高性能/並發的保證-Netty在Redisson的應用
- 2020 年 4 月 9 日
- 筆記

前言
Redisson Github: https://github.com/redisson/redisson
Redisson 官網:https://redisson.pro/
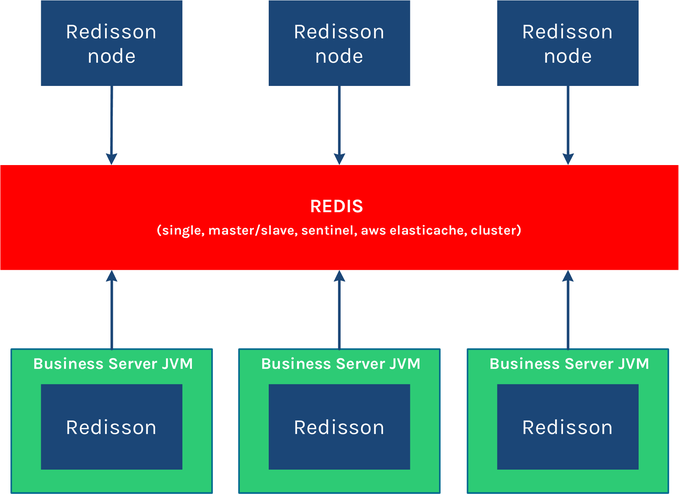
Redisson是一個在Redis的基礎上實現的Java駐內存數據網格(In-Memory Data Grid)。它不僅提供了一系列的分佈式的Java常用對象,還提供了許多分佈式服務。其中包括(BitSet, Set, Multimap, SortedSet, Map, List, Queue, BlockingQueue, Deque, BlockingDeque, Semaphore, Lock, AtomicLong, CountDownLatch, Publish / Subscribe, Bloom filter, Remote service, Spring cache, Executor service, Live Object service, Scheduler service) Redisson提供了使用Redis的最簡單和最便捷的方法。Redisson的宗旨是促進使用者對Redis的關注分離(Separation of Concern),從而讓使用者能夠將精力更集中地放在處理業務邏輯上。
以下是Redisson的結構:
-
Redisson作為獨立節點 可以用於獨立執行其他節點發佈到分佈式執行服務 和 分佈式調度任務服務 里的遠程任務。
Redisson底層採用的是Netty 框架。支持Redis 2.8以上版本,支持Java1.6+以上版本。
客戶端初始化
createBootstrap
org.redisson.client.RedisClient#createBootstrap
private Bootstrap createBootstrap(RedisClientConfig config, Type type) { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap() .resolver(config.getResolverGroup()) //1.指定配置中的IO類型 .channel(config.getSocketChannelClass()) //2.指定配置中的線程模型 .group(config.getGroup()); //3.IO處理邏輯 bootstrap.handler(new RedisChannelInitializer(bootstrap, config, this, channels, type)); //4. 指定bootstrap配置選項 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, config.getConnectTimeout()); bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, config.isKeepAlive()); bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, config.isTcpNoDelay()); config.getNettyHook().afterBoostrapInitialization(bootstrap); return bootstrap; } 從上面的代碼可以看到,客戶端啟動的引導類是 Bootstrap,負責啟動客戶端以及連接服務端,引導類創建完成之後,下面我們描述一下客戶端啟動的流程。
一. 首先,我們需要給它指定線程模型,驅動着連接的數據讀寫。然後,redisson默認指定 IO 模型為 NioSocketChannel
二. 接着,給引導類指定一系列處理鏈路,這裡主要就是定義連接的業務處理邏輯,不理解沒關係,在後面我們會詳細分析
