LeetCode刷題總結-數組篇(下)
- 2019 年 11 月 12 日
- 筆記
本期講O(n)類型問題,共14題。3道簡單題,9道中等題,2道困難題。數組篇共歸納總結了50題,本篇是數組篇的最後一篇。其他三個篇章可參考:
本系列50道題是作者在LeetCode題庫數組標籤中包含的202道題中,按照解答考點分類歸納總結的題型。解法僅供參考,主要在於題目和考點的分類。希望對準備刷LeetCode,而感覺題目繁多、標籤太多、時間較少,不知道從何開始刷題的同學一點小小的幫助^~^,也是自己後期二刷的資料吧(PS:如果有時間的話)。
O(n)類型問題,是指要求算法的時間複雜度為O(n)。這類題目的特點是題意一般比較容易理解,而且其暴力求解的方案也比較容易想到。但是,題目確要求你不能採用暴力法求解,這往往是考察我們對雙指針、快慢指針、動態規劃、哈希數組和特定數學思想的應用。
在雙指針方面,一般基礎的策略是採用空間換取時間的策略。即先採用一個數組從原數組右邊開始遍歷,保存當前更新的臨時變量。最後,從數組的左邊開始依次遍歷,不斷更新最終的結果。此思路的應用,可以參考例9、例10和例11。
另外,雙指針的應用解法也可以在O(1)的空間複雜度裏面實現,採用一個臨時變量隨着遍歷不斷更新當前狀態,夾雜着動態規劃的思想。這類考點的應用,可以參考例5和例12。
在數學思維考察方面,組合數學的知識應用也是比較常見。比如考察對組合數學中字典序求解的應用,可以參考例1。數學中正負數轉換為數組下標的思想,可以參考例2、例6。快速找到當前示例的數學規律,歸納出遞推公式,可以參考例8、例13。
例3是一道非常經典的面試題,題目有多種解法,本文中給出是採用三次翻轉求得最終結果的解法。在矩陣應用中,利用翻轉操作一般也可以取得令人驚奇的效果。活用翻轉也是一種技巧。
例4則是讓人感嘆的解法。採用摩爾投票法尋找數組中最多的元素。該思維應該可以歸納為尋找最多元素的一種特解思路。
在數組哈希思路的應用方面,可以參考例7和例14,是很典型的以空間換取時間的例題。
例1 下一個排列
題號:31,難度:中等
題目描述:

解題思路:
本題需要注意的關鍵點:原地修改,字典序。此題的解答用到了組合數學的知識,尋找比當前序列大的最小字典序。即從該序列尾部開始遍歷,直到當前元素(假設位置為i)比該元素前面的元素大的時候停止。然後從i道最後一個元素序列中找到比第i-1個元素大的最小元素進行交換,最後把最後i個元素從小到大排序即可。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) { int i = nums.length - 2; while(i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i+1]) i--; if(i >= 0) { int j = nums.length - 1; while(nums[j] <= nums[i]) j--; int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; reverse(nums, i+1, nums.length - 1); } else { reverse(nums, 0, nums.length-1); } } public void reverse(int[] nums, int i, int j) { while(i < j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i++] = nums[j]; nums[j--] = temp; } } }
執行結果:

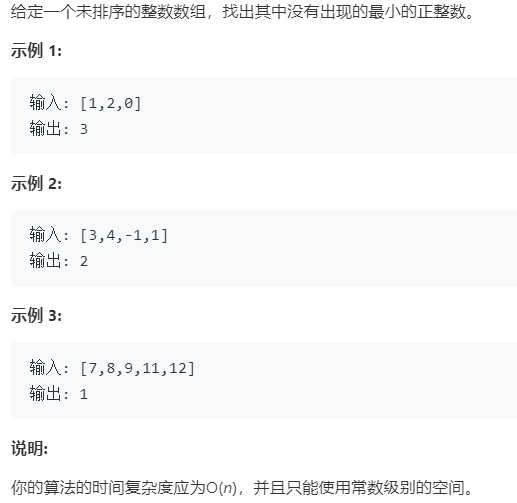
例2 缺失的第一個正數
題號:41,難度:困難
題目描述:
解題思路:
此題雖然被劃分為困難題,實際上比較簡單。題目要求是沒有出現的最小正整數,那麼返回的結果最大值只能是數組長度加1,最小值是1。那麼只需要利用原有數組,把其中小於等於0的數字標記為大於數組長度*2的元素,剩下的把在1到數組長度之間的元素採用數組的下標元素取負數表示。最後,從數組第一個元素開始遍歷,一旦出現大於0的元素,那麼該元素下標即為最終結果。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) { int len = nums.length * 2; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) { if(nums[i] <= 0) nums[i] = len++; } int j = 0; for(;j < nums.length;j++) { if(Math.abs(nums[j]) <= nums.length && nums[Math.abs(nums[j]) - 1] > 0) nums[Math.abs(nums[j]) - 1] *= -1; } for(j = 0;j < nums.length;j++) { if(nums[j] > 0) break; } return j + 1; } }
執行結果:

例3 旋轉數組
題號:189,難度:簡單
題目描述:

解題思路:
採用三次翻轉操作。第一次將整個數組翻轉一次,第二次將要右移的前K個元素翻轉一次,第三次將剩餘的k-n-1個元素翻轉一次。最終得到的結構即為目標值。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; k %= n; reverse(nums, 0, n - 1); reverse(nums, 0, k - 1); reverse(nums, k, n - 1); } private void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { int temp = nums[start]; nums[start++] = nums[end]; nums[end--] = temp; } } }
執行結果:

例4 求眾數II
題號:229,難度:中等
題目描述:

解題思路:
採用摩爾投票法,具體就是遇到相等的數,統計該數的個數自動加1,否則自動減一,一旦減到0後,更換當前存儲的數字。摩爾投票法首次運用的題是求一維數組中數目超過一半的數(具體可參考題目:求眾數, 題號169, 難度:簡單)。本題稍作變換即可,開啟兩個變量計數和存儲當前的數。開啟兩個數的數學意義在於,一個數組最多只能有兩個數超過數組的三分之一。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public List<Integer> majorityElement(int[] nums) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); //摩爾投票法 int count1 = 0, temp1 = 0; int count2 = 0, temp2 = 0; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) { if((count1 == 0 || temp1 == nums[i]) && temp2 != nums[i]) { count1++; temp1 = nums[i]; } else if(count2 == 0 || temp2 == nums[i]) { count2++; temp2 = nums[i]; } else{ count1--; count2--; } } count1 = 0; count2 = 0; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) { if(nums[i] == temp1) count1++; else if(nums[i] == temp2) count2++; } if(count1 > nums.length / 3) result.add(temp1); if(temp1 != temp2 && count2 > nums.length / 3) result.add(temp2); return result; } }
執行結果:

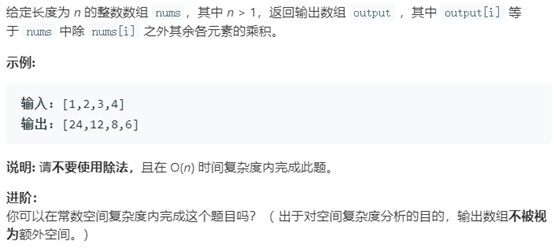
例5 除自身以外數組的乘積
題號:238,難度:中等
題目描述:
解題思路:
以空間換時間的策略,從數組左邊依次遍歷,保存連續乘積;然後,從數組右邊依次遍歷,保存連續乘積。最後,從數組第一數字開始遍歷,取該數組左邊的連續乘積和右邊的連續乘積相乘即可。時間複雜度為O(n),空間複雜度為O(n)。
進階如何使得空間複雜度為O(1)呢?即採用常數空間保存左邊連續乘積,和右邊連續乘積即可。這裡感覺採用了動態規劃的思路來臨時保存左右連續乘積。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) { int[] result = new int[nums.length]; int left = 1; int right = 1; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) { result[i] = left; left *= nums[i]; } for(int i = nums.length - 1;i >= 0;i--) { result[i] *= right; right *= nums[i]; } return result; } }
執行結果:

例6 數組中重複的數據
題號:442,難度:中等
題目描述:

解題思路:
此題採用數組下標來判定出現兩次的元素。題目中表明1 <= a[i] <= n,那麼出現兩次的元素i,對應下標i -1,出現一次時使得a[i – 1] * -1,當再次出現a[i – 1]小於零時,那麼i就出現了兩次。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) { int j = Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1; if(nums[j] < 0) result.add(j + 1); else nums[j] *= -1; } return result; } }
執行結果:

例7 數組拆分I
題號:561,難度:簡單
題目描述:

解題思路:
題目中有說明元素的範圍,且比較小。觀察示例的數據發現,只需要對數據進行從小到大排序,依次選取兩個元素中第一個元素作為最終結果的一部分即可。此時,可以採取數據哈希的思路來完成數據的排序操作,時間複雜度為O(n)。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int arrayPairSum(int[] nums) { int[] temp = new int[20001]; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++) { int j = nums[i] + 10000; temp[j]++; } int result = 0; for(int i = 0;i < temp.length;i++) { if(temp[i] > 0) { int a = i - 10000; temp[i]--; while(i < temp.length && temp[i] <= 0) { i++; } // if(i < temp.length) // System.out.println("i = "+i+", temp[i] = "+temp[i]); if(i < temp.length) { result += a; temp[i]--; } if(temp[i] > 0) i--; } } return result; } }
執行結果:

例8 優美的排列II
題號:667,難度:中等
題目描述:

解題思路:
此題考察我們尋找數學規律。先從1到k存儲每個元素,然後從k+1開始每兩個數存儲(n–, k++)即可。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int[] constructArray(int n, int k) { int[] result = new int[n]; int temp = 1; for(int i = 0;i < n - k;i++) result[i] = temp++; int count = n; boolean judge = true; for(int i = n - k;i < n;i++) { if(judge) { result[i] = count--; judge = false; } else { result[i] = temp++; judge = true; } } return result; } }
執行結果:

例9 最多能完成排序的塊 II
題號:768,難度:困難
題目描述:

解題思路:
此題考察雙指針和動態規劃思想的應用。雙指針,從右邊依次遍歷存儲當前的最小值。從左邊開始依次遍歷,存儲當前的最大值。如果左邊當前的最大值小於等於右邊的最小值,則可以分割為一個塊。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int maxChunksToSorted(int[] arr) { int[] right_min = new int[arr.length]; for(int i = arr.length - 1;i >= 0;i--) { if(i == arr.length - 1) right_min[i] = arr[i]; else right_min[i] = Math.min(arr[i], right_min[i+1]); } int result = 1; int left_max = 0; for(int i = 0;i < arr.length - 1;i++) { if(arr[left_max] <= right_min[i + 1]) { result++; left_max = i + 1; } else { if(arr[left_max] < arr[i]) left_max = i; } } return result; } }
執行結果:

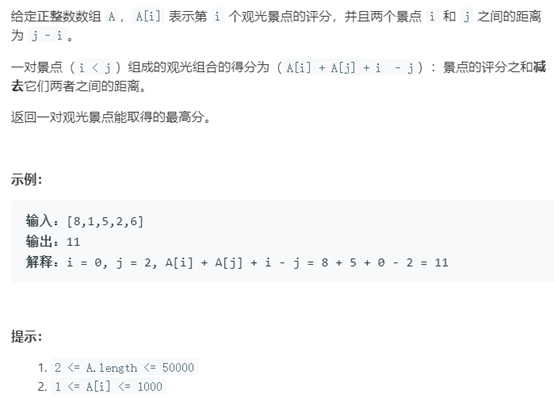
例10 最佳觀光組合
題號:1014,難度:中等
題目描述:
解題思路:
此題是一個雙指針和動態規劃思想的應用。可以把得分拆為兩個部分,左邊遍歷,尋找max(A[i] + i);右邊遍歷,尋找max(A[j] – j)。可以採用一個數組保存右邊最大值,讓後從左邊開始遍歷,不斷更新最終的最大值。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) { int[] right_max = new int[A.length]; for(int i = A.length - 1;i >= 0;i--) { if(i == A.length - 1) right_max[i] = A[i] - i; else right_max[i] = Math.max(A[i] - i, right_max[i+1]); } int result = 0; for(int i = 0;i < A.length - 1;i++) result = Math.max(result, A[i] + i + right_max[i+1]); return result; } }
執行結果:

例11 到最近的人的最大距離
題號:849,難度:簡單
題目描述:

解題思路:
此題考察我們雙指針的思想應用。可以採用一個指針從右邊依次遍歷,存儲到當前元素的連續零的個數(此處需要注意尾部全為零的特殊情況)。然後,從左邊開始遍歷,計算左邊連續零的個數,最後比較左邊和右邊零個數的大小即可。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int maxDistToClosest(int[] seats) { int[] right = new int[seats.length]; for(int i = seats.length - 1;i >= 0;i--) { if(i == seats.length - 1) { right[i] = seats[i] == 1 ? 0 : 1; } else if(seats[i] == 0){ right[i] = 1 + right[i+1]; } } int result = 0, left = seats.length; for(int i = 0;i < seats.length;i++) { // System.out.println("i = "+i+", left = "+left+", right = "+right[i]+", result = "+result); if(seats[i] == 1) left = 1; else { int temp = left; if(right[i] < left && right[i] + i < seats.length) temp = right[i]; result = Math.max(result, temp); left++; } } return result; } }
執行結果:

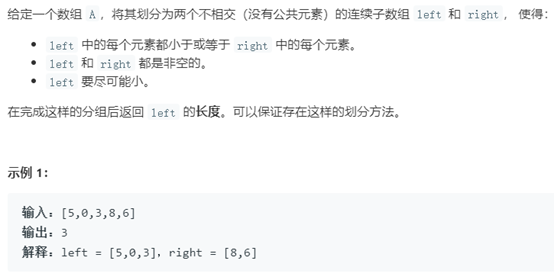
例12 分割數組
題號:915,難度:中等
題目描述:
解題思路:
此題同樣是雙指針思路的應用,但是可採用當前最大值和左數組最大值的思想來做。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int partitionDisjoint(int[] A) { int[] right_min = new int[A.length]; for(int i = A.length - 1;i >= 0;i--) { if(i == A.length - 1) right_min[i] = A[i]; else right_min[i] = Math.min(A[i], right_min[i+1]); } int result = 0, left_max = A[0]; for(;result < A.length - 1;result++) { left_max = Math.max(A[result], left_max); if(left_max <= right_min[result + 1]) break; } return result + 1; } /* 當前最大值和左邊最大值 public int partitionDisjoint(int[] A) { if (A == null || A.length == 0) { return 0; } int leftMax = A[0]; int max = A[0]; int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) { max = Math.max(max, A[i]); if(A[i] < leftMax) { leftMax = max; index = i; } } return index + 1; } */ }
執行結果:

例13 將字符串翻轉到單調遞增
題號:926, 難度:中等
題目描述:

解題思路:
此題考察我們的數學思維。統計從左到右遍歷時0的個數和1的個數,一旦零的個數大於1,結果自動增加1的個數,同時把0和1的個數置零,從新開始統計。
具體代碼:
class Solution { /* * 某一位為1時,前面一位是0或者1都可以 * 某一位為0時,前面一位只能為0 */ public int minFlipsMonoIncr(String S) { int zero = 0, one = 0; int result = 0; for(char s: S.toCharArray()){ if(s == '0') zero++; else one++; if(zero > one) { result += one; zero = 0; one = 0; } } result += zero; return result; } }
執行結果:

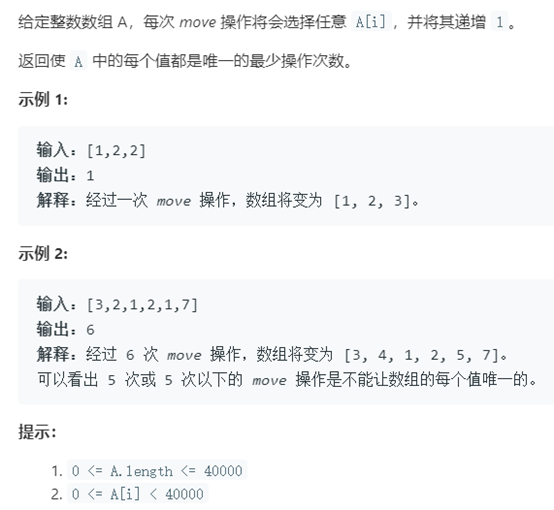
例14 使數組唯一的最小增量
題號:945,難度:中等
題目描述:
解題思路:
此題提示說明,0 <= A[i] < 40000。可知可以採用數組哈希的思想來求解本題,以空間換時間的思想,最終的時間複雜度為O(n)。
具體代碼:
class Solution { public int minIncrementForUnique(int[] A) { int[] value_A = new int[41000]; for(Integer a: A) value_A[a]++; int result = 0; for(int i = 0;i < A.length;i++) { if(value_A[A[i]] == 1) continue; int temp = A[i]; int count = 0; while(value_A[temp] > 1) { value_A[temp]--; while(value_A[A[i]] > 0) { count++; A[i]++; } value_A[A[i]]++; result += count; } } return result; } }
執行結果: