【數據結構與算法】非比較排序(計數排序、桶排序、基數排序)
計數排序
概念
一句話︰用輔助數組對數組中出現的數字計數,元素轉下標,下標轉元素
假設元素均大於等於0,依次掃描原數組,將元素值k記錄在輔助數組的k位上
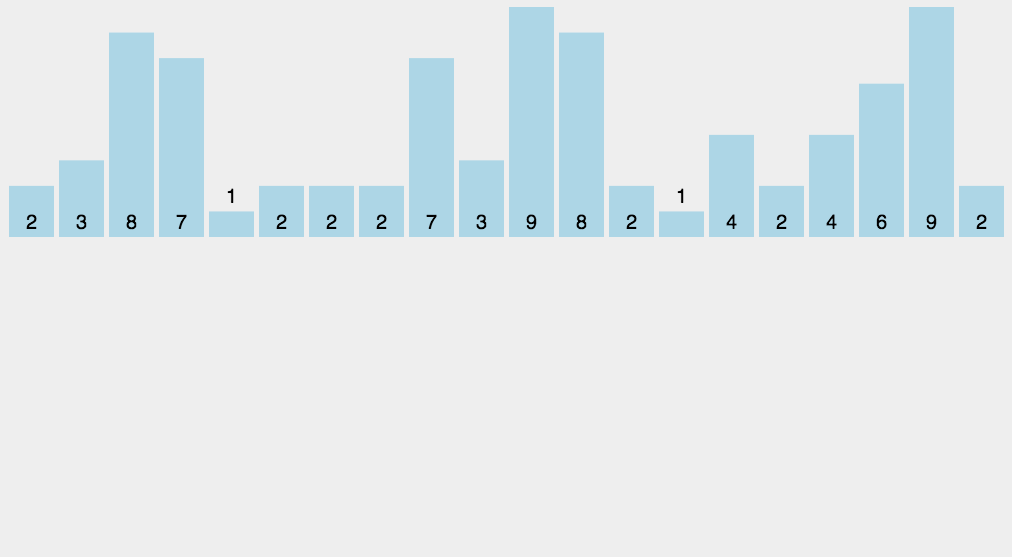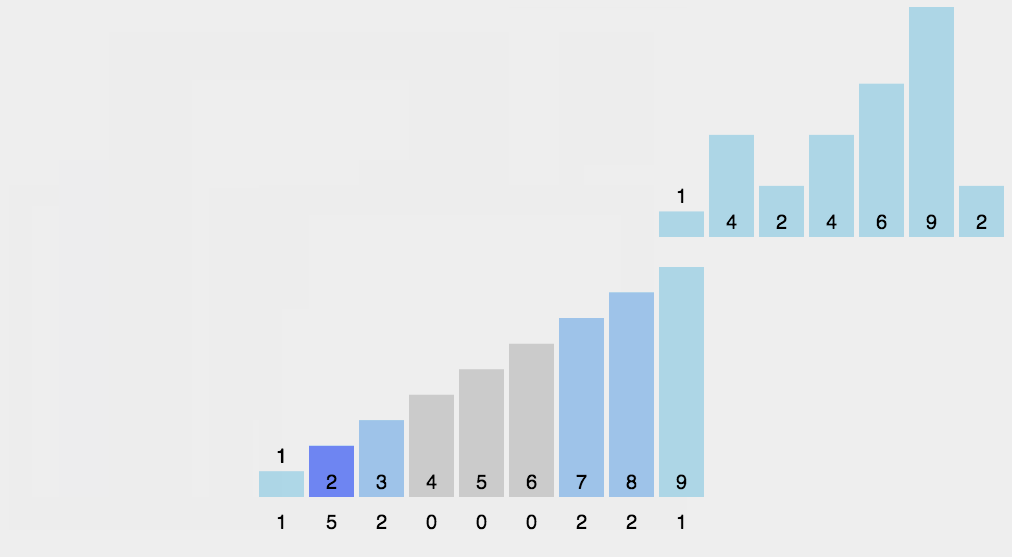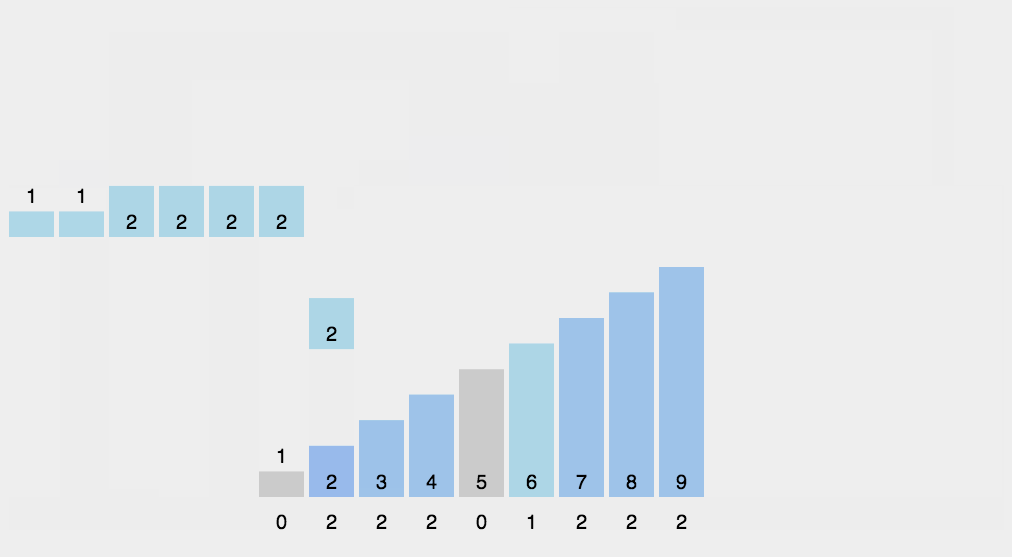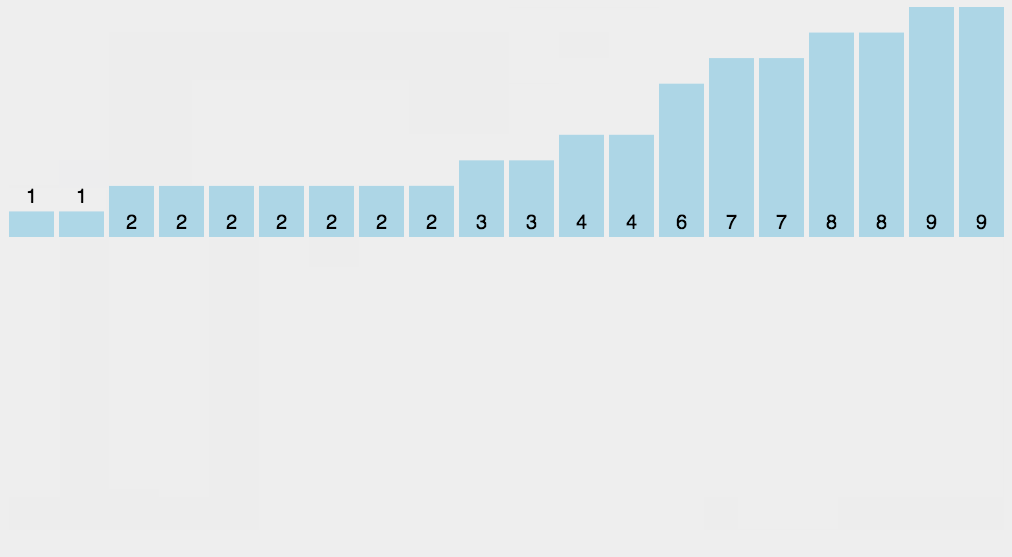
思路:開闢新的空間,空間大小為max(source)掃描source,將value作為輔助空間的下標,用輔助空間的改位置元素記錄value的個數。如:9 7 5 3 1 ,helper=arr(10)。一次掃描,value為9,將helper[9]++,value為7,將helper[7]++……
如此這般之後,我們遍歷helper,如果該位(index)的值為0,說明index不曾在source中出現
如果該位(index)的值為1,說明index在source中出現了1次,為2自然是出現了2次
遍歷helper就能將source修復為升序排列
- 時間複雜度: 掃描一次source,掃描一次helper,複雜度為O(N+k)
- 空間複雜度:輔助空間k,k=maxOf(source)
- 非原址排序
- 穩定性:相同元素不會出現交叉,非原址都是拷來拷去
- 如果要優化一下空間,可以求minOf(source),helper的長度位max-min+1,這樣能短點
- 計數有缺陷,數據較為密集或範圍較小時,適用。
代碼實現
public static void countSort(int[] source) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < source.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, source[i]);
