【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】3-3 Yarn Application Master 编写
- 2022 年 11 月 18 日
- 笔记
- hadoop, yarn, 大数据, 深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现
本篇文章继续介绍 Yarn Application 中 ApplicationMaster 部分的编写方法。
一、Application Master 编写方法
上一节讲了 Client 提交任务给 RM 的全流程,RM 收到任务后,由 ApplicationsManager 向 NM 申请 Container,并根据 Client 提供的 ContainerLaunchContext 启动 ApplicationMaster。
本篇代码已上传 Github:
Github – MyApplicationMaster
一)整体流程
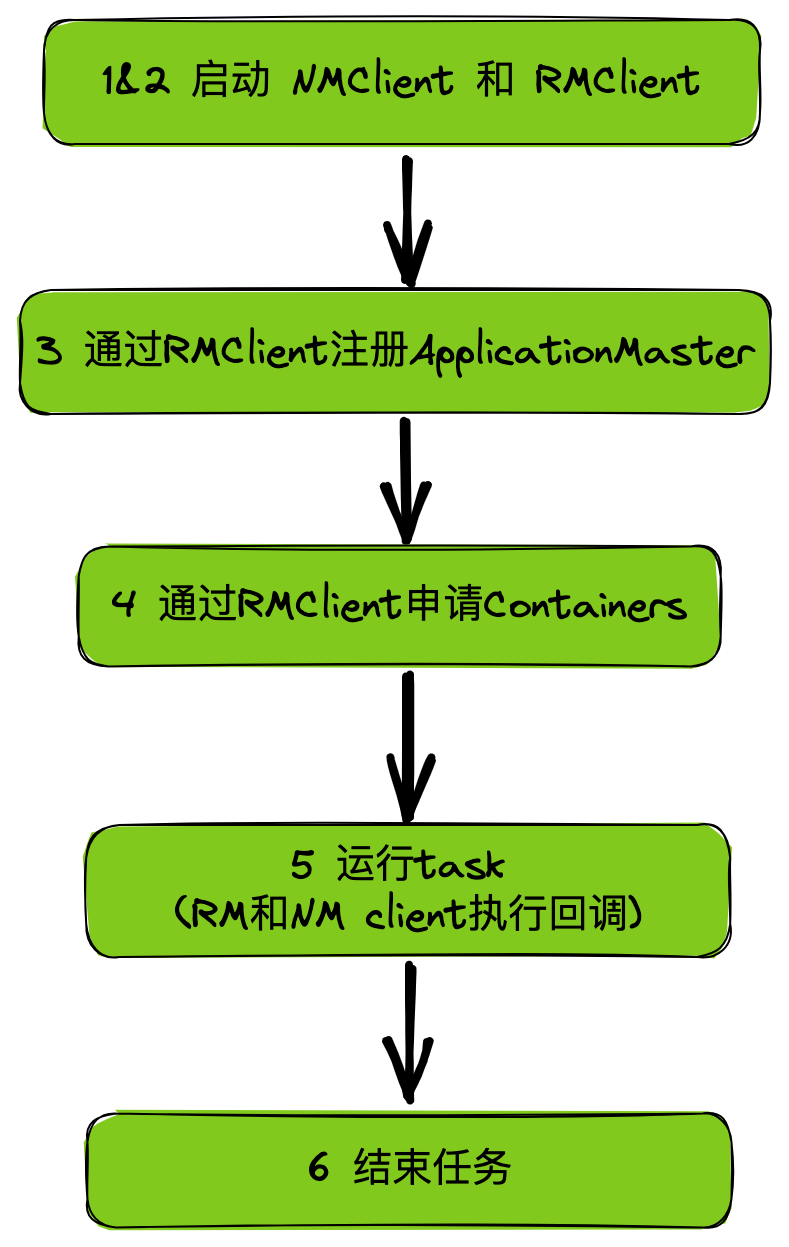
1&2、启动 NMClient 和 RMClient
在 AM 中需要分别启动 NMClient 和 RMClient 进行通信。
两个客户端中都注册了我们自定义的 eventHandler,将会在后面进行介绍。
在 amRMClient 中会定义 AM 向 RM 定时发送心跳的间隔。(在 RM 中会有心跳容忍时间,注意不要超过 RM 配置的时间)
// logInformation();
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 1 create amRMClient
// 第一个参数是心跳时间 ms
amRMClient = AMRMClientAsync.createAMRMClientAsync(1000, new RMCallbackHandler());
amRMClient.init(conf);
amRMClient.start();
// 2 Create nmClientAsync
amNMClient = new NMClientAsyncImpl(new NMCallbackHandler());
amNMClient.init(conf);
amNMClient.start();
3、向 RM 注册 ApplicationMaster
// 3 register with RM and this will heart beating to RM
RegisterApplicationMasterResponse response = amRMClient
.registerApplicationMaster(NetUtils.getHostname(), -1, "");
4、申请 Containers
首先需要从 response 中确认资源池剩余资源,然后再根据需求申请 container
// 4 Request containers
response.getContainersFromPreviousAttempts();
// 4.1 check resource
long maxMem = response.getMaximumResourceCapability().getMemorySize();
int maxVCores = response.getMaximumResourceCapability().getVirtualCores();
// 4.2 request containers base on avail resource
for (int i = 0; i < numTotalContainers.get(); i++) {
ContainerRequest containerAsk = new ContainerRequest(
