从Go语言编码角度解释实现简易区块链——实现交易
- 2019 年 10 月 30 日
- 笔记
在公链基础上实现区块链交易
区块链的目的,是能够安全可靠的存储交易,比如我们常见的比特币的交易,这里我们会以比特币为例实现区块链上的通用交易。上一节用简单的数据结构完成了区块链的公链,本节在此基础上对区块链的交易部分进行实现。实现公链
交易机制
在区块链中,交易一旦被创建,就没有任何人能够再去修改或是删除它,本节将实现一个交易的基本框架,具体交易细节将会在之后给出。
以比特币为例,不同于一般概念的账户模型,其交易采用的是UTXO模型。我们所需要的信息,都间接的包含在了每一笔交易中,包括用户的余额信息。
对于每一笔交易,你可以想象成一个通道,通道的左端有若干个输入信息,通道的右端会有若干输出信息。输入信息代表的意义是,该交易所用的币是从何而来,一条交易可以有0到多个币源(0是特殊情况,即被挖出的矿,因为没有用户来源,所以没有输入信息)。输出信息代表的意义是,进行该交易后,数字货币变动到哪里去了。因此,一条交易信息中货币的输入数量与输出数量应该是等价的,数字货币的来源总和,等于数字货币的输出总和。不难想象,与传统的账户模型相比,在UTXO模型中用户的账户余额是记录在交易的输出部分。
举个最简单的例子,假设A需要给B支付了一个比特币,将执行以下流程:
- 查看当前已有的交易信息,找到交易输出指向自己的交易并将余额计入总和
- 判断当前交易信息输出中是否有足够的数字货币属于自己
- 当余额不足时,提示余额不足信息
- 当余额充足时,新建一条交易,即一个UTXO
- 该UTXO的输出信息是消费用户的部分余额(不需要消费用户的所有余额,只要满足够用就行),而用户的余额是记录在之前已有的UTXO的输出中,所以新交易的输入,便是之前某些交易的输出。
- 当用户找到的余额数量与本次交易所需的数量不相等时,用户可以将剩下的货币再向自己输出,即找零,以保证交易的输入与输出相等
这样我们就实现了一个简单的交易,在这场交易中有货币的来源,货币有明确的去向,同时携带了我们正在进行的交易信息。
之后我们将结合代码,让这种逻辑变得更加清晰,下面这张图是对UTXO模型的简单描述:
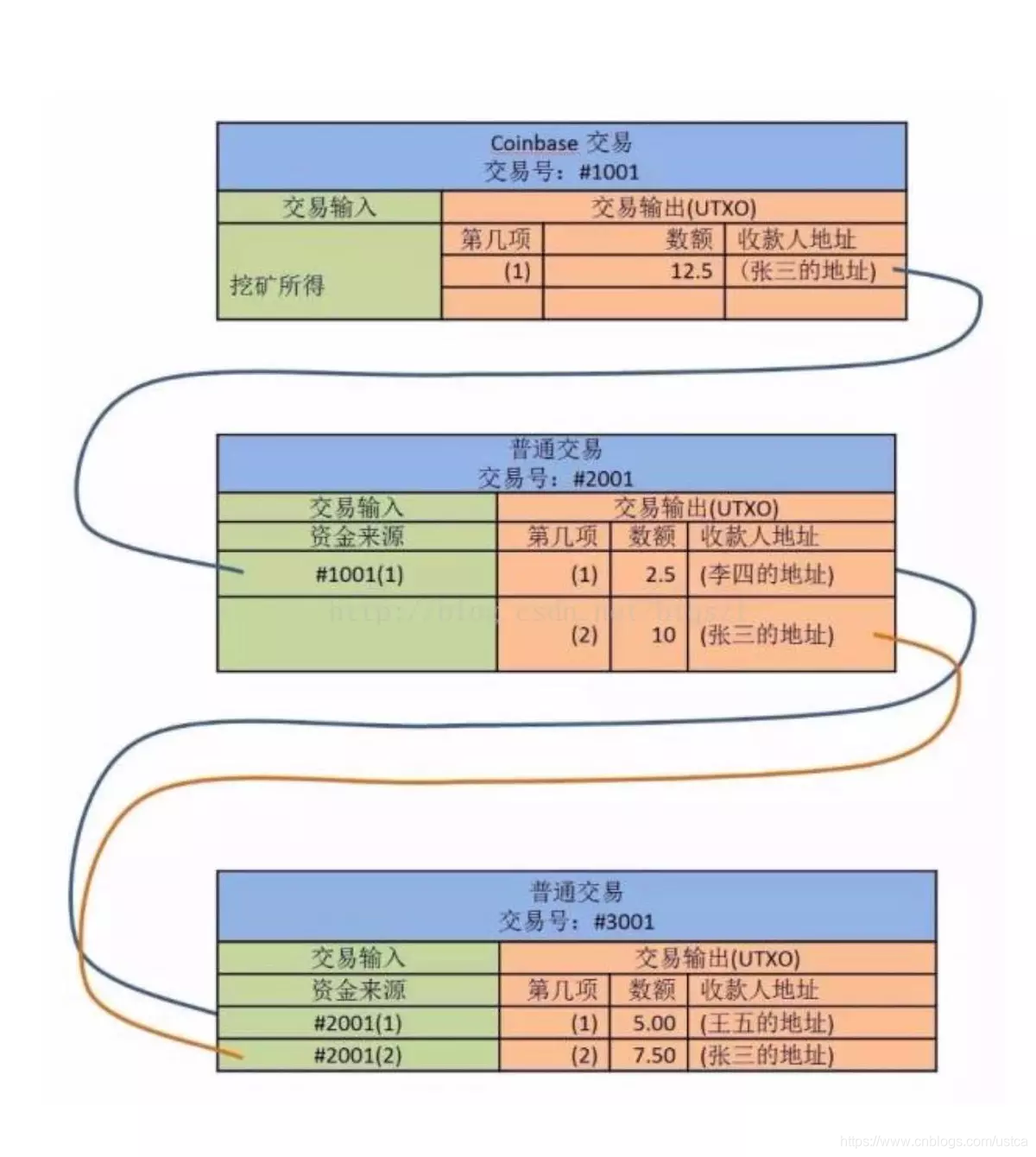
Coinbase交易是特殊的一种交易,它表示矿工挖出了新的矿,作用是将新挖出的矿加入公链中并将输出指向挖矿的矿工。
该例子表示,张三挖矿得到12.5个比特币,然后支付了2.5个给李四,自己剩余10比特币,之后张三李四各支付2.5个比特币给王五,最终张三还剩7.5个比特币,李四余额用尽,王五剩余5个比特币,总和12.5等于张三挖出的总矿币。
编码实现
与之前已经完成的实现公链的代码相比,区块链的交易需要新建一个transaction.go文件,用来实现交易逻辑。其余文件中的代码,会跟随交易机制的加入进行微小的调整。
transaction.go
以下为transaction.go的代码:
package main import ( "bytes" "crypto/sha256" "encoding/gob" "encoding/hex" "fmt" "log" ) const subsidy = 10 // Transaction represents a Bitcoin transaction type Transaction struct { ID []byte Vin []TXInput Vout []TXOutput } // IsCoinbase checks whether the transaction is coinbase func (tx Transaction) IsCoinbase() bool { return len(tx.Vin) == 1 && len(tx.Vin[0].Txid) == 0 && tx.Vin[0].Vout == -1 } // SetID sets ID of a transaction func (tx *Transaction) SetID() { var encoded bytes.Buffer var hash [32]byte enc := gob.NewEncoder(&encoded) err := enc.Encode(tx) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } hash = sha256.Sum256(encoded.Bytes()) tx.ID = hash[:] } // TXInput represents a transaction input type TXInput struct { Txid []byte Vout int ScriptSig string } // TXOutput represents a transaction output type TXOutput struct { Value int ScriptPubKey string } // CanUnlockOutputWith checks whether the address initiated the transaction func (in *TXInput) CanUnlockOutputWith(unlockingData string) bool { return in.ScriptSig == unlockingData } // CanBeUnlockedWith checks if the output can be unlocked with the provided data func (out *TXOutput) CanBeUnlockedWith(unlockingData string) bool { return out.ScriptPubKey == unlockingData } // NewCoinbaseTX creates a new coinbase transaction func NewCoinbaseTX(to, data string) *Transaction { if data == "" { data = fmt.Sprintf("Reward to '%s'", to) } txin := TXInput{[]byte{}, -1, data} txout := TXOutput{subsidy, to} tx := Transaction{nil, []TXInput{txin}, []TXOutput{txout}} tx.SetID() return &tx } // NewUTXOTransaction creates a new transaction func NewUTXOTransaction(from, to string, amount int, bc *Blockchain) *Transaction { var inputs []TXInput var outputs []TXOutput acc, validOutputs := bc.FindSpendableOutputs(from, amount) if acc < amount { log.Panic("ERROR: Not enough funds") } // Build a list of inputs for txid, outs := range validOutputs { txID, err := hex.DecodeString(txid) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } for _, out := range outs { input := TXInput{txID, out, from} inputs = append(inputs, input) } } // Build a list of outputs outputs = append(outputs, TXOutput{amount, to}) if acc > amount { outputs = append(outputs, TXOutput{acc - amount, from}) // a change } tx := Transaction{nil, inputs, outputs} tx.SetID() return &tx }代码主要包含以下内容:
- Transaction 结构体,包含当前交易的ID(交易需要ID)、输入数组以及输出数组
- IsCoinbase函数,用来判断当前交易是否是Coinbase交易(挖矿交易)
- SetID函数给交易设置id
- TXInput 结构体,包含输入的某条交易的id,该交易某个输出的金额与地址
- TXOutput 结构体,包含当前交易的某个输出的金额与地址
- CanUnlockOutputWith函数判断提供的地址能否匹配某条交易记录的输入地址
- CanBeUnlockedWith函数判断提供的地址能否匹配某条交易记录的输出地址
- NewCoinbaseTX函数创建一条挖矿交易
- NewUTXOTransaction函数创建一条新的交易
关于TXInput与TXOutput中地址的问题,因为目前还没有实现区块链中的地址,所以本节涉及的地址直接用字符串代替,验证地址也只是进行了字符串对比。地址是必要的,它标注了当前的余额属于谁,这里因为刚实现交易机制,还没有引入真正的地址机制,所以是存在漏洞的,用户只要知道有哪些用户就可以直接往自己地址转钱,在下一节会实现地址机制进行完善。
block.go
在transaction.go中实现了交易的结构体,如何创建一条新的交易,以及简单的交易对象判断。在其余文件中,block.go文件做了一些改动,主要是将原本的data字符串换成了Transaction交易。同样的,下一节中我们会将本节的地址字符串换成相应机制的地址,以下是改动后的block.go文件:
package main import ( "bytes" "crypto/sha256" "encoding/gob" "log" "time" ) // Block keeps block headers type Block struct { Timestamp int64 Transactions []*Transaction PrevBlockHash []byte Hash []byte Nonce int } // Serialize serializes the block func (b *Block) Serialize() []byte { var result bytes.Buffer encoder := gob.NewEncoder(&result) err := encoder.Encode(b) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } return result.Bytes() } // HashTransactions returns a hash of the transactions in the block func (b *Block) HashTransactions() []byte { var txHashes [][]byte var txHash [32]byte for _, tx := range b.Transactions { txHashes = append(txHashes, tx.ID) } txHash = sha256.Sum256(bytes.Join(txHashes, []byte{})) return txHash[:] } // NewBlock creates and returns Block func NewBlock(transactions []*Transaction, prevBlockHash []byte) *Block { block := &Block{time.Now().Unix(), transactions, prevBlockHash, []byte{}, 0} pow := NewProofOfWork(block) nonce, hash := pow.Run() block.Hash = hash[:] block.Nonce = nonce return block } // NewGenesisBlock creates and returns genesis Block func NewGenesisBlock(coinbase *Transaction) *Block { return NewBlock([]*Transaction{coinbase}, []byte{}) } // DeserializeBlock deserializes a block func DeserializeBlock(d []byte) *Block { var block Block decoder := gob.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(d)) err := decoder.Decode(&block) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } return &block }添加了HashTransactions函数,用来将交易转换成哈希值,其余函数随结构体中Data->Transactions的变动相应调整。
