萬字剖析Ribbon核心組件以及運行原理
- 2022 年 6 月 15 日
- 筆記
- ribbon, SpringCloud
大家好,本文我將繼續來剖析SpringCloud中負載均衡組件Ribbon的源碼。本來我是打算接着OpenFeign動態代理生成文章直接講Feign是如何整合Ribbon的,但是文章寫了一半發現,如果不把Ribbon好好講清楚,那麼有些Ribbon的細節理解起來就很困難,所以我還是打算單獨寫一篇文章來剖析Ribbon的源碼,這樣在講Feign整合Ribbon的時候,我就不再贅述這些細節了。好了,話不多說,直接進入主題。
一、Ribbon的核心組件
1、Server
這是個很簡單的東西,就是服務實例數據的封裝,裏面封裝了服務實例的ip和端口之類的,一個服務有很多台機器,那就有很多個Server對象。
2、ServerList
public interface ServerList<T extends Server> {
public List<T> getInitialListOfServers();
/**
* Return updated list of servers. This is called say every 30 secs
* (configurable) by the Loadbalancer's Ping cycle
*
*/
public List<T> getUpdatedListOfServers();
}
ServerList是個接口,泛型是Server,提供了兩個方法,都是獲取服務實例列表的,這兩個方法其實在很多實現類中實現是一樣的,沒什麼區別。這個接口很重要,因為這個接口就是Ribbon獲取服務數據的來源接口,Ribbon進行負載均衡的服務列表就是通過這個接口來的,那麼可以想一想是不是只要實現這個接口就可以給Ribbon提供服務數據了?事實的確如此,在SpringCloud中,eureka、nacos等註冊中心都實現了這個接口,都將註冊中心的服務實例數據提供給Ribbon,供Ribbon來進行負載均衡。
3、ServerListUpdater
通過名字也可以知道,是用來更新服務註冊表的數據,他有唯一的實現,就是PollingServerListUpdater,這個類有一個核心的方法,就是start,我們來看一下start的實現。
@Override
public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
final Runnable wrapperRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!isActive.get()) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
return;
}
try {
updateAction.doUpdate();
lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed one update cycle", e);
}
}
};
scheduledFuture = getRefreshExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
wrapperRunnable,
initialDelayMs,
refreshIntervalMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} else {
logger.info("Already active, no-op");
}
}
通過這段方法我們可以看出,首先通過isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)來保證這個方法只會被調用一下,然後封裝了一個Runnable,這個Runnable幹了一件核心的事,就是調用傳入的updateAction的doUpdate方法,然後將Runnable扔到了帶定時調度功能的線程池,經過initialDelayMs(默認1s)時間後,會調用一次,之後都是每隔refreshIntervalMs(默認30s)調用一次Runnable的run方法,也就是調用updateAction的doUpdate方法。
所以這個類的核心作用就是每隔30s會調用一次傳入的updateAction的doUpdate方法的實現,記住這個結論。
4、IRule
public interface IRule{
/*
* choose one alive server from lb.allServers or
* lb.upServers according to key
*
* @return choosen Server object. NULL is returned if none
* server is available
*/
public Server choose(Object key);
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb);
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}
IRule是負責負載均衡的算法的,也就是真正實現負載均衡獲取一個服務實例就是這個接口的實現。比如說實現類RandomRule,就是從一堆服務實例中隨機選取一個服務實例。
5、IClientConfig
就是一個配置接口,有個默認的實現DefaultClientConfigImpl,通過這個可以獲取到一些配置Ribbon的一些配置。
6、ILoadBalancer
public interface ILoadBalancer {
public void addServers(List<Server> newServers);
public Server chooseServer(Object key);
public void markServerDown(Server server);
@Deprecated
public List<Server> getServerList(boolean availableOnly);
public List<Server> getReachableServers();
public List<Server> getAllServers();
}
這個接口的作用,對外主要提供了獲取服務實例列表和選擇服務實例的功能。雖然對外主要提供獲取服務的功能,但是在實現的時候,主要是用來協調上面提到的各個核心組件的,使得他們能夠協調工作,從而實現對外提供獲取服務實例的功能。
這個接口的實現有好幾個實現類,但是我講兩個比較重要的。
BaseLoadBalancer
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
private final static IRule DEFAULT_RULE = new RoundRobinRule();
protected IRule rule = DEFAULT_RULE;
private IClientConfig config;
protected volatile List<Server> allServerList = Collections
.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>());
protected volatile List<Server> upServerList = Collections
.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>());
public BaseLoadBalancer(String name, IRule rule, LoadBalancerStats stats,
IPing ping, IPingStrategy pingStrategy) {
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: initialized", name);
this.name = name;
this.ping = ping;
this.pingStrategy = pingStrategy;
setRule(rule);
setupPingTask();
lbStats = stats;
init();
}
public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config) {
initWithNiwsConfig(config);
}
public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, IRule rule, IPing ping) {
initWithConfig(config, rule, ping, createLoadBalancerStatsFromConfig(config));
}
void initWithConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping, LoadBalancerStats stats) {
this.config = clientConfig;
String clientName = clientConfig.getClientName();
this.name = clientName;
int pingIntervalTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerPingInterval,
Integer.parseInt("30")));
int maxTotalPingTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerMaxTotalPingTime,
Integer.parseInt("2")));
setPingInterval(pingIntervalTime);
setMaxTotalPingTime(maxTotalPingTime);
// cross associate with each other
// i.e. Rule,Ping meet your container LB
// LB, these are your Ping and Rule guys ...