//100*10M + 1vcpu
Resource.newInstance(100, 1), null, null,
Priority.newInstance(0));
amRMClient.addContainerRequest(containerAsk);
}
5、运行任务
将在 RMCallbackHandler 中的 onContainersAllocated 回调函数中处理,并在其中调用 NMCallbackHandler 的方法,执行对应的 task。
(RMCallbackHandler、NMCallbackHandler将在后面进行详细介绍。)
// RMCallbackHandler
public void onContainersAllocated(List<Container> containers) {
for (Container c : containers) {
log.info("Container Allocated, id = " + c.getId() + ", containerNode = " + c.getNodeId());
// LaunchContainerTask 实现在下面
exeService.submit(new LaunchContainerTask(c));
}
}
private class LaunchContainerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// ……
// 发送事件交给 nm 处理
amNMClient.startContainerAsync(container, ctx);
}
}
6、结束任务
当全部子任务完成后,需要做收尾工作,将 amNMClient 和 amRMClient 停止。
while(numTotalContainers.get() != numCompletedContainers.get()){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("waitComplete" +
", numTotalContainers=" + numTotalContainers.get() +
", numCompletedConatiners=" + numCompletedContainers.get());
} catch (InterruptedException ex){}
}
log.info("ShutDown exeService Start");
exeService.shutdown();
log.info("ShutDown exeService Complete");
amNMClient.stop();
log.info("amNMClient stop Complete");
amRMClient.unregisterApplicationMaster(FinalApplicationStatus.SUCCEEDED, "dummy Message", null);
log.info("unregisterApplicationMaster Complete");
amRMClient.stop();
log.info("amRMClient stop Complete");
二)NMClient 和 RMClient Callback Handler 编写
1、RMCallbackHandler
本质是个 eventHandler,对事件库不熟悉的同学可以翻之前的文章“2-3 Yarn 基础库 – 服务库与事件库”进行学习。
其会处理 Container 启动、停止、更新等事件。
收到不同的事件时,会执行相应的回调函数。这里仅给出两个函数的实现。
💡 思考:之前版本中(2.6之前)还是实现 CallbackHandler 接口,为何后面改为了抽象类?
