线程——线程实现方式和线程属性
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 笔记
进程和线程
进程是计算机系统中能独立运行并作为资源分配的基本单位,它是由PCB(进程控制块),数据段和代码段组成,是一个能独立运行的基本单位.进程的创建,调度,分派都需要较大的时间和空间开销,在操作系统中引入线程,以线程作为调度和分派的基本单位,以此来改进多处理机系统的性能
线程是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位,同一个进程中的多条线程共享该进程中的全部系统资源
进程与线程的区别:
- 进程每次调度时,都需要进行上下文切换将断点的信息保存在PCB中,开销较大.线程调度时,只需要保存和设置少量的寄存器内容,切换代价比较小
- 进程作为系统资源分配的基本单位,拥有一定的资源,包括用于存放程序,数据的磁盘和内存地址空间,以及在它运行时所需要的I/O设备,已打开的信号量等.而线程只拥有一点必不可少的,能保证独立运行的资源(如控制线程运行的TCB,用于指示被执行指令序列的程序计数器,保存局部变量,少数状态参数和返回地址等的一组寄存器和堆栈),允许多个线程共享该进程中的内存地址空间和资源
java中实现线程的两种方式
java中允许程序并发地运行多个线程,并发是指同一时间间隔中有两个或多个事件同时发生,并行是指同一时刻有两个或多个事件同时执行.
1. 继承Thread类并重写run()方法
Thread表示线程类,run方法中是我们启动线程时要做的事,应该使用start()方法启动线程,直接调用run方法相当于普通的方法调用,下面我们通过继承Thread类的方式定义了一个线程类用来输出0到9,接着在main方法中创建两个线程类的实例并启动线程,可以看出线程的执行情况是随机的.线程的调度细节取决于操作系统,抢占式的线程调度给每个线程一个时间片的时间运行该线程,当该时间片完时,系统会保存当前线程的状态,然后终止当前线程的执行,执行另一个线程,当下一个时间片完时,又会终止当前执行线程,依次类推.直到所有线程终止.
1 public class FirstThread extends Thread{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"打印"+i); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class FirstDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 Thread thread = new FirstThread(); 12 Thread thread2 = new FirstThread(); 13 thread.start(); 14 thread2.start(); 15 } 16 }
2.实现Runnable接口
Thread类有一个参数为Runnable对象的构造函数,它可以使用给定的Runnable对象创建一个线程.
1 public class FirstThread implements Runnable{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"打印"+i); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class FirstDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 Thread thread = new Thread(new FirstThread()); 12 Thread thread2 = new Thread(new FirstThread()); 13 thread.start(); 14 thread2.start(); 15 } 16 }
线程属性
线程名(默认Thread-线程初始化时的序号)
1 private String name; 2 3 // 设置线程的名字 4 public final synchronized void setName(String name) { 5 checkAccess(); // 检查是否允许更改线程的参数 6 7 if (name == null) { 8 throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); 9 } 10 11 this.name = name; 12 if (threadStatus != 0) { // 判断线程的状态 13 setNativeName(name); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // 获取线程的名字 18 public final String getName() { 19 return name; 20 }
线程的优先级(默认是父线程的优先级)
1 private int priority; 2 3 public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1; // 线程的最小优先级 4 5 public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5; // 线程的默认优先级 6 7 public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10; // 线程的最大优先级 8 9 // 设置线程的优先级 10 public final void setPriority(int newPriority) { 11 ThreadGroup g; 12 checkAccess(); // 安全检查 13 14 // 检查设定的优先级是否大于最大优先级或最小优先级,如果是抛出参数不合法异常 15 if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) { 16 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 17 } 18 19 // 获取当前的线程组 20 if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) { 21 // 如果当前设定的优先级大于它所在线程组的最大优先级 22 if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) { 23 // 设置当前线程的优先级为当前线程组的最大优先级 24 newPriority = g.getMaxPriority(); 25 } 26 // 调用本地方法setPriority0设置线程优先级 27 setPriority0(priority = newPriority); 28 } 29 } 30 31 // 获取当前线程的优先级 32 public final int getPriority() { 33 return priority; 34 } 35
线程是否是守护线程(默认是父线程的值)
守护线程是为其他线程提供服务的线程,当一个程序只剩下守护线程了,java虚拟机就会退出程序,也就是说守护线程是依托用户线程而存在的,用户线程的终止将会导致守护线程终止,不管当前处于什么状态,在使用守护线程时,应该避免守护线程去访问固有的资源,如文件,数据库等.它会在任何一个操作的中间发生中断.