RedisChannelInitializer
org.redisson.client.handler.RedisChannelInitializer
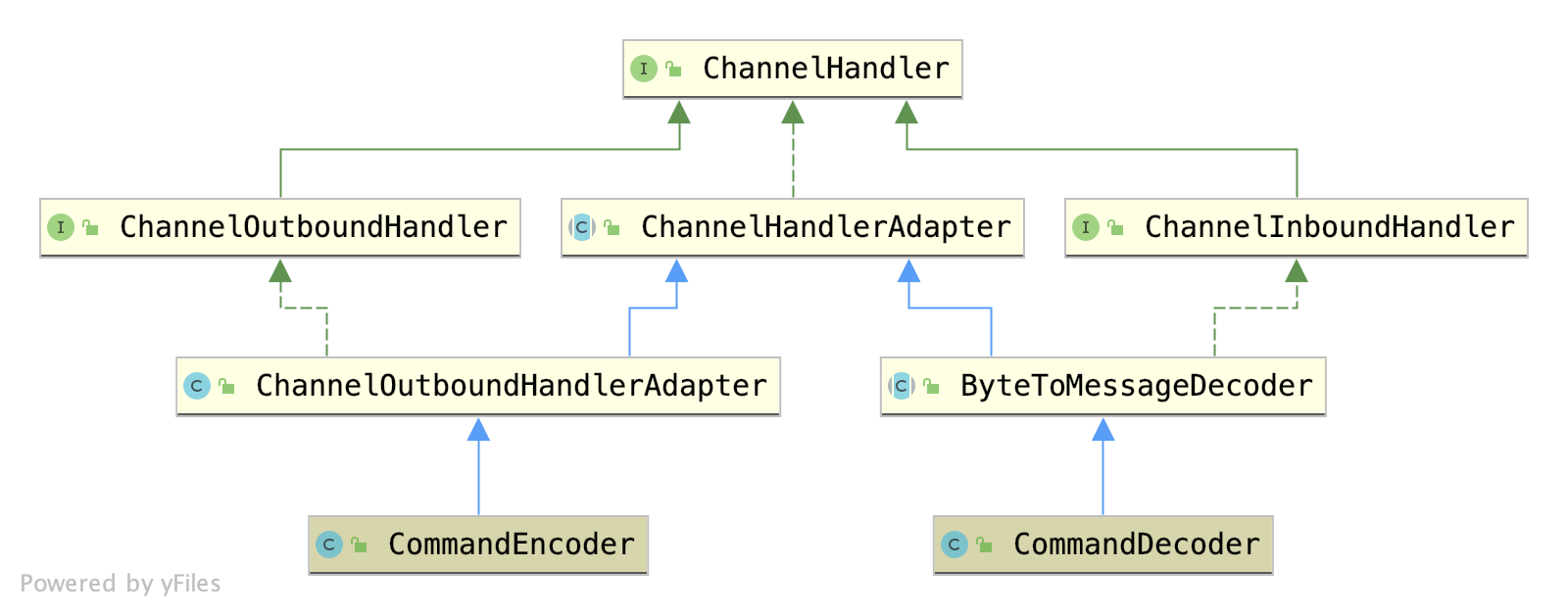
@Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { // 開啟SSL終端識別能力 initSsl(config, ch); if (type == Type.PLAIN) { //Redis正常連接處理類 ch.pipeline().addLast(new RedisConnectionHandler(redisClient)); } else { //Redis訂閱發佈處理類 ch.pipeline().addLast(new RedisPubSubConnectionHandler(redisClient)); } ch.pipeline().addLast( //鏈路檢測狗 connectionWatchdog, //Redis協議命令編碼器 CommandEncoder.INSTANCE, //Redis協議命令批量編碼器 CommandBatchEncoder.INSTANCE, //Redis命令隊列 new CommandsQueue()); if (pingConnectionHandler != null) { //心跳包連接處理類 ch.pipeline().addLast(pingConnectionHandler); } if (type == Type.PLAIN) { //Redis協議命令解碼器 ch.pipeline().addLast(new CommandDecoder(config.getExecutor(), config.isDecodeInExecutor())); } else { //Redis訂閱發佈解碼器 ch.pipeline().addLast(new CommandPubSubDecoder(config.getExecutor(), config.isKeepPubSubOrder(), config.isDecodeInExecutor())); } config.getNettyHook().afterChannelInitialization(ch); } 圖1 Redisson 鏈路處理圖
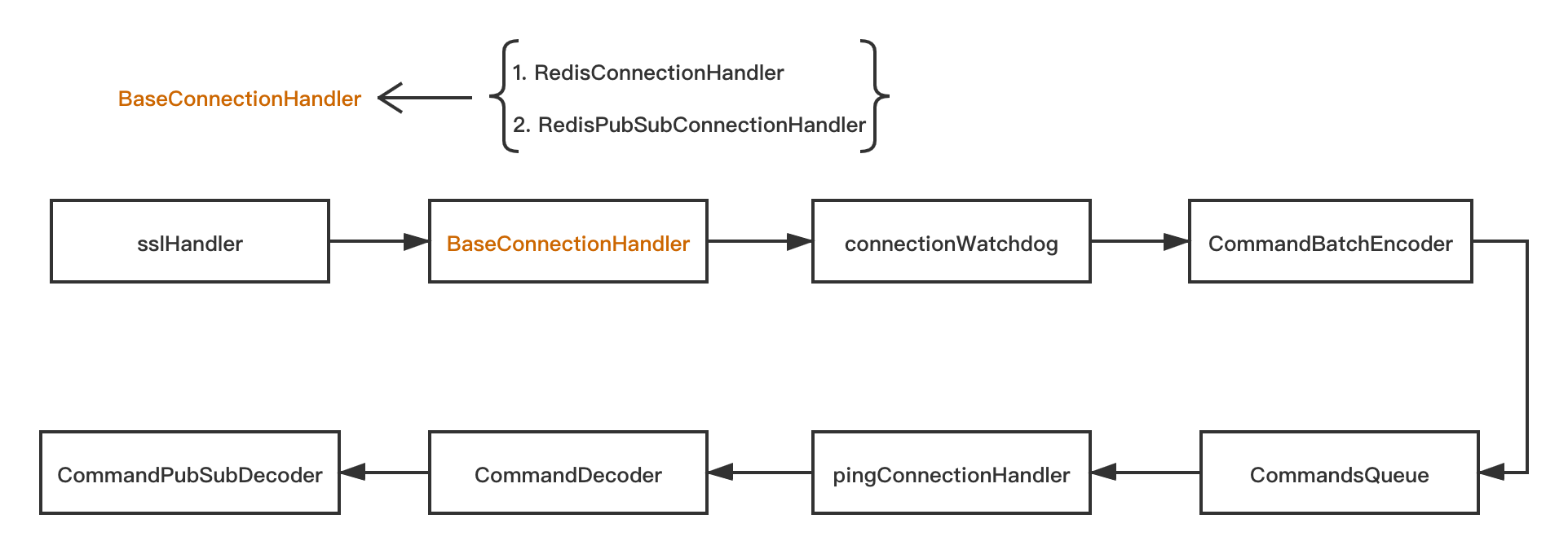
Redisson的處理鏈
Redisson的Pipeline裏面的ChannelHandler比較多,我挑選其中
CommandEncoder和CommandDecoder進行源碼剖析。
失敗重連
org.redisson.client.handler.ConnectionWatchdog#reconnect 重連機制
private void reconnect(final RedisConnection connection, final int attempts){ //重試時間越來越久 int timeout = 2 << attempts; if (bootstrap.config().group().isShuttingDown()) { return; } try { timer.newTimeout(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception { tryReconnect(connection, Math.min(BACKOFF_CAP, attempts + 1)); } }, timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (IllegalStateException e) { // skip } } netty中的Timer管理,使用了的Hashed time Wheel的模式,Time Wheel翻譯為時間輪,是用於實現定時器timer的經典算法。
這個方法的聲明是這樣的:
/** * Schedules the specified {@link TimerTask} for one-time execution after * the specified delay. * * @return a handle which is associated with the specified task * * @throws IllegalStateException if this timer has been {@linkplain #stop() stopped} already * @throws RejectedExecutionException if the pending timeouts are too many and creating new timeout * can cause instability in the system. */ Timeout newTimeout(TimerTask task, long delay, TimeUnit unit); 這個方法需要一個TimerTask對象以知道當時間到時要執行什麼邏輯,然後需要delay時間數值和TimeUnit時間的單位。
Redis協議命令編碼器
Redis 的作者認為數據庫系統的瓶頸一般不在於網絡流量,而是數據庫自身內部邏輯處理上。所以即使 Redis 使用了浪費流量的文本協議,依然可以取得極高的訪問性能。Redis 將所有數據都放在內存,用一個單線程對外提供服務,單個節點在跑滿一個 CPU 核心的情況下可以達到了 10w/s 的超高 QPS。
RESP 是 Redis 序列化協議的簡寫。它是一種直觀的文本協議,優勢在於實現異常簡單,解析性能極好。
Redis 協議將傳輸的結構數據分為 5 種最小單元類型,單元結束時統一加上回車換行符號rn。
- 單行字符串 以
+符號開頭。 - 多行字符串 以
$符號開頭,後跟字符串長度。 - 整數值 以
:符號開頭,後跟整數的字符串形式。 - 錯誤消息 以
-符號開頭。 - 數組 以
*號開頭,後跟數組的長度。
單行字符串 hello world
+hello worldrn 多行字符串 hello world
$11rnhello worldrn 多行字符串當然也可以表示單行字符串。
整數 1024
:1024rn 錯誤 參數類型錯誤
-WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of valuern 數組 [1,2,3]
*3rn:1rn:2rn:3rn NULL 用多行字符串表示,不過長度要寫成-1。
$-1rn 空串 用多行字符串表示,長度填 0。
$0rnrn 注意這裡有兩個rn。為什麼是兩個?因為兩個rn之間,隔的是空串。
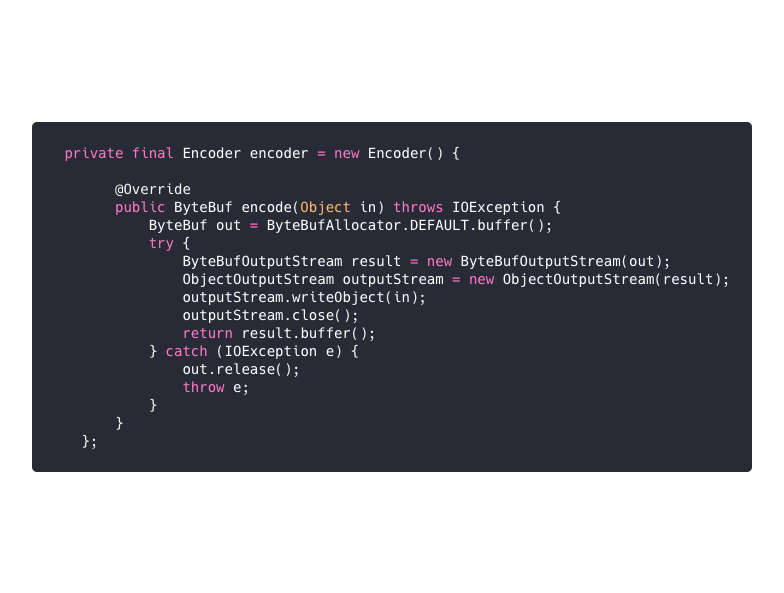
org.redisson.client.handler.CommandEncoder#encode()
private static final char ARGS_PREFIX = '*'; private static final char BYTES_PREFIX = '$'; private static final byte[] CRLF = "rn".getBytes(); @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CommandData<?, ?> msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { try { //redis命令前綴 out.writeByte(ARGS_PREFIX); int len = 1 + msg.getParams().length; if (msg.getCommand().getSubName() != null) { len++; } out.writeCharSequence(Long.toString(len), CharsetUtil.US_ASCII); out.writeBytes(CRLF); writeArgument(out, msg.getCommand().getName().getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); if (msg.getCommand().getSubName() != null) { writeArgument(out, msg.getCommand().getSubName().getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } ...... } catch (Exception e) { msg.tryFailure(e); throw e; } } private void writeArgument(ByteBuf out, ByteBuf arg) { out.writeByte(BYTES_PREFIX); out.writeCharSequence(Long.toString(arg.readableBytes()), CharsetUtil.US_ASCII); out.writeBytes(CRLF); out.writeBytes(arg, arg.readerIndex(), arg.readableBytes()); out.writeBytes(CRLF); } Redis協議命令解碼器
org.redisson.client.handler.CommandDecoder#readBytes
private static final char CR = 'r'; private static final char LF = 'n'; private static final char ZERO = '0'; private ByteBuf readBytes(ByteBuf is) throws IOException { long l = readLong(is); if (l > Integer.MAX_VALUE) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Java only supports arrays up to " + Integer.MAX_VALUE + " in size"); } int size = (int) l; if (size == -1) { return null; } ByteBuf buffer = is.readSlice(size); int cr = is.readByte(); int lf = is.readByte(); //判斷是否以rn開頭 if (cr != CR || lf != LF) { throw new IOException("Improper line ending: " + cr + ", " + lf); } return buffer; } 數據序列化
Redisson的對象編碼類是用於將對象進行序列化和反序列化,以實現對該對象在Redis里的讀取和存儲。Redisson提供了以下幾種的對象編碼應用,以供大家選擇:
| 編碼類名稱 | 說明 |
|---|---|
org.redisson.codec.JsonJacksonCodec |
Jackson JSON 編碼 默認編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.AvroJacksonCodec |
Avro 一個二進制的JSON編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.SmileJacksonCodec |
Smile 另一個二進制的JSON編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.CborJacksonCodec |
CBOR 又一個二進制的JSON編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.MsgPackJacksonCodec |
MsgPack 再來一個二進制的JSON編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.IonJacksonCodec |
Amazon Ion 亞馬遜的Ion編碼,格式與JSON類似 |
org.redisson.codec.KryoCodec |
Kryo 二進制對象序列化編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.SerializationCodec |
JDK序列化編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.FstCodec |
FST 10倍於JDK序列化性能而且100%兼容的編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.LZ4Codec |
LZ4 壓縮型序列化對象編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.SnappyCodec |
Snappy 另一個壓縮型序列化對象編碼 |
org.redisson.client.codec.JsonJacksonMapCodec |
基於Jackson的映射類使用的編碼。可用於避免序列化類的信息,以及用於解決使用byte[]遇到的問題。 |
org.redisson.client.codec.StringCodec |
純字符串編碼(無轉換) |
org.redisson.client.codec.LongCodec |
純整長型數字編碼(無轉換) |
org.redisson.client.codec.ByteArrayCodec |
位元組數組編碼 |
org.redisson.codec.CompositeCodec |
用來組合多種不同編碼在一起 |

Codec
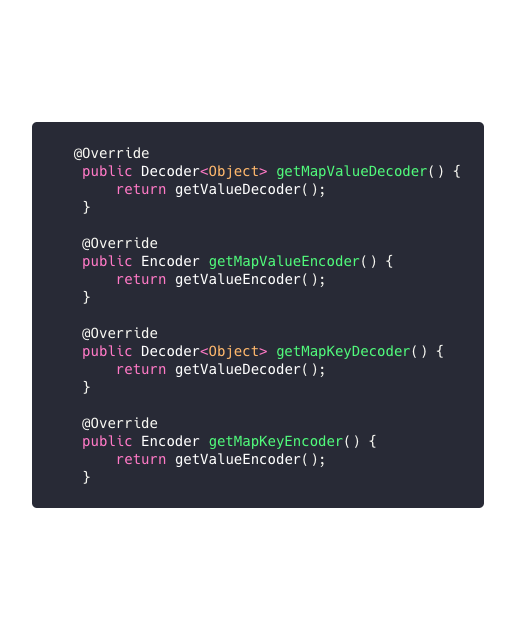
public interface Codec { //返回用於HMAP Redis結構中哈希映射值的對象解碼器 Decoder<Object> getMapValueDecoder(); //返回用於HMAP Redis結構中哈希映射值的對象編碼器 Encoder getMapValueEncoder(); //返回用於HMAP Redis結構中哈希映射鍵的對象解碼器 Decoder<Object> getMapKeyDecoder(); //返回用於HMAP Redis結構中哈希映射鍵的對象編碼器 Encoder getMapKeyEncoder(); //返回用於除HMAP之外的任何存儲Redis結構的對象解碼器 Decoder<Object> getValueDecoder(); //返回用於除HMAP之外的任何存儲Redis結構的對象編碼器 Encoder getValueEncoder(); //返回用於加載解碼過程中使用的類的類加載器對象 ClassLoader getClassLoader(); } BaseCodec
org.redisson.client.codec.BaseCodec
-
HashMap的鍵值對的編解碼的處理類使用普通的對象編解碼處理類進行分解。
//返回用於除HMAP之外的任何存儲Redis結構的對象解碼器 Decoder<Object> getValueDecoder(); //返回用於除HMAP之外的任何存儲Redis結構的對象編碼器 Encoder getValueEncoder();
SerializationCodec
org.redisson.codec.SerializationCodec
Decoder

Encoder