setRule(rule);
setPing(ping);
setLoadBalancerStats(stats);
rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
if (ping instanceof AbstractLoadBalancerPing) {
((AbstractLoadBalancerPing) ping).setLoadBalancer(this);
}
logger.info("Client: {} instantiated a LoadBalancer: {}", name, this);
boolean enablePrimeConnections = clientConfig.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.EnablePrimeConnections, DefaultClientConfigImpl.DEFAULT_ENABLE_PRIME_CONNECTIONS);
if (enablePrimeConnections) {
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(true);
PrimeConnections primeConnections = new PrimeConnections(
this.getName(), clientConfig);
this.setPrimeConnections(primeConnections);
}
init();
}
public void setRule(IRule rule) {
if (rule != null) {
this.rule = rule;
} else {
/* default rule */
this.rule = new RoundRobinRule();
}
if (this.rule.getLoadBalancer() != this) {
this.rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
}
}
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
}
}
核心屬性
allServerList:緩存了所有的服務實例數據
upServerList:緩存了能夠使用的服務實例數據。
rule:負載均衡算法組件,默認是RoundRobinRule
核心方法
setRule:這個方法是設置負載均衡算法的,並將當前這個ILoadBalancer對象設置給IRule,從這可以得出一個結論,IRule進行負載均衡的服務實例列表是通過ILoadBalancer獲取的,也就是 IRule 和 ILoadBalancer相互引用。setRule(rule)一般是在構造對象的時候會調用。
chooseServer:就是選擇一個服務實例,是委派給IRule的choose方法來實現服務實例的選擇。
BaseLoadBalancer這個實現類總體來說,已經實現了ILoadBalancer的功能的,所以這個已經基本滿足使用了。
說完BaseLoadBalancer這個實現類,接下來說一下DynamicServerListLoadBalancer實現類。DynamicServerListLoadBalancer繼承自BaseLoadBalancer,DynamicServerListLoadBalancer主要是對BaseLoadBalancer功能進行擴展。
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.class);
volatile ServerList<T> serverListImpl;
volatile ServerListFilter<T> filter;
protected final ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction updateAction = new ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction() {
@Override
public void doUpdate() {
updateListOfServers();
}
};
protected volatile ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater;
public DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping,
ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping);
this.serverListImpl = serverList;
this.filter = filter;
this.serverListUpdater = serverListUpdater;
if (filter instanceof AbstractServerListFilter) {
((AbstractServerListFilter) filter).setLoadBalancerStats(getLoadBalancerStats());
}
restOfInit(clientConfig);
}
@Override
public void setServersList(List lsrv) {
super.setServersList(lsrv);
List<T> serverList = (List<T>) lsrv;
Map<String, List<Server>> serversInZones = new HashMap<String, List<Server>>();
for (Server server : serverList) {
// make sure ServerStats is created to avoid creating them on hot
// path
getLoadBalancerStats().getSingleServerStat(server);
String zone = server.getZone();
if (zone != null) {
zone = zone.toLowerCase();
List<Server> servers = serversInZones.get(zone);
if (servers == null) {
servers = new ArrayList<Server>();
serversInZones.put(zone, servers);
}
servers.add(server);
}
}
setServerListForZones(serversInZones);
}
protected void setServerListForZones(
Map<String, List<Server>> zoneServersMap) {
LOGGER.debug("Setting server list for zones: {}", zoneServersMap);
getLoadBalancerStats().updateZoneServerMapping(zoneServersMap);
}
@VisibleForTesting
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
/**
* Update the AllServer list in the LoadBalancer if necessary and enabled
*
* @param ls
*/
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
}
成員變量
serverListImpl:上面說過,通過這個接口獲取服務列表
filter:起到過濾的作用,一般不care
updateAction:是個匿名內部類,實現了doUpdate方法,會調用updateListOfServers方法
serverListUpdater:上面說到過,默認就是唯一的實現類PollingServerListUpdater,也就是每個30s就會調用傳入的updateAction的doUpdate方法。
這不是巧了么,serverListUpdater的start方法需要一個updateAction,剛剛好成員變量有個updateAction的匿名內部類的實現,所以serverListUpdater的start方法傳入的updateAction的實現其實就是這個匿名內部類。
那麼哪裡調用了serverListUpdater的start方法傳入了updateAction呢?是在構造的時候調用的,具體的調用鏈路是調用 restOfInit -> enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature(),這裡就不貼源碼了
所以,其實DynamicServerListLoadBalancer在構造完成之後,默認每隔30s中,就會調用updateAction的匿名內部類的doUpdate方法,從而會調用updateListOfServers。所以我們來看一看 updateListOfServers 方法幹了什麼。
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
這個方法實現很簡單,就是通過調用 ServerList 的getUpdatedListOfServers獲取到一批服務實例數據,然後過濾一下,最後調用updateAllServerList方法,進入updateAllServerList方法。
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
其實很簡單,就是調用每個服務實例的setAlive方法,將isAliveFlag設置成true,然後調用setServersList。setServersList這個方法的主要作用是將服務實例更新到內部的緩存中,也就是上面提到的allServerList和upServerList,這裡就不貼源碼了。
其實分析完updateListOfServers方法之後,再結合上面源碼的分析,我們可以清楚的得出一個結論,那就是默認每隔30s都會重新通過ServerList組件獲取到服務實例數據,然後更新到BaseLoadBalancer緩存中,IRule的負載均衡所需的服務實例數據,就是這個內部緩存。
從DynamicServerListLoadBalancer的命名也可以看出,他相對於父類BaseLoadBalancer而言,提供了動態更新內部服務實例列表的功能。
為了便於大家記憶,我畫一張圖來描述這些組件的關係以及是如何運作的。
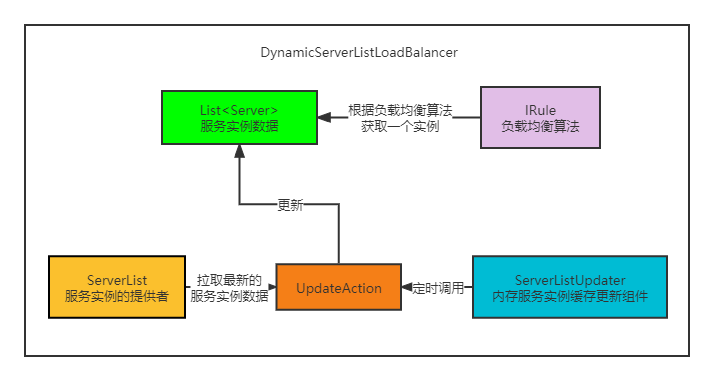
說完一些核心的組件,以及他們跟ILoadBalancer的關係之後,接下來就來分析一下,ILoadBalancer是在ribbon中是如何使用的。
8、AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient
ILoadBalancer是一個可以獲取到服務實例數據的組件,那麼服務實例跟什麼有關,那麼肯定是跟請求有關,所以在Ribbon中有這麼一個抽象類,AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient,這個是用來執行請求的,我們來看一下這個類的構造。
public AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient(ILoadBalancer lb) {
super(lb);
}
/**
* Delegate to {@link #initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig)}
* @param clientConfig
*/
public AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient(ILoadBalancer lb, IClientConfig clientConfig) {
super(lb, clientConfig);
}
通過上面可以看出,在構造的時候需要傳入一個ILoadBalancer。
AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient中有一個方法executeWithLoadBalancer,這個是用來執行傳入的請求,以負載均衡的方式。
public T executeWithLoadBalancer(final S request, final IClientConfig requestConfig) throws ClientException {
