死磕 java線程系列之線程池深入解析——體系結構
- 2019 年 10 月 14 日
- 筆記

(手機橫屏看源碼更方便)
註:java源碼分析部分如無特殊說明均基於 java8 版本。
簡介
Java的線程池是塊硬骨頭,對線程池的源碼做深入研究不僅能提高對Java整個並發編程的理解,也能提高自己在面試中的表現,增加被錄取的可能性。
本系列將分成很多個章節,本章作為線程池的第一章將對整個線程池體系做一個總覽。
體系結構
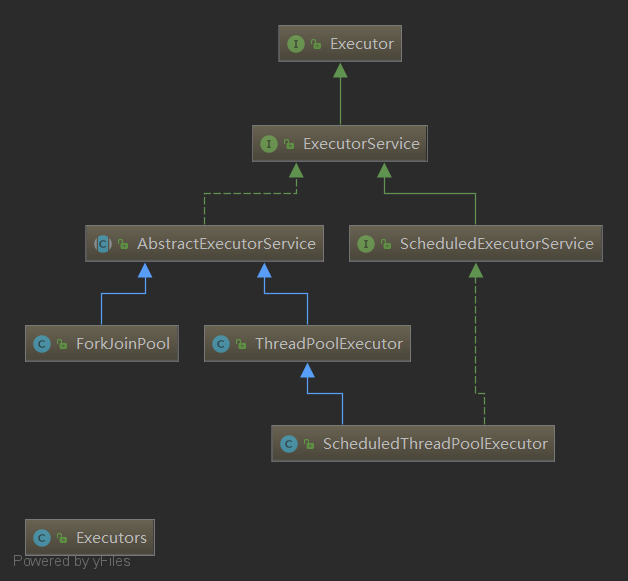
上圖列舉了線程池中非常重要的接口和類:
(1)Executor,線程池頂級接口;
(2)ExecutorService,線程池次級接口,對Executor做了一些擴展,增加一些功能;
(3)ScheduledExecutorService,對ExecutorService做了一些擴展,增加一些定時任務相關的功能;
(4)AbstractExecutorService,抽象類,運用模板方法設計模式實現了一部分方法;
(5)ThreadPoolExecutor,普通線程池類,這也是我們通常所說的線程池,包含最基本的一些線程池操作相關的方法實現;
(6)ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,定時任務線程池類,用於實現定時任務相關功能;
(7)ForkJoinPool,新型線程池類,java7中新增的線程池類,基於工作竊取理論實現,運用於大任務拆小任務、任務無限多的場景;
(8)Executors,線程池工具類,定義了一些快速實現線程池的方法(謹慎使用);
Executor
線程池頂級接口,只定義了一個執行無返回值任務的方法。
public interface Executor { // 執行無返回值任務【本篇文章由公眾號「彤哥讀源碼」原創】 void execute(Runnable command); }ExecutorService
線程池次級接口,對Executor做了一些擴展,主要增加了關閉線程池、執行有返回值任務、批量執行任務的方法。
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor { // 關閉線程池,不再接受新任務,但已經提交的任務會執行完成 void shutdown(); // 立即關閉線程池,嘗試停止正在運行的任務,未執行的任務將不再執行 // 被迫停止及未執行的任務將以列表的形式返回 List<Runnable> shutdownNow(); // 檢查線程池是否已關閉 boolean isShutdown(); // 檢查線程池是否已終止,只有在shutdown()或shutdownNow()之後調用才有可能為true boolean isTerminated(); // 在指定時間內線程池達到終止狀態了才會返回true boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; // 執行有返回值的任務,任務的返回值為task.call()的結果 <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); // 執行有返回值的任務,任務的返回值為這裡傳入的result // 當然只有當任務執行完成了調用get()時才會返回 <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result); // 執行有返回值的任務,任務的返回值為null // 當然只有當任務執行完成了調用get()時才會返回 Future<?> submit(Runnable task); // 批量執行任務,只有當這些任務都完成了這個方法才會返回 <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException; // 在指定時間內批量執行任務,未執行完成的任務將被取消 // 這裡的timeout是所有任務的總時間,不是單個任務的時間 <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; // 返回任意一個已完成任務的執行結果,未執行完成的任務將被取消 <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; // 在指定時間內如果有任務已完成,則返回任意一個已完成任務的執行結果,未執行完成的任務將被取消 <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException; }ScheduledExecutorService
對ExecutorService做了一些擴展,增加一些定時任務相關的功能,主要包含兩大類:執行一次,重複多次執行。
