
}
注册:
services.Configure<SelfServiceOption>(Configuration.GetSection("SelfService"), BinderOptions =>
{
BinderOptions.BindNonPublicProperties = true;
});
services.AddSingleton<ISelfService, SelfService>();
services.AddOptions<SelfServiceOption>().Validate(options =>
{
return options.Name != "zhangsan";
});
配置:
{
"SelfService": {
"name": "zhangsan"
}
}
测试:
[HttpGet]
public int GetService([FromServices]ISelfService selfService)
{
Console.WriteLine(selfService.ShowOptionName());
return 1;
}
结果:

使用Microsoft.Extensions.Options.DataAnnotations
services.AddOptions
加上这个函数ValidateDataAnnotations。
然后我们的配置类上加一些属性之类的:
public class SelfServiceOption
{
[Required]
[StringLength(5)]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
因为zhangsan 这个字符超过了5。
结果:

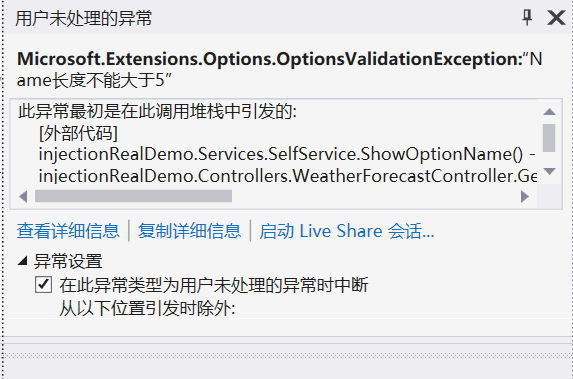
实现IValidteOptions
书写验证函数:
public class SelfServiceValidateOptions : IValidateOptions<SelfServiceOption>
{
public ValidateOptionsResult Validate(string name, SelfServiceOption options)
{
if (options.Name.Length >5)
{
return ValidateOptionsResult.Fail("Name长度不能大于5");
}
else
{
return ValidateOptionsResult.Success;
}
}
}
注册进去:
services.AddSingleton<IValidateOptions
结果:
至于验证的原理。
举下面这个例子:
services.AddOptions<SelfServiceOption>().Validate(options =>
{
return options.Name != "zhangsan";
});
查看Validate:
public virtual OptionsBuilder<TOptions> Validate(Func<TOptions, bool> validation)
{
return this.Validate(validation, "A validation error has occured.");
}
public virtual OptionsBuilder<TOptions> Validate(
Func<TOptions, bool> validation,
string failureMessage)
{
if (validation == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (validation));
this.Services.AddSingleton<IValidateOptions<TOptions>>((IValidateOptions<TOptions>) new ValidateOptions<TOptions>(this.Name, validation, failureMessage));
return this;
}
就十二中也介绍了,在OptionFactory Create的函数中:
//这是_validations的类型
private readonly IEnumerable<IValidateOptions<TOptions>> _validations;
//下面是Create 函数部分:
if (_validations != null)
{
var failures = new List<string>();
foreach (var validate in _validations)
{
var result = validate.Validate(name, options);
if (result.Failed)
{
failures.AddRange(result.Failures);
}
}
if (failures.Count > 0)
{
throw new OptionsValidationException(name, typeof(TOptions), failures);
}
}
会把我们的验证全部验证运行一遍,然后给出全部的错误,所以如果报错的时候,应该把错误看齐,不是只显示一个错误,因为可能不止一个错误。
结
以上只是个人整理,如有错误,望请指点。
下一节,日志系统之战地记者


