一文搞懂Java8 Lambda表達式(附帶視頻教程)
Lambda表達式介紹
Java 8的一個大亮點是引入Lambda表達式,使用它設計的代碼會更加簡潔。通過Lambda表達式,可以替代我們以前經常寫的匿名內部類來實現接口。Lambda表達式本質是一個匿名函數;
體驗Lambda表達式
我們通過一個小例子來體驗下Lambda表達式;
我們定義一個計算接口 只有一個方法add;
public class Program { public static void main(String[] args) { Cal c1=new Cal() { @Override public int add(int a, int b) { return a+b; } }; int c=c1.add(1,2); System.out.println(c); } } interface Cal{ int add(int a,int b); }
這個是我們以前的實現,匿名內部類,然後調用執行;
我們現在用Lambda表達式改寫下:
public class Program { public static void main(String[] args) { Cal c1=(int a,int b) ->{return a+b;}; int c=c1.add(1,2); System.out.println(c); } int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; } } interface Cal{ int add(int a,int b); }
匿名內部類,直接改成了:
Cal c1=(int a,int b) ->{return a+b;};
簡潔多了;
是不是感覺Lambda表達式挺強大,
接下來我們來看看Lambda表達式的語法吧;
Lambda表達式語法
我們看下這個Lambda表達式:
(int a,int b) ->{return a+b;};
這個本質是一個函數;
一般的函數類似如下:
int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; }
有返回值,方法名,參數列表,方法體
Lambda表達式函數的話,只有參數列表,和方法體;
( 參數列表 ) -> { 方法體 }
說明:
( ) :用來描述參數列表;
{ } : 用來描述方法體;
-> :Lambda運算符,可以叫做箭頭符號,或者goes to
Lambda表達式語法細講
我們搞一個案例,接口方法參數,無參,單個參數,兩個參數,有返回值,沒有返回值,這六種情況都羅列下:
interface If1{ /** * 無參數無返回值 */ void test(); } interface If2{ /** * 單個參數無返回值 * @param a */ void test(int a); } interface If3{ /** * 兩個參數無返回值 * @param a * @param b */ void test(int a,int b); } interface If4{ /** * 無參數有返回值 * @return */ int test(); } interface If5{ /** * 單個參數有返回值 * @param a * @return */ int test(int a); } interface If6{ /** * 多個參數有返回值 * @param a * @param b * @return */ int test(int a,int b); }
我們用Lambda表達式實現:
// 無參數無返回值 If1 if1=()->{ System.out.println("無參數無返回值"); }; if1.test(); // 單個參數無返回值 If2 if2=(int a)->{ System.out.println("單個參數無返回值 a="+a); }; if2.test(3); // 兩個參數無返回值 If3 if3=(int a,int b)->{ System.out.println("兩個參數無返回值 a+b="+(a+b)); }; if3.test(2,3); // 無參數有返回值 If4 if4=()->{ System.out.print("無參數有返回值 "); return 100; }; System.out.println(if4.test()); // 單個參數有返回值 If5 if5=(int a)->{ System.out.print("單個參數有返回值 "); return a; }; System.out.println(if5.test(200)); // 多個參數有返回值 If6 if6=(int a,int b)->{ System.out.print("多個參數有返回值 "); return a+b; }; System.out.println(if6.test(1,2));
運行輸出:
無參數無返回值 單個參數無返回值 a=3 兩個參數無返回值 a+b=5 無參數有返回值 100 單個參數有返回值 200 多個參數有返回值 3
Lambda表達式精簡語法
那件語法注意點:
- 參數類型可以省略
- 假如只有一個參數,()括號可以省略
- 如果方法體只有一條語句,{}大括號可以省略
- 如果方法體中唯一的語句是return返回語句,那省略大括號的同事return也要省略
改寫實例:
/** * @author java1234_小鋒 * @site www.java1234.com * @company Java知識分享網 * @create 2020-08-12 16:43 */ public class Program2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1,參數類型可以省略 // 2,假如只有一個參數,()括號可以省略 // 3,如果方法體只有一條語句,{}大括號可以省略 // 4,如果方法體中唯一的語句是return返回語句,那省略大括號的同事return也要省略 // 無參數無返回值 If1 if1=()->System.out.println("無參數無返回值"); if1.test(); // 單個參數無返回值 If2 if2=a->System.out.println("單個參數無返回值 a="+a); if2.test(3); // 兩個參數無返回值 If3 if3=(a,b)->{ System.out.println("兩個參數無返回值 a+b="+(a+b)); }; if3.test(2,3); // 無參數有返回值 If4 if4=()->100; System.out.println(if4.test()); // 單個參數有返回值 If5 if5=a->{ System.out.print("單個參數有返回值 "); return a; }; System.out.println(if5.test(200)); // 多個參數有返回值 參數類型可以省略 If6 if6=(a,b)->a+b; System.out.println(if6.test(1,2)); } }
方法引用
有時候多個lambda表達式實現函數是一樣的話,我們可以封裝成通用方法,以便於維護;
這時候可以用方法引用實現:
語法是:對象::方法
假如是static方法,可以直接 類名::方法
實例如下:
public class Program2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 方法引用 // 語法: // static方法 類名::方法名 // 普通方法 對象名::方法名 Program2 program2=new Program2(); If5 if5=program2::test; If5 if52=Program2::test2; System.out.println(if5.test(1)); System.out.println(if52.test(1)); } public int test(int a){ return a-2; } public static int test2(int a){ return a-2; } }
構造方法引用
如果函數式接口的實現恰好可以通過調用一個類的構造方法來實現,
那麼就可以使用構造方法引用;
語法:類名::new
實例:
先定義一個Dog實體,實現無參和有參構造方法;
public class Dog { private String name; private int age; public Dog() { System.out.println("無參構造方法"); } public Dog(String name, int age) { System.out.println("有參構造方法"); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
在定義兩個接口:
interface DogService{ Dog getDog(); } interface DogService2{ Dog getDog(String name,int age); }
測試:
public class Program3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 普通方式 DogService dogService=()->{ return new Dog(); }; dogService.getDog(); // 簡化方式 DogService dogService2=()->new Dog(); dogService2.getDog(); // 構造方法引用 DogService dogService3=Dog::new; dogService3.getDog(); // 構造方法引用 有參 DogService2 dogService21=Dog::new; dogService21.getDog("小米",11); } }
執行結果:
無參構造方法
無參構造方法
無參構造方法
有參構造方法
綜合實例
下面我們通過一個lambda操作集合的綜合實例,來深入體驗下Lambda表達式用法;
public class Program4 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Dog> list=new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Dog("aa",1)); list.add(new Dog("bb",4)); list.add(new Dog("cc",3)); list.add(new Dog("dd",2)); list.add(new Dog("ee",5)); // 排序 System.out.println("lambda集合排序"); list.sort((o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge()); System.out.println(list); // 遍歷集合 System.out.println("lambda遍歷集合"); list.forEach(System.out::println); } }
運行輸出:
lambda集合排序 [Dog{name='aa', age=1}, Dog{name='dd', age=2}, Dog{name='cc', age=3}, Dog{name='bb', age=4}, Dog{name='ee', age=5}] lambda遍歷集合 Dog{name='aa', age=1} Dog{name='dd', age=2} Dog{name='cc', age=3} Dog{name='bb', age=4} Dog{name='ee', age=5}
我們來分析下集合的sort方法,
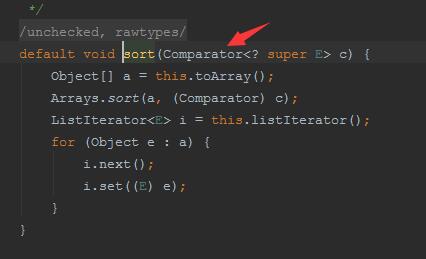
sort方法里有一個Comparator接口,再點進去看下:
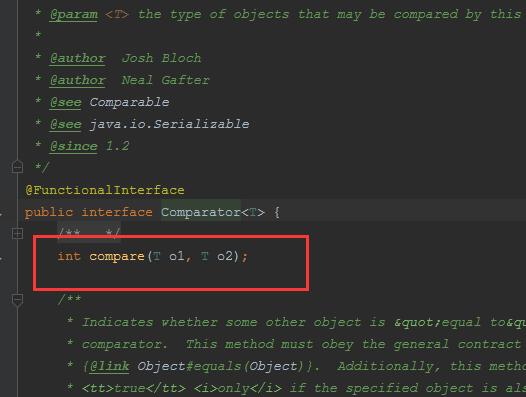
我們通過lambda就可以輕鬆實現排序:
(o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge()
再看下集合的forEach方法,點進去:

有個消費者Consumer接口,再點進去:

接口裡有個接口參數的accept的方法;
所以我們直接方法引用 直接輸出每次的遍歷值即可;
System.out::println
@FunctionalInterface註解
前面我們會發現Consumer接口,Comparator接口都有
@FunctionalInterface註解;
這個註解是函數式接口註解,所謂的函數式接口,當然首先是一個接口,然後就是在這個接口裏面只能有一個抽象方法。
這種類型的接口也稱為SAM接口,即Single Abstract Method interfaces
特點
-
接口有且僅有一個抽象方法
-
允許定義靜態方法
-
允許定義默認方法
-
允許java.lang.Object中的public方法
該註解不是必須的,如果一個接口符合”函數式接口”定義,那麼加不加該註解都沒有影響。加上該註解能夠更好地讓編譯器進行檢查。如果編寫的不是函數式接口,但是加上了@FunctionInterface,那麼編譯器會報錯
實例
// 正確的函數式接口 @FunctionalInterface public interface TestInterface { // 抽象方法 public void sub(); // java.lang.Object中的public方法 public boolean equals(Object var1); // 默認方法 public default void defaultMethod(){ } // 靜態方法 public static void staticMethod(){ } } // 錯誤的函數式接口(有多個抽象方法) @FunctionalInterface public interface TestInterface2 { void add(); void sub(); }
系統內置函數式接口
Java8的推出,是以Lambda重要特性,一起推出的,其中系統內置了一系列函數式接口;
再jdk的java.util.function包下,有一系列的內置函數式接口:
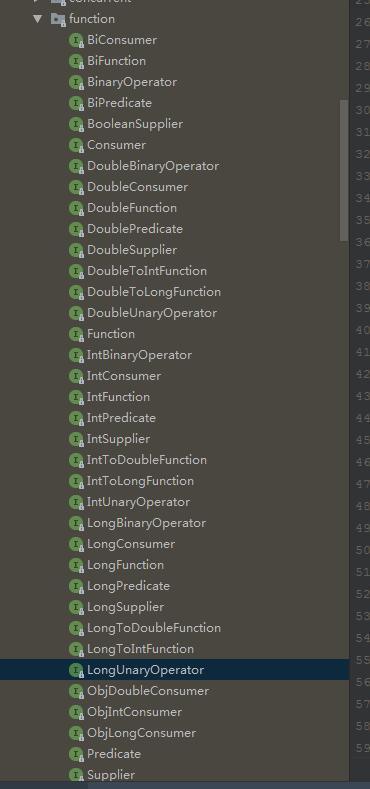
比如常用的Consumer,Comparator,Predicate,Supplier等;
Lambda表達式視頻教程
感謝各位兄弟姐妹關注,鋒哥為了大夥能更深刻的掌握Lambda的原理和應用,專門錄製了一期視頻教程。主要以IDEA開發工具,來講解lambda表達式,希望小夥伴們快速的掌握。
紙上得來終覺淺,絕知此事要躬行。
需要多實戰,多思考
B站視頻教程在線地址:
//www.bilibili.com/video/bv1ci4y1g7qD
——————————————————————————————————————————
作者: java1234_小鋒
出處://www.cnblogs.com/java688/p/13511720.html
版權:本站使用「CC BY 4.0」創作共享協議,轉載請在文章明顯位置註明作者及出處。
——————————————————————————————————————————
