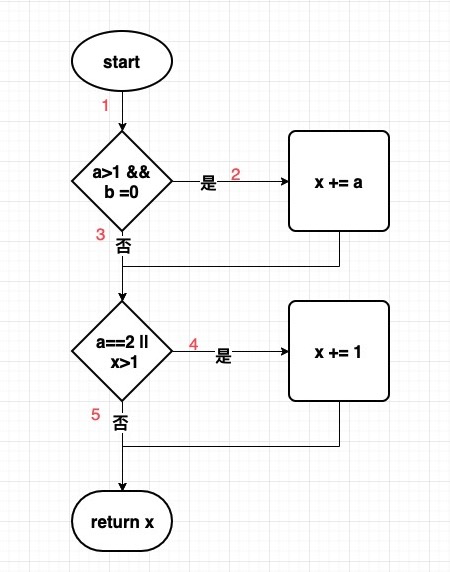
如何判斷單向鏈表有環?
- 2019 年 10 月 29 日
- 筆記
前言:鏈表在開發過程中屬於出現頻次十分高的一種數據結構,在java中,比如我們熟知的LinkedList、HashMap底層結構、LinkedHashMap、AQS等都使用到了鏈表,關於單向鏈表有幾個經典問題 1:如何判斷鏈表有環 2:如果有環,找出入環的節點 3:環的長度是多少?本篇博客就圍繞這三個問題來展開討論
目錄
一:如何判斷單向鏈表有環?
二:如果有環,找出入環的節點
三:環的長度是多少?
四:測試
五:總結
一:如何判斷單向鏈表有環?
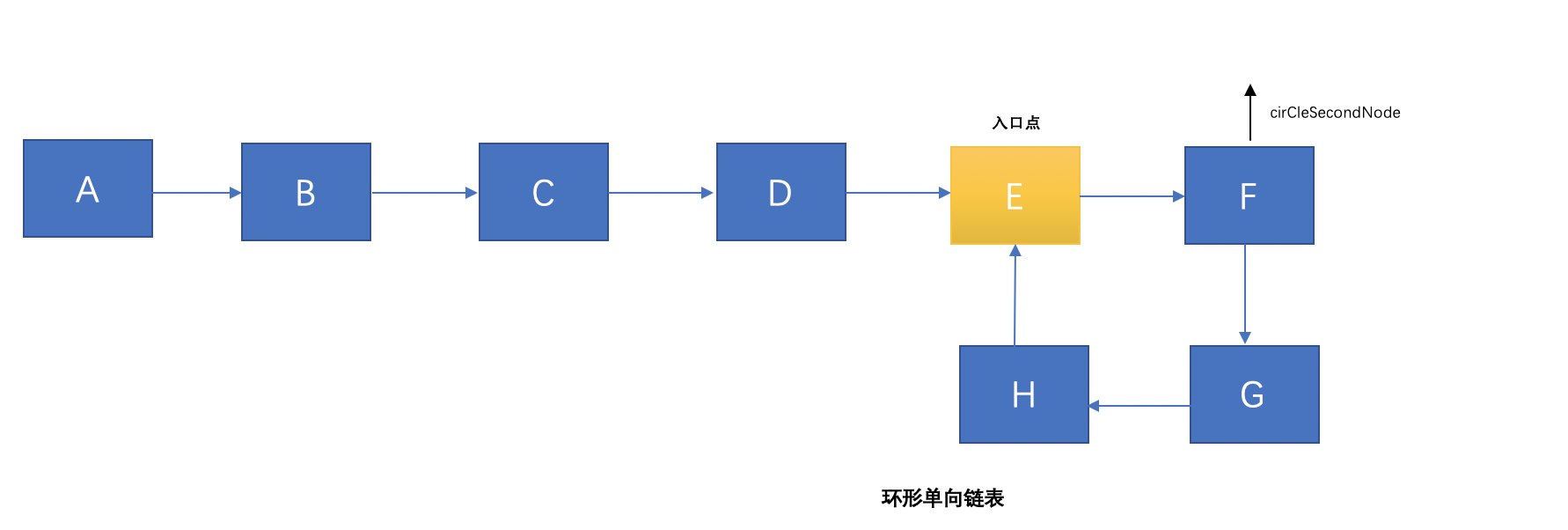
首先我們來畫一個普通的單向鏈表和環狀鏈表的結構圖:
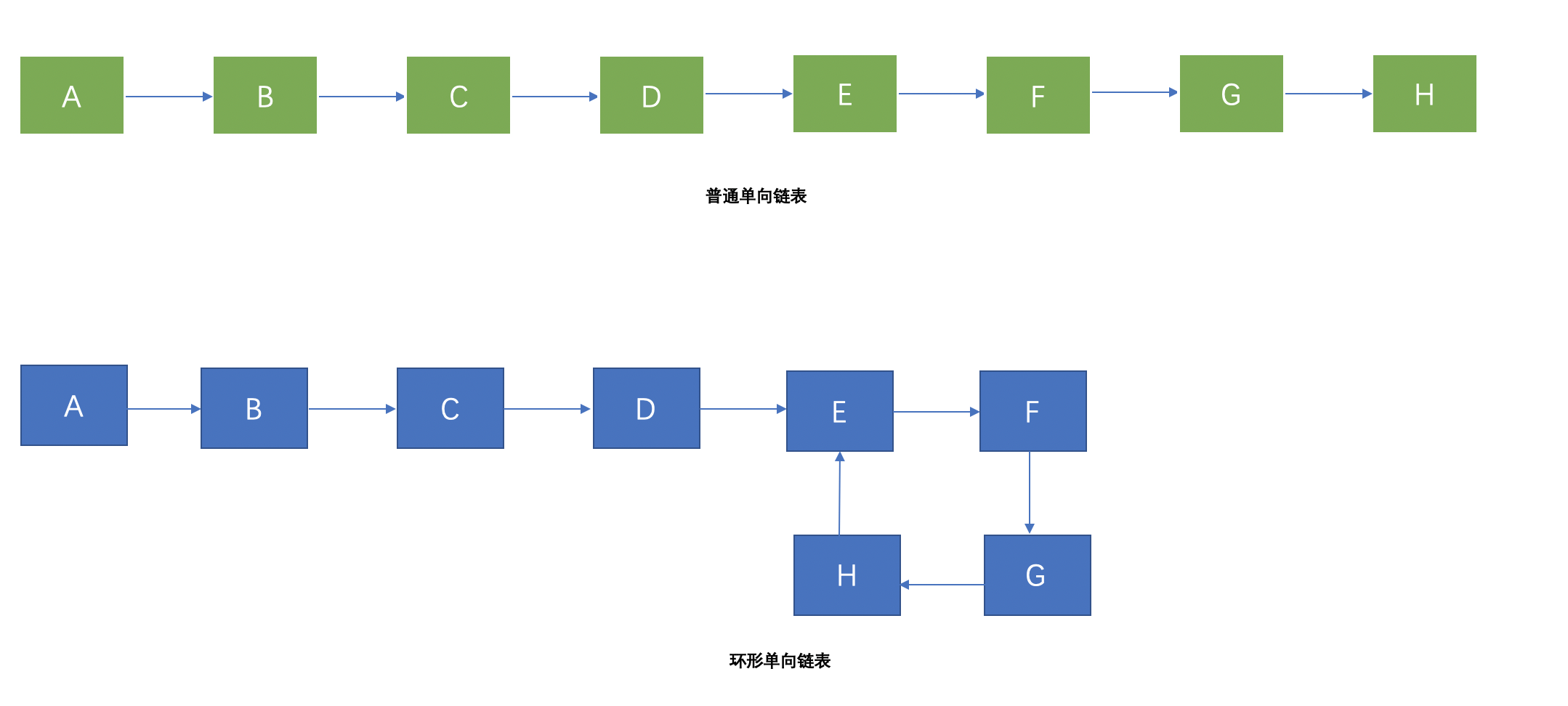
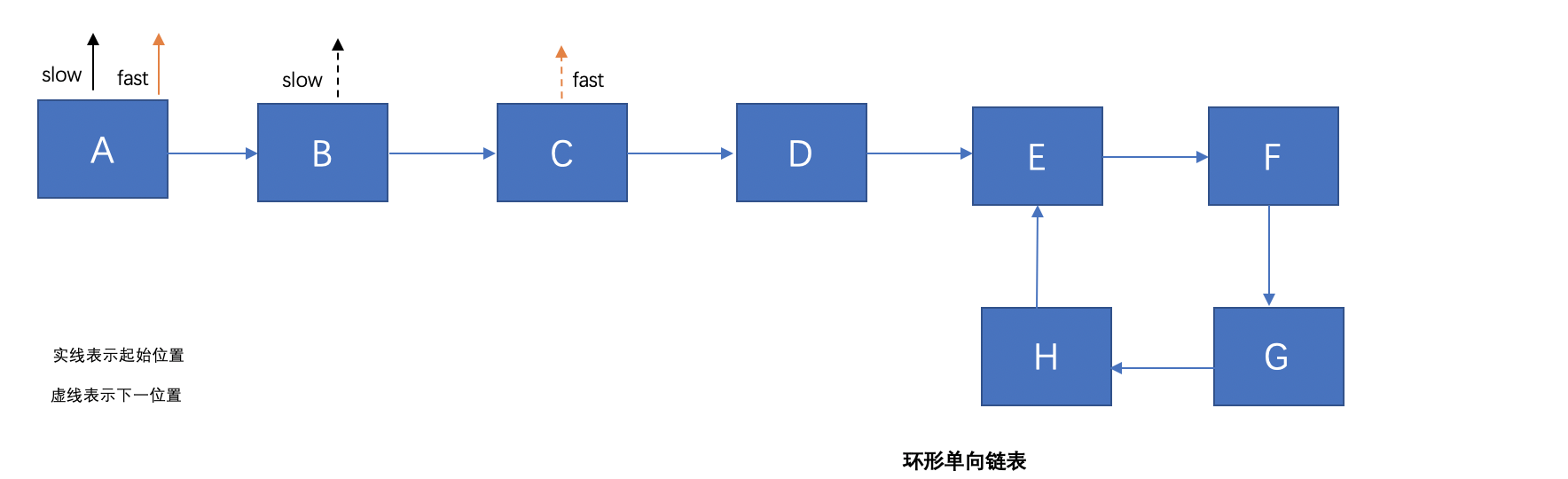
可以看出在環形單向鏈表的EFGH形成了一個環狀,那麼如何用程序判斷它成環呢?這裡要藉助一個跑道的思想:假如有一個環形的跑道,跑道上有兩個人P和Q,假設P的速度是1km/10分鐘,Q的速度是2km/10分鐘,速度恆定不變。如果這個跑道是環型的,他們同時出發,起初Q領先,而在某一個時刻,Q終將從後面追上過P,他們兩一定會相遇,而如果是直線跑道,P和Q一定不會相遇。藉助於這個思想,我們可以設置快慢指針去繞着環狀鏈表去走,如果兩個指針相遇,那麼它肯定是環形的。
下面是java版的實現:通過設定兩個不同速度的快慢指針來遍歷整個鏈表,如果快慢相遇,則整個鏈表一定有環:
程序的具體實現:
/** * 鏈表節點 */ public static class Node { private String value; private Node next; public String getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(String value) { this.value = value; } public Node getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node next) { this.next = next; } }
