Tomcat源碼分析 (八)—– HTTP請求處理過程(一)
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
終於進行到Connector的分析階段了,這也是Tomcat裏面最複雜的一塊功能了。Connector中文名為連接器,既然是連接器,它肯定會連接某些東西,連接些什麼呢?
Connector用於接受請求並將請求封裝成Request和Response,然後交給Container進行處理,Container處理完之後再交給Connector返回給客戶端。
要理解Connector,我們需要問自己4個問題。
- (1)
Connector如何接受請求的? - (2)如何將請求封裝成Request和Response的?
- (3)封裝完之後的Request和Response如何交給
Container進行處理的? - (4)
Container處理完之後如何交給Connector並返回給客戶端的?
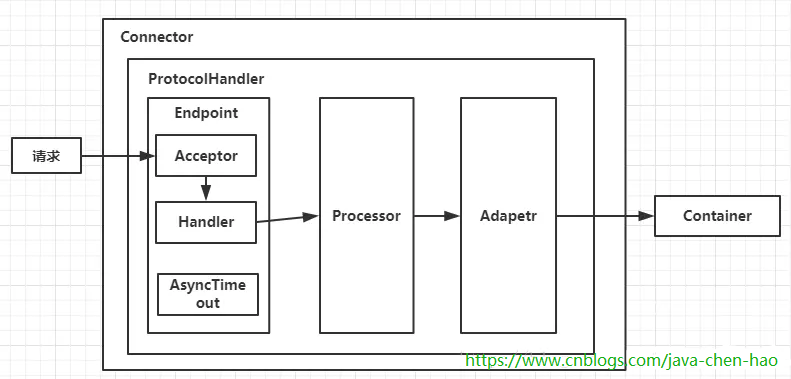
先來一張Connector的整體結構圖
【注意】:不同的協議、不同的通信方式,ProtocolHandler會有不同的實現。在Tomcat8.5中,ProtocolHandler的類繼承層級如下圖所示。

針對上述的類繼承層級圖,我們做如下說明:
- ajp和http11是兩種不同的協議
- nio、nio2和apr是不同的通信方式
- 協議和通信方式可以相互組合。
ProtocolHandler包含三個部件:Endpoint、Processor、Adapter。
Endpoint用來處理底層Socket的網絡連接,Processor用於將Endpoint接收到的Socket封裝成Request,Adapter用於將Request交給Container進行具體的處理。Endpoint由於是處理底層的Socket網絡連接,因此Endpoint是用來實現TCP/IP協議的,而Processor用來實現HTTP協議的,Adapter將請求適配到Servlet容器進行具體的處理。Endpoint的抽象實現類AbstractEndpoint裏面定義了Acceptor和AsyncTimeout兩個內部類和一個Handler接口。Acceptor用於監聽請求,AsyncTimeout用於檢查異步Request的超時,Handler用於處理接收到的Socket,在內部調用Processor進行處理。
至此,我們已經明白了問題(1)、(2)和(3)。至於(4),當我們了解了Container自然就明白了,前面章節內容已經詳細分析過了。
Connector源碼分析入口
我們在Service標準實現StandardService的源碼中發現,其init()、start()、stop()和destroy()方法分別會對Connectors的同名方法進行調用。而一個Service對應着多個Connector。
Service.init()
@Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); if (engine != null) { engine.init(); } // Initialize any Executors for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) { if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) { ((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain()); } executor.init(); } // Initialize mapper listener mapperListener.init(); // Initialize our defined Connectors synchronized (connectorsLock) { for (Connector connector : connectors) { try { connector.init(); } catch (Exception e) { String message = sm.getString( "standardService.connector.initFailed", connector); log.error(message, e); if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) throw new LifecycleException(message); } } } }
Service.start()
@Override protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { if(log.isInfoEnabled()) log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name)); setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); // Start our defined Container first if (engine != null) { synchronized (engine) { engine.start(); } } synchronized (executors) { for (Executor executor: executors) { executor.start(); } } mapperListener.start(); // Start our defined Connectors second synchronized (connectorsLock) { for (Connector connector: connectors) { try { // If it has already failed, don't try and start it if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) { connector.start(); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error(sm.getString( "standardService.connector.startFailed", connector), e); } } } }
我們知道Connector實現了Lifecycle接口,所以它是一個生命周期組件。所以Connector的啟動邏輯入口在於init()和start()。
Connector構造方法
在分析之前,我們看看server.xml,該文件已經體現出了tomcat中各個組件的大體結構。
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" /> <Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" /> <GlobalNamingResources> <Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container" type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase" description="User database that can be updated and saved" factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory" pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" /> </GlobalNamingResources> <Service name="Catalina"> <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443" /> <Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" /> <Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm"> <Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm" resourceName="UserDatabase"/> </Realm> <Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"> <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs" prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt" pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" /> </Host> </Engine> </Service> </Server>
在這個文件中,我們看到一個Connector有幾個關鍵屬性,port和protocol是其中的兩個。server.xml默認支持兩種協議:HTTP/1.1和AJP/1.3。其中HTTP/1.1用於支持http1.1協議,而AJP/1.3用於支持對apache服務器的通信。
接下來我們看看構造方法。
public Connector() { this(null); // 1. 無參構造方法,傳入參數為空協議,會默認使用`HTTP/1.1` } public Connector(String protocol) { setProtocol(protocol); // Instantiate protocol handler // 5. 使用protocolHandler的類名構造ProtocolHandler的實例 ProtocolHandler p = null; try { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocolHandlerClassName); p = (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error(sm.getString( "coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e); } finally { this.protocolHandler = p; } if (Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE) { uriCharset = StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1; } else { uriCharset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; } } @Deprecated public void setProtocol(String protocol) { boolean aprConnector = AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() && AprLifecycleListener.getUseAprConnector(); // 2. `HTTP/1.1`或`null`,protocolHandler使用`org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol`,不考慮apr if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol) || protocol == null) { if (aprConnector) { setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol"); } else { setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"); } } // 3. `AJP/1.3`,protocolHandler使用`org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol`,不考慮apr else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) { if (aprConnector) { setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol"); } else { setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol"); } } // 4. 其他情況,使用傳入的protocol作為protocolHandler的類名 else { setProtocolHandlerClassName(protocol); } }
從上面的代碼我們看到構造方法主要做了下面幾件事情:
- 無參構造方法,傳入參數為空協議,會默認使用
HTTP/1.1 HTTP/1.1或null,protocolHandler使用org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol,不考慮aprAJP/1.3,protocolHandler使用org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol,不考慮apr- 其他情況,使用傳入的protocol作為protocolHandler的類名
- 使用protocolHandler的類名構造ProtocolHandler的實例
Connector.init()
@Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // Initialize adapter // 1. 初始化adapter adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this); protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter); // Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default // 2. 設置接受body的method列表,默認為POST if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) { setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods()); } if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() && !AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoApr", getProtocolHandlerClassName())); } if (AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() && AprLifecycleListener.getUseOpenSSL() && protocolHandler instanceof AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol) { AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?> jsseProtocolHandler = (AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol<?>) protocolHandler; if (jsseProtocolHandler.isSSLEnabled() && jsseProtocolHandler.getSslImplementationName() == null) { // OpenSSL is compatible with the JSSE configuration, so use it if APR is available jsseProtocolHandler.setSslImplementationName(OpenSSLImplementation.class.getName()); } } // 3. 初始化protocolHandler try { protocolHandler.init(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e); } }
init()方法做了3件事情
- 初始化adapter
- 設置接受body的method列表,默認為POST
- 初始化protocolHandler
從ProtocolHandler類繼承層級我們知道ProtocolHandler的子類都必須實現AbstractProtocol抽象類,而protocolHandler.init();的邏輯代碼正是在這個抽象類裏面。我們來分析一下。
@Override public void init() throws Exception { if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) { getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init", getName())); } if (oname == null) { // Component not pre-registered so register it oname = createObjectName(); if (oname != null) { Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null); } } if (this.domain != null) { rgOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + getName()); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent( getHandler().getGlobal(), rgOname, null); } // 1. 設置endpoint的名字,默認為:http-nio-{port} String endpointName = getName(); endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1)); endpoint.setDomain(domain); // 2. 初始化endpoint endpoint.init(); }
我們接着分析一下Endpoint.init()裏面又做了什麼。該方法位於AbstactEndpoint抽象類,該類是基於模板方法模式實現的,主要調用了子類的bind()方法。
public abstract void bind() throws Exception; public abstract void unbind() throws Exception; public abstract void startInternal() throws Exception; public abstract void stopInternal() throws Exception; public void init() throws Exception { // 執行bind()方法 if (bindOnInit) { bind(); bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_INIT; } if (this.domain != null) { // Register endpoint (as ThreadPool - historical name) oname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name="" + getName() + """); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null); ObjectName socketPropertiesOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=ThreadPool,name="" + getName() + "",subType=SocketProperties"); socketProperties.setObjectName(socketPropertiesOname); Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(socketProperties, socketPropertiesOname, null); for (SSLHostConfig sslHostConfig : findSslHostConfigs()) { registerJmx(sslHostConfig); } } }
繼續分析bind()方法,我們終於看到了我們想要看的東西了。關鍵的代碼在於serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());,用於綁定ServerSocket到指定的IP和端口。
@Override public void bind() throws Exception { if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) { serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort())); //綁定ServerSocket到指定的IP和端口 serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount()); } else { // Retrieve the channel provided by the OS Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel(); if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) { serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic; } if (serverSock == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited")); } } serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior // Initialize thread count defaults for acceptor, poller if (acceptorThreadCount == 0) { // FIXME: Doesn't seem to work that well with multiple accept threads acceptorThreadCount = 1; } if (pollerThreadCount <= 0) { //minimum one poller thread pollerThreadCount = 1; } setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(pollerThreadCount)); // Initialize SSL if needed initialiseSsl(); selectorPool.open(); }
好了,我們已經分析完了init()方法,接下來我們分析start()方法。關鍵代碼就一行,調用ProtocolHandler.start()方法。
Connector.start()
@Override protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Validate settings before starting if (getPort() < 0) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString( "coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort()))); } setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); try { protocolHandler.start(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e); } }
我們深入ProtocolHandler.start()方法。
- 調用
Endpoint.start()方法 - 開啟異步超時線程,線程執行單元為
Asynctimeout
@Override public void start() throws Exception { if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) { getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName())); } // 1. 調用`Endpoint.start()`方法 endpoint.start(); // Start async timeout thread // 2. 開啟異步超時線程,線程執行單元為`Asynctimeout` asyncTimeout = new AsyncTimeout(); Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(asyncTimeout, getNameInternal() + "-AsyncTimeout"); int priority = endpoint.getThreadPriority(); if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) { priority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY; } timeoutThread.setPriority(priority); timeoutThread.setDaemon(true); timeoutThread.start(); }
這兒我們重點關注Endpoint.start()方法
public final void start() throws Exception { // 1. `bind()`已經在`init()`中分析過了 if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) { bind(); bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START; } startInternal(); } @Override public void startInternal() throws Exception { if (!running) { running = true; paused = false; processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getProcessorCache()); eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getEventCache()); nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE, socketProperties.getBufferPool()); // Create worker collection // 2. 創建工作者線程池 if ( getExecutor() == null ) { createExecutor(); } // 3. 初始化連接latch,用於限制請求的並發量 initializeConnectionLatch(); // Start poller threads // 4. 開啟poller線程。poller用於對接受者線程生產的消息(或事件)進行處理,poller最終調用的是Handler的代碼 pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()]; for (int i=0; i<pollers.length; i++) { pollers[i] = new Poller(); Thread pollerThread = new Thread(pollers[i], getName() + "-ClientPoller-"+i); pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority); pollerThread.setDaemon(true); pollerThread.start(); } // 5. 開啟acceptor線程 startAcceptorThreads(); } } protected final void startAcceptorThreads() { int count = getAcceptorThreadCount(); acceptors = new Acceptor[count]; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { acceptors[i] = createAcceptor(); String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i; acceptors[i].setThreadName(threadName); Thread t = new Thread(acceptors[i], threadName); t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority()); t.setDaemon(getDaemon()); t.start(); } }
bind()已經在init()中分析過了- 創建工作者線程池
- 初始化連接latch,用於限制請求的並發量
- 創建輪詢Poller線程。poller用於對接受者線程生產的消息(或事件)進行處理,poller最終調用的是Handler的代碼
- 創建Acceptor線程
Connector請求邏輯
分析完了Connector的啟動邏輯之後,我們就需要進一步分析一下http的請求邏輯,當請求從客戶端發起之後,需要經過哪些操作才能真正地得到執行?
