18道經典鏈表題刷題總結——WeetCode1 鏈表系列
- 2022 年 11 月 19 日
- 筆記
前言:
WeetCode = Week leetCode 寓意每周刷點leetCode 題目
鏈表是我恢復刷題手感最喜歡做的系列,其沒用太多的算法思想,單純考驗對指針的理解,和coding能力,但是其中也是有一些技巧的,比如啞節點,這個是非常使用的解題技巧,能避免繁瑣的if else 處理頭部,下面是筆者本周刷的一些鏈表題目。下周準備刷單調棧,或者樹等其他系列題目。
一丶 [ 兩數相加](2. 兩數相加 – 力扣(Leetcode))
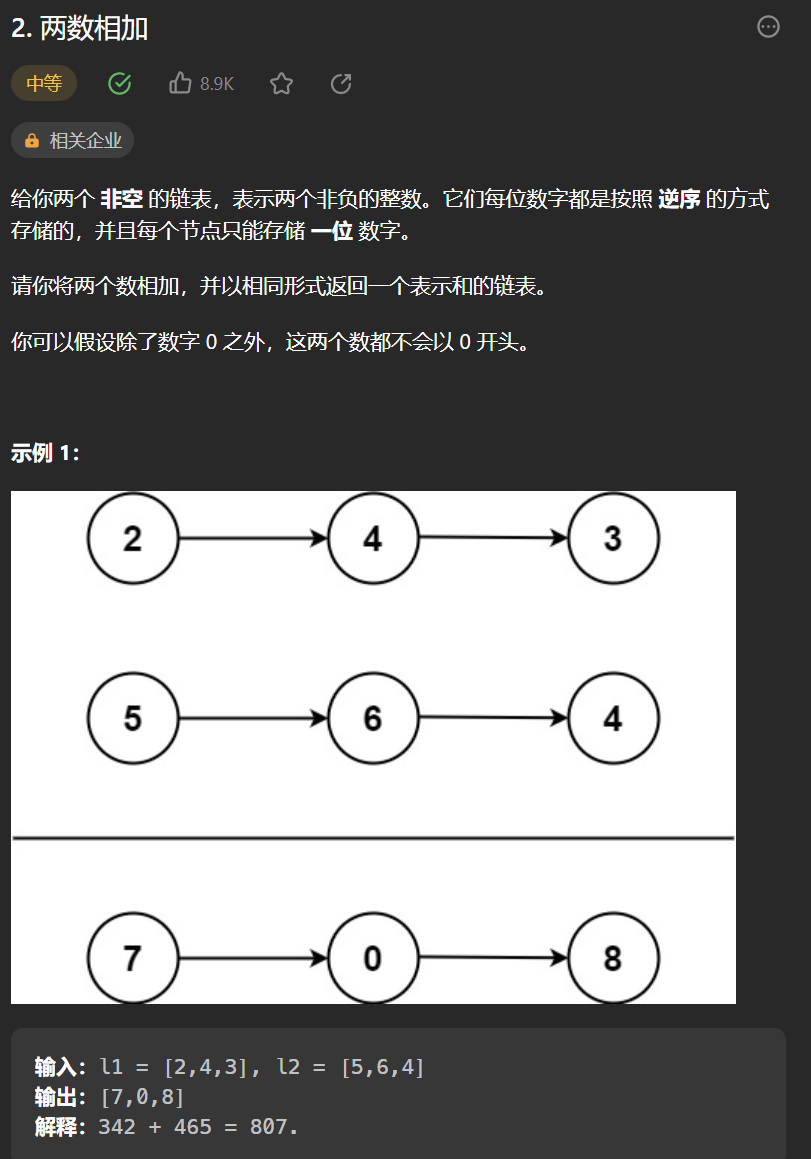
思路:
簡簡單單就是一手模擬,兩個指針分別位於兩個鏈表頭,然後一起向右,沒經過一個節點,就求和得到sum,如果之前存在進位,那麼sum需要加1,然後如果sum大於等於10,需要記錄存在進位,方便下一輪判斷是否需要進位,然後new除一個鏈表節點,其值位sum%10。
注意:
-
兩個鏈表同時結束,但是最後兩個節點值之和存在進位,比如
1->2->3
2->6->8
這時候答案應該是:3->8->1->
1,注意最後的1,這裡我們需要判斷,如果二者同時結束,那麼需要在末尾加1 -
兩個鏈表不是同時結束,這時候有點合併有序數組的意思,需要繼續遍歷長的鏈表,並且還是需要處理進位。比如
1->2->3
2->3->8->6->5
答案應該是 3->5->1->(注意到此存在一個進位3+8>10下一個節點應該是1+6)->7->5
代碼:
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//兩個鏈表存在任何一個為null 都返回另外一個
if(l1 == null ){
return l2;
}
if(l2 == null ){
return l1;
}
//記錄是否存在進位
boolean hasCarry = false;
//啞巴節點,其next就是頭節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
//forward 用來串聯求和後生成的節點,其實是結果鏈表的尾巴
ListNode forward = preHead;
//二者都不為null的時候
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
//求和 如果之前存在進位 那麼需要加1
int sum = (l1.val + l2.val)+ (hasCarry?1:0);
//記錄是否進位 為下輪做準備
hasCarry = sum>=10;
//取模
sum = sum%10;
//連接
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum);
forward.next = newNode;
//一起向下
forward = forward.next;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
//鏈表長度相同 且存在進位 那麼需要特殊處理
if(l1 == null && l2 == null ){
if(hasCarry){
forward.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return preHead.next;
}
//拿到更長的鏈表
ListNode longerList = (l1 == null)?l2:l1;
//繼續循環
while(longerList != null){
int sum = longerList.val+(hasCarry?1:0);
hasCarry = sum>=10;
sum = sum%10;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum);
forward.next = newNode;
forward = forward.next;
longerList = longerList.next;
}
//如果最後還存在進位 那麼new 一個節點
if(hasCarry){
forward.next = new ListNode(1);
}
//返回節點
return preHead.next;
}
二丶 刪除鏈表的倒數第 N 個結點
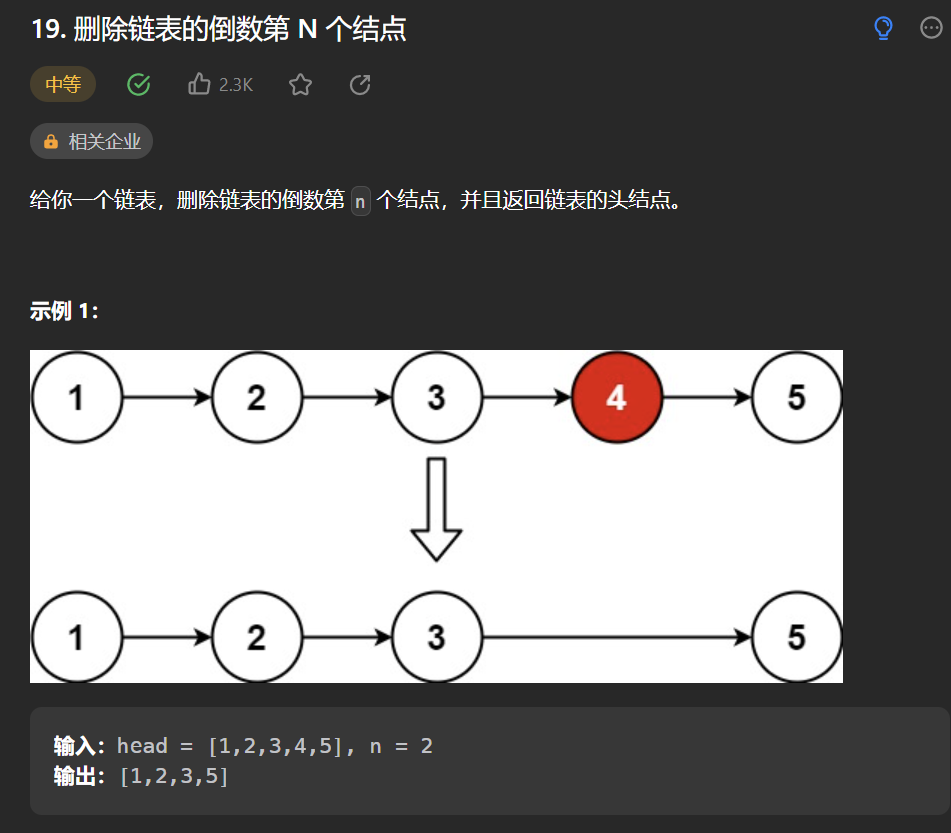
思路:
粗暴的思路:先遍歷一次拿到鏈表長度為sz,然後就可以倒數第n是第幾個節點了,然後再遍歷一次刪除即可。但是這樣做層次就低了,這時候我們可以使用快慢指針,快指針先走n步,等快指針走到尾部的時候,慢指針就是要刪除的倒數第n個節點了。我們可以使用額外的一個指針記錄慢指針的前一個,或者使用啞節點,讓慢指針從啞節點開始,這樣slow最後就是刪除節點的前一個