A:对原接口有了扩展增加了方法 onContainersUpdated。推测是因为避免使用接口继承。
private class RMCallbackHandler extends AMRMClientAsync.AbstractCallbackHandler {
@Override
public void onContainersCompleted(List<ContainerStatus> statuses) {
for (ContainerStatus status : statuses) {
log.info("Container completed: " + status.getContainerId().toString()
+ " exitStatus=" + status.getExitStatus());
if (status.getExitStatus() != 0) {
log.error("Container return error status: " + status.getExitStatus());
log.warn("Need rerun container!");
// do something restart container
continue;
}
ContainerId containerId = status.getContainerId();
runningContainers.remove(containerId);
numCompletedContainers.addAndGet(1);
}
}
@Override
// 这里在 container 中启动相应的 task
public void onContainersAllocated(List<Container> containers) {
for (Container c : containers) {
log.info("Container Allocated, id = " + c.getId() + ", containerNode = " + c.getNodeId());
// LaunchContainerTask 实现在下面
exeService.submit(new LaunchContainerTask(c));
}
}
// 其他方法实现……
}
private class LaunchContainerTask implements Runnable {
Container container;
public LaunchContainerTask(Container container) {
this.container = container;
}
@Override
public void run() {
LinkedList<String> commands = new LinkedList<>();
commands.add("sleep " + sleepSeconds.addAndGet(1));
ContainerLaunchContext ctx = ContainerLaunchContext.newInstance(null, null, commands, null, null, null);
// 这里去执行 amNMClient 的回调
amNMClient.startContainerAsync(container, ctx);
}
}
2、NMCallbackHandler
定义 nm container 需要执行的各种事件处理。
private class NMCallbackHandler extends NMClientAsync.AbstractCallbackHandler {
@Override
public void onContainerStarted(ContainerId containerId, Map<String, ByteBuffer> allServiceResponse) {
log.info("Container Stared " + containerId.toString());
}
// ……
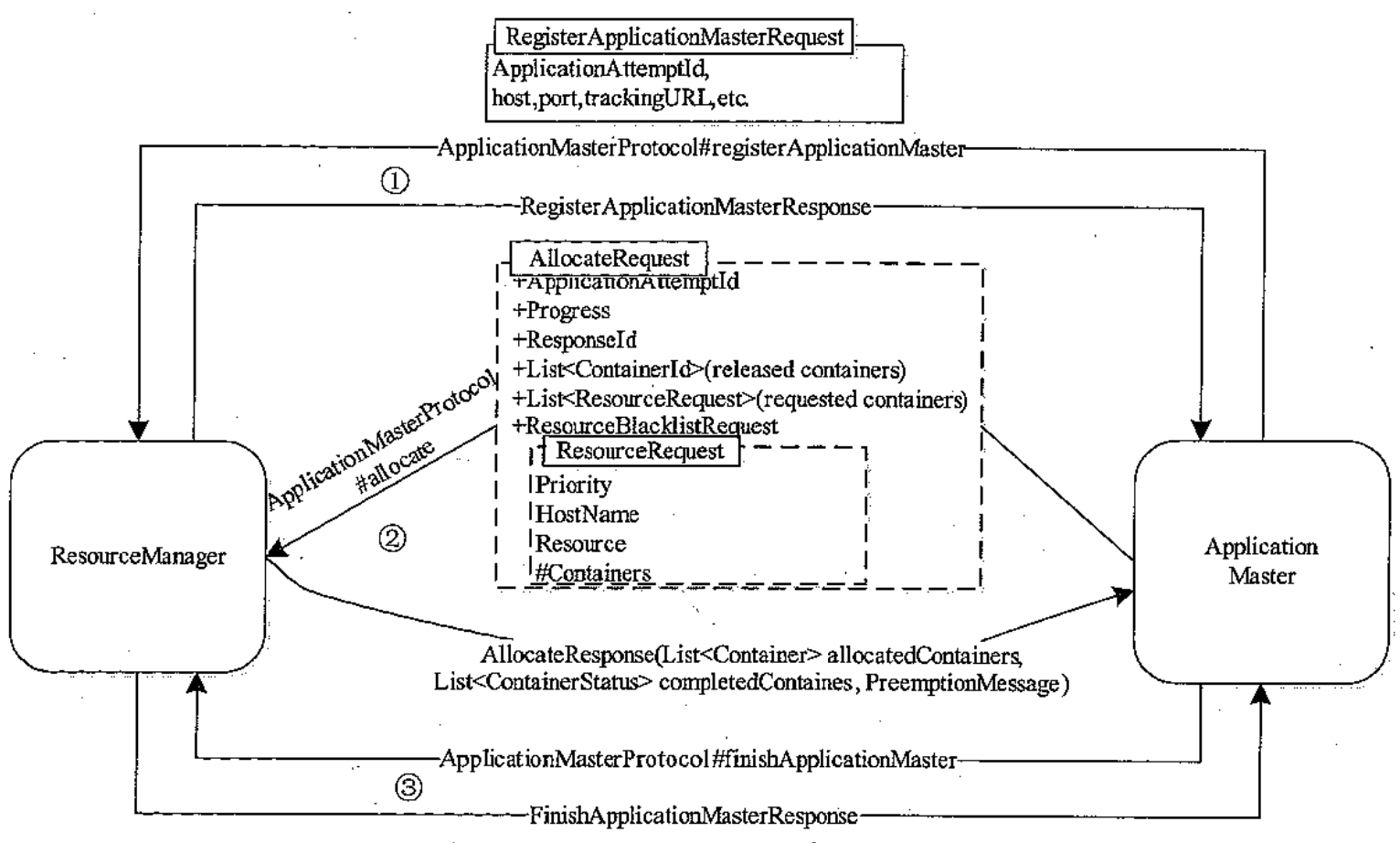
三)涉及的通信协议
AM 与 RM
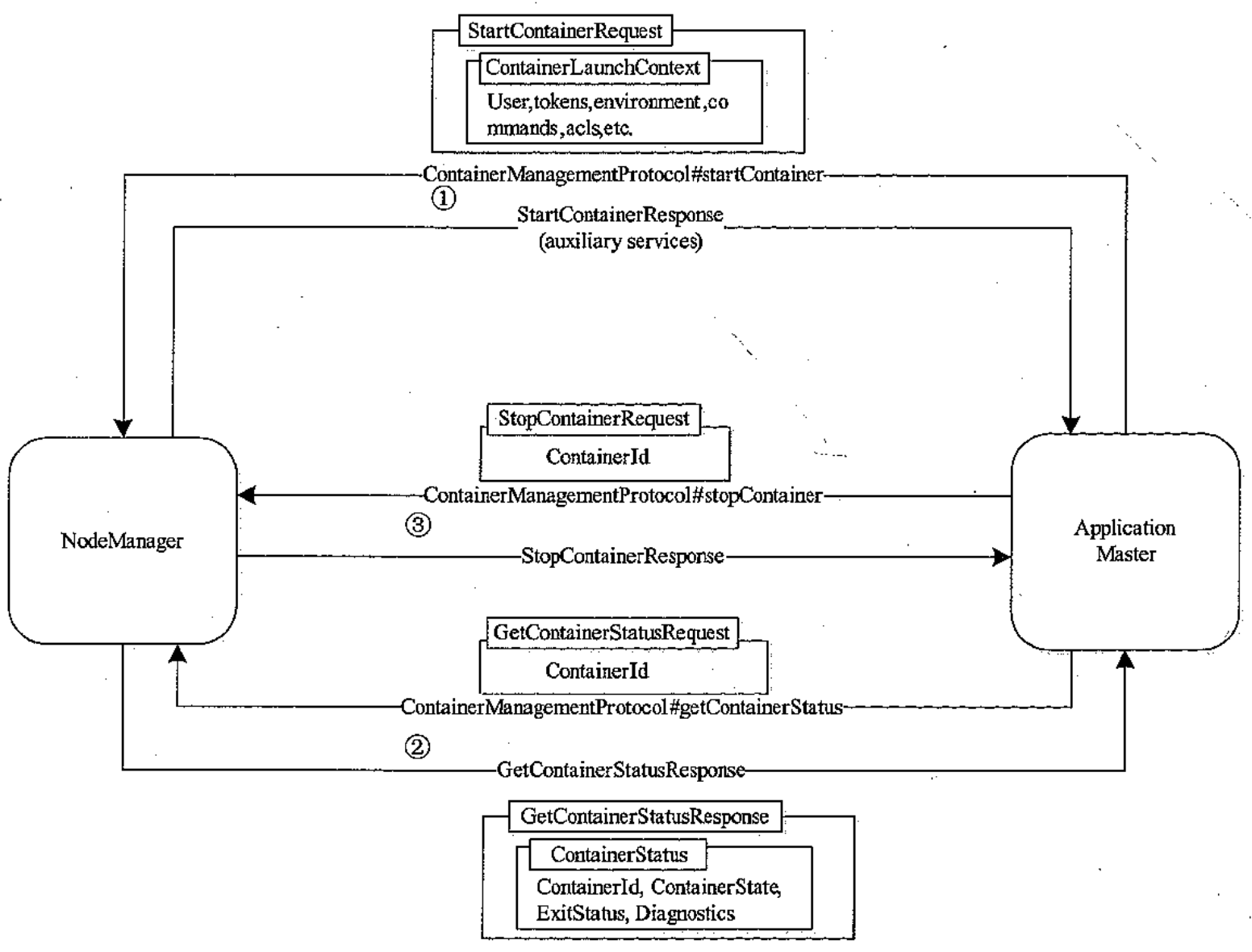
AM 与 NM
二、小结
至此我们学习了编写 Yarn Application 的整体流程和实现方法,相信各位同学对其有了更深的认识。之后可以从 hadoop 提供的 DistributedShell 入手,再到其他框架(Hive、Flink)等探究工业级框架是如何提交 Application 的。
参考文章:
Hadoop Doc: Writing an ApplicationMaster (AM)
《Hadoop 技术内幕 – 深入解析 Yarn 结构设计与实现原理》第四章


