基础分类网络VGG
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 笔记
vgg16是牛津大学视觉几何组(Oxford Visual Geometry Group)2014年提出的一个模型. vgg模型也得名于此.
2014年,vgg16拿了Imagenet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2014 (ILSVRC2014)
比赛的冠军.
论文连接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/very_deep/牛津大学视觉研究小组在这里放出了他们在ImageNet比赛训练得到的模型文件.
网上有很多vgg16的实现,下面
-
https://github.com/machrisaa/tensorflow-vgg/blob/master/vgg16.py
这个是推理的实现,即加载权重文件,实现图像预测 -
https://github.com/ppplinday/tensorflow-vgg16-train-and-test/blob/master/train_vgg.py
这个是训练的实现,即如何得到权重文件
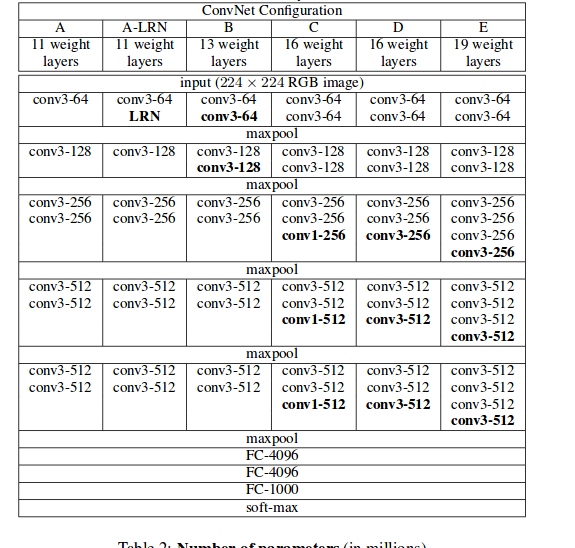
vgg的模型结构如下:
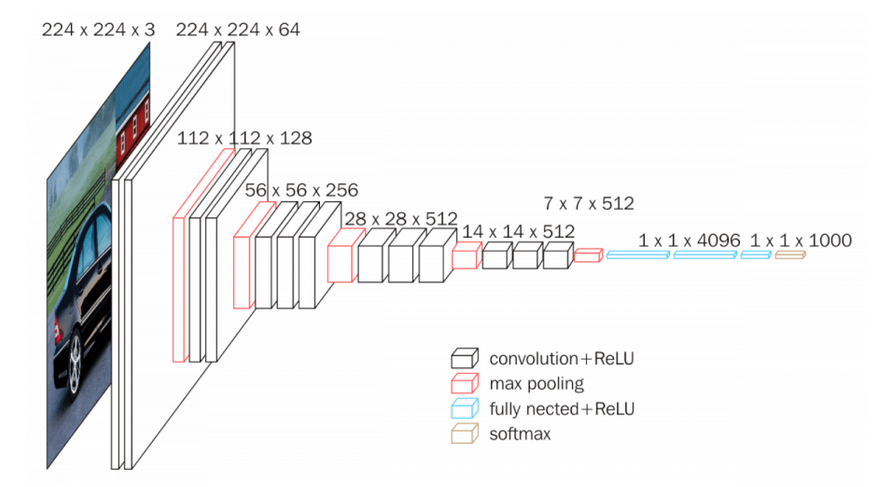
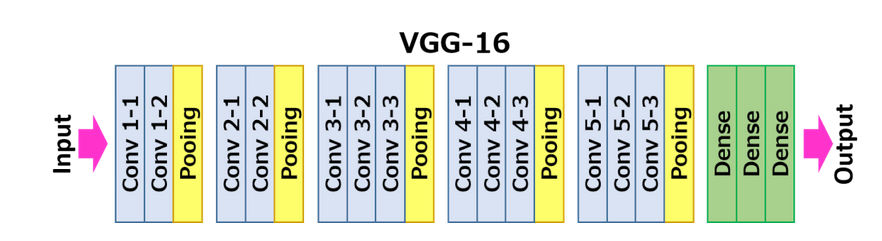
每一层的卷积核的大小都是3*3.
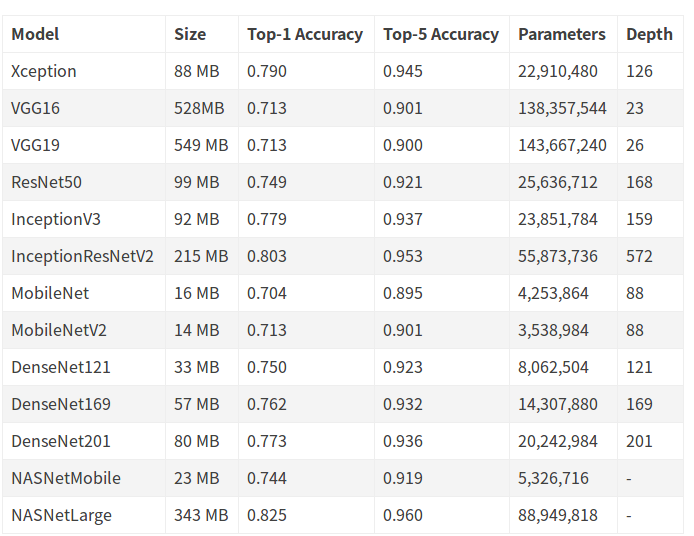
现在的keras里已经集成了很多模型,具体可以参考keras的文档.
https://keras.io/applications/#models-for-image-classification-with-weights-trained-on-imagenet
下面是keras_applications/vgg16.py的实现.比tensorflow的代码更易于理解.