代碼:
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return null;
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = preHead;
//快指針先走
while(n>0){
fast=fast.next;
n--;
}
while(fast!=null){
fast =fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return preHead.next;
}
三丶[合併兩個有序鏈表](21. 合併兩個有序鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
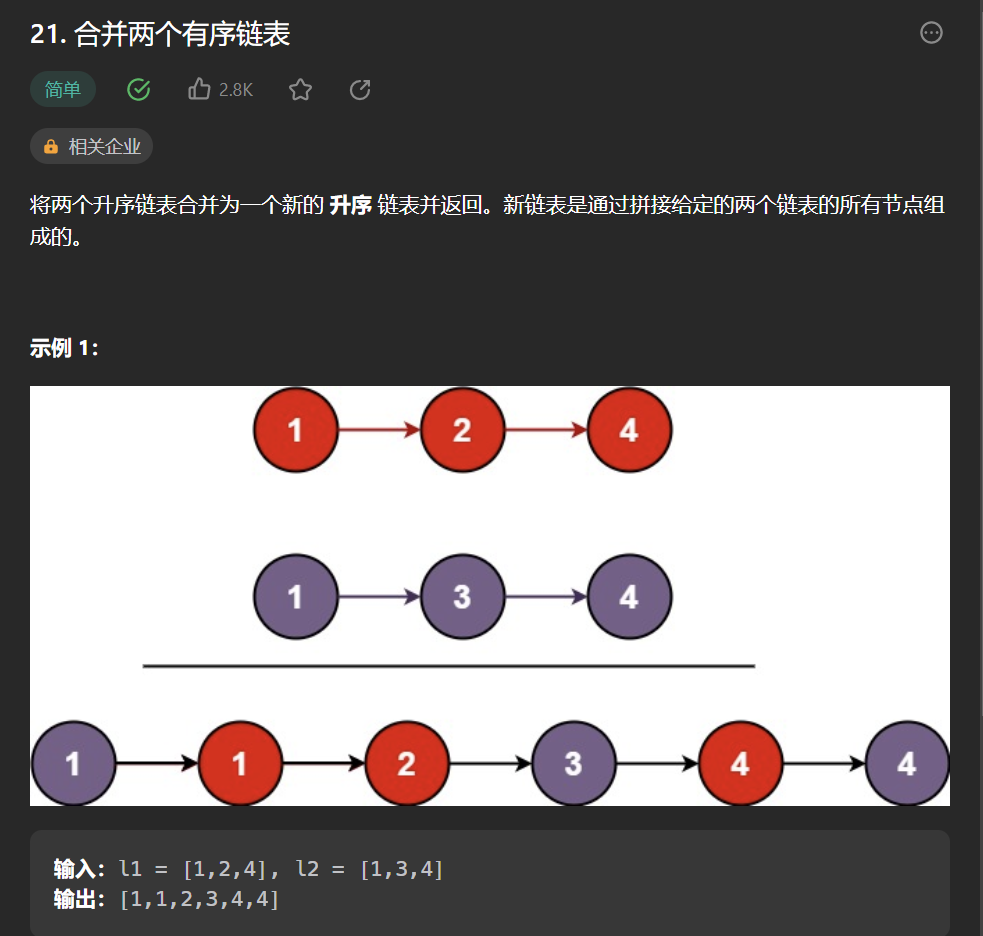
思路:
沒啥好說的,和第一題幾乎一模一樣
代碼:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = preHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val >= list2.val){
tail.next = list2;
ListNode nextNode = list2.next;
list2.next = null;
list2 = nextNode;
}else {
tail.next = list1;
ListNode nextNode = list1.next;
list1.next = null;
list1 = nextNode;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
return preHead.next;
}
四丶 合併K個升序鏈表
思路&對應代碼:
1.遞歸,分治
第三題我們寫了合併兩個有序鏈表,我們把大規模的合併k個分解成n個合併2個即可,首先我們把大任務,分解成合併左半部分,和合併右半部分
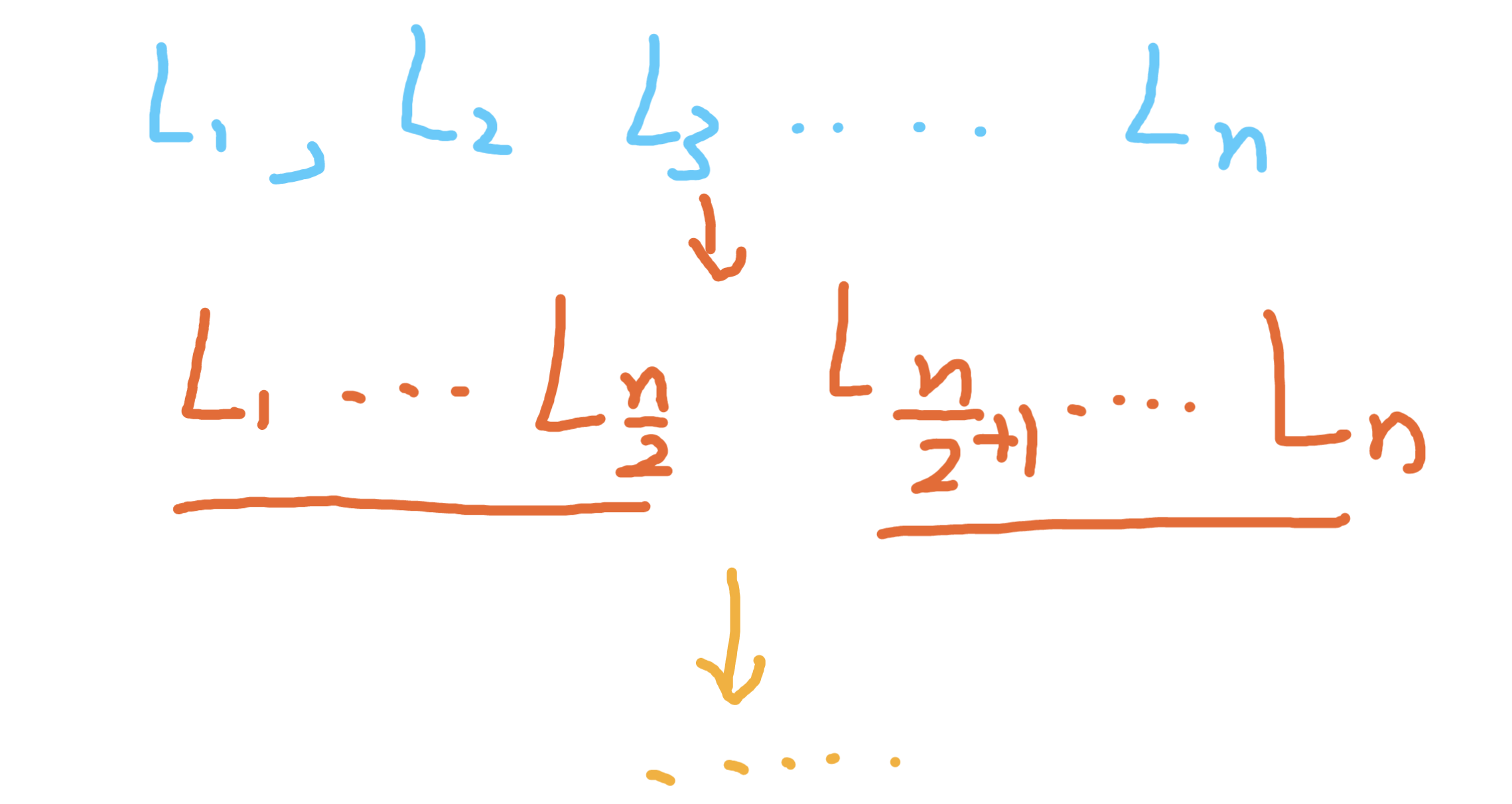
和歸併排序的思路是一致的
- 遞歸的出口是什麼,子任務只有一個鏈表,只是直接返回一個鏈表即可,子任務只有兩個鏈表,這時候合併兩個鏈表即可
- 怎麼合併兩個有序鏈表,如題三
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//入參數組為null 返回null
//空數組 返回null
if(lists==null || lists.length==0){
return null;
}
//調用遞歸方法
return merge2(lists ,0 ,lists.length-1);
}
private ListNode merge2(ListNode[] lists,int start,int end){
//base case 只有一個鏈表 直接返回一個鏈表
if(start == end){
return lists[start];
}
//子任務只有兩個鏈表
if(start == end-1){
return mergeTwoLists(lists[start],lists[end]);
}
//分治
int mid = (start+end)/2;
//合併左邊
ListNode mergeLeft = merge2(lists,start,mid);
//合併右邊
ListNode mergeRight = merge2(lists,mid+1,end);
//把左右合併
return mergeTwoLists(mergeLeft,mergeRight);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = preHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val >= list2.val){
tail.next = list2;
ListNode nextNode = list2.next;
list2.next = null;
list2 = nextNode;
}else {
tail.next = list1;
ListNode nextNode = list1.next;
list1.next = null;
list1 = nextNode;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
return preHead.next;
}
2.優先隊列
我們想下暴力解法,每次合併一個節點就遍歷整個數組找最小節點合併,這種做法慢在哪兒,慢在我們需要找到數組中剩下節點中最小節點,進行合併。那麼有沒有一種數據結構,可以讓拿到最小節點的o(1)時間複雜度昵——優先隊列
