freeswitch APR-UTIL庫線程池實現分析

概述
freeswitch的核心源代碼是基於apr庫開發的,在不同的系統上有很好的移植性。
APR庫在之前的文章中已經介紹過了,APR-UTIL庫是和APR並列的工具庫,它們都是由APACHE開源出來的跨平台可移植庫,不同點在於庫中實現的功能接口有區別。
在應用的開發過程中,多線程並發是提高效率的常用方案,但是多線程管理並不好做。
在很多大型應用中,都會引入線程池的框架。線程池是一個線程集合,有統一的管理,當有一個新的任務下發,線程池管理會按照一定的策略將任務分配給空閑的線程。當任務積壓較多時,線程池會創建新的線程來加快處理效率。
APR-UTIL庫中就提供了一套線程池接口。
我對幾個問題比較好奇,線程池如何管理?線程池什麼情況要增加線程?什麼情況會減少線程?線程池線程數目如何設置才有最優的效率?
下面我們對apr-util庫的線程池實現做一個介紹。
環境
centos:CentOS release 7.0 (Final)或以上版本
APR-UTIL:1.6.1
GCC:4.8.5
本來要使用freeswitch1.8.7中帶的apr-util庫源代碼來梳理,但是很遺憾的是這個apr-util庫版本是1.2.8,裏面沒有apr_thread_pool接口。。。所以從APR官網上下載了最新的1.6.1版本來做分析。
數據結構
apr線程池源文件:
apr-util-1.6.1\include\apr_thread_pool.h
apr-util-1.6.1\misc\apr_thread_pool.c
號碼池數據結構定義在apr_thread_pool.c中
typedef struct apr_thread_pool_task
{
APR_RING_ENTRY(apr_thread_pool_task) link;
apr_thread_start_t func;
void *param;
void *owner;
union
{
apr_byte_t priority;
apr_time_t time;
} dispatch;
} apr_thread_pool_task_t;
APR_RING_HEAD(apr_thread_pool_tasks, apr_thread_pool_task);
struct apr_thread_list_elt
{
APR_RING_ENTRY(apr_thread_list_elt) link;
apr_thread_t *thd;
volatile void *current_owner;
volatile enum { TH_RUN, TH_STOP, TH_PROBATION } state;
};
APR_RING_HEAD(apr_thread_list, apr_thread_list_elt);
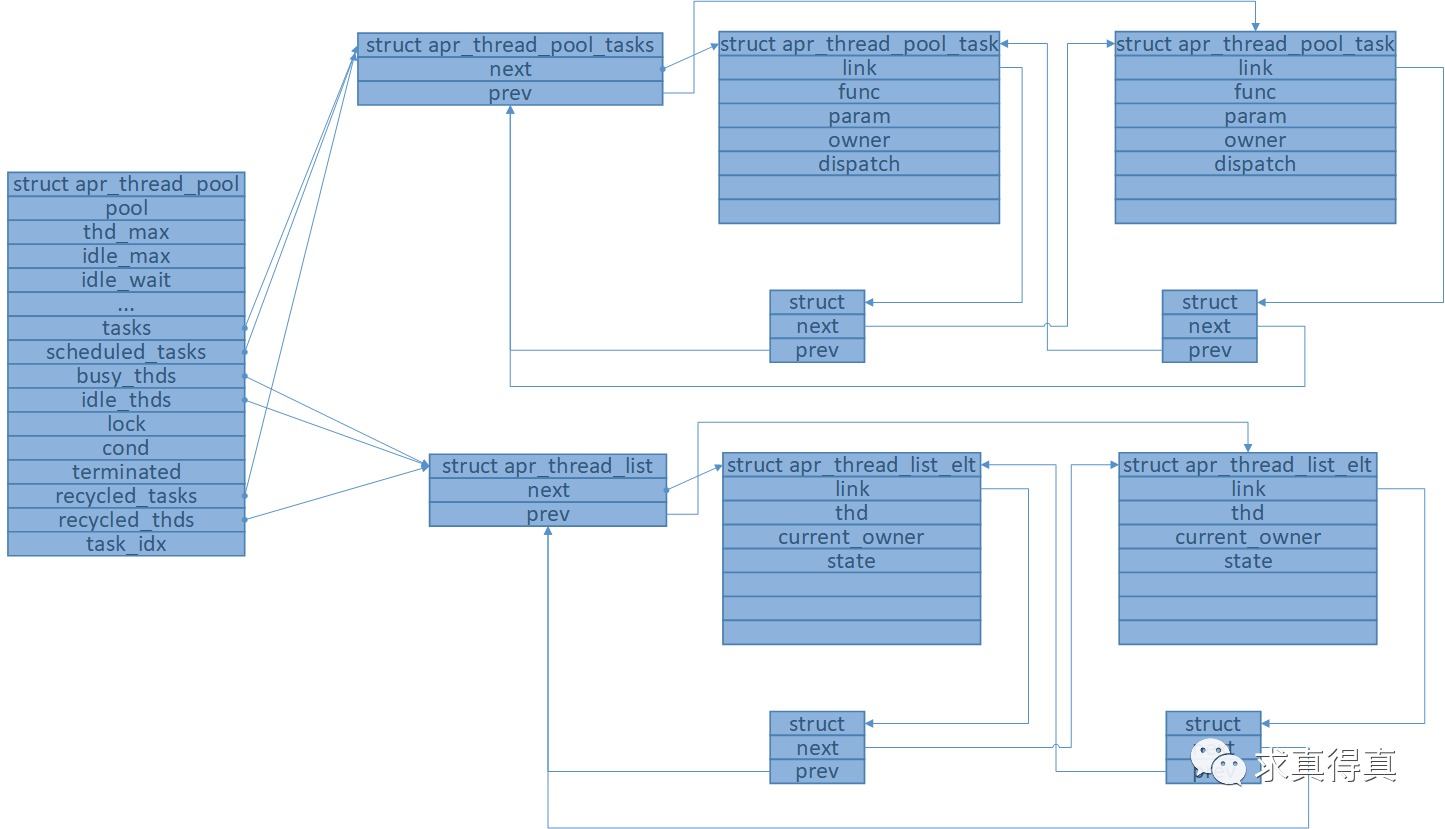
struct apr_thread_pool
{
apr_pool_t *pool;
volatile apr_size_t thd_max;
volatile apr_size_t idle_max;
volatile apr_interval_time_t idle_wait;
volatile apr_size_t thd_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t idle_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t task_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t scheduled_task_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t threshold;
volatile apr_size_t tasks_run;
volatile apr_size_t tasks_high;
volatile apr_size_t thd_high;
volatile apr_size_t thd_timed_out;
struct apr_thread_pool_tasks *tasks;
struct apr_thread_pool_tasks *scheduled_tasks;
struct apr_thread_list *busy_thds;
struct apr_thread_list *idle_thds;
apr_thread_mutex_t *lock;
apr_thread_cond_t *cond;
volatile int terminated;
struct apr_thread_pool_tasks *recycled_tasks;
struct apr_thread_list *recycled_thds;
apr_thread_pool_task_t *task_idx[TASK_PRIORITY_SEGS];
};
線程池內存模型總圖,線程池,任務隊列,線程隊列。
常用函數
常用函數接口
apr_thread_pool_create //Create a thread pool