}
int[] helper = new int[max + 1];
for (int e : source) {
helper[e]++;
}
int current = 0; //數據回填的下標
for (int i = 1; i < helper.length; i++) {
while (helper[i] > 0) {
source[current++] = i;
helper[i]--;
}
}
}
桶排序
概念

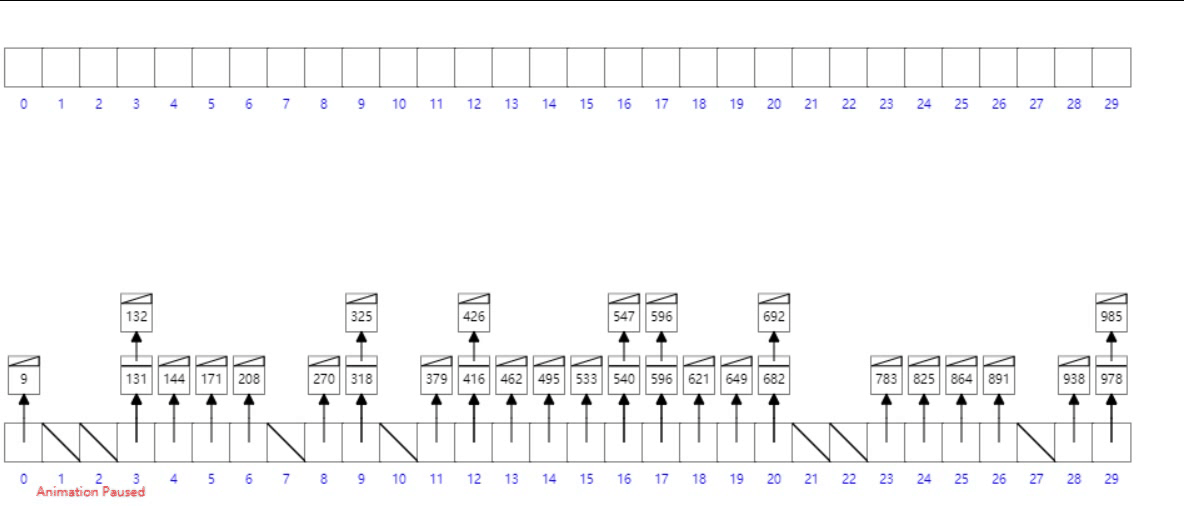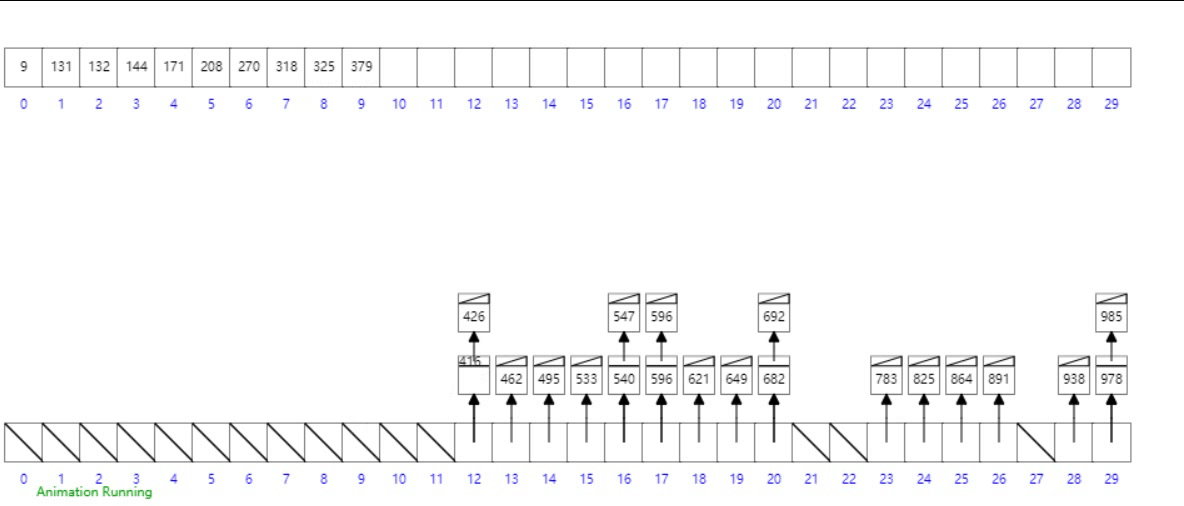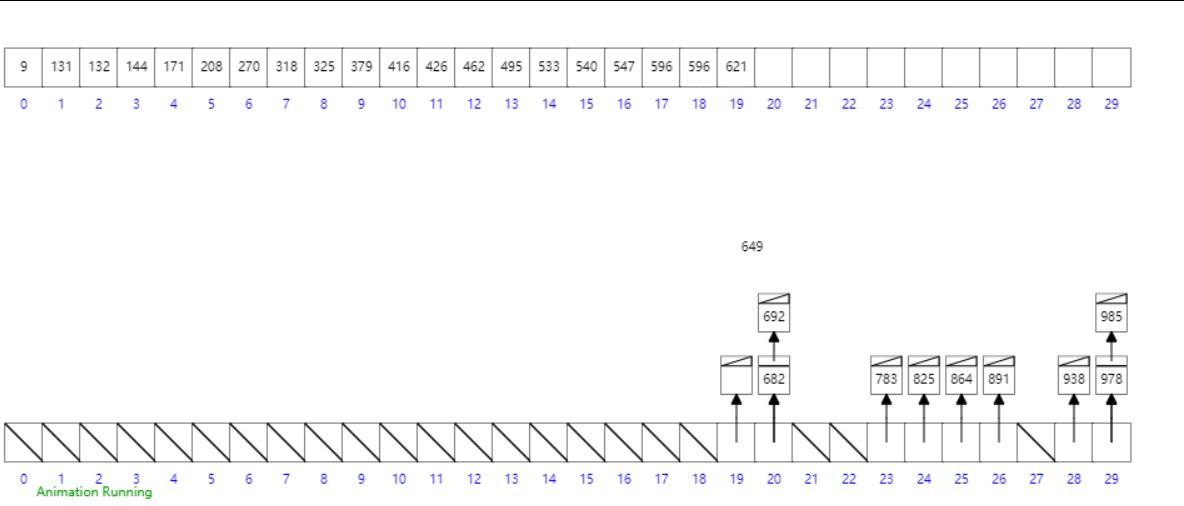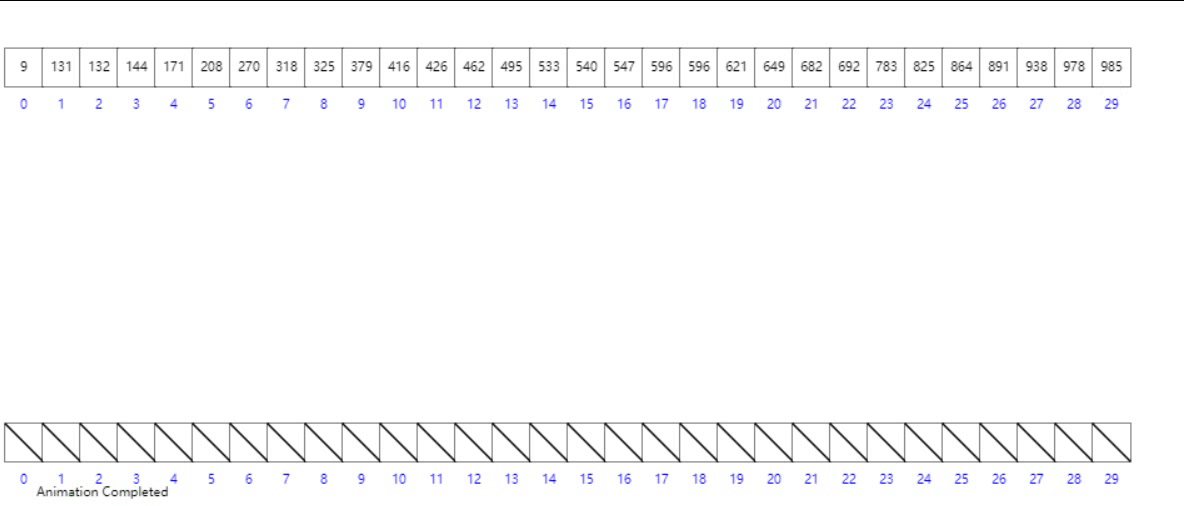
工作的原理是將數組分到有限數量的桶子里。每個桶子再個別排序(有可能再使用別的排序算法或是以遞歸方式繼續使用桶排序進行排序)。
- 設置一個定量的數組當作空桶;
- 遍歷輸入數據,並且把數據一個一個放到對應的桶里去;
- 對每個不是空的桶進行排序;
- 從不是空的桶里把排好序的數據拼接起來。
- 最後按照數組下標遍歷鏈表即可
桶排序是鴿巢排序的一種歸納結果。當要被排序的數組內的數值是均勻分配的時候,桶排序使用線性時間(Θ(n))。
但桶排序並不是 比較排序,他不受到 O(n log n) 下限的影響。
- 時間複雜度: O(N+C),其中C=N*(logN-logM)
- 空間複雜度:N+M,M為桶的個數
- 非原址排序
- 穩定性:穩定
桶排序假設數據會均勻入桶,在這個前提下,桶排序很快!
代碼實現
鏈表定義
class LinkedNode{
LinkedNode next;
int value;
LinkedNode(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
桶排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2,3,6,5,2,4,8,6};
sort(arr);
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// 根據桶的個數來確定hash函數,這份代碼適合桶的個數等於數組長度
private static int hash(int element, int max, int length) { //哈希規則
return (element * length) / (max + 1);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
LinkedNode[] bucket = new LinkedNode[length]; // 桶的個數=length
int max = maxOf(arr);// 求max
// 入桶
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int value = arr[i];//掃描每個元素
int hash = hash( arr[i], max, length ); // 桶的下標
if (bucket[hash] == null) {
bucket[hash] = new LinkedNode( value ); // 初始化鏈表表頭
} else {
insertInto( value, bucket[hash], bucket, hash ); // 插入鏈表
}
}
int k = 0; // 記錄數組下標
//出桶,回填arr
for (LinkedNode node : bucket) {
if (node != null) {
while (node != null) {
arr[k++] = node.value;
node = node.next;
}
}
}
}
private static int maxOf(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int num: arr){
max = Math.max(max,num);
}
return max;
}
private static void insertInto(int value, LinkedNode head, LinkedNode[] bucket, int hash) {
LinkedNode newNode = new LinkedNode( value );
//小於頭節點,放在頭上
if (value <= head.value) {
newNode.next = head;
// 替換頭節點
bucket[hash] = newNode;
return;
}
/*往後找第一個比當前值大的節點,放在這個節點的前面*/
LinkedNode p = head;
LinkedNode pre = p;
while (p != null && value > p.value) {
pre = p;
p = p.next;
}
if (p == null) { // 跑到末尾了
pre.next = newNode;
} else { // 插入pre和p之間
pre.next = newNode;
newNode.next = p;
}
}
基數排序
概念

思路:是一種特殊的桶排序
初始化0-9號十個桶,
按個位數字,將關鍵字入桶,入完後,依次遍歷10個桶,按檢出順序回填到數組中,如