1 private boolean daemon; 2 3 // 设置该线程是否是守护线程 4 public final void setDaemon(boolean on) { 5 // 安全检查 6 checkAccess(); 7 8 // 如果线程处于活动状态,抛出表示没有在线程适当状态操作进行的异常 9 if (isAlive()) { 10 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 11 } 12 // 设置线程是否为守护线程 13 daemon = on; 14 } 15 // 判断当前线程是否处于活动状态 16 public final native boolean isAlive(); 17 18 // 判断当前线程是否是 守护线程 19 public final boolean isDaemon() { 20 return daemon; 21 }
线程的状态
线程的状态使用一个内部静态枚举类表示
1 public enum State { 2 3 NEW, // 新建状态 4 5 RUNNABLE, // 可运行状态 6 7 BLOCKED, // 阻塞状态 8 9 WAITING, // 等待状态 10 11 TIMED_WAITING, // 等待一段时间的状态 12 13 TERMINATED; // 终止状态 14 } 15 16 // 获取当前线程的状态 17 public State getState() { 18 // get current thread state 19 return sun.misc.VM.toThreadState(threadStatus); 20 }
线程的未捕获异常处理器
线程的run方法没有抛出任何的受查异常,如果在运行时抛出异常,然而并未捕获处理该异常,该线程即将终止,此时就会将该线程和异常作为参数调用未捕获异常处理器的方法,未捕获异常处理器是一个实现UncaughtExceptionHandler接口的类,UncaughtException是Thread的一个静态内部类,它的内部只有一个方法 void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e); 该方法将会在线程因未捕获的异常而终止时调用.ThreadGroup类实现了该接口.Thread类有两个UncaughtExceptionHandler接口的变量,一个是默认的处理器(用static修饰),供所有的线程使用,另一个只供当前线程使用.默认情况下这两个变量都为null,线程使用的未捕获异常处理器是该线程组的处理器.
1 // 供当前线程使用 2 private volatile UncaughtExceptionHandler uncaughtExceptionHandler; 3 4 // 获取当前线程的未捕获异常处理器 5 public UncaughtExceptionHandler getUncaughtExceptionHandler() { 6 // 如果当前线程无未捕获异常处理器,则返回该线程所属线程组的处理器 7 return uncaughtExceptionHandler != null ? 8 uncaughtExceptionHandler : group; 9 } 10 // 设置当前线程的未捕获异常处理器 11 public void setUncaughtExceptionHandler(UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) { 12 checkAccess(); 13 uncaughtExceptionHandler = eh; 14 } 15 16 // 供所有线程使用 17 private static volatile UncaughtExceptionHandler defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler; 18 19 // 获取默认的未捕获异常处理器 20 public static UncaughtExceptionHandler getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(){ 21 return defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler; 22 } 23 // 设置默认的未捕获异常处理器 24 public static void setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) { 25 26 // 获取系统安全管理器 27 SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); 28 if (sm != null) { 29 // 检查是否允许执行给定权限的请求,如果不允许,抛出SecurityException异常 30 sm.checkPermission( 31 32 // 创建一个在线程由于未捕获的异常而突然终止时,设置将要使用的默认处理程序的运行时权限对象 33 new RuntimePermission("setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler") 34 ); 35 } 36 // 设置默认的未捕获异常处理器 37 defaultUncaughtExceptionHandler = eh; 38 }
1 // ThreadGroup 实现Thread.Uncaughtexception接口的源码解析 2 public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) { 3 // 如果该线程组有父线程组,则使用父线程组的处理器 4 if (parent != null) { 5 parent.uncaughtException(t, e); 6 } else { 7 8 // 获取默认的未捕获异常处理器 9 Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler ueh = 10 Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(); 11 12 // 如果有默认的异常处理器就使用它 13 if (ueh != null) { 14 ueh.uncaughtException(t, e); 15 16 } 17 // 否则判断引起线程终止的异常是否是ThreadDeath的子类,如果是,什么也不做,负责将线程名和堆栈信息输出到标准错误流中,ThreadDeath是 18 else if (!(e instanceof ThreadDeath)) { 19 System.err.print("Exception in thread "" 20 + t.getName() + "" "); 21 e.printStackTrace(System.err); 22 } 23 } 24 }
线程组ThreadGroup
线程组是一个统一管理线程的集合,除了初始线程组,每个线程组有一个父线程组,线程组也可以包含其他线程组,允许线程访问有关自己的线程组的信息,但是不允许它访问有关其线程组的父线程组或其他任何线程组的信息.默认情况下,创建的线程组都属于main线程组.线程组有两个构造方法
线程组属性
1 private final ThreadGroup parent; // 父线程组,一旦指定不可修改 2 String name; // 线程组名 3 int maxPriority; // 线程组的最大优先级 4 boolean destroyed; // 线程组是否被销毁 5 boolean daemon; // 线程组是否是守护线程组 6 boolean vmAllowSuspension; // 虚拟机自动挂起 7 8 int nUnstartedThreads = 0; // 线程组中未启动线程的数量 9 int nthreads; // 此线程组包含的线程数 10 Thread[] threads[]; // 该线程组中包含的线程 11 12 int ngroups; // 子线程组计数器 13 ThreadGroup[] groups; // 该线程组中包含的线程组
1 构造函数调用顺序从上到下 2 3 //使用指定的线程组名构造线程组 4 public ThreadGroup(String name) { 5 // 获取当前线程组的父线程组 6 this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name); 7 } 8 9 //创建一个父线程组时指定线程,并且名字为name的线程组 10 public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) { 11 // 检查父线程组 12 this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name); 13 } 14 15 16 //检查线程组的安全 17 private static Void checkParentAccess(ThreadGroup parent) { 18 parent.checkAccess(); 19 return null; 20 } 21 //安全检查 22 public final void checkAccess() { 23 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); 24 if (security != null) { 25 security.checkAccess(this); 26 } 27 } 28 29 private ThreadGroup(Void unused, ThreadGroup parent, String name) { 30 // 设置线程组名 31 this.name = name; 32 // 最大优先级是父线程组的最大优先级 33 this.maxPriority = parent.maxPriority; 34 // 是否是守护线程组合父线程组保持一致 35 this.daemon = parent.daemon; 36 // 虚拟机参数 37 this.vmAllowSuspension = parent.vmAllowSuspension; 38 this.parent = parent; 39 parent.add(this); 40 } 41 // 添加指定的线程组 42 private final void add(ThreadGroup g) { 43 synchronized (this) { 44 // 如果线程组已经被销毁,抛出异常 45 if (destroyed) { 46 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 47 } 48 // 判断此线程组子线程组数组是否为空或已满 49 // 如果为空,创建子线程数组,初始容量为4,将指定线程组加入该数组,计数器加一; 50 // 如果子线程数组已满,数组容量扩容两倍,将指定线程组存入数组,计数器加一 51 // 如果子线程数组未满,将指定线程组加入该数组,计数器加一 52 if (groups == null) { 53 groups = new ThreadGroup[4]; 54 } else if (ngroups == groups.length) { 55 groups = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroups * 2); 56 } 57 groups[ngroups] = g; 58 ngroups++; 59 } 60 }
其他方法

1 // 移除指定的线程组 2 private void remove(ThreadGroup g) { 3 synchronized (this) { 4 // 判断该线程组是否死亡 5 if (destroyed) { 6 return; 7 } 8 // 循环遍历子线程组数组,找到要删除的线程组,如果找到,子线程组计数器减一 9 // 将处于该线程组元素后的元素向前移动,将最后一个元素置空,跳出循环 10 for (int i = 0; i < ngroups; i++) { 11 if (groups[i] == g) { 12 ngroups -= 1; 13 System.arraycopy(groups, i + 1, groups, i, ngroups - i); 14 groups[ngroups] = null; 15 break; 16 } 17 } 18 19 // 唤醒在此对象上所有等待的线程 20 if (nthreads == 0) { 21 notifyAll(); 22 } 23 // 如果此线程组同时满足以下条件,销毁该线程组及其子组 24 // 1. 是守护线程组 25 // 2. 包含的线程数为0 26 // 3. 未启动线程数量为0 27 // 4. 包含的线程组数为0 28 if (daemon && (nthreads == 0) && (nUnstartedThreads == 0) && (ngroups == 0)) { 29 destroy(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 // 将指定线程加入该线程组 35 void add(Thread t) { 36 synchronized (this) { 37 if (destroyed) { 38 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 39 } 40 if (threads == null) { 41 threads = new Thread[4]; 42 } else if (nthreads == threads.length) { 43 threads = Arrays.copyOf(threads, nthreads * 2); 44 } 45 threads[nthreads] = t; 46 nthreads++; 47 // 为了防止线程组被销毁,未启动线程数递减 48 nUnstartedThreads--; 49 } 50 } 51 52 // 移除指定的线程 53 private void remove(Thread t) { 54 synchronized (this) { 55 if (destroyed) { 56 return; 57 } 58 for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 59 if (threads[i] == t) { 60 System.arraycopy(threads, i + 1, threads, i, --nthreads - i); 61 threads[nthreads] = null; 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 68 // 