Acceptor
Acceptor線程主要用於監聽套接字,將已連接套接字轉給Poller線程。Acceptor線程數由AbstracEndPoint的acceptorThreadCount成員變量控制,默認值為1
AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor是AbstractEndpoint類的靜態抽象類,實現了Runnable接口,部分代碼如下:
public abstract static class Acceptor implements Runnable { public enum AcceptorState { NEW, RUNNING, PAUSED, ENDED } protected volatile AcceptorState state = AcceptorState.NEW; public final AcceptorState getState() { return state; } private String threadName; protected final void setThreadName(final String threadName) { this.threadName = threadName; } protected final String getThreadName() { return threadName; } }
NioEndpoint的Acceptor成員內部類繼承了AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor:
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor { @Override public void run() { int errorDelay = 0; // Loop until we receive a shutdown command while (running) { // Loop if endpoint is paused // 1. 運行過程中,如果`Endpoint`暫停了,則`Acceptor`進行自旋(間隔50毫秒) ` while (paused && running) { state = AcceptorState.PAUSED; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } } // 2. 如果`Endpoint`終止運行了,則`Acceptor`也會終止 if (!running) { break; } state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { //if we have reached max connections, wait // 3. 如果請求達到了最大連接數,則wait直到連接數降下來 countUpOrAwaitConnection(); SocketChannel socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server // socket // 4. 接受下一次連接的socket socket = serverSock.accept(); } catch (IOException ioe) { // We didn't get a socket countDownConnection(); if (running) { // Introduce delay if necessary errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); // re-throw throw ioe; } else { break; } } // Successful accept, reset the error delay errorDelay = 0; // Configure the socket if (running && !paused) { // setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to // an appropriate processor if successful // 5. `setSocketOptions()`這兒是關鍵,會將socket以事件的方式傳遞給poller if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) { closeSocket(socket); } } else { closeSocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t); } } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; } }
從以上代碼可以看到:
- countUpOrAwaitConnection函數檢查當前最大連接數,若未達到maxConnections則加一,否則等待;
- socket = serverSock.accept()這一行中的serverSock正是NioEndpoint的bind函數中打開的ServerSocketChannel。為了引用這個變量,NioEndpoint的Acceptor類是成員而不再是靜態類;
- setSocketOptions函數調用上的注釋表明該函數將已連接套接字交給Poller線程處理。
setSocketOptions方法接着處理已連接套接字:
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) { // Process the connection try { //disable blocking, APR style, we are gonna be polling it socket.configureBlocking(false); Socket sock = socket.socket(); socketProperties.setProperties(sock); NioChannel channel = nioChannels.pop(); if (channel == null) { SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler( socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(), socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(), socketProperties.getDirectBuffer()); if (isSSLEnabled()) { channel = new SecureNioChannel(socket, bufhandler, selectorPool, this); } else { channel = new NioChannel(socket, bufhandler); } } else { channel.setIOChannel(socket); channel.reset(); } // 將channel註冊到poller,注意關鍵的兩個方法,`getPoller0()`和`Poller.register()` getPoller0().register(channel); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); try { log.error("",t); } catch (Throwable tt) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt); } // Tell to close the socket return false; } return true; }
- 從NioChannel棧中出棧一個,若能重用(即不為null)則重用對象,否則新建一個NioChannel對象;
- getPoller0方法利用輪轉法選擇一個Poller線程,利用Poller類的register方法將上述NioChannel對象註冊到該Poller線程上;
- 若成功轉給Poller線程該函數返回true,否則返回false。返回false後,Acceptor類的closeSocket函數會關閉通道和底層Socket連接並將當前最大連接數減一。
Poller
Poller線程主要用於以較少的資源輪詢已連接套接字以保持連接,當數據可用時轉給工作線程。
Poller線程數由NioEndPoint的pollerThreadCount成員變量控制,默認值為2與可用處理器數二者之間的較小值。
Poller實現了Runnable接口,可以看到構造函數為每個Poller打開了一個新的Selector。
public class Poller implements Runnable { private Selector selector; private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events = new SynchronizedQueue<>(); // 省略一些代碼 public Poller() throws IOException { this.selector = Selector.open(); } public Selector getSelector() { return selector;} // 省略一些代碼 }
將channel註冊到poller,注意關鍵的兩個方法,getPoller0()和Poller.register()。先來分析一下getPoller0(),該方法比較關鍵的一個地方就是以取模的方式對poller數量進行輪詢獲取。
/** * The socket poller. */ private Poller[] pollers = null; private AtomicInteger pollerRotater = new AtomicInteger(0); /** * Return an available poller in true round robin fashion. * * @return The next poller in sequence */ public Poller getPoller0() { int idx = Math.abs(pollerRotater.incrementAndGet()) % pollers.length; return pollers[idx]; }
接下來我們分析一下Poller.register()方法。因為Poller維持了一個events同步隊列,所以Acceptor接受到的channel會放在這個隊列裏面,放置的代碼為events.offer(event);
public class Poller implements Runnable { private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events = new SynchronizedQueue<>(); /** * Registers a newly created socket with the poller. * * @param socket The newly created socket */ public void register(final NioChannel socket) { socket.setPoller(this); NioSocketWrapper ka = new NioSocketWrapper(socket, NioEndpoint.this); socket.setSocketWrapper(ka); ka.setPoller(this); ka.setReadTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout()); ka.setWriteTimeout(getSocketProperties().getSoTimeout()); ka.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); ka.setSecure(isSSLEnabled()); ka.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); ka.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout()); PollerEvent r = eventCache.pop(); ka.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into. if ( r==null) r = new PollerEvent(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER); else r.reset(socket,ka,OP_REGISTER); addEvent(r); } private void addEvent(PollerEvent event) { events.offer(event); if ( wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0 ) selector.wakeup(); } }