321 322 331 500 423 476 926
0:500
1:321 331
2:322
3:423
4:無
5:無
6:476 926
檢出後數組序列為: 500 321 331 423 476 926,然後取十位數字重複過程一,得到
0:500
1:無
2:321 423 926
3:331
4:無
5:無
7:476
檢出後數組序列為: 500 321 423 926 331 476,然後取百位數字重複過程一,得到
0:無
1:無
2:無
3:321 331
4:423 476
5:500
9:926
檢出後數組序列為: 321 331 423 476 500 926,已然有序
但是我們應該繼續入桶,不過因為再高位全部是0了,這些元素會按順序全部進入0號桶,這時0號桶的size==數組的size,這時結束標誌
最後再回填到數組,數組就是升序排列的了
代碼實現
法一:ArrayList實現二維數組(形象表示桶)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 6, 3, 2, 5, 32, 42, 2, 5, 4, 7, 9, 3};
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// 10個桶,每個桶裝的數個數不定,適合用數組加ArrayList
private static ArrayList[] bucket = new ArrayList[10];
// 初始化桶
static {
for (int i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
bucket[i] = new ArrayList();
}
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
int d = 1; //入桶依據的位初始化為1
int dNum = maxbits(arr, begin, end); //獲取最大數字的位數
while (d <= dNum) { //做dNum次入桶出桶操作
radixSort(arr, begin, end, d++); //依據第二個參數d入桶和出桶
}
}
private static void radixSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int d) {
//全部入桶
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
putInBucket(arr[i], getDigitOn(arr[i], d)); //把每個數字的第d位入桶
}
//每個桶中的元素依次壓入原數組
int k = 0; //k是原數組下標
for (int j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) {// 每個桶
for (Object m : bucket[j]) {
arr[k++] = (Integer) m;
}
}
clearAll(); // 記得清空桶
}
private static int getDigitOn(int num, int d) { //獲取num的第d位的數字
return ((num / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10);
}
private static void putInBucket(int data, int digitOn) { //入桶
bucket[digitOn].add(data);
}
private static void clearAll() { //對每個桶調用clear方法進行清空
for (ArrayList b : bucket) {
b.clear();
}
}
private static int maxbits(int[] arr, int begin, int end) { //獲取數組中的最大元素的位數
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int dNum = 0;
while (max != 0) { //獲取最大值的位數
dNum++;
max /= 10;
}
return dNum;
}
法二:前綴和數組模擬
- 首先按照數組元素的個位數組將其入桶
- 其次構造前綴和數組
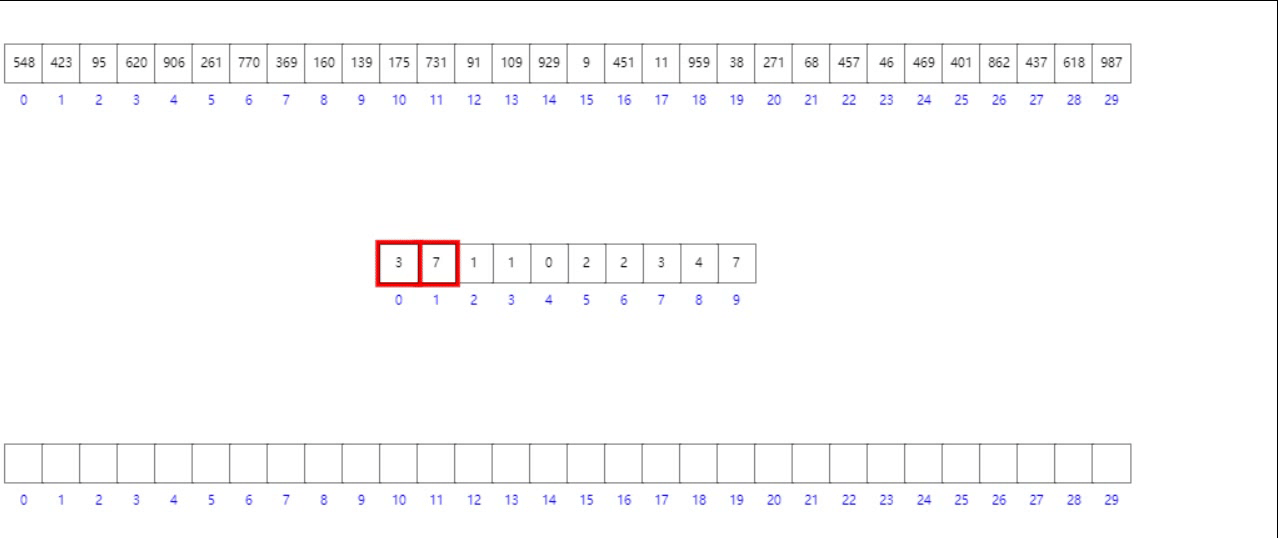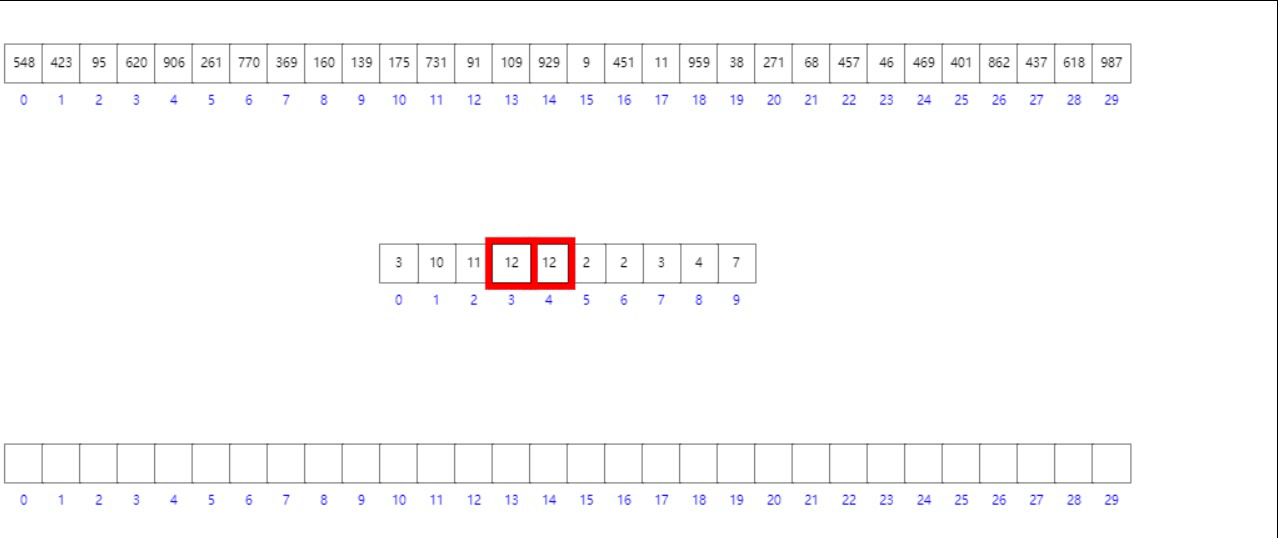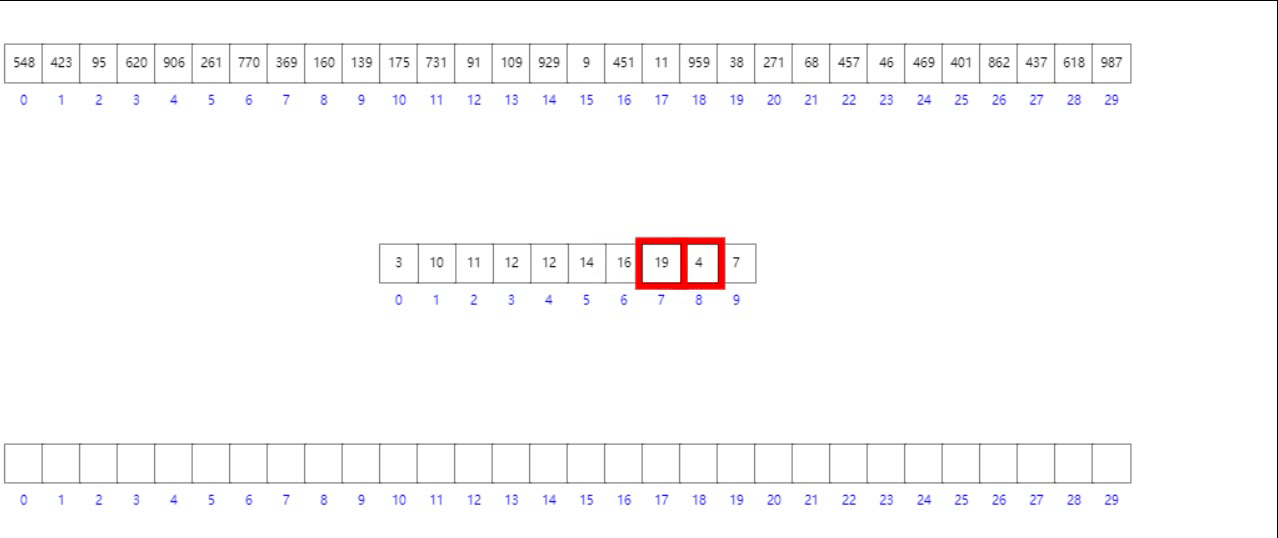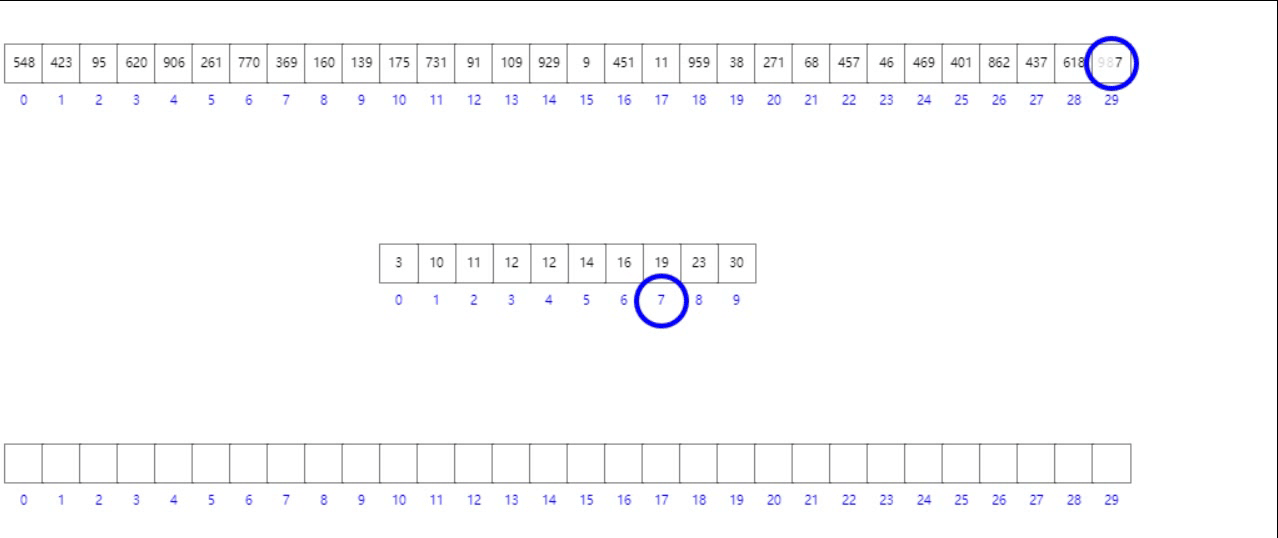
- 逆向遍歷原數組,根據個位數字找到其在目標有序數組中的位置
- 循環最大數的位數次,模擬了入桶出桶過程
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, maxbits(arr));
}
public static int maxbits(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int res = 0;
while (max != 0) {
res++;
max /= 10;
}
return res;
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int digit) {
final int radix = 10;
int i = 0, j = 0;
int[] bucket = new int[end - begin + 1];
for (int d = 1; d <= digit; d++) {
int[] count = new int[radix];
for (i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
count[j]++;
}
for (i = 1; i < radix; i++) { //獲得前綴和數組
count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1];
}
for (i = end; i >= begin; i--) { //倒敘遍歷原數組
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
bucket[count[j] - 1] = arr[i];
count[j]--;
}
for (i = begin, j = 0; i <= end; i++, j++) { //輔助數組拷貝回原數組
arr[i] = bucket[j];
}
}
}
public static int getDigit(int x, int d) { //獲取數字x的第d位數字
return ((x / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10);
}
-
時間複雜度O(kN)
假設最大的數有k位,就要進行k次入桶和回填,每次入桶和回填是線性的,所以整體複雜度為kN,
其中k為最大數的10進制位數 -
空間複雜度O(N+k)
桶是10個,10個桶裏面存n個元素,這些空間都是額外開闢的,所以額外的空間是N+k,k是進制 -
非原址排序
-
穩定性:穩定
假設有相等的元素,它們會次第入桶,次第回數組,不會交叉,所以是穩定的