- 隊列優先級是啥——節點的值
- 隊列如何初始化——首先放入數組中所有鏈表的頭節點
- 隊列如何入隊——每次一個節點合併的後都把其next節點進行入隊
- 何時停止循環——隊列為空、
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists==null){
return null;
}
if(lists.length==0){
return null;
}
return mergewithHeap(lists);
}
private ListNode mergewithHeap(ListNode[] lists){
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
//尾巴用於串聯這些節點
ListNode tail =preHead;
//優先隊列 傳入Comparetor 比較val
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>((l1,l2)->l1.val-l2.val);
//初始化隊列
for(int i = 0;i<lists.length;i++){
if(lists[i]!=null){
heap.offer(lists[i]);
}
}
//隊列不為空
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
//當前最西澳
ListNode min = heap.poll();
//串聯起來
tail.next =min;
//更新尾巴
tail =tail.next;
//繼續入隊
if(min.next!=null){
heap.offer(min.next);
}
}
return preHead.next;
//這裡我把優先隊列變量名命為heap 是因為java中的優先隊列是基於數組的堆實現
//需要注意入隊時offer 出隊時poll 並且入隊不能是null
五丶[兩兩交換鏈表中的節點](24. 兩兩交換鏈表中的節點 – 力扣(Leetcode))
思路:
簡簡單單模擬,初始化如下變量
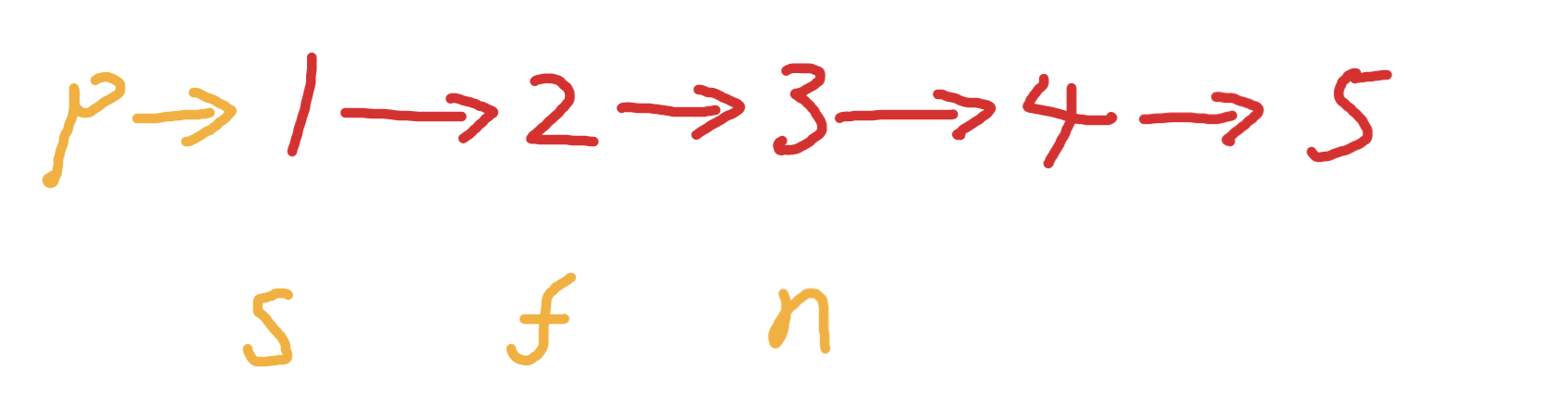
交換s和f 如下效果
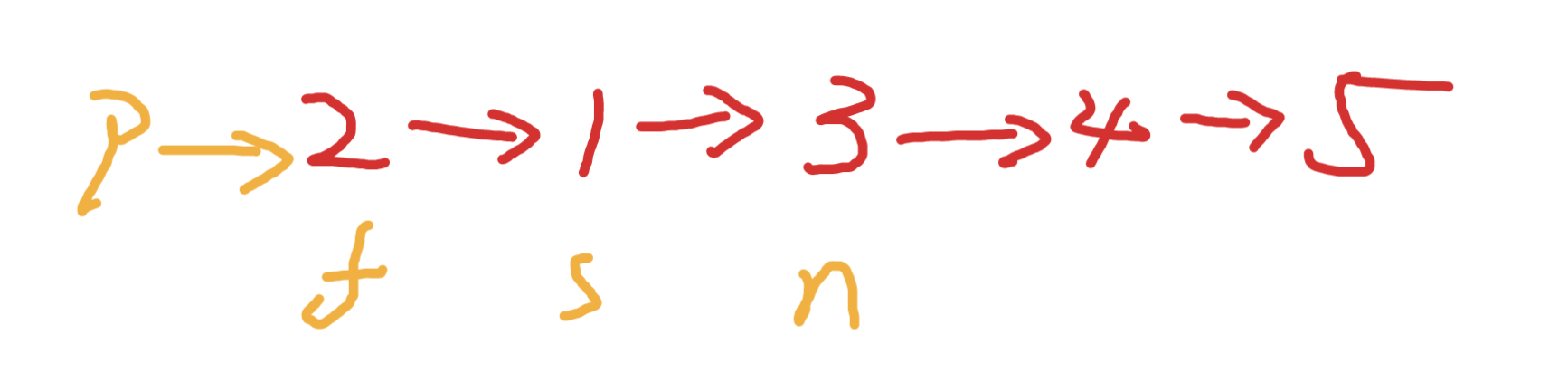
接下來需要更新這些變量
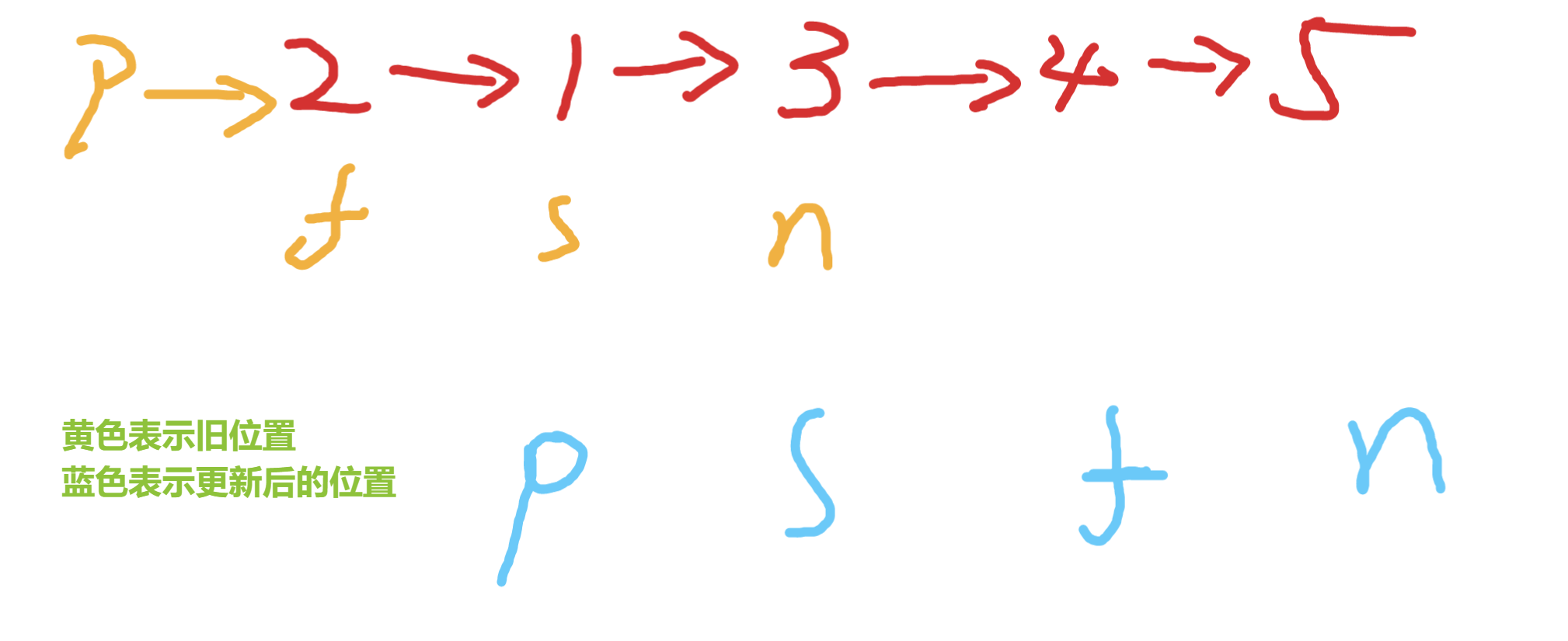
如此往複直到f為null,但是需要注意空指針的處理
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
//沒必要交換
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//只有兩個節點
if(head.next.next == null){
ListNode newHead = head.next;
newHead.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode pre = preHead;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
ListNode next = fast.next;
//交換
while(fast != null){
pre.next = fast;
fast.next = slow;
slow.next = next;
if(next == null){
return preHead.next;
}
pre = slow;
slow = next;
fast = slow.next;
if(fast == null){
return preHead.next;
}
next = fast.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
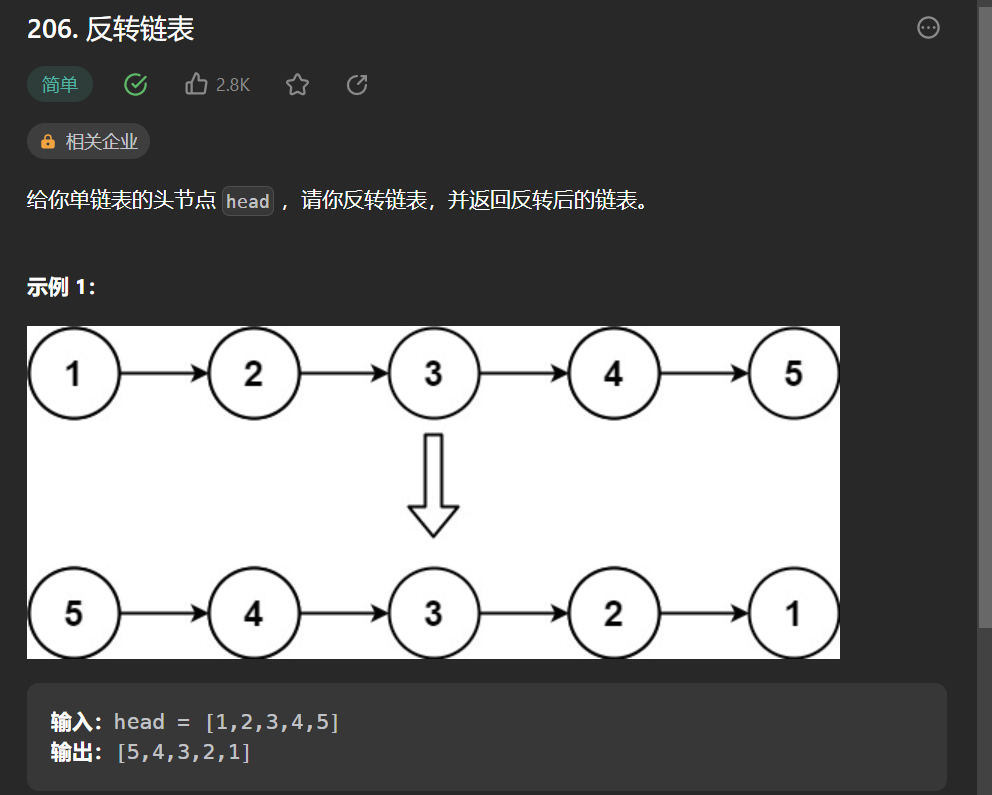
六丶[反轉鏈表](206. 反轉鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
思路:
簡簡單單模擬
先初始化如下節點
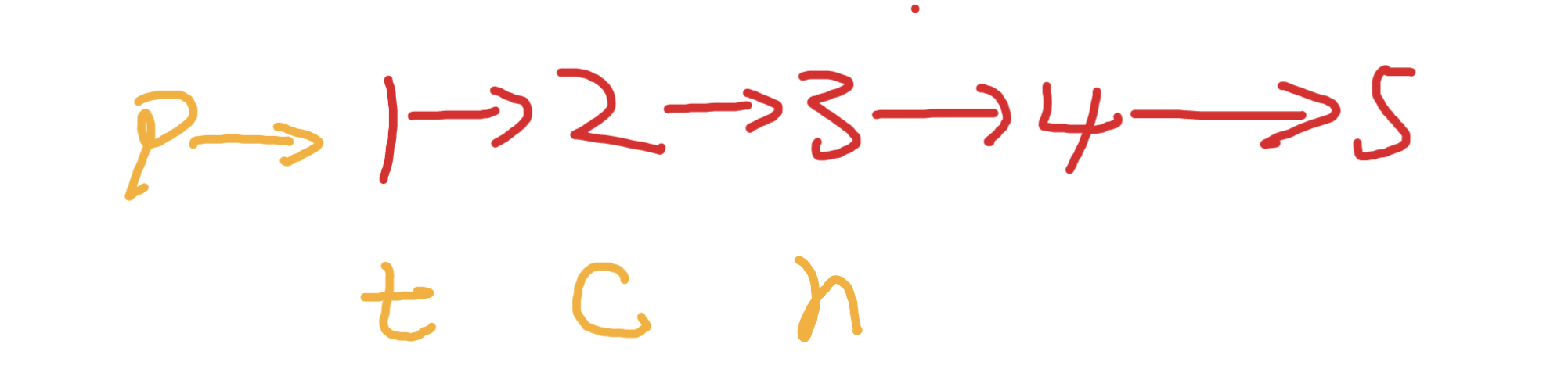
實現反轉
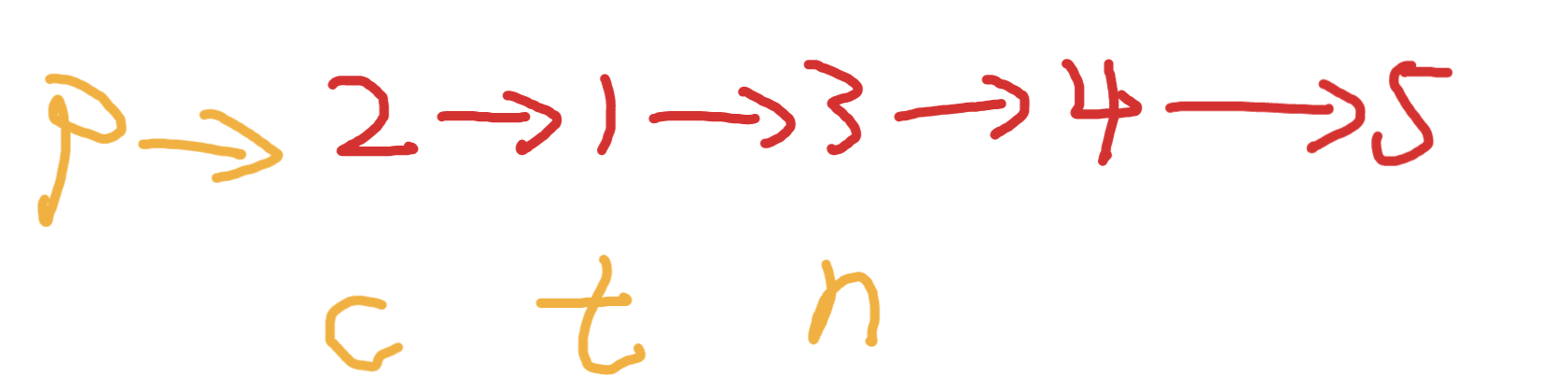
更新變量
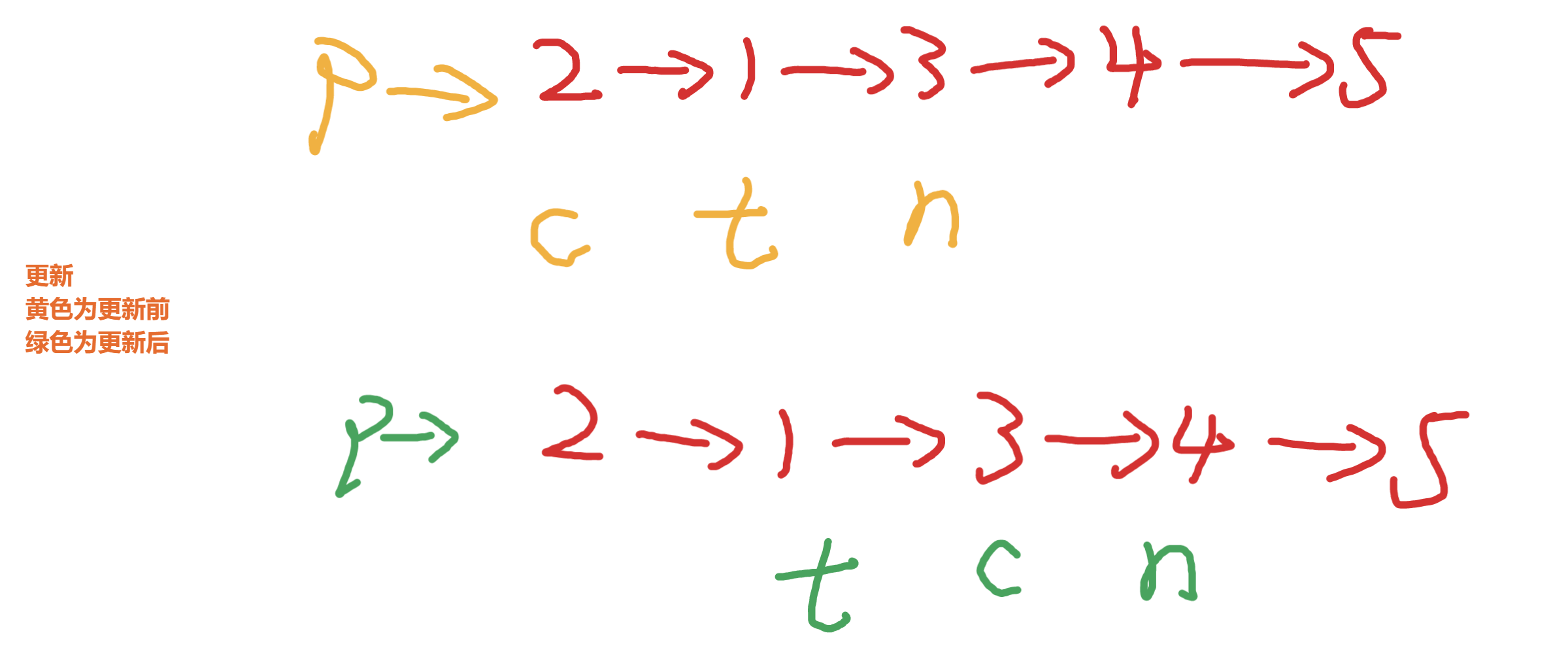
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//當前需要操作的節點
ListNode cur = head.next;
//下一個節點
ListNode next = cur.next;
//尾巴