LoadBalancerCommand<T> command = buildLoadBalancerCommand(request, requestConfig);
try {
return command.submit(
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof ClientException) {
throw (ClientException) t;
} else {
throw new ClientException(e);
}
}
}
這個方法構建了一個LoadBalancerCommand,隨後調用了submit方法,傳入了一個匿名內部類,這個匿名內部類中有這麼一行代碼很重要。
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
這行代碼是根據給定的一個Server重構了URI,這是什麼意思呢?舉個例子,在OpenFeign那一篇文章我說過,會根據服務名拼接出類似//ServerA的地址,那時是沒有服務器的ip地址的,只有服務名,假設請求的地址是//ServerA/api/sayHello,那麼reconstructURIWithServer乾的一件事就是將ServerA服務名替換成真正的服務所在的機器的ip和端口,假設ServerA所在的一台機器(Server裏面封裝了某台機器的ip和端口)是192.168.1.101:8088,那麼重構後的地址就變成//192.168.1.101:8088/api/sayHello,這樣就能發送http請求到ServerA服務所對應的一台服務器了。
之後根據新的地址,調用這個類中的execute方法來執行請求,execute方法是個抽象方法,也就是交給子類實現,子類就可以通過實現這個方法,來發送http請求,實現rpc調用。
那麼這台Server是從獲取的呢?其實猜猜也知道,肯定是通過ILoadBalancer獲取的,因為submit方法比較長,這裡我直接貼出submit方法中核心的一部分代碼
Observable<T> o =
(server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
就是通過selectServer來選擇一個Server的,selectServer我就不翻源碼了,其實最終還是調用ILoadBalancer的方法chooseServer方法來獲取一個服務,之後就會調用上面的說的匿名內部類的方法,重構URI,然後再交由子類的execut方法來實現發送http請求。
所以,通過對AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient的executeWithLoadBalancer方法,我們可以知道,這個抽象類的主要作用就是通過負載均衡算法,找到一個合適的Server,然後將你傳入的請求路徑//ServerA/api/sayHello重新構建成類似//192.168.1.101:8088/api/sayHello這樣,之後調用子類實現的execut方法,來發送http請求,就是這麼簡單。到這裡其實Ribbon核心組件和執行原理我就已經說的差不多了,再來畫一張圖總結一下
二、SpringCloud中使用的核心組件的實現都有哪些
說完了Ribbon的一些核心組件和執行原理之後,我們再來看一下在SpringCloud環境下,這些組件到底是用的哪些實現,畢竟有寫時接口,有的是抽象類。
Ribbon的自動裝配類:RibbonAutoConfiguration,我拎出了核心的源碼
@Configuration
@RibbonClients
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
}
RibbonAutoConfiguration配置類上有個@RibbonClients註解,接下來講解一下這個註解的作用
@Import(RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar.class)
public @interface RibbonClients {
RibbonClient[] value() default {};
Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {};
}
看過我寫的OpenFeign的文章小夥伴肯定知道,要使用Feign,得需要使用@EnableFeignClients,@EnableFeignClients的作用可以掃描指定包路徑下的@FeignClient註解,也可以聲明配置類;同樣RibbonClients的作用也是可以聲明配置類,同樣也使用了@Import註解註解來實現的,RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar這個配置類的作用就是往spring容器中注入每個服務的Ribbon組件(@RibbonClient裏面可以聲明每個服務對應的配置)的配置類和默認配置類,將配置類封裝為RibbonClientSpecification注入到spring容器中,其實就跟@FeignClient註解聲明配置的作用是一樣的。
RibbonAutoConfiguration的主要作用就是注入了一堆RibbonClientSpecification,就是每個服務對應的配置類,然後聲明了SpringClientFactory這個bean,將配置類放入到裏面。
SpringClientFactory是不是感覺跟OpenFeign中的FeignContext很像,其實兩個的作用是一樣的,SpringClientFactory也繼承了NamedContextFactory,實現了配置隔離,同時也在構造方法中傳入了每個容器默認的配置類RibbonClientConfiguration。至於什麼是配置隔離,我在OpenFeign那篇文章說過,不清楚的小夥伴可以後台回復feign01即可獲得文章鏈接。
配置優先級問題
這裡我說一下在OpenFeign里沒仔細說的配置優先級的事情,因為有這麼多配置類,都可以在配置類中聲明對象,那麼到底使用哪個配置類聲明的對象呢。
優先級最高的是springboot啟動的時候的容器,因為這個容器是每個服務的容器的父容器,而在配置類聲明bean的時候,都有@ConditionalOnMissingBean註解,一旦父容器有這個bean,那麼子容器就不會初始化。
優先級第二高的是每個客戶端聲明的配置類,也就是通過@FeignClient和@RibbonClient的configuration屬性聲明的配置類
優先級第三高的是@EnableFeignClients和@RibbonClients註解中configuration屬性聲明的配置類
優先級最低的就是FeignContext和SpringClientFactory構造時傳入的配置類
至於優先級怎麼來的,其實是在NamedContextFactory中createContext方法中構建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext時按照配置的優先級一個一個傳進去的。
RibbonClientConfiguration提供的默認的bean
接下來我們看一下RibbonClientConfiguration都提供了哪些默認的bean
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() {
DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl();
config.loadProperties(this.name);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.GZipPayload, DEFAULT_GZIP_PAYLOAD);
return config;
}
配置類對應的bean,這裡設置了ConnectTimeout和ReadTimeout都是1s中。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, name);
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule();
rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return rule;
}
IRule,默認是ZoneAvoidanceRule,這個Rule帶有過濾的功能,過濾哪些不可用的分區的服務(這個過濾可以不用care),過濾成功之後,繼續採用線性輪詢的方式從過濾結果中選擇一個出來。至於這個propertiesFactory,可以不用管,這個是默認讀配置文件的中的配置,一般不設置,後面看到都不用care。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, name);
}
ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList();
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
默認是ConfigurationBasedServerList,也就是基於配置來提供服務實例列表。但是在SpringCloud環境中,這是不可能的,因為服務信息是在註冊中心,所以應該是服務註冊中心對應實現的,比如Nacos的實現NacosServerList,這裡我貼出NacosServerList的bean的聲明,在配置類NacosRibbonClientConfiguration中
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerList<?> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config,
NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosDiscoveryProperties) {
NacosServerList serverList = new NacosServerList(nacosDiscoveryProperties);
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
至於為什麼容器選擇NacosServerList而不是ConfigurationBasedServerList,主要是因為NacosRibbonClientConfiguration這個配置類是通過@RibbonClients導入的,也就是比SpringClientFactory導入的RibbonClientConfiguration配置類優先級高。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) {
return new PollingServerListUpdater(config);
}
ServerListUpdater,就是我們剖析的PollingServerListUpdater,默認30s更新一次BaseLoadBalancer內部服務的緩存。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
ILoadBalancer,默認是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer,構造的時候也傳入了上面聲明的的bean,ZoneAwareLoadBalancer這個類繼承了DynamicServerListLoadBalancer,所以這個類功能也符合我們剖析的源碼,至於ZoneAwareLoadBalancer多餘的特性,也不用care。
到這裡,Ribbon在SpringCloud的配置我們就講完了,主要就是聲明了很多核心組件的bean,最後都設置到ZoneAwareLoadBalancer中。但是,AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient這個對象的聲明我們並沒有在配置類中找到,主要是因為這個對象是OpenFeign整合Ribbon的一個入口,至於是如何整合的,這個坑就留給下篇文章吧。
那麼在springcloud中,上圖就可以加上註冊中心。

三、總結
本文剖析了Ribbon這個負載均衡組件中的一些核心組件的源碼,並且將這些組件之間的關係一一描述清楚,同時也剖析了在發送請求的時候是如何通過ILoadBalancer獲取到一個服務實例,重構URI的過程。希望本篇文章能夠讓你知道Ribbon是如何工作的。至於OpenFeign整合Ribbon,詳見文章 【SpringCloud原理】OpenFeign原來是這麼基於Ribbon來實現負載均衡的。
往期熱門文章推薦
掃碼或者搜索關注公眾號 三友的java日記 ,及時乾貨不錯過,公眾號致力於通過畫圖加上通俗易懂的語言講解技術,讓技術更加容易學習。