PollerEvent
接下來看一下PollerEvent,PollerEvent實現了Runnable接口,用來表示一個輪詢事件,代碼如下:
public static class PollerEvent implements Runnable { private NioChannel socket; private int interestOps; private NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper; public PollerEvent(NioChannel ch, NioSocketWrapper w, int intOps) { reset(ch, w, intOps); } public void reset(NioChannel ch, NioSocketWrapper w, int intOps) { socket = ch; interestOps = intOps; socketWrapper = w; } public void reset() { reset(null, null, 0); } @Override public void run() { if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) { try { socket.getIOChannel().register( socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper); } catch (Exception x) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x); } } else { final SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector()); try { if (key == null) { socket.socketWrapper.getEndpoint().countDownConnection(); ((NioSocketWrapper) socket.socketWrapper).closed = true; } else { final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment(); if (socketWrapper != null) { //we are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter. int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps; socketWrapper.interestOps(ops); key.interestOps(ops); } else { socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } } } catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) { try { socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } catch (Exception ignore) {} } } } }
在run函數中:
- 若感興趣集是自定義的OP_REGISTER,則說明該事件表示的已連接套接字通道尚未被輪詢線程處理過,那麼將該通道註冊到Poller線程的Selector上,感興趣集是OP_READ,通道註冊的附件是一個NioSocketWrapper對象。從Poller的register方法添加事件即是這樣的過程;
- 否則獲得已連接套接字通道註冊到Poller線程的Selector上的SelectionKey,為key添加新的感興趣集。
重訪Poller
上文提到Poller類實現了Runnable接口,其重寫的run方法如下所示。
public boolean events() { boolean result = false; PollerEvent pe = null; for (int i = 0, size = events.size(); i < size && (pe = events.poll()) != null; i++ ) { result = true; try { //直接調用run方法 pe.run(); pe.reset(); if (running && !paused) { eventCache.push(pe); } } catch ( Throwable x ) { log.error("",x); } } return result; } @Override public void run() { // Loop until destroy() is called while (true) { boolean hasEvents = false; try { if (!close) { /執行PollerEvent的run方法 hasEvents = events(); if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) { //if we are here, means we have other stuff to do //do a non blocking select keyCount = selector.selectNow(); } else { keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout); } wakeupCounter.set(0); } if (close) { events(); timeout(0, false); try { selector.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe); } break; } } catch (Throwable x) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x); log.error("",x); continue; } //either we timed out or we woke up, process events first if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events()); // 獲取當前選擇器中所有註冊的“選擇鍵(已就緒的監聽事件)” Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; // Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch // any active event. // 對已經準備好的key進行處理 while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment(); // Attachment may be null if another thread has called // cancelledKey() if (attachment == null) { iterator.remove(); } else { iterator.remove(); // 真正處理key的地方 processKey(sk, attachment); } }//while //process timeouts timeout(keyCount,hasEvents); }//while getStopLatch().countDown(); }
- 若隊列里有元素則會先把隊列里的事件均執行一遍,PollerEvent的run方法會將通道註冊到Poller的Selector上;
- 對select返回的SelectionKey進行處理,由於在PollerEvent中註冊通道時帶上了NioSocketWrapper附件,因此這裡可以用SelectionKey的attachment方法得到,接着調用processKey去處理已連接套接字通道。
我們接着分析processKey(),該方法又會根據key的類型,來分別處理讀和寫。
- 處理讀事件,比如生成Request對象
- 處理寫事件,比如將生成的Response對象通過socket寫回客戶端
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment) { try { if ( close ) { cancelledKey(sk); } else if ( sk.isValid() && attachment != null ) { if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() ) { if ( attachment.getSendfileData() != null ) { processSendfile(sk,attachment, false); } else { unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps()); boolean closeSocket = false; // 1. 處理讀事件,比如生成Request對象 // Read goes before write if (sk.isReadable()) { if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } // 2. 處理寫事件,比如將生成的Response對象通過socket寫回客戶端 if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) { if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } if (closeSocket) { cancelledKey(sk); } } } } else { //invalid key cancelledKey(sk); } } catch ( CancelledKeyException ckx ) { cancelledKey(sk); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error("",t); } }
我們繼續來分析方法processSocket()。
- 從
processorCache裏面拿一個Processor來處理socket,Processor的實現為SocketProcessor - 將
Processor放到工作線程池中執行