ListNode tail = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){
//翻轉
cur.next = preHead.next;
tail.next = next;
preHead.next = cur;
//更新
cur = next;
if(next == null){
return preHead.next;
}
next = next.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
七丶[K 個一組翻轉鏈表](25. K 個一組翻轉鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
思路:
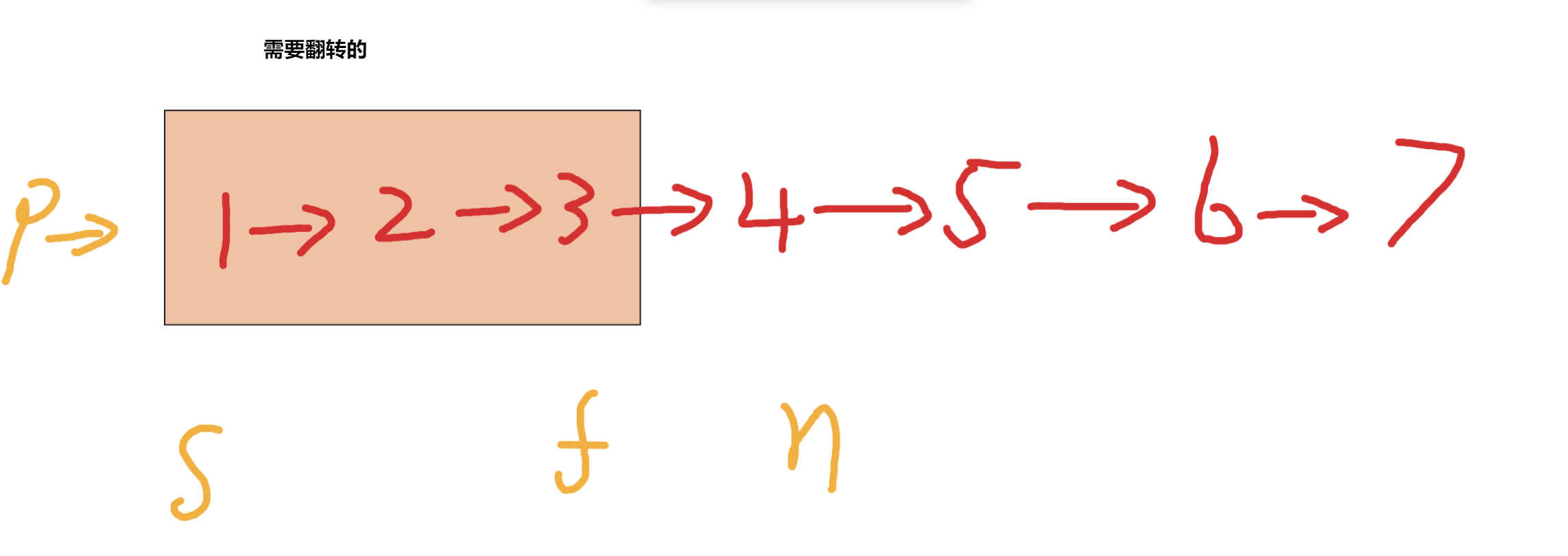
第六題,我們實現了反轉鏈表,那麼k個一翻轉的邏輯,這個翻轉的過程是一樣的,接下來我們只需要把這k個節點先摘下來,然後進行翻轉,翻轉返回新的頭和尾巴,然後和原來鏈表連接起來繼續翻轉即可

代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
//無需翻轉的情況
if(head == null || head.next == null || k == 1){
return head;
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//翻轉後負責把鏈表重新連接起來
ListNode pre = preHead;
//翻轉 快慢之間的部分
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = findKNext(slow,k);
//如果上來就不足k 個 直接g
if(fast == null){
return preHead.next;
}
//循環翻轉
while(fast != null) {
//先保存下 更新的時候需要用
ListNode next = fast.next;
//斷開 不然reverseList會一直翻轉下去
fast.next = null;
//翻轉快慢之間的部分返回翻轉後的尾巴
ListNode[] resArray = reverseList(slow);
ListNode rHead = resArray[0];
ListNode rTail = resArray[1];
// 連接 把翻轉後的內容連接上去
pre.next = rHead;
rTail.next = next;
//更新
slow = next;
fast = findKNext(slow,k);
pre = rTail;
}
return preHead.next;
}
//node 慢節點。k是題目中的k個一反轉,我們要找到fast
//如果不足fast 和 slow 之間一共k個節點(包括自己)
private ListNode findKNext(ListNode node,int k){
while(k>1){
if(node == null){
return null;
}
node = node.next;
k--;
}
return node;
}
//翻轉 並返回 頭和尾
private ListNode[] reverseList(ListNode head) {
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//當前需要操作的節點
ListNode cur = head.next;
//下一個節點
ListNode next = cur.next;
//尾巴
ListNode tail = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){
//翻轉
cur.next = preHead.next;
tail.next = next;
preHead.next = cur;
//更新
cur = next;
if(next == null){
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
next = next.next;
}
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
}
八丶[旋轉鏈表](61. 旋轉鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
思路:
首先需要注意的是,如果鏈表長度為len,向右移動len個位置,其實和原本鏈表一樣,所有其實我們只需要移動k%len個位置即可
移動k個,其實就是把最後k個節點連接到鏈表頭部
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null || head.next==null || k == 0){
