Spring(DI,AOP) 理解(一)
- 2020 年 4 月 17 日
- 筆記
感覺自己的spring理解的不好.所以重新開始學習.
這篇文章主要是來理解DI(依賴注入),Aop(切面)
一.DI(依賴注入,這裡沒有涉及到注釋.只是用xml文件和Bean的方法來註冊pojo,)
依賴注入就是將創建bean對象的權利交給spring框架(控制反轉) 然後用Applicationcontext.getBean() 來獲取對象.
容器:spring容器創建對象,管理對象,並負責管理對象的生命周期. 容器有兩種 BeanFactiory ..ApplicationContext ..多的就不解釋了,BeanFactiory 比較low,這裡使用ApplicaitonContext
ApplicaitonContext:
1 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:以基於文件系統的XML配置文件創建ApplicationContext實例。
2 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:以類加載路徑下的XML配置文件創建的ApplicationContext實例
3 XmlWebApplicationContext:從web應用下的一個或者多個xml配置文件加載創建ApplicationContext實例
4 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 從一個或者多個基於java的配置類中加載Spring ApplicaitonContext實例
5 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 基於一個或者多個java的配置類來創建spring web 的應用上下文
二. Aop :面向切面編程.(將復用性很強的模塊抽離出來,然後通過配置,將抽離出來的模塊(比如日誌模塊),覆蓋到其他需要日誌模塊的服務上)
一個項目假設有講師服務,學生服務,計費服務…….還有日誌模塊,安全模塊,事務模塊
講師服務,學生服務,計費服務 每一個服務都需要與日誌模塊,安全模塊,事務模塊 進行耦合…..如果這個樣子,,每一個服務裏面的代碼不能夠專註於解決本服務的問題.需要調用日誌模塊,安全模塊,事務模塊的代碼.
這樣,代碼的復用性會很低,耦合性很高.
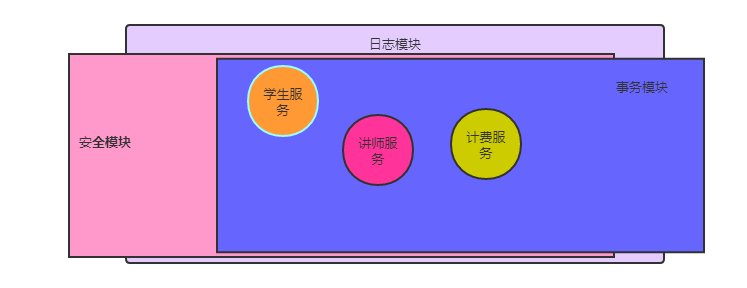
創建一個Person類…裏面有一個doSomething方法
package com.start.demo; /** * 男孩,女孩,工程師,程序員.... */ public class Person { private String name; private int age; private Play play; public Person(Play p) { this.play = p; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } void doSomething() { System.out.println(" we can play " + play.getType() +"together"); } }
創建一個Play類 type 表示可以做的事情
package com.start.demo; /** * 各種活動,,玩遊戲,讀書,看電視..... */ public class Play { private String type="computer game"; public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } }
測試Aop的一個類
package com.start.demo; /** * 這個類是用來測試Aop.在切點之前,之後,分別調用對應的方法 */ public class Asker { private String name; void doSomethingBefore(){ System.out.println("what can we do "); } void doSomethingAfter(){ System.out.println("that's fine"); } }
裝配bean的xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="//www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="//www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="//www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="//www.springframework.org/schema/beans //www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd //www.springframework.org/schema/aop //www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--裝配bean--> <bean id="person" class="com.start.demo.Person"> <constructor-arg ref="play"/> </bean> <bean id="play" class="com.start.demo.Play"/> <bean id="asker" class="com.start.demo.Asker"/> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="asker"> <!-- pointcut 的id 不能與 配置切點bean的id一樣了,會報錯.--> <aop:pointcut id="personPointcut" expression="execution(* *.doSomething())"/><!--execution(* * .doSomething(..)) 要是有參數,需要在方法體裏面加 ..--> <aop:before pointcut-ref="personPointcut" method="doSomethingBefore"/> <aop:after pointcut-ref="personPointcut" method="doSomethingAfter"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
用javaBean來裝配對象
package com.start.confBean; import com.start.demo.Person; import com.start.demo.Play; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class PersonConf { @Bean public Person person() { return new Person(play()); } @Bean public Play play() { return new Play(); } }
測試Main類
package com.start.demo; import com.start.confBean.PersonConf; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext appcontext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //從beans.xml 文件獲取ApplicaitonContext // AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PersonConf.class);//PersonConf.java 文件獲取ApplicaitonContext // Person person1 = annotationApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class); //獲取bean ,直接指定Bean 為Person // Person person = (Person) appcontext.getBean("person");//獲取bean person 為配置文件裏面的 id Person pers = (Person) appcontext.getBean("person"); pers.doSomething(); } }
這些代碼雖然很簡單,卻讓我認識清楚了DI和Aop的作用


