從零開始實現放置遊戲(十二)——實現戰鬥掛機(3)數據字典和緩存改造
- 2019 年 11 月 1 日
- 筆記
上一章,我們添加了遊戲的主界面和註冊登錄功能。由於距離上上篇間隔較長,可能有些內容想些的後來就忘了。同時,邏輯也不複雜,所以描述比較粗略。
現在隨着模塊的增加,整個架構也暴露出一些問題。本章我們將對整個系統進行大規模重構。
比如,之前為了快速開發,rms模塊,我們採用了直接訪問數據庫的方式,對於rms模塊本身來說,沒有什麼問題。
但是,在game模塊中,對於頻繁訪問的、不經常改變的數據或接口,希望採用緩存的方式,將數據緩存起來,減少後端壓力,同時加快響應速度,從而提升體驗。
之前rms模塊中嘗試使用了EhCache,作為內存緩存。但現在增加了game模塊,內存緩存無法在兩個進程中共享。因此,我們引入redis,把緩存數據統一存到redis中。這裡我們先使用spring-data-redis來進行緩存。通過在Service的方法上標記註解,來將方法返回結果進行緩存。這樣一個粗粒度的緩存,目前能滿足大部分需求。後面有需要時,我們再手動操作redis,進行細粒度的緩存。
除了緩存改造,發現一些枚舉值,比如:種族、職業、陣營等,目前以靜態類、枚舉類的形式,在各個模塊定義,這樣每當我修改時,需要同時修改幾個地方。因此,我添加了數據字典表,將這類數據統一配置到數據庫中,同時由於不常修改,各個模塊可以直接將其讀到緩存中。數據字典的UML類圖如下。
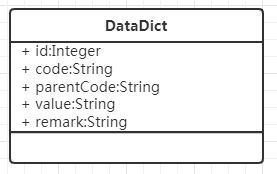
這樣,我只需要一個靜態類,枚舉出父級配置即可,以後只會增加,一般情況下都不會修改。代碼如下:

package com.idlewow.datadict.model; import java.io.Serializable; public enum DataType implements Serializable { Occupy("10100", "領土歸屬"), Faction("10110", "陣營"), Race("10200", "種族"), Job("10250", "職業"), MobType("10300", "怪物類型"), MobClass("10310", "怪物種類"); private String code; private String value; DataType(String code, String value) { this.code = code; this.value = value; } public String getCode() { return code; } public String getValue() { return value; } }
DataType.java
附一、spring-data-redis
此緩存組件使用比較簡單,安裝好redis,添加好依賴和配置後。在需要緩存的方法上標記註解即可。主要有@Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut。
例一:下面的註解,代表此方法執行成功後,將返回結果緩存到redis中, key為 mapMob:#{id},當結果為NULL時,不緩存。
@Cacheable(value = "mapMob", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null") public CommonResult find(String id) { return super.find(id); }
例二:下面的註解,代表此方法執行成功後,將緩存 dataDict: 中的鍵全部清除
@CacheEvict(value = "dataDict", allEntries = true) public CommonResult update(DataDict dataDict) { return super.update(dataDict); }
例三:下面的註解,代表方法執行成功後,將key為 levelExp:#{id} 的緩存更新為方法返回的結果
@CachePut(value = "levelExp", key = "#levelExp.getId()") public CommonResult update(LevelExp levelExp) { return super.update(levelExp); }
一、緩存改造
因為是在hessian的方法上進行緩存,這裡我們在hessian模塊的pom.xml中添加依賴如下:

<!-- 緩存相關 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> <version>2.2.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency>
pom.xml
這裡,我們需要配置一個叫 cacheManager 的 bean。之前我們一直使用xml對各組件進行配置,此 cacheManager 也可以使用xml進行配置。但在實際使用中,我想將redis的key統一配置成 idlewow:xxx:…,研究了半天未找到xml形式的配置方法,因此這裡使用Java代碼進行配置。在hessian模塊添加包 com.idlewow,然後新建 CacheConfig 類,如下:

package com.idlewow.config; import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig; import java.time.Duration; @EnableCaching @Configuration public class CacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport { @Bean public JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig() { JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig(); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(200); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(50); jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(20); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(5000); jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnReturn(false); return jedisPoolConfig; } @Bean public JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory() { JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory(jedisPoolConfig()); return jedisConnectionFactory; } @Bean public CacheManager cacheManager() { RedisCacheConfiguration configuration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() .entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)) .disableCachingNullValues() .computePrefixWith(cacheName -> "idlewow:" + cacheName + ":"); RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(jedisConnectionFactory()) .cacheDefaults(configuration) .build(); return redisCacheManager; } }
CacheConfig
這裡我只簡單的配置了下,緩存的有效期為1小時,當結果為NULL時不緩存,key前綴為 idlewow:。 有興趣的話可以研究下到底能否用xml配置key前綴,注意這裡用的是spring-data-redis 2.x版本,和 1.x 版本配置區別較大。
添加好依賴後,我們需要在服務的方法上打上標記即可。服務的實現類,在core模塊下。
比如,我們這裡以 MapMobServiceImpl 為例,此服務的方法update、delete、find執行成功後,我們均需要更新緩存。因為我們不緩存NULL值,因此add執行後,無需更新緩存。這裡的方法已經在BaseServiceImpl里實現過來,但需要打註解,不能直接在父類里標記,因此各個子類重寫一下方法簽名,內容直接 super.find(id),即可,也比較方便。代碼如下:

package com.idlewow.mob.service.impl; import com.idlewow.common.BaseServiceImpl; import com.idlewow.common.model.CommonResult; import com.idlewow.mob.manager.MapMobManager; import com.idlewow.mob.model.MapMob; import com.idlewow.mob.service.MapMobService; import com.idlewow.query.model.MapMobQueryParam; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service("mapMobService") public class MapMobServiceImpl extends BaseServiceImpl<MapMob, MapMobQueryParam> implements MapMobService { @Autowired MapMobManager mapMobManager; /** * 更新數據 * * @param mapMob 數據對象 * @return */ @Override @CachePut(value = "mapMob", key = "#mapMob.getId()") public CommonResult update(MapMob mapMob) { return super.update(mapMob); } /** * 刪除數據 * * @param id 主鍵id * @return */ @Override @CacheEvict(value = "mapMob", key = "#id") public CommonResult delete(String id) { return super.delete(id); } /** * 根據ID查詢 * * @param id 主鍵id * @return */ @Override @Cacheable(value = "mapMob", key = "#id") public CommonResult find(String id) { return super.find(id); } /** * 根據地圖ID查詢列表 * * @param mapId 地圖ID * @return */ @Override @Cacheable(value = "mapMobList", key = "#mapId", unless = "#reuslt==null") public List<MapMob> listByMapId(String mapId) { try { return mapMobManager.listByMapId(mapId); } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error(ex.getMessage(), ex); return null; } } }
MapMobServiceImpl
OK, hessian模塊的緩存已改造完畢。可以嘗試調用一下,redis里應該已經可以寫入數據。
另外:這裡我還添加了一個listByMapId方法,後面game模塊會調用。這裡沒有再統一返回CommonResult類型。因為我在實際寫代碼過程中,發現每次調接口都去做判斷實在太繁瑣了,對內調用一般無需這麼麻煩。一般在跨部門、公司之間的接口對接,或者對容錯要求比較高時,可以將異常全部捕獲處理。因此,後面對內的即接口都直接返回需要的數據類型。
二、RMS系統對應改造
hessian既然已經改成了redis緩存。RMS系統需要做對應的改造。game模塊中讀取了緩存,如果rms模塊修改了數據,卻沒有更新redis緩存,會造成最終的數據不一致。
因此,我們將rms模塊改造為通過訪問hessian服務來讀寫數據,這樣調用hessian方法時就能觸發緩存,不再直接訪問數據庫。
這裡把EhCache、數據庫相關的代碼、配置、依賴都刪掉。並在pom中添加對hessian的引用,並像game模塊一樣,配置hessian-client.xml並在applicationContext.xml中引入。
在代碼中,我們將CrudController中的BaseManager替換成BaseService,並將其他地方做對應修改。如下圖:

package com.idlewow.rms.controller; import com.idlewow.common.model.BaseModel; import com.idlewow.common.model.CommonResult; import com.idlewow.common.model.PageList; import com.idlewow.common.model.QueryParam; import com.idlewow.common.service.BaseService; import com.idlewow.util.validation.ValidateGroup; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; public abstract class CrudController<T extends BaseModel, Q extends QueryParam> extends BaseController { private final String path = this.getClass().getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class).value()[0]; @Autowired BaseService<T, Q> baseService; @Autowired HttpServletRequest request; @RequestMapping("/list") public Object list() { return this.path + "/list"; } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.POST) public Object list(@RequestParam(value = "page", defaultValue = "1") int pageIndex, @RequestParam(value = "limit", defaultValue = "10") int pageSize, Q q) { try { q.setPage(pageIndex, pageSize); CommonResult commonResult = baseService.list(q); if (commonResult.isSuccess()) { PageList<T> pageList = (PageList<T>) commonResult.getData(); return this.parseTable(pageList); } else { request.setAttribute("errorMessage", commonResult.getMessage()); return "/error"; } } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error(ex.getMessage(), ex); request.setAttribute("errorMessage", ex.getMessage()); return "/error"; } } @RequestMapping("/add") public Object add() { return this.path + "/add"; } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST) public Object add(@RequestBody T t) { try { CommonResult commonResult = this.validate(t, ValidateGroup.Create.class); if (!commonResult.isSuccess()) return commonResult; t.setCreateUser(this.currentUserName()); commonResult = baseService.insert(t); return commonResult; } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error(ex.getMessage(), ex); return CommonResult.fail(ex.getMessage()); } } @RequestMapping(value = "/edit/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public Object edit(@PathVariable String id, Model model) { try { CommonResult commonResult = baseService.find(id); if (commonResult.isSuccess()) { T t = (T) commonResult.getData(); model.addAttribute(t); return this.path + "/edit"; } else { request.setAttribute("errorMessage", commonResult.getMessage()); return "/error"; } } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error(ex.getMessage(), ex); request.setAttribute("errorMessage", ex.getMessage()); return "/error"; } } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/edit/{id}", method = RequestMethod.POST) public Object edit(@PathVariable String id, @RequestBody T t) { try { if (!id.equals(t.getId())) { return CommonResult.fail("id不一致"); } CommonResult commonResult = this.validate(t, ValidateGroup.Update.class); if (!commonResult.isSuccess()) return commonResult; t.setUpdateUser(this.currentUserName()); commonResult = baseService.update(t); return commonResult; } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error(ex.getMessage(), ex); return CommonResult.fail(ex.getMessage()); } } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/delete/{id}", method = RequestMethod.POST) public Object delete(@PathVariable String id) { try { baseService.delete(id); return CommonResult.success(); } catch (Exception ex) { logger.error(ex.getMessage(), ex); return CommonResult.fail(ex.getMessage()); } } }
CrudController.java
另外,因為添加了數據字典。rms模塊需要添加對應的contoller和頁面。這裡不一一贅述。既然已經有了數據字典,之前寫死的枚舉,EnumUtil都可以廢除了。直接從hessian讀取數據字典配置到緩存。
在com.idlewow.rms.support.util包下添加DataDictUtil類,代碼如下:

package com.idlewow.rms.support.util; import com.idlewow.common.model.CommonResult; import com.idlewow.datadict.model.DataDict; import com.idlewow.datadict.model.DataType; import com.idlewow.datadict.service.DataDictService; import com.idlewow.query.model.DataDictQueryParam; import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager; import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @Component public class DataDictUtil implements Serializable { private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(DataDictUtil.class); @Autowired DataDictService dataDictService; public static Map<String, Map<String, String>> ConfigMap = new HashMap<>(); public void initialize() { DataDictQueryParam dataDictQueryParam = new DataDictQueryParam(); CommonResult commonResult = dataDictService.list(dataDictQueryParam); if (commonResult.isSuccess()) { List<DataDict> dataDictList = (List<DataDict>) commonResult.getData(); for (DataDict dataDict : dataDictList) { if (ConfigMap.containsKey(dataDict.getParentCode())) { ConfigMap.get(dataDict.getParentCode()).put(dataDict.getCode(), dataDict.getValue()); } else { Map map = new HashMap(); map.put(dataDict.getCode(), dataDict.getValue()); ConfigMap.put(dataDict.getParentCode(), map); } } } else { logger.error("緩存加載失敗!"); } } public static Map<String, String> occupy() { return ConfigMap.get(DataType.Occupy.getCode()); } public static Map<String, String> job() { return ConfigMap.get(DataType.Job.getCode()); } public static Map<String, String> faction() { return ConfigMap.get(DataType.Faction.getCode()); } public static Map<String, String> mobClass() { return ConfigMap.get(DataType.MobClass.getCode()); } public static Map<String, String> mobType() { return ConfigMap.get(DataType.MobType.getCode()); } }
DataDictUtil.java
在StartUpListener中,初始化緩存:
@Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { logger.info("緩存初始化。。。"); dataDictUtil.initialize(); logger.info("緩存初始化完畢。。。"); }
後端緩存有了,同樣的,前端寫死的枚舉也不需要了。可以使用localStorage進行緩存。代碼如下:

/* 數據字典緩存 */ var _cache = { version: new Date().getTime(), configmap: null }; /* 讀取緩存 */ function loadCache() { if (_cache.configmap == null || (new Date().getTime() - _cache.version) > 1000 * 60 * 30) { var localConfigMap = localStorage.getItem("configmap"); if (localConfigMap) { _cache.configmap = JSON.parse(localConfigMap); } else { /* 讀取數據字典緩存 */ $.ajax({ url: '/manage/data_dict/configMap', type: 'post', success: function (data) { _cache.configmap = data; localStorage.setItem("configmap", JSON.stringify(_cache.configmap)); }, error: function () { alert('ajax error'); } }); } } } /* 數據字典Key */ var DataType = { "Occupy": "10100", // 領土歸屬 "Faction": "10110", // 陣營 "Race": "10200", // 種族 "Job": "10250", // 職業 "MobType": "10300", // 怪物類型 "MobClass": "10310" // 怪物種類 }; DataDict.prototype = { occupy: function (value) { return _cache.configmap[DataType.Occupy][value]; }, job: function (value) { return _cache.configmap[DataType.Job][value]; }, faction: function (value) { return _cache.configmap[DataType.Faction][value]; }, mobClass: function (value) { return _cache.configmap[DataType.MobClass][value]; }, mobType: function (value) { return _cache.configmap[DataType.MobType][value]; } }; loadCache();
Helper.js
注意,這裡使用了jQuery的ajax請求,必須在引用之前引用jquery。
小結
內容有些許遺漏,下周再補充些。
源碼下載地址:https://545c.com/file/14960372-405053633