获得该线程组的名字 69 public final String getName() { 70 return name; 71 } 72 73 // 获得该线程组的最大优先级 74 public final int getMaxPriority() { 75 return maxPriority; 76 } 77 78 // 获得该线程组的父线程组 79 public final ThreadGroup getParent() { 80 if (parent != null) 81 parent.checkAccess(); 82 return parent; 83 } 84 85 // 判断该线程组是否是守护线程组 86 public final boolean isDaemon() { 87 return daemon; 88 } 89 90 // 判断该线程组是否被销毁 91 public synchronized boolean isDestroyed() { 92 return destroyed; 93 } 94 95 // 设置该线程组的最大优先级 96 public final void setMaxPriority(int pri) { 97 int ngroupsSnapshot; 98 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 99 100 synchronized (this) { 101 checkAccess(); 102 // 判断给定优先级是否符合要求,不符合要求直接返回 103 if (pri < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || pri > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) { 104 return; 105 } 106 107 // 如果当前线程组没有父线程组,最大优先级就为给定的值 108 // 否则判断父线程组最大优先级和指定优先级,取最小值为该线程组的最大优先级 109 maxPriority = (parent != null) ? Math.min(pri, parent.maxPriority) : pri; 110 111 // 获取该线程子线程组的快照(如果存在的话 112 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 113 if (groups != null) { 114 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 115 } else { 116 groupsSnapshot = null; 117 } 118 } 119 // 遍历该线程组的所有子线程组,递归将最大优先级设置为指定值 120 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 121 groupsSnapshot[i].setMaxPriority(pri); 122 } 123 } 124 125 // 设置该线程组是否是守护线程 126 public final void setDaemon(boolean daemon) { 127 checkAccess(); 128 this.daemon = daemon; 129 } 130 131 // 测试此线程组是否是指定线程组的祖先 132 public final boolean parentOf(ThreadGroup g) { 133 for (; g != null; g = g.parent) { 134 if (g == this) { 135 return true; 136 } 137 } 138 return false; 139 } 140 141 // 销毁此线程组及其子组 142 public final void destroy() { 143 int ngroupsSnapshot; 144 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 145 synchronized (this) { 146 checkAccess(); 147 // 如果线程组已经销毁或该线程组还有活动的线程,抛出一个异常 148 if (destroyed || (nthreads > 0)) { 149 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); 150 } 151 // 获取子线程组的快照(如果存在的话) 152 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 153 if (groups != null) { 154 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 155 } else { 156 groupsSnapshot = null; 157 } 158 159 // 如果该线程组存在父线程组,将各种属性置空 160 if (parent != null) { 161 destroyed = true; 162 ngroups = 0; 163 groups = null; 164 nthreads = 0; 165 threads = null; 166 } 167 } 168 // 循环遍历子线程组,对每个子线程组进行递归处理 169 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i += 1) { 170 groupsSnapshot[i].destroy(); 171 } 172 173 // 如果一个线程组存在父线程组,从父线程组中移除该线程组 174 if (parent != null) { 175 parent.remove(this); 176 } 177 } 178 179 // 获得此线程组中活动的线程数 180 public int activeCount() { 181 int result; 182 int ngroupsSnapshot; 183 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 184 synchronized (this) { 185 if (destroyed) { 186 return 0; 187 } 188 result = nthreads; 189 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 190 if (groups != null) { 191 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 192 } else { 193 groupsSnapshot = null; 194 } 195 } 196 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 197 result += groupsSnapshot[i].activeCount(); 198 } 199 return result; 200 } 201 202 // 获得此线程组中活动的线程组数 203 public int activeGroupCount() { 204 int ngroupsSnapshot; 205 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 206 