return head;
}
//求長度
ListNode lenTemp = head;
int len = 0;
while(lenTemp != null){
lenTemp = lenTemp.next;
len ++;
}
//我們需要旋轉的次數
k = k % len;
//剛好整數倍 那麼直接返回頭
if(k == 0){
return head;
}
//移動k個,其實就是把最後k個節點連接到鏈表頭部
//快慢指針找到倒數第k個的前一個
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(k!=0){
fast = fast.next;
k--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//到這fast 就是尾巴 slow是倒數第k+1個 slow.next 就是新的頭
//那麼顛倒下倒數k個節點 和 頭的位置
ListNode newHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
fast.next= head;
return newHead;
}
}
九丶[刪除排序鏈表中的重複元素](83. 刪除排序鏈表中的重複元素 – 力扣(Leetcode))
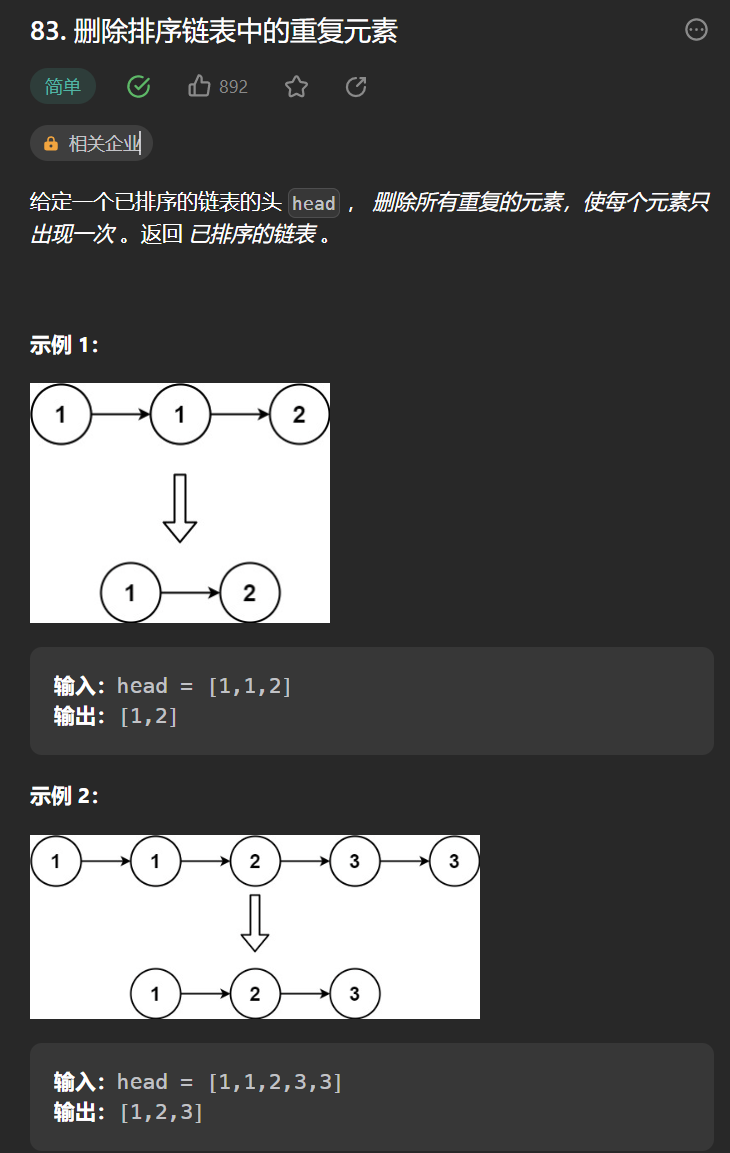
思路:
首先這是一個排序鏈表,這意味着相同值的節點是相鄰的。
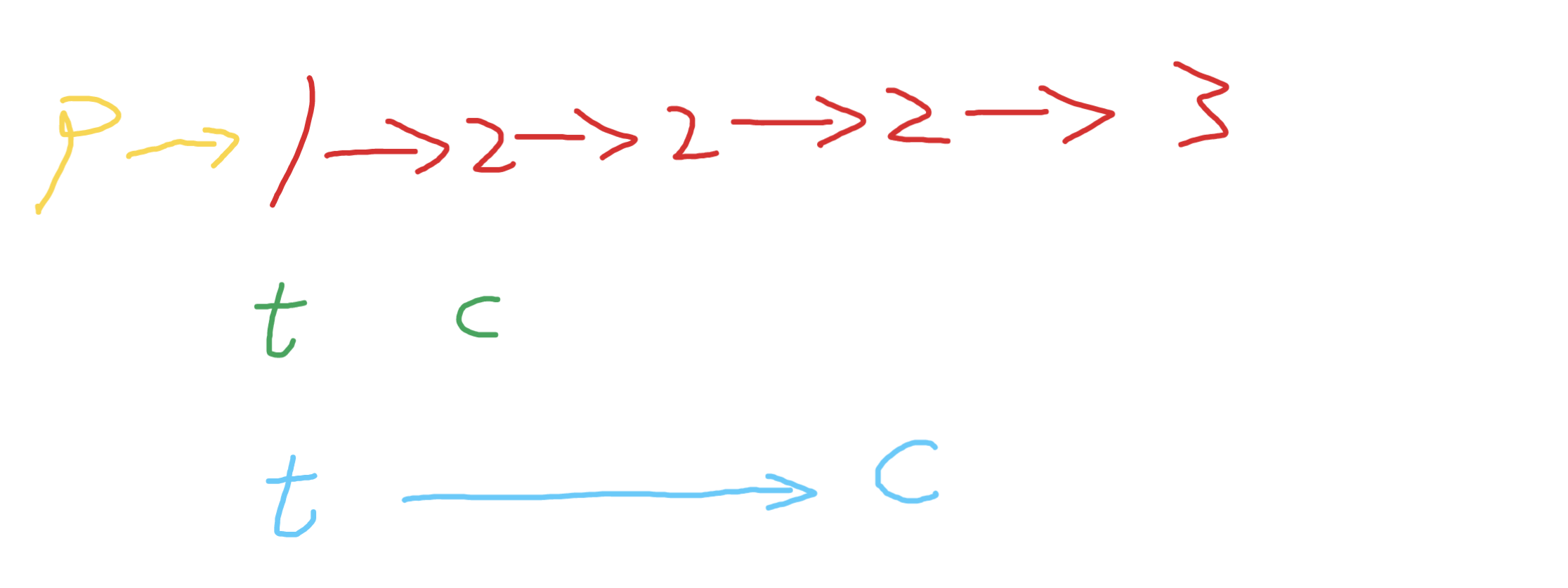
初始化一個啞節點p,和新鏈表的尾巴節點t,c表示當前遍歷的節點

如果c和下一個節點值不同 那麼c可以保留,串到t後,更新到綠色位置,遇到重複的節點,就讓c走到最後一個重複的節點,然後讓t指向c,後更新t和c繼續遍歷
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//尾巴節點
ListNode tail = preHead;
//當前遍歷的節點
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//如果下一個節點為空 或者 下一個節點和當前節點值不為空
//那麼當前節點保留,讓tail的下一個指向當前節點
if(cur.next == null || cur.val != cur.next.val){
tail.next = cur;
tail = cur;
cur = cur.next;
continue;
}
//到此說明重複了 記錄下重複的值
int duplicateValue = cur.val;
//下一個節點
ListNode nextNode = cur.next;
//一直到下一個節點為空 或者值不重複了
while(nextNode != null && nextNode.val == duplicateValue){
nextNode = nextNode.next;
}
//到這就是不重複的 刪除這其中的重複的節點
cur.next = nextNode;
//連接
tail.next = cur;
//刷新進入下一輪循環
tail = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
十丶[刪除排序鏈表中的重複元素 II](82. 刪除排序鏈表中的重複元素 II – 力扣(Leetcode))
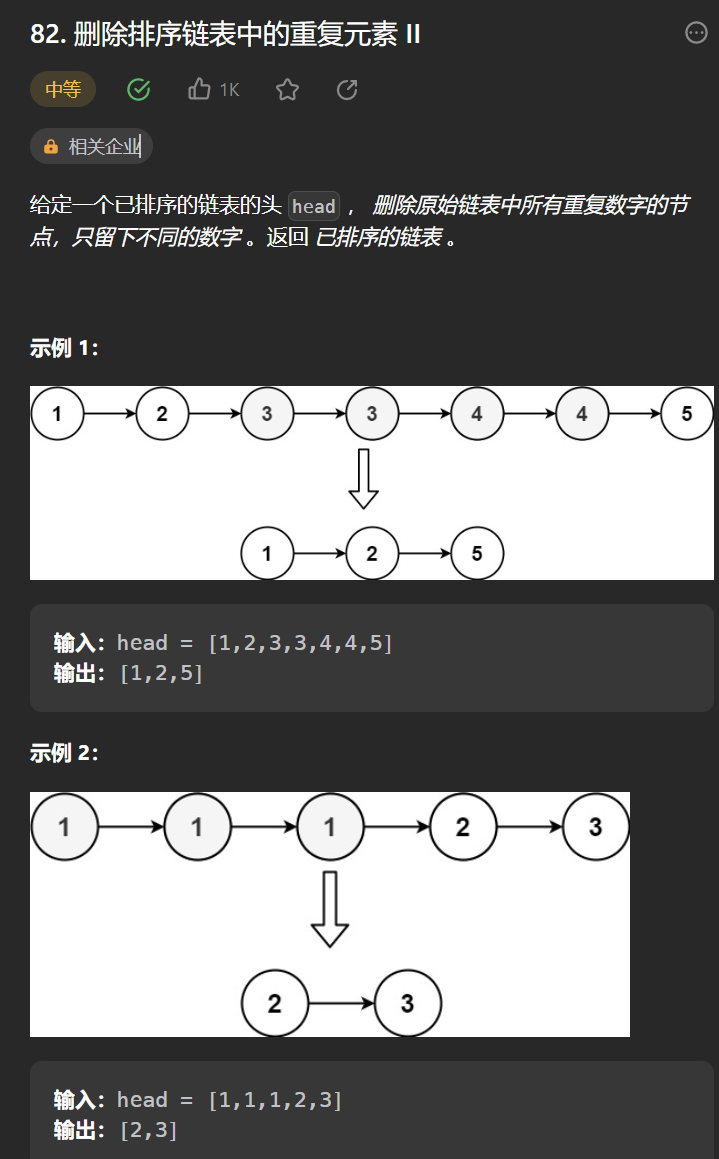
思路:
思路和第九題差不多,唯一的差別是重複節點不能保留,所以發生重複的時候需要把tail的下一個節點置為null
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//新鏈表尾節點
ListNode tail = preHead;
//當前變遍歷到的節點
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//如果下一個節點為null 那麼必然不會與下一個節點值相同
//或者下一個節點和當前節點 值不同
//那麼說明當前節點可以假如到新鏈表中
//讓尾巴的下一個指向當前節點
if(cur.next == null || cur.val != cur.next.val){
tail.next = cur;
tail = cur;
}
//如果相同 那麼一直到最後一個值相等的節點
while(cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val){
//說明這部分重複了,我們首先讓新鏈表不要和這部分連接到一起
tail.next = null;
cur = cur.next;
}
//cur向下 就必然是不相同的節點
