Django之CBV視圖源碼分析(工作原理)
- 2019 年 10 月 28 日
- 筆記
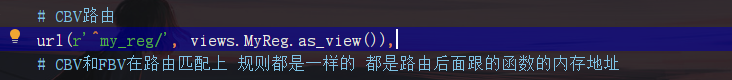
1.首先我們先在urls.py定義CBV的路由匹配。
FBV的路由匹配:
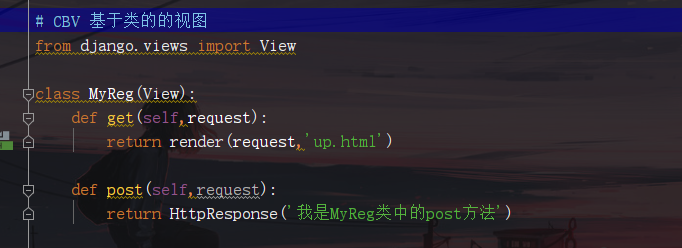
2.然後,在views.py創建一名為MyReg的類:
注意:該類必須繼續View類,且方法名必須與請求方式相同(後面會詳解)
3.回到第一步的路由匹配可以看到MyReg.as_view(),直接調用了as_view函數。那麼現在進去as_view函數看看裏面運行了什麼?
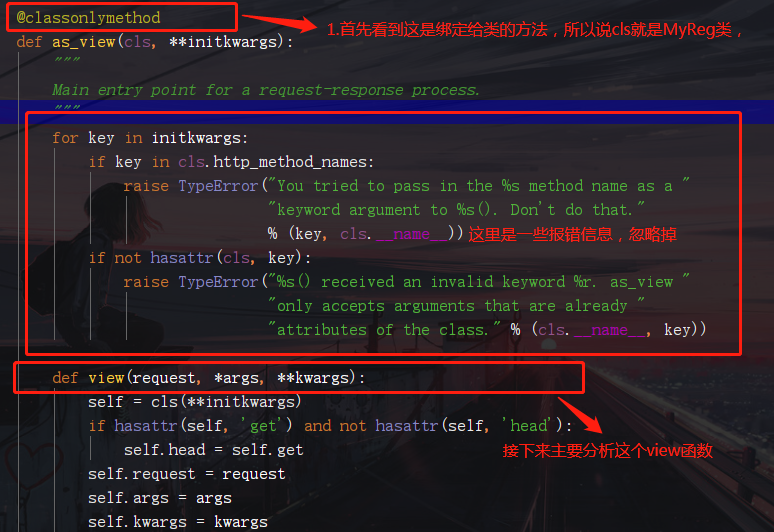
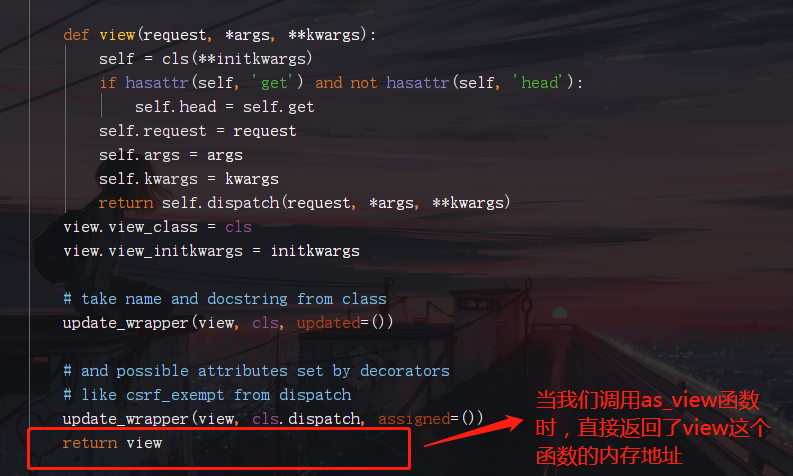
4.由上面的分析可以知道執行as_view函數時,返回該函數下嵌套的一個叫view函數的內存地址,這樣,urls.py里的url(r'^my_reg/', views.MyReg.as_view())就相當於url(r'^my_reg/', views.view)了,這樣跟我們之前的FBV就沒區別了,當url匹配成功,就會執行view函數。
5.假設url匹配成功,執行view函數:

首先view函數完成了MyReg類的初始化
最後view函數 先調用dispatch函數, 然後返回dispatch函數執行後返回值,
6.現在進入dispatch函數看看它返回了什麼數據
dispatch函數為CBV最精髓的部分
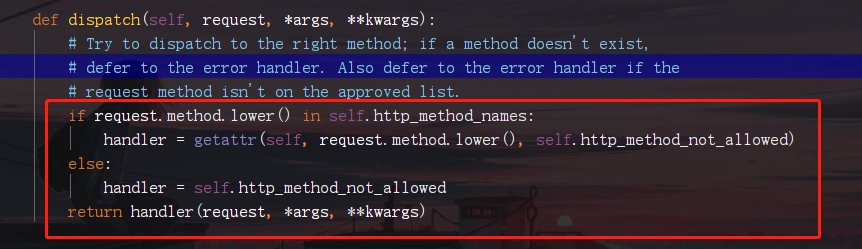
分析:
request.method.lower()為請求方式的小寫
self.http_method_names點進去為一個列表,該列表是所有八個請求方式的小寫
self.http_method_not_allowed返回一個報錯信息為405的函數
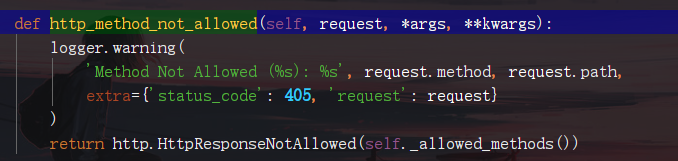
getattr是反射,通過字符串獲取方法的內存地址。拿到內存地址可以直接加()調用
最後總分析 dispatch函數
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # Try to dispatch to the right method; if a method doesn't exist, # defer to the error handler. Also defer to the error handler if the # request method isn't on the approved list. # 判斷用戶發送的請求方式是否在http_method_names列表裏面 if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: # 通過反射判斷MyReg類是否有跟請求方式同名的方法,若有,返回該方法的內存地址,沒有返回報錯405 handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: # 如果不在就返回一個報錯405的函數 handler = self.http_method_not_allowed # 最後直接執行上面返回的函數 return handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
