Spring Cache 缺陷,我好像有解決方案了
- 2020 年 4 月 7 日
- 筆記
Spring Cache 缺陷
Spring Cache 是一個非常優秀的緩存組件。
但是在使用 Spring Cache 的過程當中,小黑同學也遇到了一些痛點。
比如,現在有一個需求:通過多個 userId 來批量獲取用戶信息。
方案 1
此時,我們的代碼可能是這樣:
List<User> users = ids.stream().map(id -> { return getUserById(id); }) .collect(Collectors.toList()); @Cacheable(key = "#p0", unless = "#result == null") public User getUserById(Long id) { // ··· } 這種寫法的缺點在於:
在 for 循環中操作 redis。如果數據命中緩存還好,一旦緩存沒有命中,則會訪問數據庫。
方案 2
也有的同學可能會這樣做:
@Cacheable(key = "#ids.hash") public Collection<User> getUsersByIds(Collection<Long> ids) { // ··· } 這種做法的問題是:
緩存是基於 id 列表的 hashcode ,只有在 id 列表的 hashcode 值相等的情況下,緩存才會命中。而且,一旦列表中的其中一個數據被修改,整個列表緩存都要被清除。
例如:
第一次請求 id 列表是
1,2,3,第二次請求的 id 列表為
1,2,4在這種情況下,前後兩次的緩存不能共享。
如果 id 為 1 的數據發生了改變,那麼,這兩次請求的緩存都要被清空
看看 Spring 官方是怎麼說的
Spring Issue:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues/24139
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues/23221
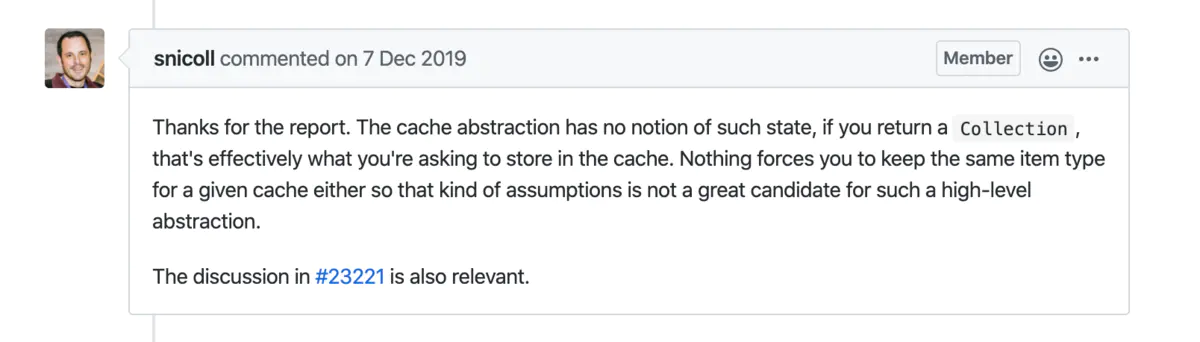
簡單翻譯一下,具體內容讀者可以自行查閱相關 issue。
譯文:
謝謝你的報告。緩存抽象沒有這種狀態的概念,如果你返回一個集合,那就是你要求在緩存中存儲的東西。也沒有什麼強迫您為給定的緩存保留相同的項類型,所以這種假設並不適合這樣的高級抽象。
我的理解是,對於 Spring Cache 這種高級抽象框架來說,Cache 是基於方法的,如果方法返回 Collection,那整個 Collection 就是需要被緩存的內容。
我的解決方案
糾結了好久,小黑同學還是決定自己來造個輪子。
那我想要達到什麼樣的效果呢?
我希望對於這種根據多個 key 批量獲取緩存的操作,可以先根據單個 key 從緩存中查找,如果緩存中不存在,就去加載數據,同時再將數據放到緩存中。

廢話不多說,直接上源碼:
https://github.com/shenjianeng/easy-cache
簡單介紹一下整體的思路:
-
核心接口
-
com.github.shenjianeng.easycache.core.Cache
-
com.github.shenjianeng.easycache.core.MultiCacheLoader
-
Cache 接口
Cache 接口定義了一些通用的緩存操作。和大部分 Cache 框架不同是,這裡支持根據 key 批量獲取緩存。
/** * 根據 keys 緩存中獲取,緩存中不存在,則返回null */ @NonNull Map<K, V> getIfPresent(@NonNull Iterable<K> keys); /** * 根據 keys 從緩存中獲取,如果緩存中不存在,調用 {@link MultiCacheLoader#loadCache(java.util.Collection)} 加載數據,並添加到緩存中 */ @NonNull Map<K, V> getOrLoadIfAbsent(@NonNull Iterable<K> keys); MultiCacheLoader 接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface MultiCacheLoader<K, V> { @NonNull Map<K, V> loadCache(@NonNull Collection<K> keys); default V loadCache(K key) { Map<K, V> map = loadCache(Collections.singleton(key)); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(map)) { return null; } return map.get(key); } } MultiCacheLoader 是一個函數式接口。在調用 Cache#getOrLoadIfAbsent 方法時,如果緩存不存在,就會通過 MultiCacheLoader 來加載數據,然後加數據放到緩存中。
RedisCache
RedisCache 是現在 Cache 接口的唯一實現。正如其類名一樣,這是基於 redis 的緩存實現。
先說一下大致的實現思路:
- 使用 redis 的 mget 命令,批量獲取緩存。為了保證效率,每次最多批量獲取 20 個。
- 如果有數據不在緩存中,則判斷是否需要自動加載數據,如果需要則通過 MultiCacheLoader 加載數據
- 將數據存放到緩存中。同時通過維護一個 zset 來保存已知的 cache key,用於清除緩存使用。
廢話不多說,直接上源碼。
private Map<K, V> doGetOrLoadIfAbsent(Iterable<K> keys, boolean loadIfAbsent) { List<String> cacheKeyList = buildCacheKey(keys); List<List<String>> partitions = Lists.partition(cacheKeyList, MAX_BATCH_KEY_SIZE); List<V> valueList = Lists.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(cacheKeyList.size()); for (List<String> partition : partitions) { // Get multiple keys. Values are returned in the order of the requested keys. List<V> values = (List<V>) redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiGet(partition); valueList.addAll(values); } List<K> keysList = Lists.newArrayList(keys); List<K> missedKeyList = Lists.newArrayList(); Map<K, V> map = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(partitions.size()); for (int i = 0; i < valueList.size(); i++) { V v = valueList.get(i); K k = keysList.get(i); if (v != null) { map.put(k, v); } else { missedKeyList.add(k); } } if (loadIfAbsent) { Map<K, V> missValueMap = multiCacheLoader.loadCache(missedKeyList); put(missValueMap); map.putAll(missValueMap); } return map; } 緩存清除方法實現:
public void evictAll() { Set<Serializable> serializables = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByScore(knownKeysName, 0, 0); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(serializables)) { List<String> cacheKeys = Lists.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(serializables.size()); serializables.forEach(serializable -> { if (serializable instanceof String) { cacheKeys.add((String) serializable); } }); redisTemplate.delete(cacheKeys); redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(knownKeysName, cacheKeys); } } 再多說幾句
更多源碼細節,如果讀者感興趣,可以自行閱讀源碼:easy-cache
歡迎大家 fork 體驗,或者評論區留言探討,寫的不好,請多多指教~~
未來計劃:
- 支持緩存 null 值
- 支持 annotation 的聲明式緩存