cur = cur.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
十一丶[分隔鏈表](86. 分隔鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
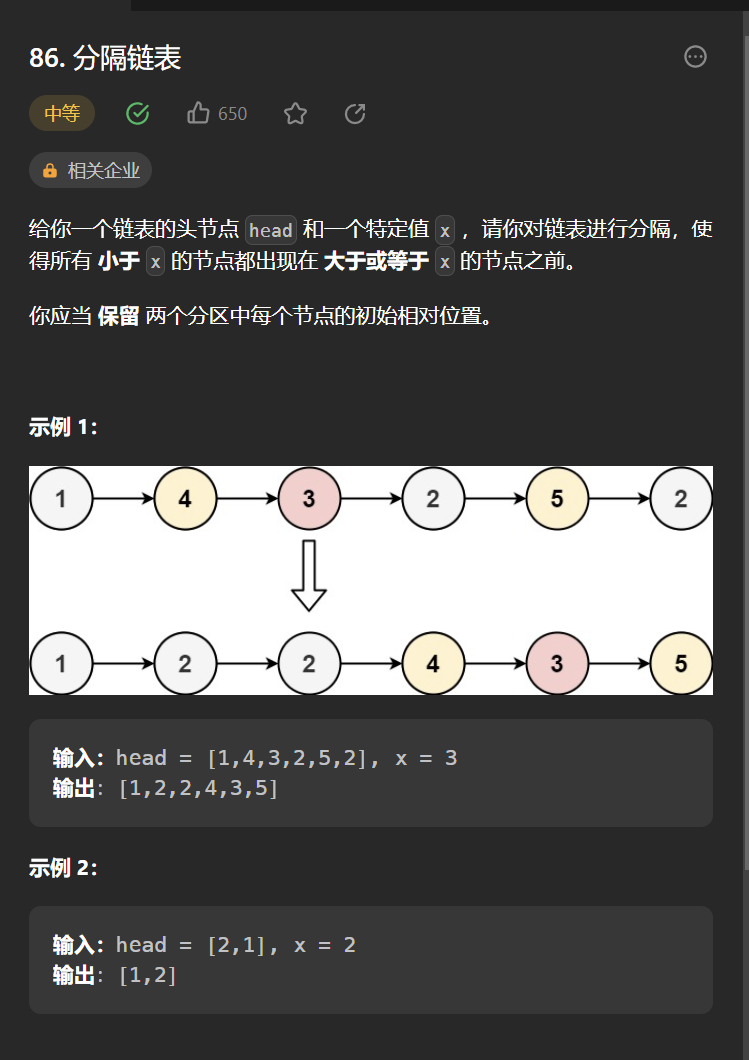
思路:
題目乍一看可能沒思路,糾結於怎麼保持相對順序不變,其實只需要使用兩個啞節點,一個記錄大於等於x,一個小於x的節點,最後把這兩個啞節點代表的鏈表的進行串聯即可
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//小於x的啞節點 和尾節點
ListNode lessPreHead = new ListNode();
ListNode lessTail = lessPreHead;
//大於等於x的啞節點 和尾節點
ListNode betterEqualHead = new ListNode();
ListNode betterEqualTail = betterEqualHead;
ListNode cur = head;
//遍歷
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
//如果小於 那麼連接到 小於鏈表上
if(cur.val < x){
lessTail.next = cur;
lessTail = lessTail.next;
cur.next = null;
}else{
//反之連接到大於等於鏈表
betterEqualTail.next = cur;
betterEqualTail = betterEqualTail.next;
cur.next = null;
}
cur = curNext;
}
lessPreHead = lessPreHead.next;
betterEqualHead = betterEqualHead.next;
//沒有大於等於x的節點 那麼返回小於頭
if(betterEqualHead == null){
return lessPreHead;
}
//沒用小於x的節點 返回大於等於頭
if(lessPreHead == null){
return betterEqualHead;
}
//連接起來
lessTail.next = betterEqualHead;
return lessPreHead;
}
}
十二丶[環形鏈表](141. 環形鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
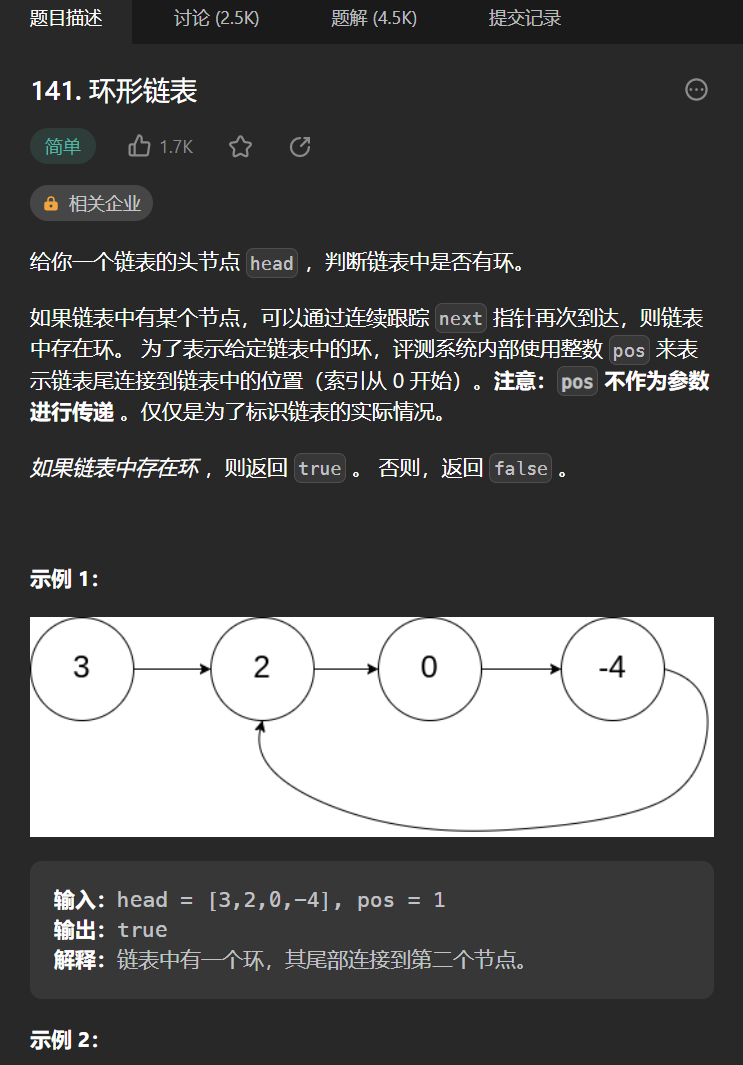
思路:
如果可以使用set緩存所有的節點,然後遍歷的時候發現next存在於set中那麼可以判斷其有環,但是這樣空間複雜度為n,所以我們需要記住一個結論,快慢指針都從頭開始出發,快指針一次走兩步,慢指針一次一步,如果二者相遇說明有環,如果慢指針為null了還沒相遇那麼說明無環(「烏龜」和「兔子」在鏈表上移動,「兔子」跑得快,「烏龜」跑得慢。當「烏龜」和「兔子」從鏈表上的同一個節點開始移動時,如果該鏈表中沒有環,那麼「兔子」將一直處於「烏龜」的前方;如果該鏈表中有環,那麼「兔子」會先於「烏龜」進入環,並且一直在環內移動。等到「烏龜」進入環時,由於「兔子」的速度快,它一定會在某個時刻與烏龜相遇,即套了「烏龜」若干圈。)
代碼:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
do{
if(fast == null||fast.next==null){
return false;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}while(slow != null);
return false;
}
}
十三丶[環形鏈表 II](142. 環形鏈表 II – 力扣(Leetcode))
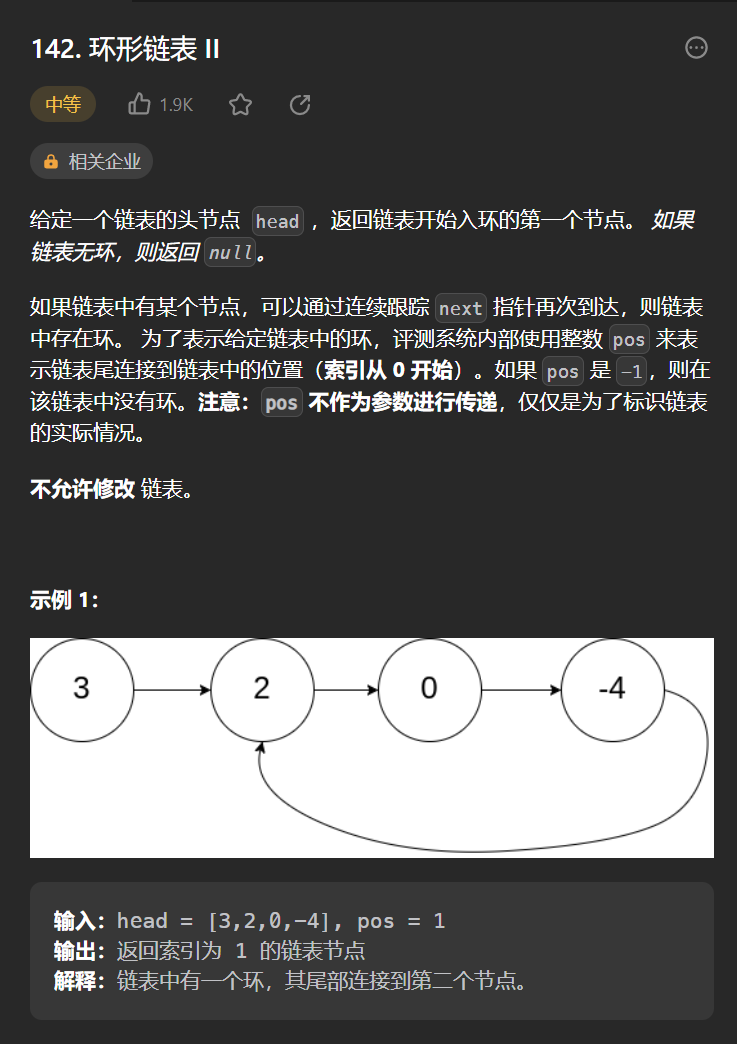
思路:
需要記住一個結論,快慢指針同時出發,快一次兩步,慢一次一步,相遇的時候就是鏈表存在環,之後快指針從頭開始,慢指針繼續運動,二者都一次走一步,相等的時候就是入環節點的位置
代碼:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
do{
if(fast == null || fast.next==null){
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}while(slow != null);
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast =fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