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) { try { if (socketWrapper == null) { return false; } // 1. 從`processorCache`裏面拿一個`Processor`來處理socket,`Processor`的實現為`SocketProcessor` SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop(); if (sc == null) { sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event); } else { sc.reset(socketWrapper, event); } // 2. 將`Processor`放到工作線程池中執行 Executor executor = getExecutor(); if (dispatch && executor != null) { executor.execute(sc); } else { sc.run(); } } catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) { getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree); return false; } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); // This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that // the pool and its queue are full getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t); return false; } return true; }
dispatch參數表示是否要在另外的線程中處理,上文processKey各處傳遞的參數都是true。
- dispatch為true且工作線程池存在時會執行executor.execute(sc),之後是由工作線程池處理已連接套接字;
- 否則繼續由Poller線程自己處理已連接套接字。
AbstractEndPoint類的createSocketProcessor是抽象方法,NioEndPoint類實現了它:
@Override protected SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> createSocketProcessor( SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) { return new SocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event); }
接着我們分析SocketProcessor.doRun()方法(SocketProcessor.run()方法最終調用此方法)。該方法將處理邏輯交給Handler處理,當event為null時,則表明是一個OPEN_READ事件。
該類的注釋說明SocketProcessor與Worker的作用等價。
/** * This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an * external Executor thread pool. */ protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> { public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) { super(socketWrapper, event); } @Override protected void doRun() { NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket(); SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector()); try { int handshake = -1; try { if (key != null) { if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) { // No TLS handshaking required. Let the handler // process this socket / event combination. handshake = 0; } else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || event == SocketEvent.ERROR) { // Unable to complete the TLS handshake. Treat it as // if the handshake failed. handshake = -1; } else { handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable()); // The handshake process reads/writes from/to the // socket. status may therefore be OPEN_WRITE once // the handshake completes. However, the handshake // happens when the socket is opened so the status // must always be OPEN_READ after it completes. It // is OK to always set this as it is only used if // the handshake completes. event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ; } } } catch (IOException x) { handshake = -1; if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Error during SSL handshake",x); } catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) { handshake = -1; } if (handshake == 0) { SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN; // Process the request from this socket // 將處理邏輯交給`Handler`處理,當event為null時,則表明是一個`OPEN_READ`事件 if (event == null) { state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ); } else { state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event); } if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) { close(socket, key); } } else if (handshake == -1 ) { close(socket, key); } else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){ socketWrapper.registerReadInterest(); } else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){ socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest(); } } catch (CancelledKeyException cx) { socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } catch (VirtualMachineError vme) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(vme); } catch (Throwable t) { log.error("", t); socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } finally { socketWrapper = null; event = null; //return to cache if (running && !paused) { processorCache.push(this); } } } }
Handler的關鍵方法是process(),雖然這個方法有很多條件分支,但是邏輯卻非常清楚,主要是調用Processor.process()方法。
@Override public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) { try { if (processor == null) { processor = getProtocol().createProcessor(); register(processor); } processor.setSslSupport( wrapper.getSslSupport(getProtocol().getClientCertProvider())); // Associate the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor); SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED; do { // 關鍵的代碼,終於找到你了 state = processor.process(wrapper, status); } while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING); return state; } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); // any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it // with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on // less-than-verbose logs. getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e); } finally { ContainerThreadMarker.clear(); } // Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current // connections connections.remove(socket); release(processor); return SocketState.CLOSED; }
Processor
createProcessor
protected Http11Processor createProcessor() { // 構建 Http11Processor Http11Processor processor = new Http11Processor( proto.getMaxHttpHeaderSize(), (JIoEndpoint)proto.endpoint, // 1. http header 的最大尺寸 proto.getMaxTrailerSize(),proto.getMaxExtensionSize()); processor.setAdapter(proto.getAdapter()); // 2. 默認的 KeepAlive 情況下, 每個 Socket 處理的最多的 請求次數 processor.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(proto.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); // 3. 開啟 KeepAlive 的 Timeout processor.setKeepAliveTimeout(proto.getKeepAliveTimeout()); // 4. http 當遇到文件上傳時的 默認超時時間 (300 * 1000) processor.setConnectionUploadTimeout( proto.getConnectionUploadTimeout()); processor.setDisableUploadTimeout(proto.getDisableUploadTimeout()); // 5. 當 http 請求的 body size超過這個值時, 通過 gzip 進行壓縮 processor.setCompressionMinSize(proto.getCompressionMinSize()); // 6. http 請求是否開啟 compression 處理 processor.setCompression(proto.getCompression()); processor.setNoCompressionUserAgents(proto.getNoCompressionUserAgents()); // 7. http body裏面的內容是 "text/html,text/xml,text/plain" 才會進行 壓縮處理 processor.setCompressableMimeTypes(proto.getCompressableMimeTypes()); processor.setRestrictedUserAgents(proto.getRestrictedUserAgents()); // 8. socket 的 buffer, 默認 9000 processor.setSocketBuffer(proto.getSocketBuffer()); // 9. 最大的 Post 處理尺寸的大小 4 * 1000 processor.setMaxSavePostSize(proto.getMaxSavePostSize()); processor.setServer(proto.getServer()); processor.setDisableKeepAlivePercentage( proto.getDisableKeepAlivePercentage()); register(processor); return processor; }
這兒我們主要關注的是Processor對於讀的操作,也只有一行代碼。調用service()方法。
public abstract class AbstractProcessorLight implements Processor { @Override public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status) throws IOException { SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED; Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null; do { if (dispatches != null) { DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next(); state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus()); } else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT) { // Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled } else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) { state = dispatch(status); if (state == SocketState.OPEN) { // There may be pipe-lined data to read. If the data isn't // processed now, execution will exit this loop and call // release() which will recycle the processor (and input // buffer) deleting any pipe-lined data. To avoid this, // process it now. state = service(socketWrapper); } } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) { // Extra write event likely after async, ignore state = SocketState.LONG; } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ){ // 調用`service()`方法 state = service(socketWrapper); } else { // Default to closing the socket if the SocketEvent passed in // is not consistent with the current state of the Processor state = SocketState.CLOSED; } if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], Status in: [" + status + "], State out: [" + state + "]"); } if (state != SocketState.CLOSED && isAsync()) { state = asyncPostProcess(); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], State after async post processing: [" + state + "]"); } } if (dispatches == null || !dispatches.hasNext()) { // Only returns non-null iterator if there are // dispatches to process. dispatches = getIteratorAndClearDispatches(); } } while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END || dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED); return state; } }
Processor.service()方法比較重要的地方就兩點。該方法非常得長,也超過了200行,在此我們不再拷貝此方法的代碼。
- 生成Request和Response對象
- 調用
Adapter.service()方法,將生成的Request和Response對象傳進去
Adapter
Adapter用於連接Connector和Container,起到承上啟下的作用。Processor會調用Adapter.service()方法。我們來分析一下,主要做了下面幾件事情:
- 根據coyote框架的request和response對象,生成connector的request和response對象(是HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的封裝)
- 補充header
- 解析請求,該方法會出現代理服務器、設置必要的header等操作
- 真正進入容器的地方,調用Engine容器下pipeline的閥門
- 通過request.finishRequest 與 response.finishResponse(刷OutputBuffer中的數據到瀏覽器) 來完成整個請求
@Override public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception { // 1. 根據coyote框架的request和response對象,生成connector的request和response對象(是HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse的封裝) Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); if (request == null) { // Create objects request = connector.createRequest(); request.setCoyoteRequest(req); response = connector.createResponse(); response.setCoyoteResponse(res); // Link objects request.setResponse(response); response.setRequest(request); // Set as notes req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request); res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response); // Set query string encoding req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset()); } // 2. 補充header if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) { response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY); } boolean async = false; boolean postParseSuccess = false; req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get()); try { // Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific // request parameters // 3. 解析請求,該方法會出現代理服務器、設置必要的header等操作 // 用來處理請求映射 (獲取 host, context, wrapper, URI 後面的參數的解析, sessionId ) postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response); if (postParseSuccess) { //check valves if we support async request.setAsyncSupported( connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); // Calling the container // 4. 真正進入容器的地方,調用Engine容器下pipeline的閥門 connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke( request, response); } if (request.isAsync()) { async = true; ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener(); if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) { // Possible the all data may have been read during service() // method so this needs to be checked here ClassLoader oldCL = null; try { oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null); if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) { req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead(); } } finally { request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL); } } Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); // If an async request was started, is not going to end once // this container thread finishes and an error occurred, trigger // the async error process if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true); } } else { //5. 通過request.finishRequest 與 response.finishResponse(刷OutputBuffer中的數據到瀏覽器) 來完成整個請求 request.finishRequest(); //將 org.apache.catalina.connector.Response對應的 OutputBuffer 中的數據 刷到 org.apache.coyote.Response 對應的 InternalOutputBuffer 中, 並且最終調用 socket對應的 outputStream 將數據刷出去( 這裡會組裝 Http Response 中的 header 與 body 裏面的數據, 並且刷到遠端 ) response.finishResponse(); } } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } finally { AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false); res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error); if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) { // Connection will be forcibly closed which will prevent // completion happening at the usual point. Need to trigger // call to onComplete() here. res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null); async = false; } // Access log if (!async && postParseSuccess) { // Log only if processing was invoked. // If postParseRequest() failed, it has already logged it. Context context = request.getContext(); // If the context is null, it is likely that the endpoint was // shutdown, this connection closed and the request recycled in // a different thread. That thread will have updated the access // log so it is OK not to update the access log here in that // case. if (context != null) { context.logAccess(request, response, System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(), false); } } req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null); // Recycle the wrapper request and response if (!async) { request.recycle(); response.recycle(); } } }
請求預處理
postParseRequest方法對請求做預處理,如對路徑去除分號表示的路徑參數、進行URI解碼、規格化(點號和兩點號)
protected boolean postParseRequest(org.apache.coyote.Request req, Request request, org.apache.coyote.Response res, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // 省略部分代碼 MessageBytes decodedURI = req.decodedURI(); if (undecodedURI.getType() == MessageBytes.T_BYTES) { // Copy the raw URI to the decodedURI decodedURI.duplicate(undecodedURI); // Parse the path parameters. This will: // - strip out the path parameters // - convert the decodedURI to bytes parsePathParameters(req, request); // URI decoding // %xx decoding of the URL try { req.getURLDecoder().convert(decodedURI, false); } catch (IOException ioe) { res.setStatus(400); res.setMessage("Invalid URI: " + ioe.getMessage()); connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Normalization if (!normalize(req.decodedURI())) { res.setStatus(400); res.setMessage("Invalid URI"); connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Character decoding convertURI(decodedURI, request); // Check that the URI is still normalized if (!checkNormalize(req.decodedURI())) { res.setStatus(400); res.setMessage("Invalid URI character encoding"); connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, 0, true); return false; } } else { /* The URI is chars or String, and has been sent using an in-memory * protocol handler. The following assumptions are made: * - req.requestURI() has been set to the 'original' non-decoded, * non-normalized URI * - req.decodedURI() has been set to the decoded, normalized form * of req.requestURI() */ decodedURI.toChars(); // Remove all path parameters; any needed path parameter should be set // using the request object rather than passing it in the URL CharChunk uriCC = decodedURI.getCharChunk(); int semicolon = uriCC.indexOf(';'); if (semicolon > 0) { decodedURI.setChars (uriCC.getBuffer(), uriCC.getStart(), semicolon); } } // Request mapping. MessageBytes serverName; if (connector.getUseIPVHosts()) { serverName = req.localName(); if (serverName.isNull()) { // well, they did ask for it res.action(ActionCode.REQ_LOCAL_NAME_ATTRIBUTE, null); } } else { serverName = req.serverName(); } // Version for the second mapping loop and // Context that we expect to get for that version String version = null; Context versionContext = null; boolean mapRequired = true; while (mapRequired) { // This will map the the latest version by default connector.getService().getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI, version, request.getMappingData()); // 省略部分代碼 } // 省略部分代碼 }
以MessageBytes的類型是T_BYTES為例:
- parsePathParameters方法去除URI中分號表示的路徑參數;
- req.getURLDecoder()得到一個UDecoder實例,它的convert方法對URI解碼,這裡的解碼只是移除百分號,計算百分號後兩位的十六進制數字值以替代原來的三位百分號編碼;
- normalize方法規格化URI,解釋路徑中的“.”和“..”;
- convertURI方法利用Connector的uriEncoding屬性將URI的位元組轉換為字符表示;
- 注意connector.getService().getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI, version, request.getMappingData()) 這行,之前Service啟動時MapperListener註冊了該Service內的各Host和Context。根據URI選擇Context時,Mapper的map方法採用的是convertURI方法解碼後的URI與每個Context的路徑去比較
容器處理
如果請求可以被傳給容器的Pipeline即當postParseRequest方法返回true時,則由容器繼續處理,在service方法中有connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response)這一行:
- Connector調用getService返回StandardService;
- StandardService調用getContainer返回StandardEngine;
- StandardEngine調用getPipeline返回與其關聯的StandardPipeline;
後續處理流程請看下一篇文章