blockchain.go
在blockchain.go中,涉及到寻找用户余额(未花费交易输出)操作,需要多做一些调整:
package main import ( "encoding/hex" "fmt" "log" "os" "bolt-master" ) const dbFile = "blockchain.db" const blocksBucket = "blocks" const genesisCoinbaseData = "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks" // Blockchain implements interactions with a DB type Blockchain struct { tip []byte db *bolt.DB } // BlockchainIterator is used to iterate over blockchain blocks type BlockchainIterator struct { currentHash []byte db *bolt.DB } // MineBlock mines a new block with the provided transactions func (bc *Blockchain) MineBlock(transactions []*Transaction) { var lastHash []byte err := bc.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) lastHash = b.Get([]byte("l")) return nil }) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } newBlock := NewBlock(transactions, lastHash) err = bc.db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) err := b.Put(newBlock.Hash, newBlock.Serialize()) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } err = b.Put([]byte("l"), newBlock.Hash) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } bc.tip = newBlock.Hash return nil }) } // FindUnspentTransactions returns a list of transactions containing unspent outputs func (bc *Blockchain) FindUnspentTransactions(address string) []Transaction { var unspentTXs []Transaction spentTXOs := make(map[string][]int) bci := bc.Iterator() for { block := bci.Next() for _, tx := range block.Transactions { txID := hex.EncodeToString(tx.ID) Outputs: for outIdx, out := range tx.Vout { // Was the output spent? if spentTXOs[txID] != nil { for _, spentOut := range spentTXOs[txID] { if spentOut == outIdx { continue Outputs } } } if out.CanBeUnlockedWith(address) { unspentTXs = append(unspentTXs, *tx) } } if tx.IsCoinbase() == false { for _, in := range tx.Vin { if in.CanUnlockOutputWith(address) { inTxID := hex.EncodeToString(in.Txid) spentTXOs[inTxID] = append(spentTXOs[inTxID], in.Vout) } } } } if len(block.PrevBlockHash) == 0 { break } } return unspentTXs } // FindUTXO finds and returns all unspent transaction outputs func (bc *Blockchain) FindUTXO(address string) []TXOutput { var UTXOs []TXOutput unspentTransactions := bc.FindUnspentTransactions(address) for _, tx := range unspentTransactions { for _, out := range tx.Vout { if out.CanBeUnlockedWith(address) { UTXOs = append(UTXOs, out) } } } return UTXOs } // FindSpendableOutputs finds and returns unspent outputs to reference in inputs func (bc *Blockchain) FindSpendableOutputs(address string, amount int) (int, map[string][]int) { unspentOutputs := make(map[string][]int) unspentTXs := bc.FindUnspentTransactions(address) accumulated := 0 Work: for _, tx := range unspentTXs { txID := hex.EncodeToString(tx.ID) for outIdx, out := range tx.Vout { if out.CanBeUnlockedWith(address) && accumulated < amount { accumulated += out.Value unspentOutputs[txID] = append(unspentOutputs[txID], outIdx) if accumulated >= amount { break Work } } } } return accumulated, unspentOutputs } // Iterator returns a BlockchainIterat func (bc *Blockchain) Iterator() *BlockchainIterator { bci := &BlockchainIterator{bc.tip, bc.db} return bci } // Next returns next block starting from the tip func (i *BlockchainIterator) Next() *Block { var block *Block err := i.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) encodedBlock := b.Get(i.currentHash) block = DeserializeBlock(encodedBlock) return nil }) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } i.currentHash = block.PrevBlockHash return block } func dbExists() bool { if _, err := os.Stat(dbFile); os.IsNotExist(err) { return false } return true } // NewBlockchain creates a new Blockchain with genesis Block func NewBlockchain(address string) *Blockchain { if dbExists() == false { fmt.Println("No existing blockchain found. Create one first.") os.Exit(1) } var tip []byte db, err := bolt.Open(dbFile, 0600, nil) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } err = db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { b := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) tip = b.Get([]byte("l")) return nil }) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } bc := Blockchain{tip, db} return &bc } // CreateBlockchain creates a new blockchain DB func CreateBlockchain(address string) *Blockchain { if dbExists() { fmt.Println("Blockchain already exists.") os.Exit(1) } var tip []byte db, err := bolt.Open(dbFile, 0600, nil) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } err = db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { cbtx := NewCoinbaseTX(address, genesisCoinbaseData) genesis := NewGenesisBlock(cbtx) b, err := tx.CreateBucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } err = b.Put(genesis.Hash, genesis.Serialize()) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } err = b.Put([]byte("l"), genesis.Hash) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } tip = genesis.Hash return nil }) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } bc := Blockchain{tip, db} return &bc }代码的主要变动是新增了三个关于交易的函数:
- FindUnspendTransactions遍历公链,寻找交易信息中没有被使用过输出的交易,即未被花费过的余额。当一条交易中的余额被其他交易用做过输入,该余额也就不在具有余额的属性,不能再次被交易
- FindUTXO在内部调用了FindUnspendTransactions函数,与FindUnspendTransactions不同的是它用于查询用户的余额信息,即所有有效未花费余额的总和
- FindSpendableOutputs在内部调用了FindUnspendTransactions函数,用于找出哪些余额是可用的
其次,原本的Addblock被改成了更具体的Mineblock挖矿函数,新增了Createblockchain函数和dbExists函数,用来判断数据库是否存在,只有当数据库中没有公链时才能创建新的区块链。
proofofwork.go
在proofofwork文件中,仅在prepareData时将Data换成了HashTransactions,在挖矿时不再打印Data部分,proofofwork.go完整代码如下:
package main import ( "bytes" "crypto/sha256" "fmt" "math" "math/big" ) var ( maxNonce = math.MaxInt64 ) const targetBits = 24 // ProofOfWork represents a proof-of-work type ProofOfWork struct { block *Block target *big.Int } // NewProofOfWork builds and returns a ProofOfWork func NewProofOfWork(b *Block) *ProofOfWork { target := big.NewInt(1) target.Lsh(target, uint(256-targetBits)) pow := &ProofOfWork{b, target} return pow } func (pow *ProofOfWork) prepareData(nonce int) []byte { data := bytes.Join( [][]byte{ pow.block.PrevBlockHash, pow.block.HashTransactions(), IntToHex(pow.block.Timestamp), IntToHex(int64(targetBits)), IntToHex(int64(nonce)), }, []byte{}, ) return data } // Run performs a proof-of-work func (pow *ProofOfWork) Run() (int, []byte) { var hashInt big.Int var hash [32]byte nonce := 0 fmt.Printf("Mining a new block") for nonce < maxNonce { data := pow.prepareData(nonce) hash = sha256.Sum256(data) // fmt.Printf("r%x", hash) hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:]) if hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1 { break } else { nonce++ } } // fmt.Print("nn") return nonce, hash[:] } // Validate validates block's PoW func (pow *ProofOfWork) Validate() bool { var hashInt big.Int data := pow.prepareData(pow.block.Nonce) hash := sha256.Sum256(data) hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:]) isValid := hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1 return isValid }cli.go
cli.go文件随底层的一些变动,做出相应的业务逻辑改变,变动主要用于实现命令行操作,不涉及区块链的逻辑:
package main import ( "flag" "fmt" "log" "os" "strconv" ) // CLI responsible for processing command line arguments type CLI struct{} func (cli *CLI) createBlockchain(address string) { bc := CreateBlockchain(address) bc.db.Close() fmt.Println("Done!") } func (cli *CLI) getBalance(address string) { bc := NewBlockchain(address) defer bc.db.Close() balance := 0 UTXOs := bc.FindUTXO(address) for _, out := range UTXOs { balance += out.Value } fmt.Printf("Balance of '%s': %dn", address, balance) } func (cli *CLI) printUsage() { fmt.Println("Usage:") fmt.Println(" getbalance -address ADDRESS - Get balance of ADDRESS") fmt.Println(" createblockchain -address ADDRESS - Create a blockchain and send genesis block reward to ADDRESS") fmt.Println(" printchain - Print all the blocks of the blockchain") fmt.Println(" send -from FROM -to TO -amount AMOUNT - Send AMOUNT of coins from FROM address to TO") } func (cli *CLI) validateArgs() { if len(os.Args) < 2 { cli.printUsage() os.Exit(1) } } func (cli *CLI) printChain() { // TODO: Fix this bc := NewBlockchain("") defer bc.db.Close() bci := bc.Iterator() for { block := bci.Next() fmt.Printf("Prev. hash: %xn", block.PrevBlockHash) fmt.Printf("Hash: %xn", block.Hash) pow := NewProofOfWork(block) fmt.Printf("PoW: %sn", strconv.FormatBool(pow.Validate())) fmt.Println() if len(block.PrevBlockHash) == 0 { break } } } func (cli *CLI) send(from, to string, amount int) { bc := NewBlockchain(from) defer bc.db.Close() tx := NewUTXOTransaction(from, to, amount, bc) bc.MineBlock([]*Transaction{tx}) fmt.Println("Success!") } // Run parses command line arguments and processes commands func (cli *CLI) Run() { cli.validateArgs() getBalanceCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("getbalance", flag.ExitOnError) createBlockchainCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("createblockchain", flag.ExitOnError) sendCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("send", flag.ExitOnError) printChainCmd := flag.NewFlagSet("printchain", flag.ExitOnError) getBalanceAddress := getBalanceCmd.String("address", "", "The address to get balance for") createBlockchainAddress := createBlockchainCmd.String("address", "", "The address to send genesis block reward to") sendFrom := sendCmd.String("from", "", "Source wallet address") sendTo := sendCmd.String("to", "", "Destination wallet address") sendAmount := sendCmd.Int("amount", 0, "Amount to send") switch os.Args[1] { case "getbalance": err := getBalanceCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:]) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } case "createblockchain": err := createBlockchainCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:]) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } case "printchain": err := printChainCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:]) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } case "send": err := sendCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:]) if err != nil { log.Panic(err) } default: cli.printUsage() os.Exit(1) } if getBalanceCmd.Parsed() { if *getBalanceAddress == "" { getBalanceCmd.Usage() os.Exit(1) } cli.getBalance(*getBalanceAddress) } if createBlockchainCmd.Parsed() { if *createBlockchainAddress == "" { createBlockchainCmd.Usage() os.Exit(1) } cli.createBlockchain(*createBlockchainAddress) } if printChainCmd.Parsed() { cli.printChain() } if sendCmd.Parsed() { if *sendFrom == "" || *sendTo == "" || *sendAmount <= 0 { sendCmd.Usage() os.Exit(1) } cli.send(*sendFrom, *sendTo, *sendAmount) } }main.go
在main.go中,我们将所有的操作有交给cli对象进行,原本旧main.go中的新建创世块操作,也放到了cli.go的逻辑中,所以只需要以下代码:
package main func main() { bc := NewBlockchain() defer bc.db.Close() cli := CLI{bc} cli.Run() }utils.go
没有新的工具函数引入,utils.go文件不变。