十四丶[複製帶隨機指針的鏈表](138. 複製帶隨機指針的鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
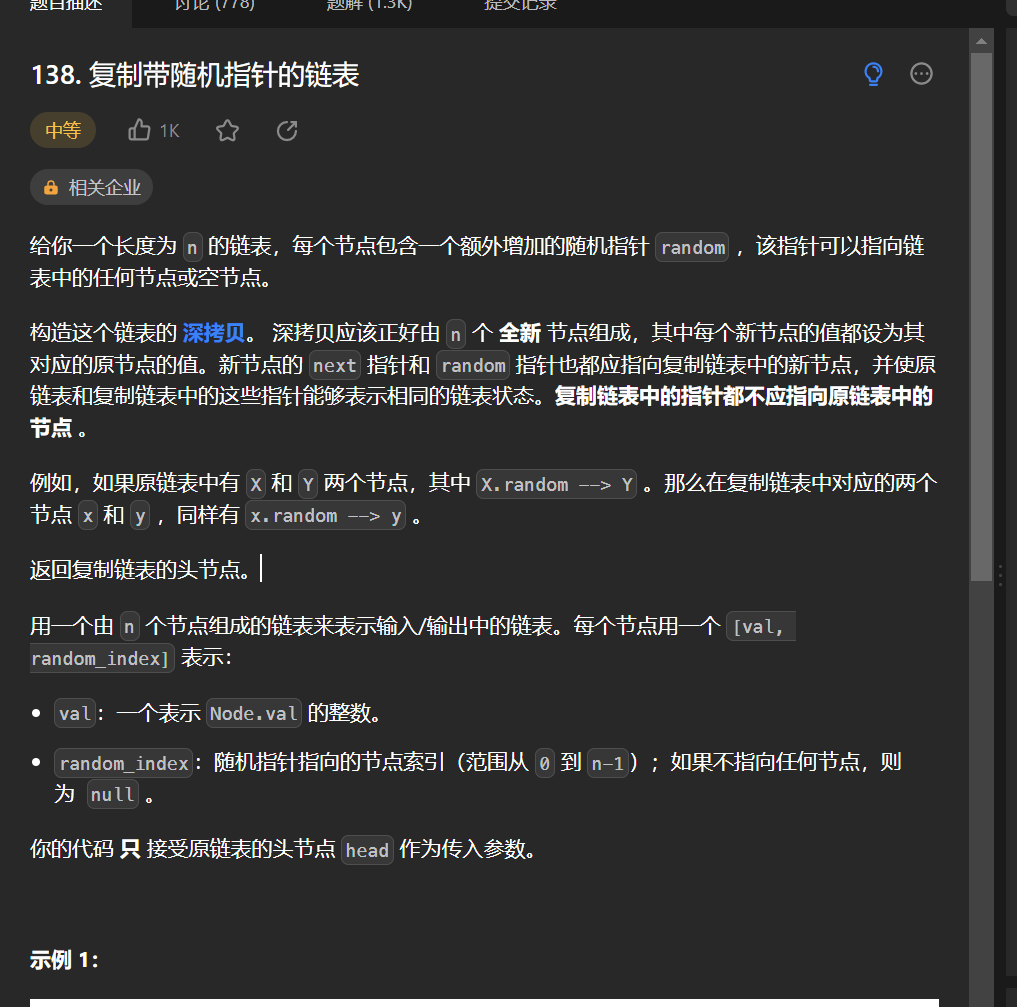
思路:
如果可以使用map存儲每一個節點的下一個節點, 和random指針節點,那麼這個題就沒什麼難度,但是如果追求極致的空間不使用額外空間的話,還是有點巧妙的
-
複製每一個節點的next,並且讓複製節點和原節點使用next串聯起來,做到如下效果
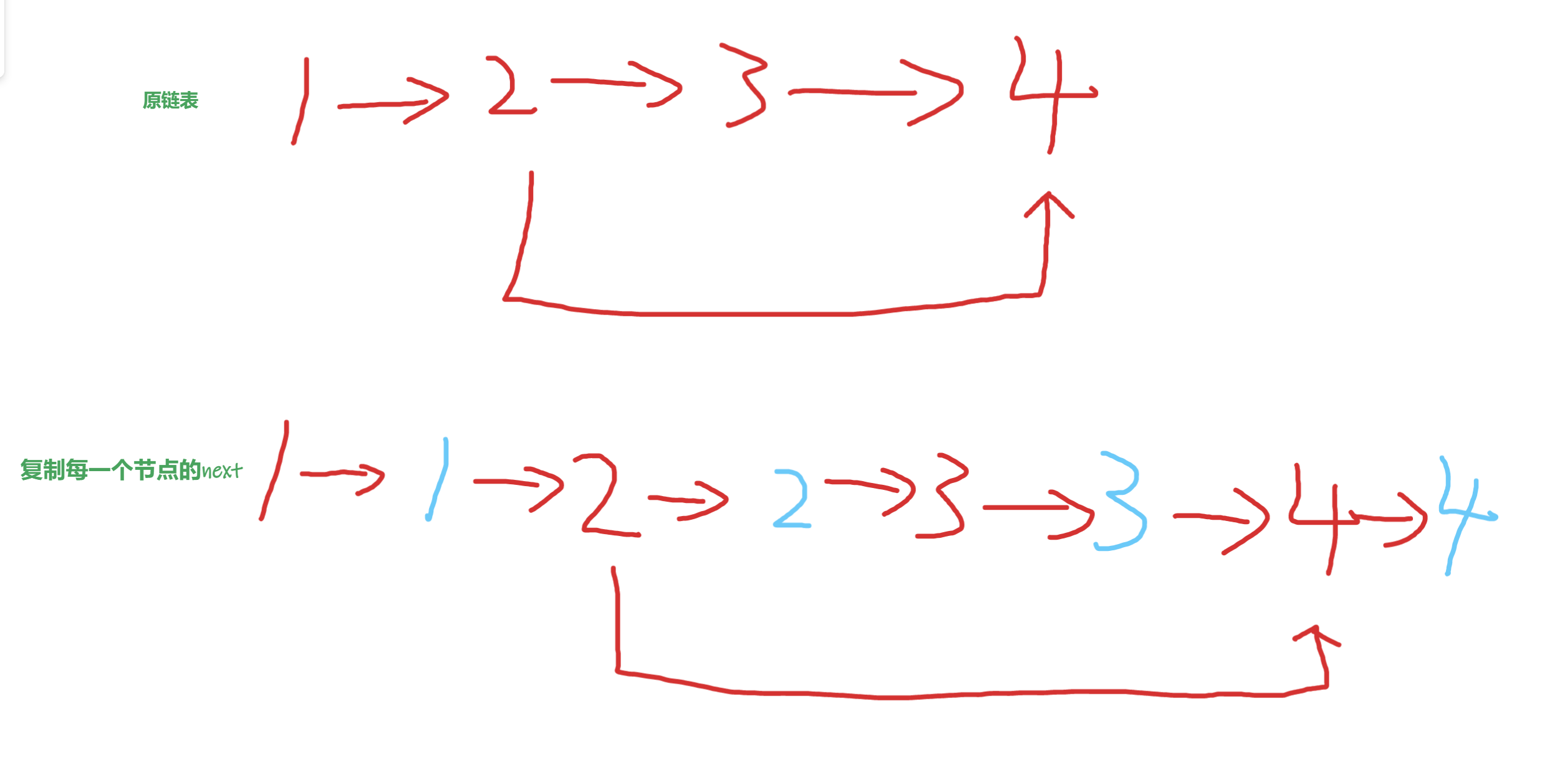
藍色是複製的節點,紅色是原節點
這時我們其實可以很快的得到藍色2的random指針指向的是藍色的4,也就是紅色4的next
-
接下來我們要把兩個鏈表拆開,並且複製random指針
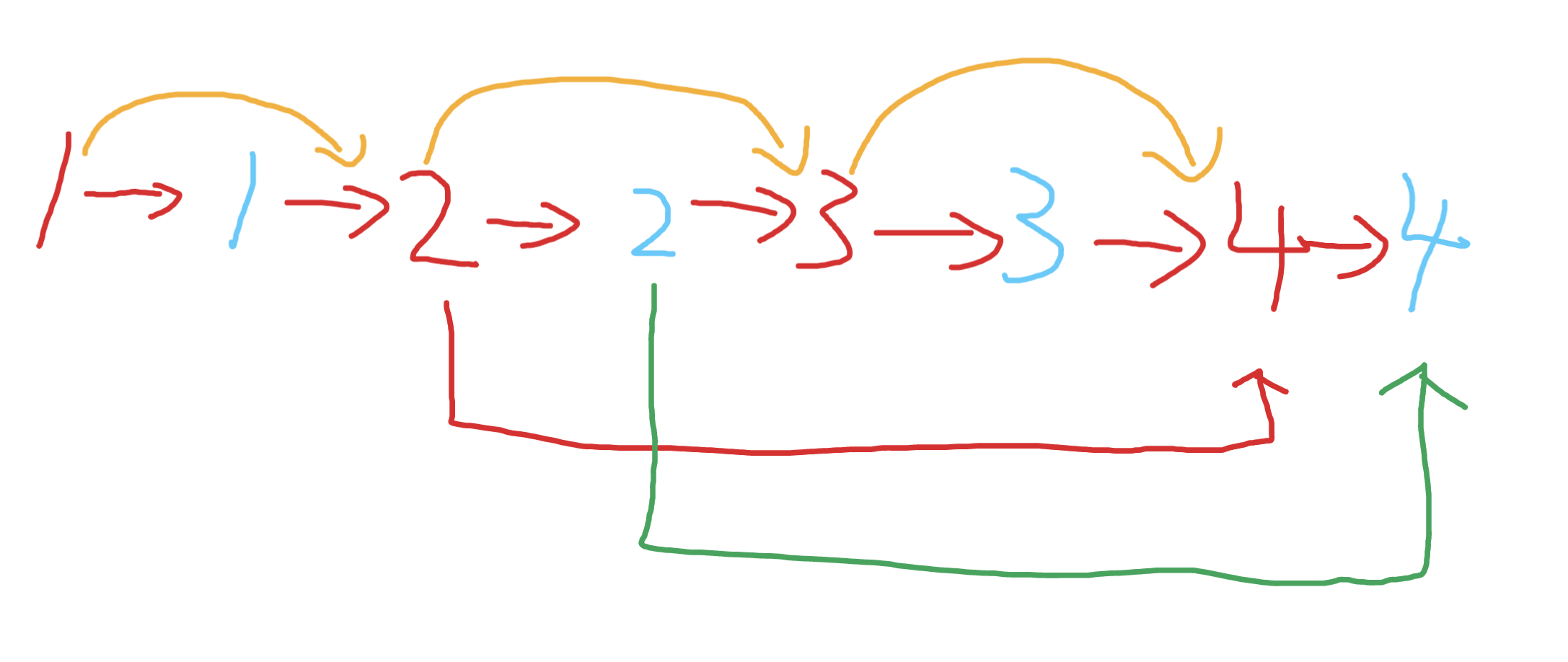
我們遍歷到紅色2的時候發現,其具備random指向了公司的4,那麼藍色2的指向就是紅色4的下一個
代碼:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null ){
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
//深拷貝
while(cur != null){
Node copy = new Node(cur.val);
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = copy;
copy.next = next;
cur = next;
}
//拷貝後的頭
Node copyHead = head.next;
//接下來需要複製random指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node copy = cur.next;
//拷貝random
if(cur.random != null){
copy.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = copy.next;
}
//拆分
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node copy = cur.next;
Node sourceNext = copy.next;
cur.next = sourceNext;
if(sourceNext != null){
copy.next = sourceNext.next;
}
cur =sourceNext;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
十五丶[LRU 緩存](146. LRU 緩存 – 力扣(Leetcode))
思路:
LRU 最近最少使用,如果看過linkedHashMap源碼,我們可以知道,讓linkedHashMap按照訪問順序排序然後複寫removeEldestEntry讓容量大於最大容量的時候刪除節點即可實現lru淘汰策略(mybatis源碼中的LRU緩存便是如此實現的)。原理便是最近被訪問(put 或者get)的內容,放在鏈表的頭部,這樣鏈表的尾部便是最近最少訪問的緩存內容,所以我們只要使用鏈表來維護這個順序,使用hashMap實現查找即可
代碼:
class LRUCache {
//雙向鏈表
static class Node {
Node pre;
Node next;
int key ;
int val;
}
//最大容量
int maxSize;
//當前容量
int size=0;
//頭 啞節點
Node head;
//尾 啞節點
Node tail;
//緩存內容
Map<Integer,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
//初始化
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
maxSize = capacity;
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node n = map.get(key);
//緩存中沒 返回-1
if(n == null){
return -1;
}
//緩存中存在,說明最近被使用到 那麼調整到隊列頭部
adjustToHead(n);
return n.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node n = map.get(key);
//緩存中最開始沒用 那麼需要 new 一個節點存到map中
if(n == null){
n = new Node();