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService { // 在指定延時後執行一次 public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit); // 在指定延時後執行一次 public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit); // 在指定延時後開始執行,並在之後以指定時間間隔重複執行(間隔不包含任務執行的時間) // 相當於之後的延時以任務開始計算【本篇文章由公眾號「彤哥讀源碼」原創】 public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit); // 在指定延時後開始執行,並在之後以指定延時重複執行(間隔包含任務執行的時間) // 相當於之後的延時以任務結束計算 public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit); }AbstractExecutorService
抽象類,運用模板方法設計模式實現了一部分方法,主要為執行有返回值任務、批量執行任務的方法。
public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService { protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) { return new FutureTask<T>(runnable, value); } protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Callable<T> callable) { return new FutureTask<T>(callable); } public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<Void> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null); execute(ftask); return ftask; } public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task, result); execute(ftask); return ftask; } public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task); execute(ftask); return ftask; } public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { // 略... } public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { // 略... } public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException { // 略... } public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { // 略... } }可以看到,這裡的submit()方法對傳入的任務都包裝成了FutureTask來進行處理,這是什麼東西呢?歡迎關注後面的章節。
ThreadPoolExecutor
普通線程池類,這也是我們通常所說的線程池,包含最基本的一些線程池操作相關的方法實現。
線程池的主要實現邏輯都在這裏面,比如線程的創建、任務的處理、拒絕策略等,我們後面單獨分析這個類。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
定時任務線程池類,用於實現定時任務相關功能,將任務包裝成定時任務,並按照定時策略來執行,我們後面單獨分析這個類。
問題:你知道定時任務線程池類使用的是什麼隊列嗎?
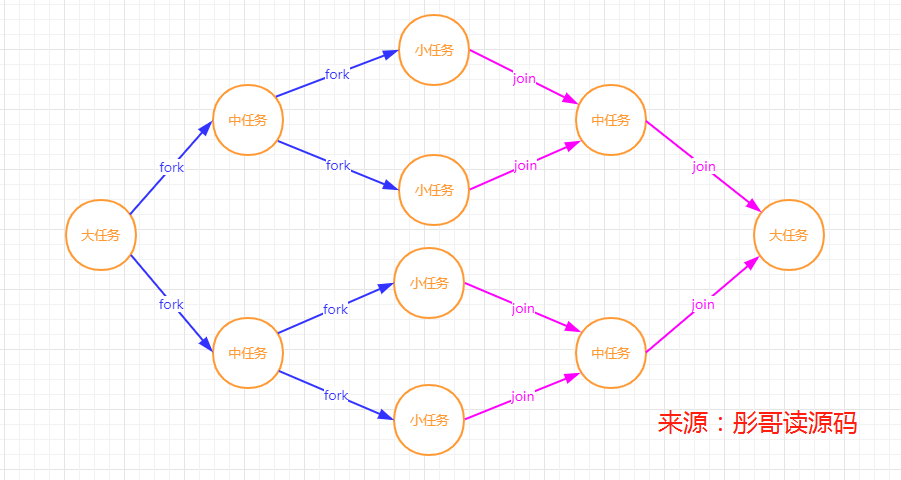
ForkJoinPool
新型線程池類,java7中新增的線程池類,這個線程池與Go中的線程模型特別類似,都是基於工作竊取理論,特別適合於處理歸併排序這種先分後合的場景。
Executors
線程池工具類,定義了一系列快速實現線程池的方法——newXXX(),不過阿里手冊是不建議使用這個類來新建線程池的,彤哥我並不這麼認為,只要能掌握其源碼,知道其利敝偶爾還是可以用的,後面我們再來說這個事。
彩蛋
無彩蛋不歡,今天的問題是定時任務線程池用的是哪種隊列來實現的?
答:延時隊列。定時任務線程池中並沒有直接使用並發集合中的DelayQueue,而是自己又實現了一個DelayedWorkQueue,不過跟DelayQueue的實現原理是一樣的。
延時隊列使用什麼數據結構來實現的呢?
答:堆(DelayQueue中使用的是優先級隊列,而優先級隊列使用的堆;DelayedWorkQueue直接使用的堆)。
關於延時隊列、優先級隊列和堆的相關內容點擊下面的鏈接直達:
歡迎關注我的公眾號「彤哥讀源碼」,查看更多源碼系列文章, 與彤哥一起暢遊源碼的海洋。