synchronized (this) { 207 if (destroyed) { 208 return 0; 209 } 210 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 211 if (groups != null) { 212 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 213 } else { 214 groupsSnapshot = null; 215 } 216 } 217 int n = ngroupsSnapshot; 218 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 219 n += groupsSnapshot[i].activeGroupCount(); 220 } 221 return n; 222 } 223 224 // 将此线程组的有关信息输出到标准输出流 225 public void list() { 226 list(System.out, 0); 227 } 228 229 void list(PrintStream out, int indent) { 230 int ngroupsSnapshot; 231 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 232 synchronized (this) { 233 for (int j = 0; j < indent; j++) { 234 out.print(" "); 235 } 236 out.println(this); 237 indent += 4; 238 for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 239 for (int j = 0; j < indent; j++) { 240 out.print(" "); 241 } 242 out.println(threads[i]); 243 } 244 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 245 if (groups != null) { 246 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 247 } else { 248 groupsSnapshot = null; 249 } 250 } 251 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 252 groupsSnapshot[i].list(out, indent); 253 } 254 } 255 256 // 返回此此类的字符串描述:类名+线程组名+最大优先级 257 public String toString() { 258 return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + getName() + ",maxpri=" + maxPriority + "]"; 259 } 260 261 // 中断线程组中所有线程和子线程组 262 public final void interrupt() { 263 int ngroupsSnapshot; 264 ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot; 265 synchronized (this) { 266 checkAccess(); 267 // 中断包含的线程 268 for (int i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { 269 threads[i].interrupt(); 270 } 271 ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups; 272 if (groups != null) { 273 groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot); 274 } else { 275 groupsSnapshot = null; 276 } 277 } 278 // 遍历子线程组,递归处理每一个子线程组 279 for (int i = 0; i < ngroupsSnapshot; i++) { 280 groupsSnapshot[i].interrupt(); 281 } 282 } 283 284 // 将线程组的所有活动线程复制到指定数组中。如果存在第二个参数,第二个参数为true表示包含子组中的活动线程,默认包含子组中的所有活动线程数, 285 // 当给定的数组不足以容纳该线程组的活动线程数时,忽略额外的线程,因此,最好调用activeCount方法确定是否小于list的长度 286 public int enumerate(Thread list[]) { 287 checkAccess(); 288 return enumerate(list, 0, true); 289 } 290 291 public int enumerate(Thread list[], boolean recurse) { 292 checkAccess(); 293 return enumerate(list, 0, recurse); 294 } 295 296 private int enumerate(Thread list[], int n, boolean recurse); 297 298 // 将线程组的所有活动子组复制到指定数组中。如果存在第二个参数,第二个参数为true表示包含子组中的活动子组,默认包含子组中的所有活动子组, 299 // 当给定的数组不足以容纳该线程组的活动子组数时,忽略额外的子组,因此,最好调用activeGroupCount方法确定是否小于list的长度 300 301 public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[]) { 302 checkAccess(); 303 return enumerate(list, 0, true); 304 } 305 306 public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], boolean recurse) { 307 checkAccess(); 308 return enumerate(list, 0, recurse); 309 } 310 311 private int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], int n, boolean recurse); 312 313 // 允许Java虚拟机在内存不足是挂起 314 @Deprecated 315 public boolean allowThreadSuspension(boolean b); 316 317 // 停止此线程组中的所有线程,不安全 318 @Deprecated 319 public final void stop(); 320 321 // 挂起此线程组中的所有线程。 容易导致死锁 322 @Deprecated 323 public final void suspend(); 324 325 // 继续此线程组中的所有线程。容易导致死锁 326 @Deprecated 327 public final void resume(); 328 329 }
View Code
线程Thread
1 // 公开的构造函数本质上都是先调用四个参数的init方法,然后调用六个参数的私有init方法构造线程对象 2 3 public Thread() { 4 // 调用无参构造时设置线程的名字,然后调用四个参数的私有init方法,由init方法去调用六个参数的init方法 5 init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); 6 } 7 8 // 构造一个新的Thread对象,使用指定的运行对象 9 public Thread(Runnable target) { 10 // 设置线程的名字,调用四个参数的init方法,由init方法去调用六个参数的init方法 11 init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); 12 } 13 14 // 构造一个指定线程组,使用指定运行对象的Thread对象 15 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) { 16 init(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); 17 } 18 19 // 构造一个指定线程名的Thread对象 20 public Thread(String name) { 21 init(null, null, name, 0); 22 } 23 24 // 构造一个指定线程组和名字的Thread对象 25 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) { 26 init(group, null, name, 0); 27 } 28 29 // 构造一个具有指定运行对象和名字的Thread对象 30 public Thread(Runnable target, String name) { 31 init(null, target, name, 0); 32 } 33 34 // 构造一个具有指定线程组,运行对象和名字的Thread对象 35 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) { 36 init(group, target, name, 0); 37 } 38 39 // 构造一个具有指定线程组,运行对象,名字和堆栈大小的Thread对象 40 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, 41 long stackSize) { 42 init(group, target, name, stackSize); 43 } 44 45 // 这个构造器不是公开的,他将创建一个 46 Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) { 47 init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc, false); 48 } 49 50 // 公开的构造函数先调用这个方法 51 private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, 52 long stackSize) { 53 init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true); 54 } 55 56 private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,boolean inheritThreadLocals) { 57 // 如果给定的线程名是null抛出空指针异常 58 if (name == null) { 59 throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); 60 } 61 // 设置线程名 62 this.name = name; 63 // 获取父线程 64 Thread parent = currentThread(); 65 // 获取安全管理器 66 SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); 67 68 // 如果未指定线程所在的线程组 69 if (g == null) { 70 // 如果安全管理器存在,就使用安全管理器的方法返回当前线程的线程组 71 if (security != null) { 72 g = security.getThreadGroup(); 73 } 74 75 // 如果所属的线程组还是没有,就使用父线程的线程组作为该线程的线程组 76 if (g == null) { 77 g = parent.getThreadGroup(); 78 } 79 } 80 // 判断当前线程是否有权限修改此g线程组,该方法时ThreadGroup的 81 g.checkAccess(); 82 83 // 检查是否有权限 84 if (security != null) { 85 // 验证是否可以构造该实例 86 if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) { 87 security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);// 验证是否有指定的运行时权限 88 } 89 } 90 // 增加线程组中未启动线程的数量。 91 g.addUnstarted(); 92 93 // 设置线程相关属性,获取父线程的相关属性作为该线程的相关属性(如果未指定) 94 this.group = g; 95 this.daemon = parent.isDaemon(); 96 this.priority = parent.getPriority(); 97 if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) 98 this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader(); 99 else 100 this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; 101 this.inheritedAccessControlContext = 102 acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext(); 103 this.target = target; 104 setPriority(priority); 105 if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) 106 this.inheritableThreadLocals = 107 ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); 108 this.stackSize = stackSize; 109 tid = nextThreadID(); 110 }
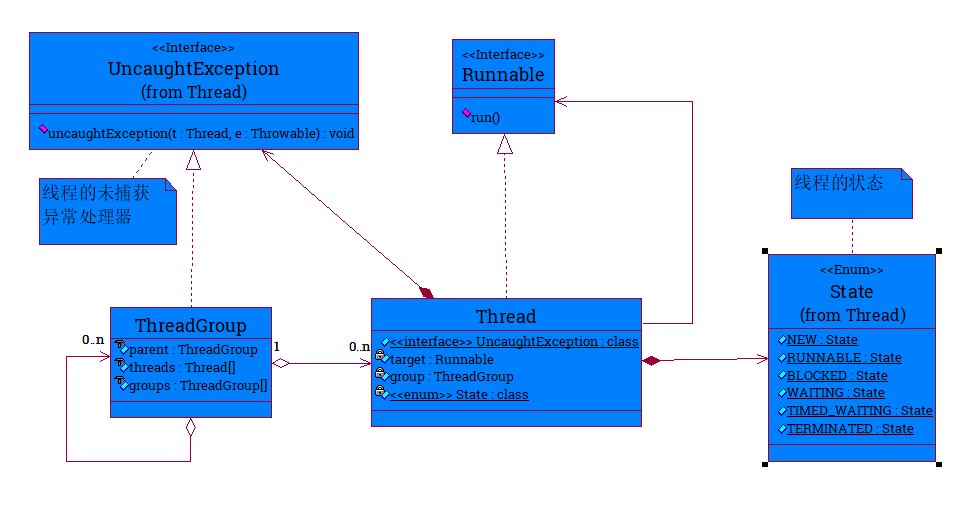
ThreadGroup,Thread,Thread.State,Thread.UncaughtException之间的类图