狀態模式-將狀態和行為封裝成對象
公號:碼農充電站pro
主頁://codeshellme.github.io
本篇文章來介紹狀態模式(State Design Pattern),狀態模式常用來實現狀態機,狀態機常用在遊戲開發等領域。
1,狀態模式
狀態模式的定義為:允許對象在內部狀態改變時,改變它的行為,對象看起來好像改變了它的類。
狀態模式將狀態和行為封裝成對象,不同的對象有着不同的行為。對象的狀態會因某個行為的發生而改變,對象的狀態一旦改變,那麼對象的行為也會發生改變。
對象的狀態和行為,可以用下面這個圖來解釋。假如一個事物有三種狀態 1,2,3,狀態之間的轉換關係如下:
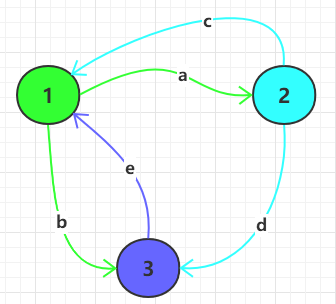
在上面的狀態轉換圖中,每種狀態對應着不同的行為:
- 狀態 1:有兩種行為
a和b- 狀態 1 經過
a行為可轉換到狀態 2 - 狀態 1 經過
b行為可轉換到狀態 3
- 狀態 1 經過
- 狀態 2:有兩種行為
c和d- 狀態 2 經過
c行為可轉換到狀態 1 - 狀態 2 經過
d行為可轉換到狀態 3
- 狀態 2 經過
- 狀態 3:有一種行為
e- 狀態 3 經過
e行為可轉換到狀態 1
- 狀態 3 經過
狀態模式的類圖如下:
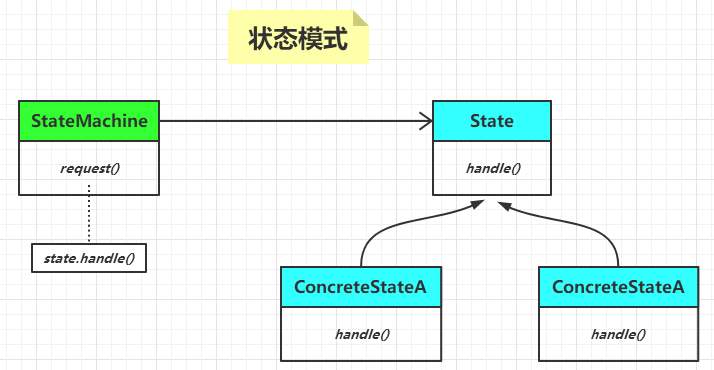
State 接口定義了狀態可能擁有的所有行為,每個具體的狀態都實現了這個接口,這樣就使得狀態之間可以互相替換。
每個具體狀態對 State 接口中的每個行為的實現是不一樣的,這就相當於每個具體狀態的行為是不一樣的。
StateMachine 是一個狀態機,它擁有着一個狀態對象,這個狀態對象會不斷的改變。
2,遊戲需求
假設我們要為一款遊戲中的角色編寫狀態轉換的程序,並且遊戲角色有積分:
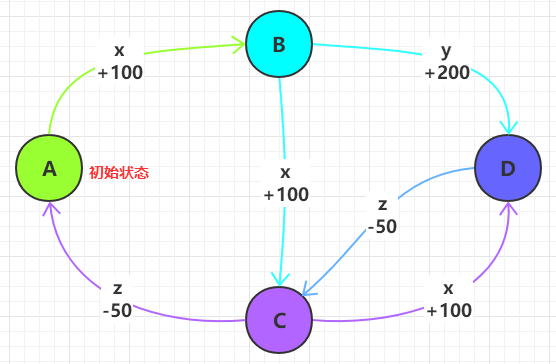
該遊戲中的角色共有 4 種狀態 A,B,C,D,共有 3 種操作 x,y,z:
- 狀態 A:只能進行 x 操作,轉化到狀態 B
- 狀態 A 為初始狀態
- 狀態 B:有兩種操作:
- x 操作:轉化到狀態 C
- y 操作:轉化到狀態 D
- 狀態 C:有兩種操作
- x 操作:轉化到狀態 D
- z 操作:轉化到狀態 A
- 狀態 D:只能進行 z 操作,轉化到狀態 C
積分變化:
- 操作 x 會使角色增加
100積分 - 操作 y 會使角色增加
200積分 - 操作 z 會使角色減少
50積分
3,編寫代碼
下面我們使用狀態模式來編寫角色的狀態轉換程序。
首先根據狀態模式的類圖,我們需要有一個 State 接口,該接口包含角色所有的操作,並且包含一個狀態機的引用。
這裡我將 State 作為一個抽象類,每個操作的默認實現是 do nothing,每個具體狀態可以根據自己的需要進行覆蓋。
代碼如下:
abstract class State {
protected String stateName;
protected RoleStateMachine machine;
void x() {
// do nothing
}
void y() {
// do nothing
}
void z() {
// do nothing
}
// 獲取當前狀態名
public String getStateName() {
return stateName;
}
}
接下來編寫角色狀態機類,代碼中也都寫了注釋:
class RoleStateMachine {
private State currentState; // 當前狀態
private int score; // 積分
public RoleStateMachine() {
this.score = 0; // 初始積分為 0
// 初始狀態為 A
this.currentState = new StateA(this);
}
// 當發生某個操作時需要轉化到相應的狀態
// 用該方法進行設置
public void setCurrentState(State state) {
currentState = state;
}
// 獲取當前狀態
public String getCurrentState() {
return currentState.getStateName();
}
// 獲取積分
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
// 增加積分
public void addScore(int score) {
this.score += score;
}
// 減少積分
public void delScore(int score) {
this.score -= score;
}
// 狀態機中也包含狀態中的所有操作
// 每個操作都委託給當前狀態的相應操作來完成
public void x() {