n.val = value;
n.key = key;
map.put(key,n);
size++;
}else{
//緩存中有 那麼改變值
n.val = value;
}
//調整到隊列頭部
adjustToHead(n);
}
//將節點移動到頭部 如果容量超過需要刪除尾部節點
void adjustToHead(Node n){
if(n == head.next){
//判斷是否需要刪除最近最少使用的內容
removeTailIfNeed();
return;
}
//調整到頭部
Node sourceFirst = head.next;
if(n.pre != null){
n.pre.next = n.next;
n.next.pre = n.pre;
}
n.next = sourceFirst;
sourceFirst.pre = n;
n.pre = head;
head.next = n;
//判斷是否需要刪除最近最少使用的內容
removeTailIfNeed();
}
//刪除最近最少使用的內容
void removeTailIfNeed(){
if(size > maxSize){
map.remove(tail.pre.key);
size -- ;
Node needRemove = tail.pre;
needRemove.pre.next = tail;
tail.pre = needRemove.pre;
}
}
}
十六丶[迴文鏈表](234. 迴文鏈表 – 力扣(Leetcode))
思路:
如果可以使用額外數據結構保存鏈表中的值,那麼這個問題非常簡單,但是如果不允許使用額外空間,這個問題就有點巧妙了
首先我們要找到鏈表的重點(1->2->3找到2,1->2->3->4 找到2)然後將中點右側部分進行反轉,返回再比較中點左半部分 和 右半部分是否相同的數值,最後還需要把右半部分翻轉回來,復原鏈表
代碼:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//0個節點, 一個節點 直接true
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return true;
}
//兩個節點 看兩個節點值是否相同
if(head.next.next == null){
return head.val == head.next.val;
}
//找中點
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//中點
ListNode half = slow;
//需要翻轉的右半部分
ListNode needReverseHead = half.next;
//翻轉 數組第1個是頭 第二個是翻轉後的尾
ListNode[]rArray = reverseList(needReverseHead);
ListNode halfHead = rArray[0];
//標記是否 迴文
boolean flag = true;
//比較是否迴文
while(halfHead!=null){
flag = halfHead.val==head.val;
if(!flag){
break;
}
halfHead = halfHead.next;
head = head.next;
}
//翻轉回去
ListNode[] recovery = reverseList(rArray[0]);
//復原鏈表
slow.next = recovery[0];
return flag;
}
//翻轉 並返回 頭和尾
private ListNode[] reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next == null){
return new ListNode[]{head,null};
}
//啞節點
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//當前需要操作的節點
ListNode cur = head.next;
//下一個節點
ListNode next = cur.next;
//尾巴
ListNode tail = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){
//翻轉
cur.next = preHead.next;
tail.next = next;
preHead.next = cur;
//更新
cur = next;
if(next == null){
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
next = next.next;
}
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
}