/** * 鏈表是否有環 * @param sourceNode * @return */ public static boolean hasCircle(Node sourceNode) { if (sourceNode == null) { return false; } if (sourceNode.next == null) { return false; } //慢指針 Node slowPointer = sourceNode; //快指針 Node fastPointer = sourceNode; while (fastPointer != null) { //慢指針每次一個鏈表格 slowPointer = slowPointer.next; //快指針每次兩個鏈表格 fastPointer = fastPointer.next.next; if (slowPointer == fastPointer) { return true; } } return false; }
二:如果有環,找出入環的節點
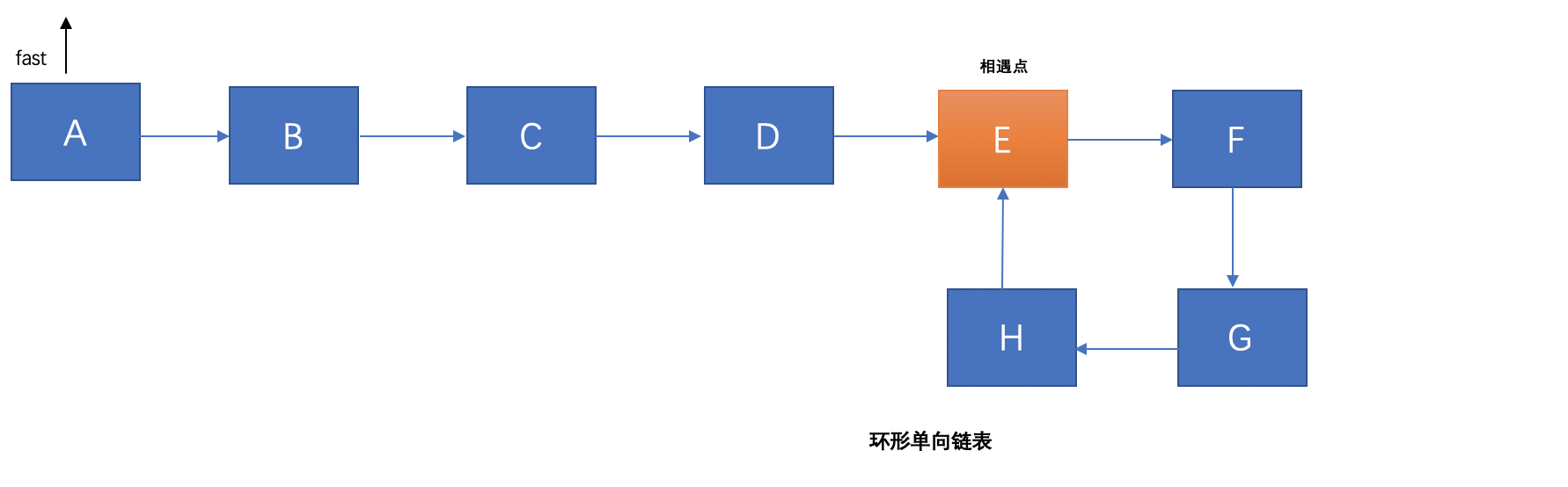
假設環形鏈表的長度是L,相遇點在M,在相遇之後,只需要將fast指針指向開始的節點,然後和slow指針保持同一的速度遍歷(相當於此時不分快慢,每個指針的每次步長為1),下一次兩個節點相遇的時候就是鏈表的環形入口:關於此結論的數學證明:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33663488
程序實現如下:
/** * 獲取入口節點 * @param sourceNode * @return */ public static Node getEnterNode(Node sourceNode) { if (sourceNode == null) { return null; } if (sourceNode.next == null) { return null; } //慢指針 Node slowPointer = sourceNode; //快指針 Node fastPointer = sourceNode; while (fastPointer != null) { slowPointer = slowPointer.next; fastPointer = fastPointer.next.next; if (slowPointer == fastPointer) { break; } } System.out.println("相遇點"+fastPointer.getValue()); fastPointer = sourceNode; while (fastPointer != null) { fastPointer = fastPointer.next; slowPointer = slowPointer.next; if (fastPointer == slowPointer) { return fastPointer; } } return null; }
三:環的長度是多少?
這個問題比較簡單,既然我們已經知道了環的入口節點,只需要新增一個指針,順着環依次循環一遍用一個變量進行累加,每次的步長設為一,然後直到和入口節點相遇(環入口的節點位置保持不變)那麼環的長度也就統計出來了:
程序具體實現:
/** * 獲取環的長度 * * @param sourceNode * @return */ public static int getCirCleLength(Node sourceNode) { if (sourceNode == null) { return 0; } final Node enterNode = getEnterNode(sourceNode); //環的下一個指針 Node cirCleSecondNode = enterNode.next; int lenght = 1; while (cirCleSecondNode != enterNode) { lenght++; cirCleSecondNode = cirCleSecondNode.next; } return lenght; }
四:測試
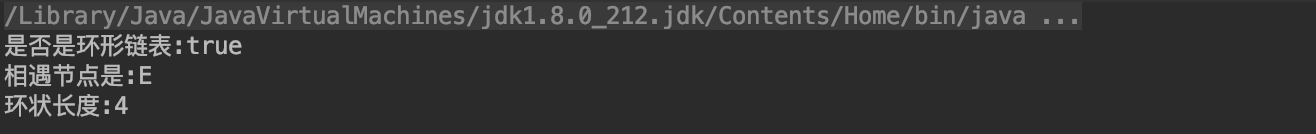
我們來寫一個測試方法來模擬一下上面的環狀節點,然後測試一下:
public static void main(String[] args) { final Node node = new Node(); node.setValue("A"); final Node node2 = new Node(); node2.setValue("B"); final Node node3 = new Node(); node3.setValue("C"); final Node node4 = new Node(); node4.setValue("D"); final Node node5 = new Node(); node5.setValue("E"); final Node node6 = new Node(); node6.setValue("F"); final Node node7 = new Node(); node7.setValue("G"); final Node node8 = new Node(); node8.setValue("H"); node.setNext(node2); node2.setNext(node3); node3.setNext(node4); node4.setNext(node5); node5.setNext(node6); node6.setNext(node7); node7.setNext(node8); node8.setNext(node5); final boolean hasCircle = hasCircle(node); System.out.println("是否是環形鏈表:"+hasCircle); final Node enterNode = getEnterNode(node); System.out.println("相遇節點是:"+enterNode.getValue()); final int cirCleLength = getCirCleLength(node); System.out.println("環狀長度:"+cirCleLength); }
程序輸出如下:
五:總結
本次主要分析了環形鏈表的一些問題,並給出了示例代碼,通過此篇博客可以學習到關於鏈表的一些東西,快慢指針的基本思想,以及如何求相遇節點和環的長度兩個問題,如何用java求解,並熟悉鏈表這種數據結構,在實際工作中可以加深對環形鏈表的一些理解。
最後: 如果對學習java有興趣可以加入群:618626589,本群旨在打造無培訓廣告、無閑聊扯淡、無注水斗圖的純技術交流群,群里每天會分享有價值的問題和學習資料,歡迎各位隨時加入