currentState.x();
}
public void y() {
currentState.y();
}
public void z() {
currentState.z();
}
}
下面編寫 4 個狀態類,每個狀態類都繼承 State 接口,並且每個狀態類中要持有一個狀態機的引用,由構造函數引入:
class StateA extends State {
public StateA(RoleStateMachine machine) {
this.machine = machine;
this.stateName = "StateA";
}
public void x() {
machine.addScore(100);
machine.setCurrentState(new StateB(machine));
}
}
class StateB extends State {
public StateB(RoleStateMachine machine) {
this.machine = machine;
this.stateName = "StateB";
}
public void x() {
machine.addScore(100);
machine.setCurrentState(new StateC(machine));
}
public void y() {
machine.addScore(200);
machine.setCurrentState(new StateD(machine));
}
}
class StateC extends State {
public StateC(RoleStateMachine machine) {
this.machine = machine;
this.stateName = "StateC";
}
public void x() {
machine.addScore(100);
machine.setCurrentState(new StateD(machine));
}
public void z() {
machine.delScore(50);
machine.setCurrentState(new StateA(machine));
}
}
class StateD extends State {
public StateD(RoleStateMachine machine) {
this.machine = machine;
this.stateName = "StateD";
}
public void z() {
machine.delScore(50);
machine.setCurrentState(new StateC(machine));
}
}
4,測試代碼
下面來測試代碼:
RoleStateMachine role = new RoleStateMachine();
// 初始狀態為 StateA,積分為 0
assert role.getCurrentState().equals("StateA");
assert role.getScore() == 0;
role.y(); // 在狀態 A 進行 y 操作
// 在狀態 A 時,沒有 y 操作
// 所以如果進行 y 操作,狀態和積分都保持不變
assert role.getCurrentState().equals("StateA");
assert role.getScore() == 0;
role.x(); // 在狀態 A 進行 x 操作
assert role.getCurrentState().equals("StateB");
assert role.getScore() == 100;
role.y(); // 在狀態 B,進行 y 操作
assert role.getCurrentState().equals("StateD");
assert role.getScore() == 300;
role.z(); // 在狀態 D,進行 z 操作
assert role.getCurrentState().equals("StateC");
assert role.getScore() == 250;
role.z(); // 在狀態 C,進行 z 操作
assert role.getCurrentState().equals("StateA");
assert role.getScore() == 200;
System.out.println("Test OK.");
注意,使用 Java assert 時,記得用 -ea 參數打開斷言功能。
我將完整的代碼放在了這裡,供大家參考。
5,總結
狀態模式將狀態和行為封裝成對象,不同的狀態有着不同的行為。這種設計使得處理狀態轉換這一類的邏輯變得非常有條理,而且不易出錯。
(本節完。)
推薦閱讀:
歡迎關注作者公眾號,獲取更多技術乾貨。