apr_thread_pool_destroy //Destroy the thread pool and stop all the threads
apr_thread_pool_push //Schedule a task to the bottom of the tasks of same priority.
apr_thread_pool_schedule //Schedule a task to be run after a delay
apr_thread_pool_top //Schedule a task to the top of the tasks of same priority.
apr_thread_pool_tasks_cancel //Cancel tasks submitted by the owner. If there is any task from the owner that is currently running, the function will spin until the task finished.
apr_thread_pool_tasks_count //Get the current number of tasks waiting in the queue
apr_thread_pool_scheduled_tasks_count //Get the current number of scheduled tasks waiting in the queue
apr_thread_pool_threads_count //Get the current number of threads
apr_thread_pool_busy_count //Get the current number of busy threads
apr_thread_pool_idle_count //Get the current number of idle threads
apr_thread_pool_idle_max_set //Access function for the maximum number of idle threads. Number of current idle threads will be reduced to the new limit.
apr_thread_pool_tasks_run_count //Get number of tasks that have run
apr_thread_pool_tasks_high_count //Get high water mark of the number of tasks waiting to run
apr_thread_pool_threads_high_count //Get high water mark of the number of threads
apr_thread_pool_threads_idle_timeout_count //Get the number of idle threads that were destroyed after timing out
apr_thread_pool_idle_max_get //Access function for the maximum number of idle threads
apr_thread_pool_thread_max_set //Access function for the maximum number of threads.
apr_thread_pool_idle_wait_set //Access function for the maximum wait time (in microseconds) of an idling thread that exceeds the maximum number of idling threads. A non-zero value allows for the reaping of idling threads to shrink over time. Which helps reduce thrashing.
apr_thread_pool_idle_wait_get //Access function for the maximum wait time (in microseconds) of an idling thread that exceeds the maximum number of idling threads
apr_thread_pool_thread_max_get //Access function for the maximum number of threads
apr_thread_pool_threshold_set //Access function for the threshold of tasks in queue to trigger a new thread.
apr_thread_pool_threshold_get //Access function for the threshold of tasks in queue to trigger a new thread.
apr_thread_pool_task_owner_get //Get owner of the task currently been executed by the thread.
apr_thread_pool_create創建
APU_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_thread_pool_create(apr_thread_pool_t ** me,
apr_size_t init_threads,
apr_size_t max_threads,
apr_pool_t * pool)
接口邏輯:
- 分配一塊大小為apr_thread_pool_t的內存tp。
- 在傳入的內存池pool中申請一個新的內存池tp->pool。
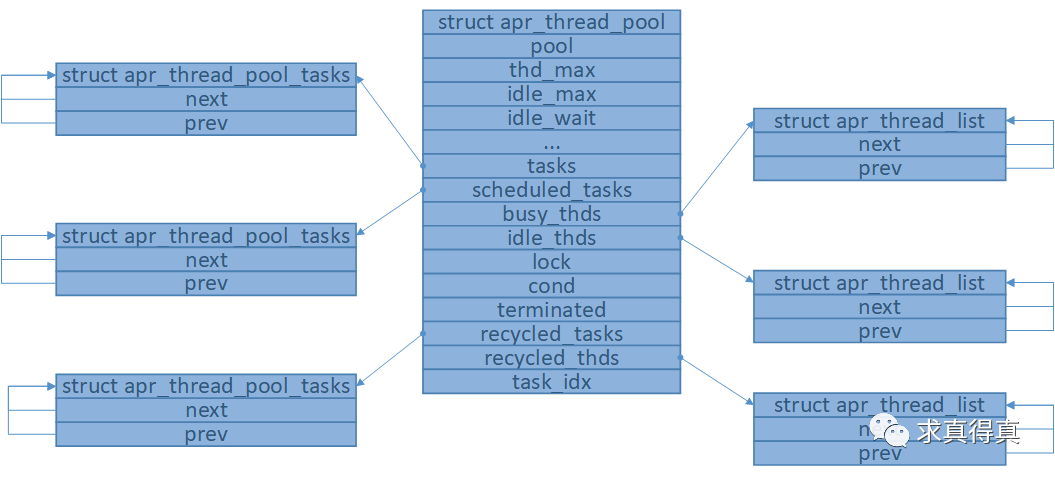
- 初始化線程池數據。
a) 線程池數據初始化。
b) 創建線程互斥鎖me->lock。
c) 創建條件變量me->cond。
d) 在內存池pool上分配一塊大小為「apr_thread_pool_tasks「的內存賦值給me->tasks。
e) 在內存池pool上分配一塊大小為「apr_thread_pool_tasks「的內存賦值給me->scheduled_tasks。
f) 在內存池pool上分配一塊大小為「apr_thread_pool_tasks「的內存賦值給me->recycled_tasks。
g) 在內存池pool上分配一塊大小為「apr_thread_list「的內存賦值給me->busy_thds。
h) 在內存池pool上分配一塊大小為「apr_thread_list「的內存賦值給me->idle_thds。
i) 在內存池pool上分配一塊大小為「apr_thread_list「的內存賦值給me->recycled_thds。
j) 線程池數據初始化。
- 在內存池tp->pool中註冊清理回調函數。
- 循環創建初始工作線程,並加入線程池的管理。工作線程的邏輯見「thread_pool_func工作線程」。
- 返回創建結果。
線程池初始化成功後,內存模型如圖(工作線程啟動未完成時)
thread_pool_func工作線程
static void *APR_THREAD_FUNC thread_pool_func(apr_thread_t * t, void *param)
接口邏輯:
- 加鎖me->lock
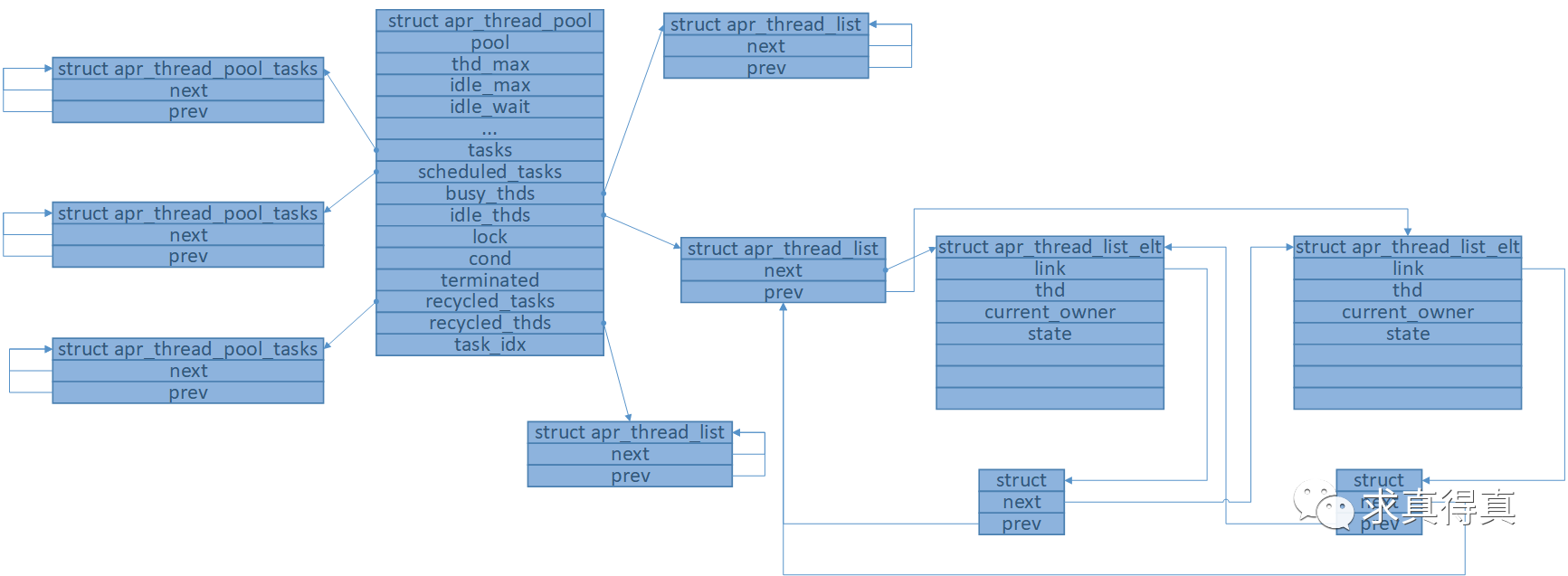
- 判斷me->recycled_thds鏈表為空?為空則創建新的apr_thread_list_elt節點elt,不為空則獲取recycled_thds中首節點elt並從recycled_thds中移除該節點。
- 循環處理。
a) 將elt節點加入me->busy_thds鏈表。
b) 獲取一個新任務task。TODO
c) 循環處理。解鎖me->lock。調用任務回調task->func。加鎖me->lock。將task加入me->recycled_tasks鏈表。獲取新任務task。線程狀態置為TH_STOP時跳出循環。獲取任務為空跳出循環。
d) 線程從busy到stop狀態,將elt加入me->recycled_thds鏈表尾部,解鎖me->lock,退出線程。
e) 線程從busy到idle狀態,將elt節點從me->busy_thds鏈表中移除,將elt加入me->idle_thds鏈表尾部。
f) 檢查是否有定時任務並獲取任務執行等待時間。
g) 檢查當前空閑線程數是否大於最大空閑數,獲取空閑等待時間me->idle_wait,並設置當前線程狀態為TH_PROBATION,下一輪循環中進入stop處理流程。
h) 線程阻塞,等待條件變量me->cond的通知或超時。
- 線程數me->thd_cnt自減。
- 解鎖me->lock。
- 退出線程。
線程池初始化成功後,內存模型如圖(工作線程啟動完成時)
apr_thread_pool_push添加任務
APU_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_thread_pool_push(apr_thread_pool_t *me,
apr_thread_start_t func,
void *param,
apr_byte_t priority,
void *owner)
接口邏輯:
- 加鎖me->lock。
- 檢查me->recycled_tasks是否為空,為空則新建任務節點t,不為空則從me->recycled_tasks獲取任務節點t。
- 任務節點t數據初始化。
- 計算任務優先級,根據優先級設置me->task_idx[seg]和me->tasks。
- 當前工作線程數為0時,或者空閑線程數為0並且當前線程數未達到最大並且當前任務數超過閾值等條件,動態創建新的工作線程。
- 對條件變量me->cond發通知。
- 解鎖me->lock。
線程池添加任務後的內存模型圖。

apr_thread_pool_tasks_cancel取消任務
APU_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_thread_pool_tasks_cancel(apr_thread_pool_t *me,
void *owner)
接口邏輯:
- 加鎖me->lock。
- 如果當前任務數大於0,則清空owner的所有任務。
- 如果定時任務數大於0,則清空owner的所有定時任務。
- 解鎖me->lock。
- 等待線程退出。
總結
APR線程池的幾個關注點。
線程從busy到stop狀態時,沒有將elt節點從me->busy_thds鏈表中刪除?
APR線程池沒有內置的管理線程,根據當前線程數和任務數進行動態的調整,而是通過任務閾值、空閑線程最大值和超時時間等設置來控制線程數的增減,這一點和我開始想的不一樣。
空空如常
求真得真