"""VGG16 model for Keras. # Reference - [Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition]( https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556) (ICLR 2015) """ from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function import os from . import get_submodules_from_kwargs from . import imagenet_utils from .imagenet_utils import decode_predictions from .imagenet_utils import _obtain_input_shape preprocess_input = imagenet_utils.preprocess_input WEIGHTS_PATH = ('https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/' 'releases/download/v0.1/' 'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5') WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP = ('https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/' 'releases/download/v0.1/' 'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5') def VGG16(include_top=True, weights='imagenet', input_tensor=None, input_shape=None, pooling=None, classes=1000, **kwargs): """Instantiates the VGG16 architecture. Optionally loads weights pre-trained on ImageNet. Note that the data format convention used by the model is the one specified in your Keras config at `~/.keras/keras.json`. # Arguments include_top: whether to include the 3 fully-connected layers at the top of the network. weights: one of `None` (random initialization), 'imagenet' (pre-training on ImageNet), or the path to the weights file to be loaded. input_tensor: optional Keras tensor (i.e. output of `layers.Input()`) to use as image input for the model. input_shape: optional shape tuple, only to be specified if `include_top` is False (otherwise the input shape has to be `(224, 224, 3)` (with `channels_last` data format) or `(3, 224, 224)` (with `channels_first` data format). It should have exactly 3 input channels, and width and height should be no smaller than 32. E.g. `(200, 200, 3)` would be one valid value. pooling: Optional pooling mode for feature extraction when `include_top` is `False`. - `None` means that the output of the model will be the 4D tensor output of the last convolutional block. - `avg` means that global average pooling will be applied to the output of the last convolutional block, and thus the output of the model will be a 2D tensor. - `max` means that global max pooling will be applied. classes: optional number of classes to classify images into, only to be specified if `include_top` is True, and if no `weights` argument is specified. # Returns A Keras model instance. # Raises ValueError: in case of invalid argument for `weights`, or invalid input shape. """ backend, layers, models, keras_utils = get_submodules_from_kwargs(kwargs) if not (weights in {'imagenet', None} or os.path.exists(weights)): raise ValueError('The `weights` argument should be either ' '`None` (random initialization), `imagenet` ' '(pre-training on ImageNet), ' 'or the path to the weights file to be loaded.') if weights == 'imagenet' and include_top and classes != 1000: raise ValueError('If using `weights` as `"imagenet"` with `include_top`' ' as true, `classes` should be 1000') # Determine proper input shape input_shape = _obtain_input_shape(input_shape, default_size=224, min_size=32, data_format=backend.image_data_format(), require_flatten=include_top, weights=weights) if input_tensor is None: img_input = layers.Input(shape=input_shape) else: if not backend.is_keras_tensor(input_tensor): img_input = layers.Input(tensor=input_tensor, shape=input_shape) else: img_input = input_tensor # Block 1 x = layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block1_conv1')(img_input) x = layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block1_conv2')(x) x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block1_pool')(x) # Block 2 x = layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block2_conv1')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block2_conv2')(x) x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block2_pool')(x) # Block 3 x = layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block3_conv1')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block3_conv2')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block3_conv3')(x) x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block3_pool')(x) # Block 4 x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block4_conv1')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block4_conv2')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block4_conv3')(x) x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block4_pool')(x) # Block 5 x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block5_conv1')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block5_conv2')(x) x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', name='block5_conv3')(x) x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block5_pool')(x) if include_top: # Classification block x = layers.Flatten(name='flatten')(x) x = layers.Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc1')(x) x = layers.Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc2')(x) x = layers.Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x) else: if pooling == 'avg': x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x) elif pooling == 'max': x = layers.GlobalMaxPooling2D()(x) # Ensure that the model takes into account # any potential predecessors of `input_tensor`. if input_tensor is not None: inputs = keras_utils.get_source_inputs(input_tensor) else: inputs = img_input # Create model. model = models.Model(inputs, x, name='vgg16') # Load weights. if weights == 'imagenet': if include_top: weights_path = keras_utils.get_file( 'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5', WEIGHTS_PATH, cache_subdir='models', file_hash='64373286793e3c8b2b4e3219cbf3544b') else: weights_path = keras_utils.get_file( 'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5', WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP, cache_subdir='models', file_hash='6d6bbae143d832006294945121d1f1fc') model.load_weights(weights_path) if backend.backend() == 'theano': keras_utils.convert_all_kernels_in_model(model) elif weights is not None: model.load_weights(weights) return model 可以清楚地看出来,所用的卷积核全部是3*3的.
用keras做预测也很简单,
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16 model = VGG16() print(model.summary())上面代码会把权重文件下载到
这里贴一段网上找的代码
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input, decode_predictions from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array import numpy as np # VGG-16 instance model = VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=True) image = load_img('C:/Pictures/Pictures/test_imgs/golden.jpg', target_size=(224, 224)) image_data = img_to_array(image) # reshape it into the specific format image_data = image_data.reshape((1,) + image_data.shape) print(image_data.shape) # prepare the image data for VGG image_data = preprocess_input(image_data) # using the pre-trained model to predict prediction = model.predict(image_data) # decode the prediction results results = decode_predictions(prediction, top=3) print(results)很简单
- 加载模型
- 加载图片,预处理
- 前向传播
- 解释输出tensor
vgg19和vgg16结构基本一致的,就是多了几个卷积层.